Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Math2230 Prelim2
Uploaded by
Udit GuptaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Math2230 Prelim2
Uploaded by
Udit GuptaCopyright:
Available Formats
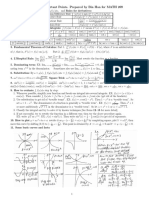
Math 2230 Prelim 2
Due: 4pm on November 26th, 2013 Rules: You may use any book you like. Please cite all references you use. You are not allowed to discuss the problems on this exam with anyone except Martin. You may not use internet, go to the library instead. 1. [15pt] A function f : R2 R is called harmonic if it satises 2f 2f + 2 = 0. 2 x y Let g denote the composition of the function f and the polar change of variable, i.e., g (r, ) = f (r cos , r sin ). Find a second order dierential equation which satised by g if and only if the function f is harmonic. 2. [20pt] A 2n 2n matrix A is called unitary if and only if AA = Id, where A is the matrix obtained by A using transposition and complex conjugation. A matrix is called symplectic if AT JA = J where J is the 0 Idn matrix . Let Vn denote the set of 2n 2n matrices which Idn 0 are both unitary and symplectic. a) [5pt] Show that the set Vn is closed under matrix multiplication, matrix inversion and complex conjugation. b) [8pt] Show that as a subset of R8n = Mat2n (C) the set Vn is a smooth manifold and nd its dimension. c) [7pt] Describe the tangent space to Vn at the identity. 3. [20pt] For which values c the zero locus of the function Fc (x, y ) = x4 + 2x2 y 2 + y 4 16x3 + 48xy 2 + 40x2 + 40y 2 c is a smooth 1 dimensional manifold? Sketch these sets for several values of c (including all values where these sets are not smooth). 4. [20pt] Find the maximal and the minimal value of the function f (x, y ) = xy x2 y 2 x2 + y 2 0 if (x, y ) = (0, 0) if (x, y ) = (0, 0)
2
on the square [2, 2] [2, 2]. Hint: Be careful!
5. [15pt] Give an example of a uniformly continuous and everywhere dierentiable function with unbounded derivative. Is there such function which is C 1 ? What about C k for k 2? 6. [25pt] Let f be a smooth function from Mat2 (R) to R and let H be a 2 2 matrix. Dene H -derivative of f as follows (DH (f )) (g ) = d f exp(tH )g dt ,
which is also a function from Mat2 (R) to R. a) [5pt] Show that DH satises the Leibnitz rule, i.e., DH (f1 f2 ) = DH (f1 )f2 + f1 DH (f2 ). b) [5pt] Express the value of DH (f ) at the point g in terms of the derivative of f (or using partial derivatives of the function f , if you prefer). c) [5pt] Give an example of two matrices H1 and H2 and a function f such that DH1 (DH2 (f )) = DH2 (DH1 (f )). d) [5pt] Prove that for any H1 and H2 there exists H such that DH1 (DH2 (f )) DH2 (DH1 (f )) = DH (f ). What is H ? e) [5pt] Which non-constant functions f satisfy the relation DH1 (DH2 (f )) = DH2 (DH1 (f )) for all H1 , H2 Mat2 (R).
7. [35pt] Let C be a smooth parameterized curve in the plane. Let N be the union of all normal lines to curve C . a) [4pt] Find a 2 parameter parametrization of the points in N . b) [4pt] Find the non-smooth points of this parametrization. c) [4pt] Show that the set of non-smooth points form a parameterized curve C in the plane. d) [4pt] Show that the curve C depends only on the curve C and not on its parametrization. e) [4pt] Compute the curve C when C is the parabola y = x2 . f) [15pt] Find a curve C such that C is the circle x2 + y 2 = 1. This is only true for a generic curve C you may assume that all expressions that appear in the denominators are non-zero. Hint: The last part is quite hard, but the curves constructed are very important they are used in many everyday objects (2pt bonus if you can explain where and why this curve is commonly used).
