Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9A03301 Materials Science and Engineering
Uploaded by
sivabharathamurthyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
9A03301 Materials Science and Engineering
Uploaded by
sivabharathamurthyCopyright:
Available Formats
Code: 9A03301
1
(Common to AE, ME and MCT)
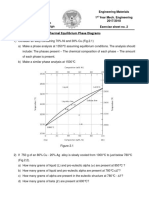
B.Tech II Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 MATERIALS SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE questions All questions carry equal marks ***** 1 Metallic iron changes from BCC to FCC at 910C and correspondingly the atomic radius vary from 1.258 A to 1.292 A. Calculate the percentage change in volume occupied by atoms in each cell during this structure change. What is an alloy and explain necessity of alloying. What is a phase and explain the congruent melting phase. Explain the following: (i) Pearlite. (ii) Ledeburite. (iii) Cementite. A binary alloy of composition of 40% B, 60% A contains two phases namely liquid and solid at a particular temperature. The composition of solid phase is 23% B and that of liquid phase is 68% B. estimate the amount of solid and liquid phases in the alloy. Classify the cast iron and explain the microstructure, properties and applications of white cast iron. Explain normalizing process. Write the properties of copper and explain why copper is a suitable material for automobile radiators. What is cermet? Explain the advantages of cermets. Classify and explain fiber reinforced composites. Max Marks: 70
2 (a) (b) 3 (a) (b)
5 6
7 8
*****
Code: 9A03301
2
(Common to AE, ME and MCT)
B.Tech II Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 MATERIALS SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE questions All questions carry equal marks ***** 1 (a) (b) 2 (a) (b) What is atomic diameter? Explain the effect of valence electrons and shells. What is atomic packing factor and find the APF for BCC unit cell? What is a solid solution? Explain the three possible conditions for a solution. What is an electron compound and give the electron to atom ratio for the following: (i) Au Mg (ii) Fe Zn (iii) Ag Al Draw the phase diagram for the congruent melting intermediate phase. Draw the phase diagram for eutectic system showing the eutectic point at 70% A and 30% B. What is tempered carbon? Explain the importance of it. Give the composition, properties and applications of structural steels. Explain the following: Hardening. Induction hardening. Hardenability. Write short notes on: Gun metal. Muntz metal. Bronze. What is an abrasive material? Give some application of abrasive materials. Give the uses of laminated composites and explain the properties of laminated composites. Max Marks: 70
3 (a) (b) 4 (a) (b) 5 (a) (b) (c) 6 (a) (b) (c) 7 8
*****
Code: 9A03301
3
(Common to AE, ME and MCT)
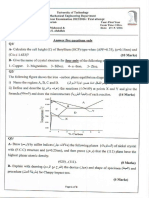
B.Tech II Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 MATERIALS SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE questions All questions carry equal marks ***** 1 (a) (b) What is grain size? Explain the factors that influence the formation of fine grain. Discuss the effect of grain boundaries on the properties of alloys and metals and schematic diagrams of different grain boundaries. What are the impurities in iron? Explain the effect of each. What is a compound? Explain the inter metallic compounds. Two metals A and B are used to form an alloy containing 75% A and 25% B. A melts at 650and B at 450C. When alloyed together A and B do not form any compound or intermediate phase. The solid solubility of metal A in B and B in A are negligible. The metal pair forms an eutectic at 40% A and 60% B which solidifies at 300C. Assume the liquidus and solidus lines to be straight. Draw the phase diagram for the alloy series and find: The temperature at which the alloy starts and completes the solidification. The percentage of eutectic in the alloy at room temperature. The amount of liquid present and its composition at a temperature of 390C. Classify the cast iron and explain the chilled cast iron. Explain isothermal transformation. List and discuss some of the important properties and applications of copper. What is ceramic? Explain ceramic chloride structure. Explain the advantages of hybrid composites. Max Marks: 70
