Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FERTILISASI
Uploaded by
Alfina WulandariCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FERTILISASI
Uploaded by
Alfina WulandariCopyright:
Available Formats
A. Basic Theory The stage began the process of development of animals after gametogenesis is fertilization.
This process bring together both kinds of gametes and while keeping the number of fixed plantles diploid chromosome like saplings. In mammalian fertilization occurs internally. The second meeting of gametes occurs within the female reproductive tract). Once it is known that female mice are on stage/time of estrus (Tim Pengajar, 2010). Fertilization is the process of melting the male gamete nuclei and female gamete nuclei. The melting is mixing that influence by genetic. Paternal and maternal traits so as to develop into new individuals. Gradually, fertilization can take place in several stages, namely (1) the penetration of sperm into ovum, (2) completion of the period of ripening ova, (3) fusion of proneleus male gamates and females gamates, and (4) amfimiksis maternal chromosomes and paternal chromosomes (Sugianto, 2000). Fertilization on various types of animals can be distinguished based on the venue, they are external fertilzation and internal fertilization. External fertilization take place in outside its mother's body. Types of fertilization is widely found in animals aquatik, among others are fish, frogs, etc. Fertilization is internal fertilization take place in the body of its mother (Adnan, 2008) Fertilization is the Union of sperm and egg cells. At the time the sperm approaches the surface of egg it came to acromosom reaction. On a number of species were formed of one or more chromosome filaments that penetrate the viteline membrane. At the same time, enzymes secreted by the acromosom dissolve the membrane so goes the driveway. If the substance of acromosom reached the plasma membrane, so the surface of egg protruding out and form a cone of fertilization (Campbell, 2008). B. Work Procedure The purpose of experiment are: 1. To understand and have skills in mated of Mus musculus. 2. Have a better understanding of the process of fertilization in mammals. C. Work Procedure 1. Mated mice a. Made vaginal smears of mice to determine the condition of the reproductive cycle of female mice. b. Maintain a female mices who were estrus with a male mice in a cage so that the mating of mice. c. The next morning, checked a vaginal plug in female mice. Vaginal plugs are white to yellowish bone, located slightly to the inside of the vaginal opening. The presence of vaginal plugs indicating the occurrence of coitus. If there are vaginal plugs, separated male mice from female mice and let the pregnant female mice. If no vaginal plug was found, wait until the next day. d. Weigh the body weight of female mice that were pregnant every day to ensure that the pregnancy occurred. e. Gave food pellets and drinking water in the form of tap water to taste, and replaced chaff periodically to maintain environmental sanitation of mice that were pregnant. 2. Observation the fertilization of female mice For this purpose, pregnant female mice were killed on the 15th day of pregnancy to observe the number of implantations, the number of live fetuses, the number of dead fetuses and the number of corpus luteum. Observation the number of implantations, the number of live fetuses, the number of dead fetuses and the number of corpus luteum. a. Killed pregnant female mice on the 15th day of pregnancy by cervical dislocation, then a surgical abdomen until the uterus is observed. b. Calculated the number of fetus in the uterus and note the number for each uterine horn. Note also whether the fetus is alive or dead by touching it.