You might also like
- Math Transform Methods: Dr. P Adraig KirwanDocument57 pagesMath Transform Methods: Dr. P Adraig KirwanXavimVXSNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical Coordinates Matlab: Electromagnetics Fields and WavesDocument12 pagesCylindrical Coordinates Matlab: Electromagnetics Fields and WavesAli AhmadNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus at A GlanceDocument24 pagesVector Calculus at A Glancedayangku zarithNo ratings yet
- Homework 5Document2 pagesHomework 5Imelda RozaNo ratings yet
- Greens Theorem ProofDocument5 pagesGreens Theorem ProofGaurav DharNo ratings yet
- EX/2-M/12S/67/07 INTER B. Sc. EXAMINATION, 2007 (2nd Semester) MATHEMATICS (Subsidiary) PAPER SOLUTIONSDocument2 pagesEX/2-M/12S/67/07 INTER B. Sc. EXAMINATION, 2007 (2nd Semester) MATHEMATICS (Subsidiary) PAPER SOLUTIONSchiranjib214No ratings yet
- DC Chap1A FunctionsDocument96 pagesDC Chap1A FunctionsRon PascualNo ratings yet
- MIT18 S096F13 Pset4Document7 pagesMIT18 S096F13 Pset4TheoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Functions and Graphs 4.1) Basics of Functions Definition 1: RelationsDocument32 pagesChapter 4: Functions and Graphs 4.1) Basics of Functions Definition 1: Relationssf1dNo ratings yet
- Surigao State College of TechnologyDocument2 pagesSurigao State College of TechnologyLiezlLzeilCarreonGalgoNo ratings yet
- 232 HWAug 27Document1 page232 HWAug 27avi_weberNo ratings yet
- MA2008 2 Hours Sample Exam 1: April 2006 SECTION A - Answer All ALL Questions - 50 MarksDocument4 pagesMA2008 2 Hours Sample Exam 1: April 2006 SECTION A - Answer All ALL Questions - 50 MarkslordpersonNo ratings yet
- Fourier Analysis: Christian Berg November 2, 2009Document116 pagesFourier Analysis: Christian Berg November 2, 2009Allah Yar KhanNo ratings yet
- Computation of Fractional Derivatives of Analytic Functions: Bengt Fornberg Cécile PiretDocument23 pagesComputation of Fractional Derivatives of Analytic Functions: Bengt Fornberg Cécile PiretYousef AlamriNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Purely Iterative Algorithms For Newton's Maps and General ConvergenceDocument27 pagesMathematics: Purely Iterative Algorithms For Newton's Maps and General ConvergenceAlberto Magreñán RuizNo ratings yet
- CourseDocument141 pagesCoursesawahkouba1No ratings yet
- IMP Harvard PDFDocument140 pagesIMP Harvard PDFTalha MirNo ratings yet
- H2 Mathematics Cheat Sheet by Sean LimDocument27 pagesH2 Mathematics Cheat Sheet by Sean LimGale HawthorneNo ratings yet
- Math Camp 1: Functional AnalysisDocument50 pagesMath Camp 1: Functional AnalysisIme OkonnaNo ratings yet
- Ch7 PDFDocument63 pagesCh7 PDF王大洋No ratings yet
- Complex Integration FundamentalsDocument3 pagesComplex Integration Fundamentalsjainabhinav05No ratings yet
- Vector Functions: Chapter ThreeDocument8 pagesVector Functions: Chapter ThreeSedulor NgawiNo ratings yet
- MATH2015 Analysis 2, 2009/2010: Contact Details (Semester 2)Document88 pagesMATH2015 Analysis 2, 2009/2010: Contact Details (Semester 2)Tom DavisNo ratings yet
- Isi Mmath-2019-PmaDocument5 pagesIsi Mmath-2019-PmaPriyalMishraNo ratings yet
- 5 - Solving Nonlinear Eigenvalue Problem by Algorithmic Differentation - ARBENZ GANDERDocument11 pages5 - Solving Nonlinear Eigenvalue Problem by Algorithmic Differentation - ARBENZ GANDERJean DujardinNo ratings yet
- M.Sc. Part-I Online Exam Sample QuestionsDocument11 pagesM.Sc. Part-I Online Exam Sample QuestionsSayli KomurlekarNo ratings yet
- Inverse Laplace Transforms and the Heaviside FunctionDocument7 pagesInverse Laplace Transforms and the Heaviside FunctionuploadingpersonNo ratings yet
- 2011 Calculus Workshop ProblemsDocument6 pages2011 Calculus Workshop ProblemsNdaru Asmara ManiestNo ratings yet
- EE5121: Convex Optimization: Assignment 1Document2 pagesEE5121: Convex Optimization: Assignment 1Subhankar Chakraborty ee17b031No ratings yet
- Annihilator MethodDocument5 pagesAnnihilator Methoddarts090No ratings yet
