Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AM and FM Modulation Techniques
Uploaded by
Ramkumar SivakaminathanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
AM and FM Modulation Techniques
Uploaded by
Ramkumar SivakaminathanCopyright:
Available Formats
WWW.VIDYARTHIPLUS.
COM
MAHALAKSHMI
ENGINEERING COLLEGE
TIRUCHIRAPALLI 621213 QUESTION BANK DEPARTMENT: ECE SEMESTER: IV
SUBJECT CODE / Name: EC2252 COMMUNICATION THEORY
UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION SYSTEMS PART -A (2 Marks) 1. Define Modulation Index for an AM Signal (AUC MAY 2010) (AUC MAY 2006)
2. What is the mid frequency of IF section of AM receivers and its bandwidth (AUC NOV 2006) 3. Draw the circuit of an envelope detector. 4. State any important spectral properties of periodic power signals 5. Define Amplitude Modulation. Give the expression for AM wave 6. Give the applications of SSBSC-AM. 7. Compare low level modulation and high level modulation. (AUC NOV 2007) (AUC NOV 2007) (AUC NOV 2007) (AUC NOV 2007) (AUC NOV 2007)
8. A transmitter radiates 9 KW without modulation and 10.125 KW after modulation. Determine depth of modulation. (AUC NOV 2007)
9. A 2 MHz carrier having amplitude of 5V is modulated by a 4 KHz audio signal having amplitude of 2V. Determine the modulation index and draw frequency spectrum of amplitude modulated wave. 10. SSB is suitable for speech signals and not for video signals. Why? (AUC MAY 2008) 11. A 500 W carrier modulated to a depth of 60 percent. Calculate the total power in modulated wave. 12. Define vestigial sideband transmission. Mention its application. 13. Compute the bandwidth of the Amplitude modulated signal a. C(t)=23*cos (230000t)[1+0.8*cos (310t)] 14. Define AM and its spectrum (AUC MAY 2009) (AUC MAY 2009) (AUC NOV 2008) (AUC NOV 2008) (AUC MAY 2008)
15. An AM DSB-FC wave with a peak unmodulated carrier voltage A C=10V, a load resistor RL=10 and the modulation index m=1. Determine the total power of the modulated wave. (AUC MAY 2009) 1
EC2252 COMMUNICATION THEORY III Sem ECE R.Vanitha Asst.Prof./ECE
WWW.VIDYARTHIPLUS.COM
16. How many AM broadcast stations can be accommodated i n a 100 kHz bandwidth if t he highest frequency modulating a carrier i s 5 kHz? 17. What are the causes of linear distortion? (AUC MAY 2010) AUC MAY 2010)
18. How many AM broadcast stations can be accommodated in a 100 kHz bandwidth (AUC DEC 2010) 19. If the highest frequency modulating a carrier i s 5 kHz? 20. State the applications of FDM 21. What are the advantage of VSB (AUC DEC 2010) (AUC MAY 2011)
22. Calculate the local oscillator frequency if incoming frequency is f 1 and translated carrier frequency (AUC MAY 2011) 23. How many AM broadcast stations can be accommodated i n a 100 kHz bandwidth if the highest frequency modulating a carrier i s 5 kHz? 24. State the applications of FDM. 25. What is meant by frequency translation? cos(310t)]cos(230000t) 27. What are the causes of linear distortion PART- B 1. Discuss coherent detection of DSB-SC modulated wave with a block diagram of the detector. (AUC NOV 2006) (AUC DEC 2011) (AUC MAY 2011) (AUC DEC 2011)
26. Compute the bandwidth of the amplitude modulated signal given by s(t)=23[1+0.8 (AUC MAY 2012) (AUC MAY 2012)
2. Draw the filtering scheme for the generation of VSB modulated wave and Explain. (AUC NOV 2007) 3. Explain the double side band suppressed carrier modulation technique (AUC NOV 2007) 4. Explain frequency translation. 5. Discuss Frequency Division Multiplexing. 6. Explain in detail about the balanced modulator with block diagram. (AUC NOV 2007) 7. Discuss the method of demodulation of DSBSC signal using costas loop. (AUC MAY 2008) (AUC NOV 2007) (AUC NOV 2007)
8. An SSB signal is generated by modulating an 800 KHz carrier by the signal m(t) = cos2000t + 2sin1200t. The amplitude of the carrier is A c=10. Obtain the magnitude spectrum of the lower sideband SSB signal. (AUC MAY 2008) 9. With a neat block diagram explain the SSB transmission. 10. Explain the operation of a ring modulator. State its advantages. (AUC NOV 2008) (AUC NOV 2008)
EC2252 COMMUNICATION THEORY III Sem ECE R.Vanitha Asst.Prof./ECE
WWW.VIDYARTHIPLUS.COM
