Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Relationship between air pressure and altitude
Uploaded by
Lily Suhany MahmoodOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Relationship between air pressure and altitude
Uploaded by
Lily Suhany MahmoodCopyright:
Available Formats
SULIT
4531/2
The following information may be useful. The symbols have their usual meaning. Maklumat berikut mungkin berfaedah. Simbol-simbol mempunyai makna yang biasa.
1.
a=
vu t
16.
Power, P
= energy time
2.
v2 = u2 + 2 as 1 at2 2
17.
V = IR
3.
s = ut
18.
Power, P = IV kuasa Ns = Vs Np Vp Efficiency = (kecekapan) Is Vs x 100 % Ip Vp 1 v
4.
Momentum = mv
19.
5.
F = ma = 1 mv2 2
20.
6.
Kinetic energy (Tenaga kinetik )
21.
1 f
= 1 + u
7.
Potential energy Tenaga keupayaan
= mgh
22.
n = sin i sin r
8.
Elastic potential energy = 1 Fx (Tenaga keupayaan kenyal) 2 =
23.
n =
Real depth Apparent depth
9.
m V
24.
= ax D Q= It
10.
Pressure, = hpg. Tekanan Pressure, = F Tekanan A Heat, Q = Haba mc
25.
11.
26. 27.
E = I (R + r) eV = mv2 g = 10 ms-2
12.
28.
13. 14. 15.
PV = Constant (pemalar) E = m c2 v=f
4531/2 2 [Lihat sebelah]
SULIT SECTION A [60 marks] Answer all questions in this section. You are advised to spend 90 minutes on this section
4531/2
1. Diagram 1.1 shows athe arrangement of apparatus for the experiment to find out the relationship between area and the rate of evaporation. A petri dish is filled with liquid X and then put on a tripple beam balance. Diagram 1.2 shows the reading of triple beam balance.
Diagram 1.1
Diagram 1.2
(a) What is physical quantity measured by the triple beam balance? . [1 mark ] (b) What is the value of the smallest division on the scale? . [1 mark ] (c) Using Diagram 1.2, state the reading shown by triple beam balance. . [1 mark ]
4531/2
[Lihat sebelah]
SULIT 2. Diagram 2.1 shows Adam is pulling a 50 kg box with tread.
4531/2
Diagram 2.1 (a) What is the meaning of frictional force? . [1 mark ] (b) Adam pull the box with force 500 N and the box moves with acceleration 40.0 m s-2. (i) Calculate the friction force acting on surface.
[2 marks ] (ii) State one modification that can be done to reduce the friction force on surface. .. [1 mark ] (c) Diagram 2.2 shows an aeroplane flying horizontally with a constant velocity. R and S are two forces which maintain the aeroplane at constant altitude. R
Air resistance
Forward trust
Diagram 2.2 (i). Name the forces R and S. S
R: .. S: .. (ii). Write equation to show the relationship between R and S. . [1 mark] (iii) Which of the forces is caused by the Bernoulli's effect? [1 mark]
4531/2 4 [Lihat sebelah]
[2 marks]
SULIT 4531/2 3. Diagram 3 shows an object, O, [placed in front of a type of lens. F is the focal point of the lense]
Diagram 3
(a) What is the meaning of focal point? [1 mark] (b) Based on the diagram, (i) Name the lens [1 mark] (ii) Draw a ray diagram on Diagram 3.1 to show how the image is formed. [3 marks]
(iii)
State one characteristic of the image formed. .. [1 mark]
(iv)
What happens to the size of image when the focal length of lens is decreased? .. [1 mark]
4531/2
[Lihat sebelah]
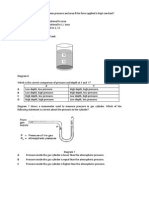
SULIT 4. Diagram 4.1 shows the foothill and mountain peak of Mount Kinabalu, Sabah.
4531/2
Diagram 4.1 (a) What is meant by atmospheric pressure? .. [1 mark] (b) Using Diagram 4.1: (i) Compare the altitude between mountain peak and foothill [1 mark] (ii) Compare the air pressure at mountain peak and foothill. (iii) [1 mark] Based on answer in (b)(i) and (b)(ii), state the relationship between the altitude and the air pressure. [1 mark] (c) Diagram 4.2 shows an instrument to measure atmospheric pressure.
76 cm
(i)
Diagram 4.2 Name the instrument shown in Diagram 4.2. ..