- A Simple Yet Efficient Two Step Fifth Order Weighted Newton Method For Nonlinear ModelsDocument23 pagesA Simple Yet Efficient Two Step Fifth Order Weighted Newton Method For Nonlinear ModelsAntmel Rodriguez CabralNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Tripos Paper 1 GuideDocument11 pagesMathematical Tripos Paper 1 GuideYannNo ratings yet
- IIT Bombay MA 205 Lecture on Complex IntegrationDocument18 pagesIIT Bombay MA 205 Lecture on Complex Integrationvishal kumarNo ratings yet
- The Convolution Theorem: PrerequisitesDocument16 pagesThe Convolution Theorem: PrerequisitesFegason FegyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 3Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet 3yash sononeNo ratings yet
- Masters Exam in Pure MathDocument13 pagesMasters Exam in Pure MathlopezmegoNo ratings yet
- A5 PDFDocument2 pagesA5 PDFjanetmayNo ratings yet
- Domain and range worksheetDocument4 pagesDomain and range worksheetEric LiNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Functional DerivativesDocument8 pagesAn Introduction To Functional DerivativesmumhdNo ratings yet
- (I) - / o o - I'i: Entire Functions of Exponential TypeDocument11 pages(I) - / o o - I'i: Entire Functions of Exponential Typevahid mesicNo ratings yet
- Solutions 27Document4 pagesSolutions 27awwalNo ratings yet
- 23 3Document10 pages23 3Mayar ZoNo ratings yet
- 209 Formula SheetDocument4 pages209 Formula SheetAlan ChoyNo ratings yet
- Math 328 Module 1 Fourier SeriesDocument26 pagesMath 328 Module 1 Fourier SeriesMelchor Jaramilla OronosNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Theorem of Line Integrals and Green's Theorem ExplainedDocument19 pagesFundamental Theorem of Line Integrals and Green's Theorem ExplainedJohnNo ratings yet
- EE261 Fourier Transform Solutions Midterm Exam Questions AnswersDocument12 pagesEE261 Fourier Transform Solutions Midterm Exam Questions AnswersNonitus OctingentiNo ratings yet
- AM Prelim 202001Document4 pagesAM Prelim 202001Al-Tarazi AssaubayNo ratings yet
- Homework 6Document3 pagesHomework 6Luis EduardoNo ratings yet
- Additional Exercises for Convex Optimization TopicsDocument152 pagesAdditional Exercises for Convex Optimization TopicsnudalaNo ratings yet
- CMI Chennai Postgraduate Entrance Exam GuideDocument3 pagesCMI Chennai Postgraduate Entrance Exam GuideKrishnaNo ratings yet
- HW 1 SolDocument3 pagesHW 1 SoljigyansuNo ratings yet
- Two Marks QuesDocument5 pagesTwo Marks QuesSiva BalaNo ratings yet
- Outline of The SyllabusDocument32 pagesOutline of The SyllabusManabendra GiriNo ratings yet
- Scalar and Vector Line IntegralsDocument13 pagesScalar and Vector Line IntegralsmweepuchibsNo ratings yet
- Regularization of Feynman IntegralsDocument28 pagesRegularization of Feynman IntegralsRonaldo Rêgo100% (1)
- Convention: Throughout This Discussion A Feasible Direction D at A Point Is by Definition TakenDocument12 pagesConvention: Throughout This Discussion A Feasible Direction D at A Point Is by Definition TakenNeelabh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Exponential Representations of InjeDocument15 pagesExponential Representations of InjeKieouNo ratings yet
- Teaching FunctionsDocument7 pagesTeaching FunctionsCatherine MitchellNo ratings yet
- Vector Valued FunctionDocument33 pagesVector Valued FunctionFarhan naseenNo ratings yet
- Log Rules Review Sheet 1 RulesDocument2 pagesLog Rules Review Sheet 1 RulesUdit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Course Textbook ListDocument1 pageCourse Textbook ListUdit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Two-Dimensional Plane GroupsDocument1 pageTwo-Dimensional Plane GroupsUdit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Course - 2013OCT Community Health Nursing (NUR-441-NU006)Document2 pagesCourse - 2013OCT Community Health Nursing (NUR-441-NU006)Udit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Fitting NR LuxDocument29 pagesFitting NR LuxUdit GuptaNo ratings yet
- CNSE Spring 2014 Course ScheduleDocument7 pagesCNSE Spring 2014 Course ScheduleUdit GuptaNo ratings yet