2 (a) (b) 3
(a) (b) (c) 4 5 6 7 8
*****
Code: 9A03301
4
(Common to AE, ME and MCT)
B.Tech II Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 MATERIALS SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING Time: 3 hours Answer any FIVE questions All questions carry equal marks ***** 1 (a) (b) (c) (d) 2 (a) (b) What is unit cell and draw the following types of unit cells with atomic arrangements and lattice parameters: BCC. FCC. Simple tetragonal. End centered orthorhombic. What is a compound? Explain with an example. What is intermediate phase and give the type of the following intermediate phases? (i) Mg Pb (ii) Fe C (iii) Cu Al Two metals A and B have their melting point at 900C and 800C respectively. The alloy pair forms an eutectic at 600C of composition 60% B and 40% A, A and B have unlimited metal liquid solubilities. Their solid solubilities are as follows: 10% B in A at 600C and 5% B in A at 0C. 8% A in B at 600C and 4% A in B at 0C. Assume the liquidus solidus and solvus lines to be straight. No solid state reactions or any intermediate phase change occur in the series. Draw the phase diagram for the series and label all salient temperatures, compositions and regions. Find the room temperature structure if an alloy of composition 60% A and 40% B with respect to the number, type, extent and composition of the phases. Explain the effect of silicon in the metallurgy of grey cast iron. Give the composition, properties and applications of 18-8 stainless steels. Define heat treatment. Explain full annealing process. Compare the outstanding properties of copper and aluminum. What is a glass? Give the applications and properties of borosilicate glass. Define composite materials. Explain particle-reinforced composites. Max Marks: 70
(a) (b)
4 (a) (b) 5 6 7 8
*****
You might also like
- B584 hpgm6441Document7 pagesB584 hpgm6441Muhammad Harits100% (1)
- ME6403-Engineering Materials and MetallurgyDocument10 pagesME6403-Engineering Materials and Metallurgykannan100% (1)
- Emm Question BankDocument6 pagesEmm Question BankMurugesan JeevaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry - Groups 1, 7 and 0Document11 pagesIGCSE Chemistry - Groups 1, 7 and 0ChemistryKlipz100% (4)
- Phase Diagrams - Equilibrium Microstructural Development: 38 WT % PBDocument45 pagesPhase Diagrams - Equilibrium Microstructural Development: 38 WT % PBpetember100% (1)
- Nelson Stud Welding - General Material SpecificationsDocument12 pagesNelson Stud Welding - General Material SpecificationsStefan IonitaNo ratings yet
- 4 Me MQ EMMDocument2 pages4 Me MQ EMMBIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANNo ratings yet
- Modul 2 FittingDocument19 pagesModul 2 Fittingpetrocamp71No ratings yet
- Joint Restraint - Improper Bead Shape - Hydrogen Pickup - Rapid Cooling Rate - High Carbon/Alloy Content - Low Melting Point ContaminantsDocument1 pageJoint Restraint - Improper Bead Shape - Hydrogen Pickup - Rapid Cooling Rate - High Carbon/Alloy Content - Low Melting Point ContaminantsLucian HoudiniNo ratings yet
- Leea Question and Answer 2cDocument3 pagesLeea Question and Answer 2cYAKUBU A. AROGENo ratings yet
- 23 22 13 Steam and Condensate PipingDocument15 pages23 22 13 Steam and Condensate PipingchabibNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials and MetallurgyDocument14 pagesEngineering Materials and Metallurgyashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- ME6403-Engineering Materials and MetallurgyDocument12 pagesME6403-Engineering Materials and Metallurgysanthanam102No ratings yet
- Previous Question Papers of Metallurgy and Material SciencesDocument10 pagesPrevious Question Papers of Metallurgy and Material SciencesRajeev SaiNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering: C and 800 C. The Alloy Pair Forms An Eutectic at 600Document2 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering: C and 800 C. The Alloy Pair Forms An Eutectic at 600நந்த_குமார்No ratings yet