(ii) (iii)
On the Diagram 4.2, draw the arrow to show the atmospheric pressure acting. State the value of atmospheric pressure shown on the diagram 4.2
[1 mark] [1 mark]
. [1 mark]
4531/2 6 [Lihat sebelah]
SULIT 5. Diagram 5.1 and Diagram 5.2 shows a stone hanging from a spring balance in two situations.
4531/2
Diagram 5.1 (a) What is the meaning of weight?
Diagram 5.2
.. [1 mark] (b) Based on Diagram : (i) What is the difference between the spring balance reading in Diagram 5.1 and Diagram 5.2? _______________________ N [1 mark] (ii) Name the force that is represented by the reading in (b)(i). .. [1 mark] (c) Complete the following sentence by underlining the correct words. The weight of the water displaced is (less than, equal to, more than) the buoyant force acting on the stone. [1 mark] (d) Calculate the volume of water displaced. [Density of water = 1000 kg m-3, g = 10 m s-2]
[2 marks] (e) What happens to the spring balance reading in Diagram 5.2 when the stone is immersed deeper into the water? . [1 mark]
4531/2 7 [Lihat sebelah]
SULIT 6. Diagram 6.1 shows air bubbles produced by fish.
4531/2
Diagram 6.1 (a) Explain why the volume of an air bubble increases as it moves towards the surface. .. [2 marks] (b) Name the physics law involved in (a). . [1 mark] (c) An air bubble of volume 5 cm is released by a fish at a depth of 0.5 m. Calculate the volume of the
3
air bubble when it reaches the surface of the water. [ Assume that the atmospheric pressure is 10 m water ]
[2 marks]
4531/2
[Lihat sebelah]
SULIT 4531/2 (d) Diagram 6.2 shows the set up of apparatus used to study the relationship between pressure and volume
of air trapped in an air-tight column at constant temperature and mass.
Instrument X
Diagram 6.2 (a) Name the measuring instrument labelled X. ............ [1 mark] (b) Name the physical quantity measured by instrument labelled X. .... [1 mark] (c) What will happen to the volume of air trapped in an air-tight column when the reading of instrument X increases?
..... [1 mark]
4531/2
[Lihat sebelah]
SULIT
4531/2
7. Diagram 7.1(a) shows a boy skating down a ramp from position X. Diagram 7.1(b) shows the velocity-time graph of the boy from X to Z.
Diagram 7.1(a)
Diagram 7.1(b)
Diagram 7.2(a) shows the same boy skating down from position Y by using another ramp. Diagram 7.2(b) shows the velocity-time graph of the boy from Y to Z.
Diagram 7.2(a)
Diagram 7.2(b)
Both ramps are of the same slope and surface. (a) Name the physical quantity represented by the gradient of the velocity-time graph. .... [1 mark] (b) Observe Diagram 7.1(a) and Diagram 7.2(a). (i) Compare the gravitational potential energy of the boy at X and Y. . [1 mark] (ii) Compare the velocity of the boy at Z in these two situations. [1 mark]
4531/2
10
[Lihat sebelah]
SULIT (iii)
4531/2 Compare the kinetic energy of the boy at Z in these two situations. . [1 mark]
(c) Based on the answers in (b), (i) State the relationship between the gravitational potential energy and the kinetic energy of the boy. .. [1 mark] (ii) State the physics concept involved. .. [1 mark] (d) (i) Based on Diagram 7.1(a), what happens to the velocity of the boy when he skates from Z to Q?
.. [1 mark] (ii) Give one reason for the answer in (d)(i).
.. [1 mark]
4531/2
11
[Lihat sebelah]
SULIT 8. Table 8 shows two types of pot and their characteristics.
4531/2
(a) What is the meaning of specific heat capacity? [1 mark] (b) Based on Table 8, state suitable characteristics of the pot if it is to be used for cooking something rapidly. Give reason for the suitability of the characteristics. (i) Material for making the pot. Reason ... [2 marks] (ii) Material for making the handle of the pot .. Reason .. [2 marks] (iii) Mass of the pot .. Reason . [2 marks]
4531/2
12
[Lihat sebelah]
SULIT 4531/2 (c) The pots are heated by using an electric hot plate of power 800 W. Based on the information in the Table 8, calculate the time taken to achieve a temperature rise of 90oC for: (i) The clay pot
[2 marks] (ii) The copper pot
[2 marks] (d) Determine the most suitable pot that is safest to handle and can be heated in the shortest period of time. . [1 mark]
4531/2
13
[Lihat sebelah]
SULIT
4531/2
SECTION B [20 marks] Answer any one question from this section 9. Diagram 9.1 shows a boy and his father sitting on two identical beach balls, A and B, respectively.