11. (i)Draw an envelope detector circuit used for demodulation of AM and ex- plain its operation. (10) (ii) How SSB can be generated using Weavers method? Illustrate with a neat block diagram. (6) (AUC MAY 2010) 12. (i) Discuss i n detail about frequency translation and frequency division multiplexing technique with diagrams. (10) (ii) Compare Amplitude Modulation and Frequency Modulation. (6) (AUC MAY 2010) 13. (i)With the help of a neat diagram, explain the generation of DSB-SC using.Balanced modulator. (8) (ii) Write about the coherent detection method in detail for DSB-SC and SSB- SC. What happens when there is phase mismatch? (8) 14. (i) Explain the concept of Frequency Translation. (4) (ii) With aid of block diagram explain the principle of FDM. (8) (iii) Illustrate the formation of Basic group and super group. (4) (AUC DEC 2010) (AUC DEC 2010)
15. With a help of a neat diagram, explain the operation of an envelope detector. Why does negative peak clipping take place (AUC MAY 2011) 16. (i)Compare the characteristics of DSBFC, DSBSC, SSBFC, SSBSC, VSB schemes. (ii)Explain the concept of FDM with a suitable block diagram (AUC MAY 2011)
17. With necessary diagrams and expressions explain the generation and demodulation of AM. 18. (i)Compare the various amplitude modulation schemes.(6) (ii)With neat block diagram, explain the transmitter and receiver section ofFrequency Division Multiplexing. (10) (AUC DEC 2011) (AUC DEC 2011)
19. (i)Draw an envelope detector circuit used for demodulation of Am and explain its operation (ii)How SSB can be generating using Weavers method? Illustrate with a neat block diagram 20. (i)What is frequency division multiplexing? Explain (ii)Compare various Amplitude modulation systems (AUC MAY 2012) (AUC MAY 2012)
EC2252 COMMUNICATION THEORY III Sem ECE R.Vanitha Asst.Prof./ECE
WWW.VIDYARTHIPLUS.COM
UNIT-II ANGLE MODULATION SYSTEMS PART- A 1. What is frequency deviation in FM? 2. What are the applications of phase locked loop? 3. What is narrow band FM? angle given by (t) = 2000t + sin 10t 5. State Carsons rule. 6. Define phase modulation. (AUC NOV 2006) (AUC NOV 2006) (AUC MAY 2006)
4. Determine and draw the instantaneous frequency of a wave having a total phase (AUC MAY 2006) (AUC NOV 2007) (AUC NOV 2007)
7. Mention advantages of angle modulation over amplitude modulation. (AUC NOV 2008) 8. State the disadvantages of FM. (AUC NOV 2008)
9. When modulating frequency in an FM system is 500 Hz and modulating voltage is 3V, modulation index is 60. Calculate maximum deviation and bandwidth. (AUC NOV 2008)
10. Draw the phasor diagram, frequency spectrum of narrowband FM. (AUC MAY 2004) (AUC NOV 2006) (AUC MAY2010) 11. Distinguish between slope detector and Foster Seeley discriminato r(AUC MAY 2009) 12. Define modulation index of the FM wave. 13. Differentiate between narrowband FM and Wideband FM. 14. Obtain the bandwidth of the FM signal c(t) = 10*cos[2*107*t + 8 cos(1000*t)] (AUC MAY 2009) 15. Draw t he block diagram of a method for generating a narrowband FM signal. (AUC MAY 2010) 16. A carrier wave of frequency 100 MHz i s frequency modulated by a signal 20 sin(200 103t). (AUC MAY 2010) (AUC MAY 2009) (AUC MAY 2009)
17. Distinguish between narrow band FM and wide band FM
(AUC MAY 2011)
18. What is meant by detection? Name the methods for detecting FM signals (AUC MAY 2011) 19. How is the Narrow band FM converted into wideband FM? 20. What are the advantages of Ratio detector? (AUC DEC 2011) (AUC DEC 2011)
21. Illustrate the relationship between FM and PM, with block diagram. (AUC MAY 2012) 22. What is meant by detection? Name the method for detecting FM signal. (AUC MAY 2012)
EC2252 COMMUNICATION THEORY III Sem ECE R.Vanitha Asst.Prof./ECE
WWW.VIDYARTHIPLUS.COM
PART- B 1. (i) Explain any two techniques of demodulation of FM. (ii) Explain how varactor diode can be used for frequency modulation. (AUC NOV 2005) 2. Derive the expression for the frequency modulated signal. Explain what is meant by narrow band FM and wide band FM using expression. 3. Discuss the indirect method of generating a wide-band FM signal (AUC NOV 2006) 4. Draw the circuit diagram of Foster-seeley discriminator and explain its working (AUC NOV 2006) 5. Explain the direct FM generation using varactor diode and VCO (AUC NOV 2007) (AUC NOV 2006)
6. Explain in detail about (i) Balanced discriminators (ii) Phase-shift discriminators. (AUC NOV 2007) 7. Derive the expression for the spectrum of a FM signal with single tone modulation. (AUC MAY 2009) 8. Give the method of generation of FM signal. (AUC MAY 2009)
9. (i) Using suitable Mathematical analysis show that FM modulation produces infinite sideband. Also deduce an expression for the frequency modulated output an d its frequency spectrum. (10) (ii) How can you generate an FM from PM and PM from FM? (6) (AUC MAY 2010)