- CNSE Nanoscience MAPDocument1 pageCNSE Nanoscience MAPUdit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Diffy QsDocument252 pagesNotes On Diffy Qsarachno85No ratings yet
- Vector Calculus SupplementDocument150 pagesVector Calculus Supplementtrashcanxtx100% (1)
- SolSQL InroductionDocument68 pagesSolSQL InroductionblazespiritNo ratings yet
- Automation Wps OfficeDocument15 pagesAutomation Wps OfficeChetainya ManchandaNo ratings yet
- Pipe-Flow Friction-Factor Calcns Head-Loss Si UnitsDocument15 pagesPipe-Flow Friction-Factor Calcns Head-Loss Si UnitsKumar sssssNo ratings yet
- How To InstallDocument2 pagesHow To Installbenzen353No ratings yet
- Failure Analysis of The Timing Belt DrivesDocument6 pagesFailure Analysis of The Timing Belt DrivesBlaza StojanovicNo ratings yet
- Pyridones PDFDocument5 pagesPyridones PDFJuanAmayaNo ratings yet
- Design Methodology and Manufacturing of Rack and Pinion For All Terrain Vehicle IJERTV8IS060334Document4 pagesDesign Methodology and Manufacturing of Rack and Pinion For All Terrain Vehicle IJERTV8IS060334Saichandra Reddy MotheNo ratings yet
- Rakh Agf Set Ren Tube ModelDocument1 pageRakh Agf Set Ren Tube Modelbenaya prasetyaNo ratings yet
- Math10 q1 Mod6 Finding The NTH Term of A Geometric Series and Geometric Means v1.5Document22 pagesMath10 q1 Mod6 Finding The NTH Term of A Geometric Series and Geometric Means v1.5rickNo ratings yet
- Orbitrap Espectrometro de MassasDocument11 pagesOrbitrap Espectrometro de MassasDiegoNo ratings yet
- Professional Control Surface / Firewire Audio-Midi InterfaceDocument42 pagesProfessional Control Surface / Firewire Audio-Midi InterfaceOwen KalauNo ratings yet
- 20 QTR SupplementDocument38 pages20 QTR SupplementsebastienNo ratings yet
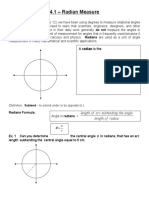
- 4.1 - Radian Measure: Degrees. There Is Another Unit of Measurement For Angles That Is Frequently Used Because ItDocument4 pages4.1 - Radian Measure: Degrees. There Is Another Unit of Measurement For Angles That Is Frequently Used Because ItBetty WangNo ratings yet
- Scale Drawing Project With Complete LinksDocument3 pagesScale Drawing Project With Complete Linksapi-298464403No ratings yet
- Charging Kit - PCMDocument2 pagesCharging Kit - PCMSrikanth ReddyNo ratings yet
- Umbrella Tool Changer - Troubleshooting Guide: Haas Technical DocumentationDocument7 pagesUmbrella Tool Changer - Troubleshooting Guide: Haas Technical Documentation2aicnNo ratings yet
- Water surface profile computation in open channelsDocument6 pagesWater surface profile computation in open channelsDaniel BriñezNo ratings yet
- Building Custom PHP ExtensionsDocument122 pagesBuilding Custom PHP Extensionsmichel-kara-8516No ratings yet
- Reflex Level Gauge SERIES 1000: Product Data Sheet No. 1Document1 pageReflex Level Gauge SERIES 1000: Product Data Sheet No. 1Sheikh Mohammad Rezaul KarimNo ratings yet
- Gropp Mpi TutorialDocument155 pagesGropp Mpi TutorialElly DecanesNo ratings yet
- Linear Wire Antennas: EE-4382/5306 - Antenna EngineeringDocument24 pagesLinear Wire Antennas: EE-4382/5306 - Antenna EngineeringJose Nathaniel BonaNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual Fisher 249 Caged Displacer Sensors en 134918Document20 pagesInstruction Manual Fisher 249 Caged Displacer Sensors en 134918Senthil KumarNo ratings yet
- 10.1007@978 3 030 47717 2Document413 pages10.1007@978 3 030 47717 2riadhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 04Document3 pagesChapter 04gebreNo ratings yet
- Rayalaseema Institute of Information and Management Sciences (RIMS)Document1 pageRayalaseema Institute of Information and Management Sciences (RIMS)Pallamala Kalyan PKNo ratings yet
- Discrete Mathematics Notes - 2012Document56 pagesDiscrete Mathematics Notes - 2012yee chong 94No ratings yet
- Math 1005 StatisticsDocument4 pagesMath 1005 Statisticssuitup10No ratings yet
- Planetary DrivesDocument277 pagesPlanetary DrivesalopezvillavicencioNo ratings yet
- CBF1000FA Owners ManualDocument259 pagesCBF1000FA Owners Manual任宇杰No ratings yet
- Contents:: Direct InputDocument13 pagesContents:: Direct Inputchandra9000No ratings yet