Their weights are balanced by the buoyant force. (a) What is the meaning of weight? [1 mark]
(b) (i) Using Diagram 9.1, compare the weight of the boy and his father, the volume of the water displaced and the buoyant force acted on both of them. (ii) State the relationship between the buoyant force and: (a) The volume of water displaced (b) The weight of water displaced (iii) Name the physics principle involved. [2 marks] [1 mark] [3 marks]
(c) Diagram 9.2 shows what happens when a wooden block is held above the water surface and then released into the water.
When the wooden block is released, it falls into the water and goes completely under the water surface. Then it moves upwards and floats on the water surface. [3 marks]
(d) The State Forestry Department is going to organize a raft competition. As a team leader, you are required to give some suggestions to design a raft which can accommodate 15 participants and be able to move quickly is water. Using your knowledge of motion, forces and properties of materials, state and explain the suggestions, based on the following aspects: (i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
4531/2
The shape of the raft. The material used for the raft. The size of the raft. The design of the raft.
14
[2 marks] [2 marks] [2 marks] [4 marks]
[Lihat sebelah]
SULIT 4531/2 10. Diagram 10.1 and 10.2 show two types of metal block of the same mass being heated using similar heaters for 10 minutes. Both metal blocks have the same initial temperatures of 30 oC. The specific heat capacity of copper is 387 J kg-1 oC -1 and 900 J kg-1 oC -1 for aluminium.
Diagram 10.1 (a) The specific heat capacity of copper is 387 J kg-1 oC-1? What is meant by the statement above?
Diagram 10.2
[1 mark ]
(b) Using Diagram 10.1 and Diagram 10.2, compare the increase in temperature and the specific heat capacity of the metals used and time of heating. Relating the time of heating, the increase in temperature and the specific heat capacity of the metals to deduce a relevant physics concept. [5 marks ] (c) A substance M of 0.1 kg mass is heated by a 70 W electrical heater from -20 C. The heating curve is shown in the diagram 10.3.
Diagram 10.3 Based on the above graph, state the physical condition of substance M at BC and CD By using kinetic theory, explain why the temperature of substance M is constant in BC even though heat is still being supplied to it. [4 marks] (d) Diagram 10.4 shows food being fried in a wok of cooking oil. (i) (i)
Diagram 10.4 Suggest and explain how the food to be fried can be cooked in a short time based on the following aspects of the material of the wok and the cooking oil. Material of the wok - Specific heat capacity - Mass - Melting point Cooking oil - Specific heat capacity - Boiling point [10 marks]
4531/2 15 [Lihat sebelah]
SULIT Section C [ 20 marks] Answer any one question from this section The time suggested to complete this section is 30 minutes
4531/2
11. Diagram 11.1 shows a helmet, gloves and jacket worn by bikers of a motorcycle racing tournament.
Diagram 11.1 (a) What is meant by impulsive force? [1 mark]
(b) The biker must wear the helmet, gloves and jacket in race to keep him in safe condition. Explain how the helmet, gloves and jacket can keep the bikers in safe condition? [2 marks]
(c) Explain why the biker moved forward and seriously injured when the motorcycle stopped suddenly. [2 marks] (d) A racing motorcycle of mass 202 kg accelerates from rest to its maximum velocity of 160 km h-1 in 10 s. (i) (ii) Convert 160 km h-1 into SI unit. Calculate the acceleration of the racing motorcycle. [ 5 marks]
(e) Table 11 shows four racing motorcycle P, Q, R and S with different specifications. You are required to determine the most suitable motorcycle to move fast and safe when racing. Study the specifications of all the four motorcycle from the following aspects: The type of brakes The width of tyres Mass of motorcycle The seat height (measured from the lowest setting of the seat to the ground)
Explain the suitability of the aspects. Justify your choice. [10 marks]
4531/2
16
[Lihat sebelah]
SULIT Racing bike A Type of brake: without ABS Mass : 205.0 kg Seat height 905 mm
4531/2
Width of the tyre 1440 mm Racing bike B Type of brake: without ABS Mass : 220.0 kg Seat height 1010 mm
Width of the tyre 940 mm
Racing bike C Type of brake: ABS Mass : 208.0 kg Seat height 815 mm
Width of the tyre 1440 mm
Racing bike D Type of brake: ABS (ABS: Antilock Brake System) Mass : 242.0 kg Seat height 1055 mm
Width of the tyre 940 mm Table 11
4531/2 17 [Lihat sebelah]
SULIT 12. Diagram 12.1 shows a submarine is sea water due to effect of buoyant force.