10. (i) A 20 MHz i s frequency modulated by a sinusoidal signal such that t he maximum frequency deviation is 100 kHz. Determine the modulation index and approximate bandwidth of t he FM signal for t he following modulating signal frequencies, (1)1 kHz (2) 100 kHz and (3) 500 kHz. (8) (ii) Derive the time domain expressions o f FM and PM signals. (8) (AUC MAY 2010) 11. (i)Derive the expression for the single tone frequency modulation and draw its frequency spectrum (ii)An angle modulated wave is described by the equation V (t) = 10 cos (2 106t +10 cos 2000t). Find (1) Power of the modulated signal (2) Maximum frequency deviation (3) Bandwidth. (AUC MAY 2011)
12. (i)A 100 kHz carrier is frequency modulated to produce a peak deviation o f This FM signal is passed through a 3 by 3 by 4 frequency.multiplierchain, t he output of which is mixed with an oscillator signal and the difference frequency taken as the new output Determine the frequency of the oscillator required to produce a 100 kHz FM output and the peak deviation of the output
EC2252 COMMUNICATION THEORY III Sem ECE R.Vanitha Asst.Prof./ECE
WWW.VIDYARTHIPLUS.COM
13. (ii)With necessary diagrams explain the operation of slope detector for demodulating FM signal. (AUC MAY 2011) 14. (i) Dene frequency modulation. Draw the FM waveform. Derive an expres-sion for single tone frequency modulation.(2 + 2 + 6) (ii) Compare Narrowband and Wideband FM.(6) (AUC DEC 2011)
15. Write about the basic principle of FM detection and explain about radio detector (AUC DEC 2011) 16. Fig. Shows block diagram of WBFM modulator used to transmit audio signal containing frequencies in the range 100 Hz to 15kHz. The desired Fm signal at the transmitter output is to have a carrier frequency of 100 MHz and minimum frequency deviation deviation of 75 k Hz. Asume the modulation index =0.2 radeian for NBFM. Find the frequency multiplier values N1,N2 and avlues of acrrier frequency and frequency deviation at the various points in WBFM modulator. (AUC MAY 2012)
Integrator
NBFM
Freq Multiplier
Mixer
Freq Multiplier
Crystal Controlled Oscillator(0.1MHz)
Crystal Controlled Oscillator(9.5MHz)
17. Draw the circuit diagram of Foster Seeley discriminator and explain its working with relevant phasor diagram. (AUC MAY 2012)
EC2252 COMMUNICATION THEORY III Sem ECE R.Vanitha Asst.Prof./ECE
WWW.VIDYARTHIPLUS.COM
UNIT-III NOISE THEORY PART-A 1. What is the classification of random process? give one example for each (AUC MAY 2006) 2. Define random process? 3. Define noise figure 4. What is white noise? 5. Define noise equivalent bandwidth 6. What is partition noise? (AUC NOV 2006) (AUC MAY 2008) (AUC MAY 2008) (AUC MAY 2008) (AUC MAY 2008)
7. Draw the auto correlation function and power spectral density of white noise. (AUC MAY 2008) 8. Define noise factor 9. Define noise temperature (AUC NOV 2008) (AUC MAY 2004)(AUC NOV 2008)
10. Calculate noise figure and equivalent noise temperature for a receiver connected to an antena whose resistance is 100 and equivalent noise resistance is 50? (AUC NOV 2008) 11. State central limit theorem. 12. Give the characteristic of shot noise 13. What are the advantages of Gaussian process? 14. Define shot noise and thermal noise? (AUC NOV 2008) (AUC MAY 2009) (AUC MAY 2009) (AUC MAY 2010)(AUC MAY 2009)
15. Determine the equivalent noise temperature for a noise figure of 10 dB (AUC MAY 2010) 16. When i s a random process called deterministic? resistance of 30. Find the receiver noise figure. (AUC MAY 2010) 17. A receiver conected to an antenaof resistance of 50 has an equivalent noise (AUC MAY 2010)
18. Define a random variable. Specify the sample space and the random variable for a coin tossing experiment. What i s white noise? Give its characteristics. 19. Write the Rayleigh and Rician probability density functions 20. What is white noise? State its power density 21. When i s a random process called deterministic? (AUC DEC 2010) (AUC DEC 2010) (AUC MAY 2011) (AUC MAY 2011) (AUC DEC 2011)
22. Two resistors of 20 K, 50 K are at room temperature (290 K). For a bandwidth of 100 KHz, calculate the thermal noise voltage generated by the two resistors in series
EC2252 COMMUNICATION THEORY III Sem ECE R.Vanitha Asst.Prof./ECE
WWW.VIDYARTHIPLUS.COM
23. Define random variable. Specify the sample space and the random variable for a coin tossing experiment 24. Give the definition of the noise equivalent temperature PART-B 1. Write notes on noise temperature and noise figure (AUC MAY2004) (AUC MAY 2012) (AUC MAY 2012)