- TYPD ExercisesDocument10 pagesTYPD ExercisesConstance Lynn'da GNo ratings yet
- Unit-I - Alloys and Phase Diagrams Part-A (2 Marks) : Question BankDocument10 pagesUnit-I - Alloys and Phase Diagrams Part-A (2 Marks) : Question BankDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Problems 5Document8 pagesTutorial Problems 5Majak MarialNo ratings yet
- ME6403 ENGINEERING MATERIALS AND METALLURGY UNIT 1.ALLOYS AND PHASE DIAGRAMDocument6 pagesME6403 ENGINEERING MATERIALS AND METALLURGY UNIT 1.ALLOYS AND PHASE DIAGRAMjamunaa83No ratings yet
- Engineering Materials and MetallurgyDocument11 pagesEngineering Materials and Metallurgyabdulhere4uNo ratings yet
- Yan Sample Exam II 4016214112Document6 pagesYan Sample Exam II 4016214112christopher_spring_3No ratings yet
- Assignment PhaseDiaDocument5 pagesAssignment PhaseDiaAnshu Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials Phase DiagramsDocument6 pagesEngineering Materials Phase DiagramsOmar AssalNo ratings yet
- Material Science and Metallurgy Question BankDocument3 pagesMaterial Science and Metallurgy Question BankVinay KorekarNo ratings yet
- 07CH22Document2 pages07CH22navneeth_krishnan1993No ratings yet
- MM Question BankDocument22 pagesMM Question BankDr.A.Maniram KumarNo ratings yet
- 9 - Phase DiagramsDocument13 pages9 - Phase DiagramsJohny SkNo ratings yet
- Regulation 2010 - Engineering Materials and Metallurgy ExamDocument4 pagesRegulation 2010 - Engineering Materials and Metallurgy ExambalakaleesNo ratings yet
- سنوات سابقة خواصDocument64 pagesسنوات سابقة خواصmechanical depNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Bonding in MaterialsDocument16 pagesAtomic Structure and Bonding in MaterialsRasyidi AhmadNo ratings yet
- Material Science and Metallurgy Question BankDocument11 pagesMaterial Science and Metallurgy Question BankMohamed SohaibNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties and Its Testing MethodDocument9 pagesMechanical Properties and Its Testing MethodMohammad Khairul Azmi Mohd KassimNo ratings yet
- 금속재료 중간고사 기출문제 (2006-2016)Document10 pages금속재료 중간고사 기출문제 (2006-2016)Li Ken LokNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 E FDocument2 pagesAssignment 1 E FSudhananda MallickNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table SQDocument17 pagesPeriodic Table SQNg Swee Loong StevenNo ratings yet
- Biomaterials II Lec 6Document14 pagesBiomaterials II Lec 6m9trdk92ksNo ratings yet
- Lista InorganicaDocument2 pagesLista InorganicaCayo FariasNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document2 pagesTutorial 3sadfadsfNo ratings yet
- Questions On Transition MetalsDocument3 pagesQuestions On Transition MetalscpliamNo ratings yet
- ME-8491 EM QB For UT1Document2 pagesME-8491 EM QB For UT1ajaymNo ratings yet
- WK 5 Engineering Chemistry Exam QuestionsDocument3 pagesWK 5 Engineering Chemistry Exam QuestionsArun KumarNo ratings yet
- Revision Worksheet Unit 1 - 3: Chem 1Document6 pagesRevision Worksheet Unit 1 - 3: Chem 1abashir7852No ratings yet
- Slow Learner TestDocument2 pagesSlow Learner Testsparkysanthosh69No ratings yet
- Eng Mat Chapter 4Document126 pagesEng Mat Chapter 4VC Chua Yee LeongNo ratings yet
- Materials science document analysisDocument7 pagesMaterials science document analysisPuspendu Roy ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Assignment Phy Chem 3Document5 pagesClass 10 Assignment Phy Chem 3vaishnavisriNo ratings yet
- PP Set 1 & 2Document3 pagesPP Set 1 & 2Raveendra kumar KosireddiNo ratings yet
- 1616403463914-Subjective Questions On Material Science MET-09Document3 pages1616403463914-Subjective Questions On Material Science MET-09praiselovesscienceNo ratings yet
- Homework Booklet (4, D)Document48 pagesHomework Booklet (4, D)LionelNo ratings yet
- InTech-Chemical and Physical Properties of Fluxes For Saw of Low Carbon SteelsDocument19 pagesInTech-Chemical and Physical Properties of Fluxes For Saw of Low Carbon SteelsSiap SiapNo ratings yet
- B. Tech. (IV Semester) : (BH) MaxDocument2 pagesB. Tech. (IV Semester) : (BH) Maxauro auroNo ratings yet