4531/2
Diagram 12.1 (a) What is the meaning of buoyant force. (b) Explain how a submarine is able to submerge into deep sea water? [1 mark] [4 marks]
(c) You asked to investigate the characteristic of each backhoes in table 12 and choose a backhoe that can do heavy works, an example of a backhoe is shown in diagram 12.2.
Diagram 12.2 Explain the suitability of the characteristics each backhoes. Determine the most suitable backhoe. Give reason for your choice. Type of backhoe Size of tyre P Q R S T Large Low Large Medium Large Centre of gravity Large Medium Low Large Low Table 2 (d) The Diagram 12.3 shows a hydraulic system with two pistons A and B, connected to a tube that contains oil. The area of pistons A and B is 5 cm2 and 50 cm2 respectively, and a force of 10 N is exerted on piston A. Characteristics Fluid used in hydraulic system Liquid Gas Liquid Liquid Gas mass Large Small Low Low Medium [10 marks]
Diagram 12.3 (i) Calculate the pressure that is exerted by piston A on the oil. (ii) What is the pressure that is exerted by the oil on piston B? Explain your answer. END OF QUESTIONS
4531/2 18 [Lihat sebelah]
[5 marks]
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Force and PressureDocument19 pagesForce and Pressurelilysuhany100% (1)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Force N Motion 3Document5 pagesForce N Motion 3Lily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Eksp pd1Document5 pagesEksp pd1Lily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Anchor Wake Up To SpringDocument2 pagesAnchor Wake Up To SpringLily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- ExplainDocument1 pageExplainLily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Forces N PressureDocument33 pagesForces N PressureLily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Introduction to Physics: Base and Derived QuantitiesDocument5 pagesIntroduction to Physics: Base and Derived QuantitiesLily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Wave 1-3 ModificationDocument3 pagesWave 1-3 ModificationLily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Direction of motion of wire between magnetsDocument8 pagesDirection of motion of wire between magnetsLily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Test LightDocument3 pagesTest LightLily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Transistor Circuits ExplainedDocument5 pagesTransistor Circuits ExplainedLily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Checklist ElectromgntDocument1 pageChecklist ElectromgntLily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Latihan PD2Document1 pageLatihan PD2Lily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Trenganu 2010 k3 PDFDocument0 pagesTrenganu 2010 k3 PDFLily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Soalan AplikasiDocument19 pagesSoalan AplikasiLily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- ExplainDocument1 pageExplainLily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Paper3 f4pd1 Okt2012Document4 pagesPaper3 f4pd1 Okt2012Lily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- E V + Ir R - GradientDocument1 pageE V + Ir R - GradientLily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Midyear Form 52013Document18 pagesMidyear Form 52013Lily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- ExplainDocument1 pageExplainLily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Test LightDocument3 pagesTest LightLily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Light PD1Document4 pagesLight PD1Lily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Modifation WavesDocument4 pagesModifation WavesLily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Plot GrafDocument3 pagesPlot GrafLily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Latihan Linear MotionDocument3 pagesLatihan Linear MotionLily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PhysicsDocument5 pagesIntroduction To PhysicsLily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Egg Egg: Breaks Does Not BreakDocument3 pagesEgg Egg: Breaks Does Not BreakLily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- SPM2010Document14 pagesSPM2010Lily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument2 pagesOhm's LawLily Suhany MahmoodNo ratings yet
- CCTV Course NotesDocument54 pagesCCTV Course NotesBadr El OuassifNo ratings yet
- Determination and Passion, the Art of Innovation Through LightDocument16 pagesDetermination and Passion, the Art of Innovation Through LightCristabel RamirezNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Iit 2011 FST1 QNS P1 PDFDocument25 pagesIit 2011 FST1 QNS P1 PDFKartikeya aroraNo ratings yet