2. Explain the following terms(i)Random variable (ii)Gaussian process(iii) Shot noise (iv) Noise temperature (AUC NOV 2006)
3. Explain the following terms (i)Thermal noise(ii)White noise(ii)Narrow band noise a. (iv) Random noise 4. Explain concept of noise equivalent bandwidth (AUC NOV 2006) (AUC NOV 2007)
5. Discuss the types causes and effects of various forms of noise created within a receiver? (AUC NOV 2008)
6. A stationary Gaussian process X (t) with zero mean and power spectral density S x(f) is applied to a linear filter whose impulses response h(t) is shown in figure. a sample Y is taken of the random process at the filter output at the time T. i)Determine the mean and variance of Y. ii) What is the probability density function of Y? (AUC NOV 2008)
7. Derive the noise figure of an receiver having input impedance R t, output impedance RL and overall voltage gain A? (AUC NOV 2008)(AUC MAY 2009)
8. Explain in detail about the white noise and filtered noise 9. Explain the following terms
(AUC NOV 2008)
i. Statistical average, correlation, covariance and ergodicity ? ii. Discuss the properties of Gaussian process ? (AUC MAY 2008)
10. i)Determine the overall noise figure of a three stage cascade amplifier; each stage having a power gain of 10dB and noise figure of 6dB ? ii) Discuss the properties of narrow band noise. (AUC MAY 2008)
11. What is thermal noise in communication? What are the different types of noise?Explain (AUC MAY 2009) 12. i)Give a random process, X (t) = A cos(t+ ), where Aand a re constants and i s a uniform random variable. Show that X (t) is ergodic in both mean and autocorrelation. (8)
EC2252 COMMUNICATION THEORY III Sem ECE R.Vanitha Asst.Prof./ECE
WWW.VIDYARTHIPLUS.COM
ii) Write a short note on shot noise an d also explain about power spectral density o f shot noise. (8) (AUC MAY 2010)
13. Write t he details about narrow band noise and t he properties of quadrature components of narrowband noise. (16) (AUC MAY 2010)
14. (i) List the different types of random process and give the definitions. (10) (ii) Write short notes on shot noise. (6) (AUC DEC 2010)
15. (i) A mixer stage has a noise figure of 20 dB and this i s preceded by an amplifier that has a noise figure of 9 dB and an available power gain of 15 dB. Calculate the overall noise figure referred to the input. (8) (ii) A receiver has a noise figure of 12 dB and it is fed by a low noise amplifierthat has a gain of 50 dB and a noise temperature of 90 K. Calculate the noise temperature of the receiver and the overall noise temperature of the receiving system. Take room temperature as 290 K. (8) 16. State and prove four properties of Gaussian process (AUC DEC 2010) (AUC MAY 2011)
17. (i)Derive the representation of narrow band noise in terms of envelop and phase component and list out its properties (ii)Consider two amplifiers are connected in cascade. First stage amplifier has gain and noise figure as 10 dB and 2 dB. Second stage has noise figure of 3 dB. (AUC MAY 2011) 18. (ii)State any 5 properties of autocorrelation function(10) (ii)When is a random process said to be strict stationary (SSS), wide sense stationary (WSS) and ergodicprocess(6) (AUC DEC 2011)
19. (i)Explain Narrowband Noise. Show that a narrow band noise n(t) can be represented in terms of its in phase and qudrature phase components (ii)Thermal noise from a measured as 4*10-17 W at a temperature of 200 C for a given bandwidth. What will be the Noise power when temperature is changed to 50 0 (AUC DEC 2011) 20. (i)List the different type of random process and give the definitions(10) (ii)Write short notes on shot noise (6) (AUC MAY 2012)
21. (i)Write the definition, power spectral density and autocorrelation function for white noise and narrow band noise(filtered white noise)(10) (ii)What causes thermal noise in a materiala? Write the expression for RMS values of the noise. (AUC MAY 2012)
EC2252 COMMUNICATION THEORY III Sem ECE R.Vanitha Asst.Prof./ECE
UNIT-IV PERFORMANCE OF CW MODULATION SYSTEMS PART-A
WWW.VIDYARTHIPLUS.COM
1. What are the advantages of the super heterodyne receiver over TRF receiver? (AUC MAY 2004) 2. What is FM threshold effect? 3. What is the (AUC MAY 2004)
S 0 / N 0 for AM (with envelope detection) with small noise case. Si / Ni
(AUC NOV 2005) (AUC NOV 2006) (AUC NOV 2006)
4. What is meant by figure of merit of a receiver? 5. What are called extended threshold demodulators? 6. What is the purpose of pre-emphasis and de-emphasis in FM?