- AF-3518 Organotransition Metal and Photo-Inorganic ChemistryDocument4 pagesAF-3518 Organotransition Metal and Photo-Inorganic ChemistryvnbmNo ratings yet
- Bonding QDocument19 pagesBonding QhamedNo ratings yet
- Phase Diagrams and Microstructures in AlloysDocument4 pagesPhase Diagrams and Microstructures in AlloysTia AgustinNo ratings yet
- Std. XII Chemistry Question Bank PDFDocument81 pagesStd. XII Chemistry Question Bank PDFSuyash DahakeNo ratings yet
- Phase Diagrams and MicrostructuresDocument3 pagesPhase Diagrams and MicrostructuresSri PuduNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry-II - May-June 2009 Question Paper Studyhaunters PDFDocument3 pagesEngineering Chemistry-II - May-June 2009 Question Paper Studyhaunters PDFSriram JNo ratings yet
- Sheet 5 - Phase Diagrams IIDocument2 pagesSheet 5 - Phase Diagrams IIroro98syamNo ratings yet
- Homework Booklet (4, D)Document49 pagesHomework Booklet (4, D)Anupa Medhekar100% (1)
- Himpunan Contoh Soalan Exam Soalan Ujian SN BHNDocument50 pagesHimpunan Contoh Soalan Exam Soalan Ujian SN BHNNur Atikah100% (1)
- Transition Metals Coordination CompoundsDocument4 pagesTransition Metals Coordination CompoundsnasyieNo ratings yet
- Phase DiagramsDocument50 pagesPhase DiagramsIbrahim MalikNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Term 1 Chemistry RevisionDocument7 pagesGrade 9 Term 1 Chemistry Revisionsiddloves.snowNo ratings yet
- UEME 1122 Material Science Tutorial 1Document2 pagesUEME 1122 Material Science Tutorial 1JamesNo ratings yet
- Endohedral Metallofullerenes: Fullerenes with Metal InsideFrom EverandEndohedral Metallofullerenes: Fullerenes with Metal InsideNo ratings yet
- Control Systems (CS) Notes As Per JntuaDocument203 pagesControl Systems (CS) Notes As Per Jntuasivabharathamurthy100% (3)
- 07A4EC01 Environmental StudiesDocument1 page07A4EC01 Environmental StudiessivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- SSC Telugu (FL) (AP)Document232 pagesSSC Telugu (FL) (AP)sivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R5410201 Neural Networks & Fuzzy LogicDocument1 pageR5410201 Neural Networks & Fuzzy LogicsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7410407 Operating SystemsDocument1 pageR7410407 Operating SystemssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- SSC Social Textbook (AP)Document100 pagesSSC Social Textbook (AP)sivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7410506 Mobile ComputingDocument1 pageR7410506 Mobile ComputingsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A05707 Software Project ManagementDocument4 pages9A05707 Software Project ManagementsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7310406 Digital CommunicationsDocument1 pageR7310406 Digital CommunicationssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7311506 Operating SystemsDocument1 pageR7311506 Operating SystemssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A13701 Robotics and AutomationDocument4 pages9A13701 Robotics and AutomationsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7310506 Design & Analysis of AlgorithmsDocument1 pageR7310506 Design & Analysis of AlgorithmssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Code: R7311306: (Electronics & Control Engineering)Document1 pageCode: R7311306: (Electronics & Control Engineering)sivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7312301 Transport Phenomena in BioprocessesDocument1 pageR7312301 Transport Phenomena in BioprocessessivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7311205 Distributed DatabasesDocument1 pageR7311205 Distributed DatabasessivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R5310204 Power ElectronicsDocument1 pageR5310204 Power ElectronicssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7311006 Process Control InstrumentationDocument1 pageR7311006 Process Control InstrumentationsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7310306 Heat TransferDocument1 pageR7310306 Heat Transfersivabharathamurthy100% (1)