- Jupiter 8 Manual de ServicioDocument8 pagesJupiter 8 Manual de ServicioJosé Antonio Ocón LópezNo ratings yet
- UIOUODocument9 pagesUIOUOEA Paul Fernandez AguraNo ratings yet
- Long Test Science 10 2nd QuarterDocument29 pagesLong Test Science 10 2nd QuarterAple RigorNo ratings yet
- 13a-Waves and Optics MC Practice Problems - Section C Geometric OpticsDocument19 pages13a-Waves and Optics MC Practice Problems - Section C Geometric OpticsIan StantonNo ratings yet
- Cbse Cl10 Ead Science ExamDocument80 pagesCbse Cl10 Ead Science ExamKrishan RickyNo ratings yet
- Sgsits ManualDocument91 pagesSgsits ManualJoyita BiswasNo ratings yet
- Photonicsspectra201307 DLDocument76 pagesPhotonicsspectra201307 DLdenghueiNo ratings yet
- Safety enDocument72 pagesSafety enAlina CiureaNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Mirrors: Lesson 4 (3 Hours)Document24 pagesMirrors: Lesson 4 (3 Hours)Donna100% (1)
- Parts of Microscope and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesParts of Microscope and Their Functionsiammiiie0150% (2)
- BIOE 4391 - Ass# 3Document5 pagesBIOE 4391 - Ass# 3Mansour AbdulazizNo ratings yet
- Fda Q&aDocument17 pagesFda Q&ablackcholoNo ratings yet
- Camera Calibration Methods ExplainedDocument14 pagesCamera Calibration Methods Explainedamalinaah100% (1)
- Guide in Reviewing Intervention MaterialsDocument6 pagesGuide in Reviewing Intervention MaterialsMichelle Gonzales Caliuag0% (1)
- 准直镜Document9 pages准直镜陈森淼No ratings yet
- Eastern Bloc New PDFDocument33 pagesEastern Bloc New PDFkurageartNo ratings yet
- Star FinderDocument5 pagesStar FinderJimNo ratings yet
- Laws of Lenses and Optical InstrumentsDocument5 pagesLaws of Lenses and Optical InstrumentsJose GalvanNo ratings yet
- Looking at lenses indexDocument1 pageLooking at lenses indexLê Xuân NamNo ratings yet
- Experiments Physics: Demonstration INDocument14 pagesExperiments Physics: Demonstration INVikas VatsNo ratings yet
- Reflection & Refraction of LightDocument60 pagesReflection & Refraction of LightgeniusamahNo ratings yet
- EAMCET-2012 Question PaperDocument56 pagesEAMCET-2012 Question PaperEdara Rajesh KumarNo ratings yet
- CTC 3D Printer ManualDocument35 pagesCTC 3D Printer Manualbeeeeel100% (1)
- Old Eyes and Iron Sights - Rear Sight Diopter Lens TestingDocument2 pagesOld Eyes and Iron Sights - Rear Sight Diopter Lens TestingHawkeye-10XNo ratings yet
- Priyanka Jillella Lens Design HW1 Zemax SoftwareDocument11 pagesPriyanka Jillella Lens Design HW1 Zemax SoftwarePriyanka JillellaNo ratings yet
- Kvpy 2009-15 Papers PDFDocument116 pagesKvpy 2009-15 Papers PDFManju MathurNo ratings yet
- Calculate bifocal lens prescription from trifocal prescriptionDocument8 pagesCalculate bifocal lens prescription from trifocal prescriptionEzal AbqaryNo ratings yet
- Crochet Impkins: Over a million possible combinations! Yes, really!From EverandCrochet Impkins: Over a million possible combinations! Yes, really!Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- Sri Yantra with Golden Ratio Triangle and InscriptionsFrom EverandSri Yantra with Golden Ratio Triangle and InscriptionsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Martha Manual: How to Do (Almost) EverythingFrom EverandThe Martha Manual: How to Do (Almost) EverythingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- 100 Micro Amigurumi: Crochet patterns and charts for tiny amigurumiFrom Everand100 Micro Amigurumi: Crochet patterns and charts for tiny amigurumiRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Sew Bags: The Practical Guide to Making Purses, Totes, Clutches & More; 13 Skill-Building ProjectsFrom EverandSew Bags: The Practical Guide to Making Purses, Totes, Clutches & More; 13 Skill-Building ProjectsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Knitting for Anarchists: The What, Why and How of KnittingFrom EverandKnitting for Anarchists: The What, Why and How of KnittingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- 100 Crochet Tiles: Charts and patterns for crochet motifs inspired by decorative tilesFrom Everand100 Crochet Tiles: Charts and patterns for crochet motifs inspired by decorative tilesNo ratings yet
- A Life in Stitches: Knitting My Way Through Love, Loss, and Laughter - Tenth Anniversary EditionFrom EverandA Life in Stitches: Knitting My Way Through Love, Loss, and Laughter - Tenth Anniversary EditionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- Martha Stewart's Very Good Things: Clever Tips & Genius Ideas for an Easier, More Enjoyable LifeFrom EverandMartha Stewart's Very Good Things: Clever Tips & Genius Ideas for an Easier, More Enjoyable LifeNo ratings yet