(AUC NOV 2006, AUC MAY 2007, AUC NOV 2007) 7. What is threshold effect with respect to noise? 8. What do you understand by capture effect in FM? 9. Compare the noise performance of AM and FM systems. 10. What do you understand by FM stereo multiplexing? 11. Compare the noise performance of AM and FM systems. 12. What is meant by FM threshold effect? 13. Draw the circuit diagram of pre-emphasis filter 14. What are the characteristics of super heterodyne receivers? 15. What are the methods to improve FM threshold reduction? 16. Define threshold effect in AM receiver. 17. Define pre-emphasis and de-emphasis. (AUC MAY 2007) (AUC MAY 2008) (AUC MAY 2008) (AUC MAY 2009) (AUC MAY 2009) (AUC MAY 2010) (AUC MAY 2010) (AUC MAY 2010) (AUC MAY 2010) (AUC DEC 2010) (AUC DEC 2010)
18. Compare the noise performance of DSBSC receiver using coherent detection with AM 19. What are the methods to improve FM threshold reduction? 20. What is FM Threshold eect? 21. Dene threshold eect in AM receiver. (AUC MAY 2011) (AUC MAY 2011) (AUC DEC 2011) (AUC DEC 2011)
22. Determine the range of tuning of a local oscillator of a super Heterodyne receiver when fLO>fc. The broadcast frequency range is 540Hz to 1600 Hz. Assume Fif=445kHz (AUC MAY 2012) 23. What is capture effect in FM? (AUC MAY 2012)
EC2252 COMMUNICATION THEORY III Sem ECE R.Vanitha Asst.Prof./ECE
10
PART-B
WWW.VIDYARTHIPLUS.COM
1. (i) Explain the noise in AM receiver using its noisy model block diagram. (ii) What are pre-emphasis and de-emphasis in FM? Draw suitable circuits and explain. (AUC MAY 2007, AUC MAY 2004, AUC NOV 2005, AUC NOV2006, AUC MAY 2008) 2. (i) Explain the capture effect and FM threshold effect. (ii) Draw the block diagram of FM demodulator and explain the effect of noise in detail and compare the performance of AM and FM in the presence of noise. (AUC NOV 2006) 3. Explain the working of super heterodyne receiver. 4. Compare the noise performance of AM and FM systems. (AUC NOV2005, AUC MAY2007) 5. (i) Derive the output SNR for envelope detection. (ii) Explain the FM receiver with block diagram. 6. Write a note on the following: (i)FM threshold Effect (ii) FM threshold reduction. (AUC MAY 2008) (AUC NOV 2007) (AUC MAY 2006)
7. Why pre-emphasis is used in FM system? Sketch a typical pre-emphasis circuit. (AUC MAY 2008) 8. State central limit theorem. (AUC NOV 2008)
9. (i) Draw the model of DSB/SC receiver that using coherent detection and derive its figure merit. (ii) Discuss about the noise performance of an FM receiver to evaluate its figure of merit. (AUC NOV 2008)
10. Derive the expression for the Power spectral density at the output of a FM discriminator when the received signal is corrupted by additive white Gaussian Noise. (AUC MAY 2009) 11. Derive a n expression for SNR at input (SNRc) and output of (SNRo) of a coherent detector. (16) 12. (i) Explain pre-emphasis and De-emphasis i n detail. (10) (ii) Compare the performances of AM and FM systems. (6) (AUC MAY 2010) (AUC MAY 2010)
13. Derive the expression for figure of merit of an AM receiver using envelope Detection. What do you infer from the expression? (16) (AUC DEC 2010)
14. Define and explain FM Threshold effect. With suitable diagram, explain threshold reduction by FMFB demodulator. (16) (AUC DEC 2010) 11
EC2252 COMMUNICATION THEORY III Sem ECE R.Vanitha Asst.Prof./ECE
15. (i)Sketch the block diagram of DSB-SC/AM system and derive the figure of merits briefly explain it 16. (i)Explain pre-emphasis and De-emphasis in detail. (ii)Compare the performances of AM and FM systems(AUC MAY 2011)
WWW.VIDYARTHIPLUS.COM
(ii)Using super heterodyneprinciple, drawthe block diagram of AM radio receiver and (AUC MAY 2011)
Obtain the expression for gure of merit of DSB -SC receiver using coherent detection. 17. (i)Derive the gure of merit for FM Receiver.(10) (ii)What is the necessity of pre-emphasis and de-emphasis used in FM System? Explain pre-emphasis and de-emphasis with neat circuit.(6) (AUC DEC 2011) (AUC DEC 2011)
18. Sketch the block diagram of DSB-SC/AM system and derive the figure of merit. (AUC MAY 2012) 19. Using super heterodyne principle, draw the block diagram of AM radio 20. Discuss the effects of noise on the carrier in FM receiver with suitable mathematical derivation. (AUC MAY 2012)
EC2252 COMMUNICATION THEORY III Sem ECE R.Vanitha Asst.Prof./ECE
12
UNIT-V INFORMATION THEORY PART-A 1. What is binary symmetric chanel 2. What is discrete chanel capacity 3. Define information rate? 4. Define entropy? 5. Define mutual information? 6. Find the entropy Symbol probability S0 0.4 S1 0.3 S2 0.1 S3 0.1
WWW.VIDYARTHIPLUS.COM
(AUC DEC 2006) (AUC DEC 2006) (AUC DEC 2007) (AUC DEC 2007) (AUC MAY 2008)
S4 0.1 (AUC DEC 2008)
7. State Shanon first theorem? 8. State chanel capacity theorem. 9. Define entropy for a discrete memory less source. 10. State chanel coding theorem.