- 9A10505 Principles of CommunicationsDocument4 pages9A10505 Principles of CommunicationssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7310206 Linear Systems AnalysisDocument1 pageR7310206 Linear Systems AnalysissivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7310106 Engineering GeologyDocument1 pageR7310106 Engineering GeologysivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A04504 Digital IC ApplicationsDocument4 pages9A04504 Digital IC ApplicationssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A15502 Digital System DesignDocument4 pages9A15502 Digital System Designsivabharathamurthy100% (1)
- R5310406 Digital CommunicationsDocument1 pageR5310406 Digital CommunicationssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A23501 Heat Transfer in BioprocessesDocument4 pages9A23501 Heat Transfer in BioprocessessivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A21506 Mechanisms & Mechanical DesignDocument8 pages9A21506 Mechanisms & Mechanical DesignsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A14503 Principles of Machine DesignDocument8 pages9A14503 Principles of Machine DesignsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A03505 Heat TransferDocument4 pages9A03505 Heat TransfersivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A05505 Operating SystemsDocument4 pages9A05505 Operating SystemssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A02505 Electrical Machines-IIIDocument4 pages9A02505 Electrical Machines-IIIsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Macalloy Brochure Tension Structures December - 2017 - V1Document16 pagesMacalloy Brochure Tension Structures December - 2017 - V1Isabel Christina Gonzalez MoralesNo ratings yet
- Differences between pure metals and alloysDocument31 pagesDifferences between pure metals and alloysSinh LeNo ratings yet
- Cable King PDFDocument1 pageCable King PDFAntonio SerranoNo ratings yet
- Pressure Seal Valves PDFDocument76 pagesPressure Seal Valves PDFsivagulfNo ratings yet
- Standard Specification For Hot Dip GalvanizingDocument4 pagesStandard Specification For Hot Dip GalvanizingNuzul Furqony100% (1)
- Cable Raws MaterialDocument7 pagesCable Raws MaterialAgustina EffendyNo ratings yet
- Limit SwitchesDocument6 pagesLimit Switchespavan3229No ratings yet
- Amt NotesDocument174 pagesAmt NotesAyush SinhaNo ratings yet
- A Finite Element Method Based Analysis of Casting Solidification Onpermanent Metallic ModelsDocument10 pagesA Finite Element Method Based Analysis of Casting Solidification Onpermanent Metallic ModelsseenisitNo ratings yet
- A507Document4 pagesA507Shakeel Ahmed100% (1)
- Passivation On Chemical TankerDocument15 pagesPassivation On Chemical TankerRonald MesinaNo ratings yet
- Jigs, Fixtures & Gauges Design GuideDocument15 pagesJigs, Fixtures & Gauges Design GuidesimiyandcNo ratings yet
- Web PSB 804Document2 pagesWeb PSB 804api-30194194No ratings yet
- Reactions of Alcohols, Phenols, Aldehydes and KetonesDocument44 pagesReactions of Alcohols, Phenols, Aldehydes and KetonesGlen Mangali100% (4)
- SV10-20 Poppet, 2-Way, Normally Closed: Solenoid ValvesDocument2 pagesSV10-20 Poppet, 2-Way, Normally Closed: Solenoid ValvesMartin Andrew TugadeNo ratings yet
- Stresses, Loads, and Factors of Safety in Structural ElementsDocument6 pagesStresses, Loads, and Factors of Safety in Structural ElementsMark Louies Mago VillarosaNo ratings yet
- Indian Standard Testing Is 13015 - 1991Document11 pagesIndian Standard Testing Is 13015 - 1991joseNo ratings yet
- CE6302-Mechanics of SolidsDocument20 pagesCE6302-Mechanics of SolidsMaharaja PlacementNo ratings yet
- Metals Guide PDF Catalog July 2012Document538 pagesMetals Guide PDF Catalog July 2012Ahmed BdairNo ratings yet
- Chemistry f4Document26 pagesChemistry f4Puvaneswari PunisNo ratings yet
- Color SchemesDocument32 pagesColor SchemesAndreas Budi SantosaNo ratings yet
- Trusted Source for Weld Test MaterialsDocument2 pagesTrusted Source for Weld Test Materialslth770310No ratings yet
- Through-Hardening Low Alloy Steel Properties & ApplicationsDocument3 pagesThrough-Hardening Low Alloy Steel Properties & Applicationsl_aguilar_mNo ratings yet