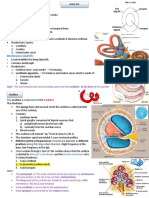
c. Opened the uterus and find the resorbed implantation. Calculated the amount of each uterine horn. d. Took the ovaries of mice and count the number of corpus luteum (note the origin of each ovary, left or right). The corpus luteum visible as small balls reddish yellow and has a size larger than tertiary follicles. D. Observation Result 1. Mated mice
2. Vaginal Smear
3. Uterus at fetus 14th days Picture
Note
1. Fetus
4. Uterus at fetus 17th days Picture
Note
1. Fetus
5. Table body weight of Mus musculus a. Body wight at fetus 14th days No. Day/ date Weight (gram) 1 December 2nd 2013 19,50 2 December 3rd 2013 18,00 3 December 4th 2013 18,40 4 December 5th 2013 19,00 5 December 6th 2013 19,60 6 December 7th 2013 20,40 7 December 8th 2013 21,20 8 December 9th 2013 23,00 9 December 10th 2013 23,60 10 December 11th 2013 24,00 11 December 12th 2013 24,80 12 December 13th 2013 25,40 13 Desember 14th 2013 26,00 14 December 15th 2013 26,80 15 December 16th 2013 27,40 16 December 17th 2013 30,00 17 December 18th 2013 31,90 th b. Body wight at fetus 17 days No. Day/ date Weight (gram) 1 December 2nd 2013 25,50 2 December 3rd 2013 23,90 3 December 4th 2013 24,10 4 December 5th 2013 24,50 5 December 6th 2013 25,00 6 December 7th 2013 25,30 7 December 8th 2013 25,70 8 December 9th 2013 30,00 9 December 10th 2013 30,40 10 December 11th 2013 30,80
Note Not pregnant Not pregnant Not pregnant Pregnant Pregnant Pregnant Pregnant Pregnant Pregnant Pregnant Pregnant Pregnant Pregnant Pregnant Pregnant Pregnant Pregnant Note Not pregnant Pregnant Pregnant Pregnant Pregnant Pregnant Pregnant Pregnant Pregnant Pregnant
11 December 12th 2013 12 December 13th 2013 13 Desember 14th 2013 14 December 15th 2013 15 December 16th 2013 16 December 17th 2013 17 December 18th 2013 6. Data Analytical a. Fetus 14th days
31,30 31,80 32,10 32,50 32,90 33,40 33,9
Pregnant Pregnant Pregnant Pregnant Pregnant Pregnant Pregnant
1) Implantation percentage
2) Percentage of death fetus
b. Fetus 17th days 1) Implantation percentage 2) Percentage of death fetus E. Discussion The fertilization can happened when female mice had been undergoing the estrus phase. Estrus phase marked by the present of vaginal smear. If the female mice produce vaginal smear, so the female mice ready to marriged by male mice. In this observation, we use 2 mice that have the different pregnant days, there are 14th days and 17th days. 1. Uterus at fetus 14th days We can see, the fetus at 14th days consist of six. Three in left side of uterus and three in right side of uterus. The feturs from this mice is small. In these mice the formation of organs already apparent, only the lining of the eye that is not yet open. Another case in mice that weight during early pregnancy has decreased. This mice is starting to pregnanat from December 5th 2013 until December 18th 2013. And there is one fetus is dead. The characteristic that can we see from the dead fetus is, they do not undergo some development so they still in blood granule form. And if we touch it, it feels weaker than lived fetus. The percentage is . th 2. Uterus at fetus 17 days Fetus at 17th days consist of two. One in left side of uterus and one in right side of uterus. The fetus from this mice is big and now has perform the organ differentiation in final stage. This mice is starting to pregnanat from December 3rd 2013 until December 18th 2013. There is no fetus dead and percentage is 0%. F. Conclusion Fertilization is happened when the female mice had been estrus phase, this is marked by the present of vaginal smear. In this observation, fertilization happened the female mice pegnannt in 14th days and 17th days. Fetus of 14th days is six and fetus in 17th days is two. G. Suggestion 1. Apprentice must be discipline. 2. Apprentice must be careful doing the surgery so that there arent fault in the experiment.
BIBLIOGRAPHY Adnan, 2008. Perkembangan Hewan. Makassar: Biology Departement FMIPA UNM. Campbell, N. A; J. B. Reece dan L. G. Mitchell. 2004. Biologi Edisi Kelima Jilid II. Jakarta: Erlangga. Sugiyanto, J. 2000. Perkembangan Hewan. Yogyakarta: FMIPA UGM. Tim Pengajar. 2010. Perkembangan Hewan. Makassar: Biology Departement FMIPA UNM.