(AUC DEC 2008) (AUC MAY2008) (AUC MAY 2007) (AUC MAY 2007)
11. What is chanel capacity of binary synchronous chanel with error probability of 0.2? (AUC DEC 2007) 12. Calculate the entropy of the source with a symbol set containing 64symbols each with a probability pi =1/64? 13. Compare Shanon and Huffman coding. (AUC APR 2008) (AUC MAY 2009)
14. A discrete memoryless source with source alphabet S={ S 0, S1, S2} with respective probabilities P={1/4,1/4,1/2}. Find the entropy. 15. Determine differential entropy. . 16. Define entropy function. 17. Define Rate Bandwidth and Bandwidth efficiency. 18. A source generates 3 messages with probability 0.5, 0.25, 0.25. Calculate source entropy. 19. Define Rate Bandwidth and Bandwidth efficiency. 20. Define entropy function. 21. Differentiate between lossless and lossy coding (AUC DEC 2010) (AUC DEC 2010) (AUC MAY 2011) (AUC MAY 2011) (AUC MAY 2010) (AUC MAY 2010)
22. State Shannons channel capacity theorem, for a power and band limited channel. (AUC DEC 2011) 23. Calculate the Entropy of the Source with symbol probabilities 0.6, 0.3 and 0.1. (AUC DEC 2011) 24. A source generate three message with probability 0.5,0.25,0.25. calculate H(x) (AUC MAY 2012) 25. State the advantages of Lempi=Ziv coding (AUC MAY 2012) 13
EC2252 COMMUNICATION THEORY III Sem ECE R.Vanitha Asst.Prof./ECE
WWW.VIDYARTHIPLUS.COM
PART-B 1. Five symbols of the alphabet of a discrete memory less source and their probabilities are given below:[s] = [so , s1 , s2 , s3 , s4] [P(s)] = [0.4 ,0.2 , 0.2 ,0.1 , 0.1] Code the symbols using Huffman coding. 2. (AUC NOV 2006)
(i) Define Mutual information. Find the relation between the mutual information and the joint entropy of the chanel input and chanel output. (ii) What are the implications of information capacity theorem? (AUC NOV 2006)
3. (i) Discuss the source coding theorem. (ii) Give the advantage and disadvantage of chanel coding in detail. (iii) Discuss the data compaction. 4. (i) Write short notes on differential entropy. (ii) Derive the chanelcapacity theorem. (iii)Discuss the implication of the information capacity theorem. (AUC MAY2007) (AUC MAY 2007)
5. A discrete memory less chanel has the following alphabet with probability of occurrence. Symbol S0 S1 0.0625 S2 0.25 S3 0.0625 S4 0.125 S5 0.125 S6 0.25
Probability 0.125
Generate the Huffman coding. Find average Coded Length, entropy and . ` (AUC NOV 2007)
6. (i)Derive the expression for chanel capacity of a binary symmetric chanel. (ii) Encode the following source using Huffman Coding. X = { x1, x2 , x3 , x4 , x5 } P(X) = {0.2, 0.02 , 0.1 , 0.38 , 0.3 } (AUC MAY 2006)
7. Derive the expression for chanel capacity of a continuous chanel. Find also the expression for chanel capacity of a continuous chanel of infinite bandwidth comment on the results. (AUC MAY 2006)
EC2252 COMMUNICATION THEORY III Sem ECE R.Vanitha Asst.Prof./ECE
14
8. Consider a sequence of letters of English occurrence as given. Letter A I 0.1 L 0.2 M 0.1
alphabet with their probabilities of
WWW.VIDYARTHIPLUS.COM
N 0.1
O 0.2
P 0.1
Y 0.1
Probability 0.1
Compute two different Huffman codes for this alphabet. Also for each of the two codes, find the average code-word length and variance of average code-word length over ensemble of letters. (AUC NOV 2008)
9. (i) Consider a discrete memory less chanel with input alphabet X, output alphabet Y and transition probabilities p(Yk / Xj ). Find the mutual information of chanel to obtain the chanel capacity. Also find the chanel capacity of binary symmetricchanel. (ii) Elaborate the chanel coding theorem with an example. 10. Discuss the various technique used for compression of information (AUC MAY 2009) I. II. III. IV. Define differential entropy. Define Mutual information. What is the relation between mutual information and chanel capacity? Give the (Shanon- Hartley) information capacity theorem and (AUC MAY 2009) (AUC NOV 2008)
Discuss the implication of the same in detail.
11. (i) Find the code words for five symbols of t he alphabet of a discrete memory- less source with probability {0.4, 0.2, 0.2, 0.1, 0.1}, using Huffman coding and determine the source entropy and average code word length. (10) (ii) Discuss the source coding theorem. (6) (AUC MAY 2010)
12. (i) Derive t hechanel capacity of a continuous band limited white Gaussian noise chanel. (10) (ii) Discuss about rate distortion theory. (6)(AUC MAY 2010) 13. (i) An Analog signal i s band limited to `B' Hz and sampled at Nyquist rate. The sampled signals are quantized into 4 levels. Each level represents
one message. The probability of occurrence of the four messages are p1=p3=1/8; p2=p4=3/8. Find out information rate of the source. (6)
(ii) Five source messages are probable to appear as m1 = 0:4, m2 = 0:15, m3 = 0:15, m4 = 0:15, m5 = 0:15. Find coding efficiency for (1) ShannonFano (10) coding, (2) Huffman coding. (AUC DEC 2010)
EC2252 COMMUNICATION THEORY III Sem ECE R.Vanitha Asst.Prof./ECE
15
14. (i)
Derive
the
chanel
capacity
for
Binary
Symmetric
WWW.VIDYARTHIPLUS.COM
chanel.(6)
(ii) Derive the chanel capacity for band limited, power limited Gaussian Chanel. (10) (AUC DEC 2010) 15. Using Huffman code I, encode the following symbols.S = [0.3, 0.2, 0.25, 0.12, 0.05, 0.08,]Calculate average code length, entropy of the source, code efficiency, redundancy 16. i)State and prove the properties of mutual information ii)The channel transition matrix [0.9 0.1 0.2 0.8 ]. Draw the channel diagram and determine the probabilities associated with output assuming equipropable inputs. (AUC MAY 2011) 17. Justify the need for an efficient source encoding process in order to increase the average transmitted information per bit, if the source emitted symbol are not equally likely with example .consider a discrete memoryless source for your justification 18. Eight possible messages m1,m2,m3,m4,m5,m6,m7 and m8 from a source and their P(m1)=0.5,P(m2)=0.15,P(m3)=0.15,P(m4)=0.08,P(m5)=0.08,P(m6)=0.02,P(m7)=0.0 1,P(m8)=0.01.Construct the Shannon fano coding for each of these message in order to increase the average information per bit. Find the coding efficiency. (AUC DEC 2011) 19. State and explain Shannon theorem on channel capacity(12) Define Mutual information. State any two propertites(4) (AUC DEC 2011) (AUC MAY 2011)
20. A Database Management System (DMS) has following alphabet with probability of occurrence as shown below Symbol S0 S1 S2 S3 S4 S5 0.125 S6 0.25 (AUC MAY 2012) 21. Derive Shannon-Hartley theorem for the channel capacity of a continous channel having an average limitation and perturbed by an additive band limited white Gaussian noise. Explain the bandwidth signal to noise radio trade off for this theorem (AUC MAY 2012)
probability 0.125
0.0625 0.25
0.06252 0.125
EC2252 COMMUNICATION THEORY III Sem ECE R.Vanitha Asst.Prof./ECE
16
You might also like
- SC Am08Document2 pagesSC Am08kvagpNo ratings yet
- AMCAT Syllabus 2015 and Question Paper PatternDocument5 pagesAMCAT Syllabus 2015 and Question Paper PatternRamkumar SivakaminathanNo ratings yet
- Sbi Po 2016Document4 pagesSbi Po 2016Aslam BagwanNo ratings yet
- Final Advt Clerical 05-04-2016-17Document5 pagesFinal Advt Clerical 05-04-2016-17UploadingfilesNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Distance MeterDocument5 pagesUltrasonic Distance Meterkowshiksarma100% (3)
- Internet and Java R2008: Text BooksDocument1 pageInternet and Java R2008: Text BooksRamkumar SivakaminathanNo ratings yet
- LiFi Technology Uses Visible Light for Wireless CommunicationDocument1 pageLiFi Technology Uses Visible Light for Wireless CommunicationRamkumar SivakaminathanNo ratings yet
- 50 Words To Get You Started in HindiDocument73 pages50 Words To Get You Started in HindimalumrobNo ratings yet
- 300 ANTONYMS QuestionsDocument11 pages300 ANTONYMS QuestionsvickyNo ratings yet
- Internet and Java R2008Document2 pagesInternet and Java R2008Ramkumar SivakaminathanNo ratings yet
- DijikstraDocument6 pagesDijikstraRamNo ratings yet
- Fast Architectures For Fpga-Based Implementation of Rsa Encryption AlgorithmDocument8 pagesFast Architectures For Fpga-Based Implementation of Rsa Encryption AlgorithmRamkumar SivakaminathanNo ratings yet
- B.E./E.Tech. D E G R E E Examination, April / May 2011Document2 pagesB.E./E.Tech. D E G R E E Examination, April / May 2011Ramkumar SivakaminathanNo ratings yet
- Internet and Java R2008: Text BooksDocument1 pageInternet and Java R2008: Text BooksRamkumar SivakaminathanNo ratings yet
- Internet and Java R2008Document2 pagesInternet and Java R2008Ramkumar SivakaminathanNo ratings yet
- TV 2 MarksDocument1 pageTV 2 MarksRamkumar SivakaminathanNo ratings yet
- Assessment Test - 8Document1 pageAssessment Test - 8Ramkumar SivakaminathanNo ratings yet
- AMCAT Syllabus 2015 and Question Paper PatternDocument5 pagesAMCAT Syllabus 2015 and Question Paper PatternRamkumar SivakaminathanNo ratings yet
- Time and Distance Important Facts and FormulaeDocument4 pagesTime and Distance Important Facts and Formulaez1y20% (1)
- Assessment Test 4Document2 pagesAssessment Test 4Ramkumar SivakaminathanNo ratings yet
- Engineering EthicsDocument1 pageEngineering EthicsRamkumar SivakaminathanNo ratings yet
- AMCAT Sample PaperDocument14 pagesAMCAT Sample PaperHima Chandu KakiNo ratings yet
- Professional EthicsDocument3 pagesProfessional EthicsRamkumar SivakaminathanNo ratings yet
- NM IMP FormulaeDocument10 pagesNM IMP FormulaeRamkumar SivakaminathanNo ratings yet
- Shakuntala Devi Puzzles Solutions PDFDocument48 pagesShakuntala Devi Puzzles Solutions PDFarvidkumar8706067% (6)
- Sample Paper R BEC V PDFDocument6 pagesSample Paper R BEC V PDFAsif MohammedNo ratings yet
- Assessment Test 4Document2 pagesAssessment Test 4Ramkumar SivakaminathanNo ratings yet
- C Faq PDFDocument17 pagesC Faq PDFLakshman BaaleNo ratings yet
- Let Us C Yashwant Kanetkar PDFDocument107 pagesLet Us C Yashwant Kanetkar PDFmorigasakiNo ratings yet
- MA2264 Numerical Methods NotesDocument47 pagesMA2264 Numerical Methods NotesRamkumar SivakaminathanNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Key Note Units 3-4Document4 pagesKey Note Units 3-4Javier BahenaNo ratings yet
- Structural Testing Facilities at University of AlbertaDocument10 pagesStructural Testing Facilities at University of AlbertaCarlos AcnNo ratings yet
- Antiepilepticdg09gdg 121231093314 Phpapp01Document145 pagesAntiepilepticdg09gdg 121231093314 Phpapp01Vaidya NurNo ratings yet
- Light Body ActivationsDocument2 pagesLight Body ActivationsNaresh Muttavarapu100% (4)
- Mitchell 1986Document34 pagesMitchell 1986Sara Veronica Florentin CuencaNo ratings yet
- Mosek UserguideDocument81 pagesMosek UserguideadethroNo ratings yet
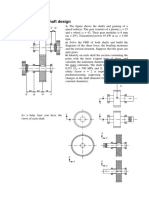
- Shaft design exercisesDocument8 pagesShaft design exercisesIvanRosellAgustíNo ratings yet
- ECE 340 Lecture 26 Avalanche Zener BreakdownDocument20 pagesECE 340 Lecture 26 Avalanche Zener BreakdownDao ZhangNo ratings yet
- The History of American School Libraries: Presented By: Jacob Noodwang, Mary Othic and Noelle NightingaleDocument21 pagesThe History of American School Libraries: Presented By: Jacob Noodwang, Mary Othic and Noelle Nightingaleapi-166902455No ratings yet
- Assignment2-9509Document5 pagesAssignment2-9509ritadhikarycseNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Basic Logical Concepts - For Students PDFDocument65 pagesChapter 3 - Basic Logical Concepts - For Students PDFTiên Nguyễn100% (1)
- A Personality Trait-Based Interactionist Model of Job PerformanceDocument18 pagesA Personality Trait-Based Interactionist Model of Job PerformanceAlvina AhmedNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Typology Concept and MethodDocument13 pagesAgricultural Typology Concept and MethodAre GalvánNo ratings yet
- Dompet Digital Di Kota SemarangDocument10 pagesDompet Digital Di Kota SemarangRikson TandelilinNo ratings yet
- What Is Architecture?Document17 pagesWhat Is Architecture?Asad Zafar HaiderNo ratings yet
- Space Gass 12 5 Help Manual PDFDocument841 pagesSpace Gass 12 5 Help Manual PDFNita NabanitaNo ratings yet
- What Is Science Cornell Notes ExampleDocument3 pagesWhat Is Science Cornell Notes Exampleapi-240096234No ratings yet
- Platon Si Academia Veche de ZellerDocument680 pagesPlaton Si Academia Veche de ZellerDan BrizaNo ratings yet
- Subject and Power - FoucaultDocument10 pagesSubject and Power - FoucaultEduardo EspíndolaNo ratings yet
- Receiving Welcoming and Greeting of GuestDocument18 pagesReceiving Welcoming and Greeting of GuestMarwa KorkabNo ratings yet
- Phase Domain Modelling of Frequency Dependent Transmission Lines by Means of An Arma ModelDocument11 pagesPhase Domain Modelling of Frequency Dependent Transmission Lines by Means of An Arma ModelMadhusudhan SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Tamil Literary Garden 2010 Lifetime Achievement Award CeremonyDocument20 pagesTamil Literary Garden 2010 Lifetime Achievement Award CeremonyAnthony VimalNo ratings yet
- Corporate Strategic Planning AssignmentDocument10 pagesCorporate Strategic Planning AssignmentSumit DuttaNo ratings yet
- Policarpio 3 - Refresher GEODocument2 pagesPolicarpio 3 - Refresher GEOJohn RoaNo ratings yet
- MySQL Cursor With ExampleDocument7 pagesMySQL Cursor With ExampleNizar AchmadNo ratings yet
- 0418 w08 QP 1Document17 pages0418 w08 QP 1pmvarshaNo ratings yet
- Dimensioning GuidelinesDocument1 pageDimensioning GuidelinesNabeela TunisNo ratings yet
- Manual For The MCPL Programming LanguageDocument74 pagesManual For The MCPL Programming Languagechri1753No ratings yet
- Grammar Booster: Lesson 1Document1 pageGrammar Booster: Lesson 1Diana Carolina Figueroa MendezNo ratings yet
- TheMindReader TeaserA WhatDocument7 pagesTheMindReader TeaserA WhatnakulshenoyNo ratings yet