You might also like
- Ibyt 06 I 6 P 748Document12 pagesIbyt 06 I 6 P 748Alfina WulandariNo ratings yet
- First Task Summary of EcologyDocument3 pagesFirst Task Summary of EcologyAlfina WulandariNo ratings yet
- First Task Summary of EcologyDocument3 pagesFirst Task Summary of EcologyAlfina WulandariNo ratings yet
- Tutor Bu AsmaDocument2 pagesTutor Bu AsmaAlfina WulandariNo ratings yet
- MetamorfosisDocument3 pagesMetamorfosisAlfina WulandariNo ratings yet
- Tabel Alat Praktikum MikrobiologyDocument13 pagesTabel Alat Praktikum MikrobiologyAlfina WulandariNo ratings yet
- Constructivis.11 WordDocument11 pagesConstructivis.11 WordAlfina WulandariNo ratings yet
- Enzyme LabDocument4 pagesEnzyme LabAlfina WulandariNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 NerveDocument12 pagesUnit 5 NerveAlfina WulandariNo ratings yet
- Anastomose The Process Wherein Branches of A Coral Grow Back Together After The InitialDocument9 pagesAnastomose The Process Wherein Branches of A Coral Grow Back Together After The InitialAlfina WulandariNo ratings yet
- Report 1Document6 pagesReport 1Alfina WulandariNo ratings yet
- Sampul CantikDocument1 pageSampul CantikAlfina WulandariNo ratings yet
- Group DataDocument3 pagesGroup DataAlfina WulandariNo ratings yet
- Bibliography: Fine Structure of Syzygial Articulations Before and After Arm Autotomy Inflorometra Crinoidea)Document2 pagesBibliography: Fine Structure of Syzygial Articulations Before and After Arm Autotomy Inflorometra Crinoidea)Alfina WulandariNo ratings yet
- CRINOIDEADocument12 pagesCRINOIDEAAlfina Wulandari100% (2)
- Abs TrakDocument1 pageAbs TrakAlfina WulandariNo ratings yet
- CRINOIDEADocument12 pagesCRINOIDEAAlfina Wulandari100% (2)
- Pemberian Obat Pada MencitDocument6 pagesPemberian Obat Pada MencitAlfina WulandariNo ratings yet
- Abs TrakDocument1 pageAbs TrakAlfina WulandariNo ratings yet
- Pemberian Obat Pada MencitDocument6 pagesPemberian Obat Pada MencitAlfina WulandariNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Growth and Development TheoriesDocument7 pagesGrowth and Development TheoriesMabes100% (1)
- 3B Arm Model - M11Document28 pages3B Arm Model - M11rswongym449No ratings yet
- LP UapDocument18 pagesLP UapHat MutisalNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyTin BernardezNo ratings yet
- 76) Book Chapter 2010Document11 pages76) Book Chapter 2010Giovanni MauroNo ratings yet
- Autopsy Report: DECEDENT: John AndersonDocument5 pagesAutopsy Report: DECEDENT: John AndersonjilliankadNo ratings yet
- The Gut Microbiota-Brain AxisDocument15 pagesThe Gut Microbiota-Brain AxisMateo MendozaNo ratings yet
- Big Can Be Beautiful, TIVA in The ObeseDocument7 pagesBig Can Be Beautiful, TIVA in The ObeseHernán GiménezNo ratings yet
- Cerebral EdemaDocument5 pagesCerebral EdemaAdilah AdeebNo ratings yet
- Medical Technologies History of Medtech in United StatesDocument1 pageMedical Technologies History of Medtech in United StatesAthaliah Del MonteNo ratings yet
- X - Problem Prioritization and NCPDocument5 pagesX - Problem Prioritization and NCPMartin Lєtmaku Espina100% (2)
- Globin Synthesis PDFDocument6 pagesGlobin Synthesis PDFmanoj_rkl_07100% (1)
- Vol IDocument273 pagesVol IReza ParkerNo ratings yet
- Sarns Modular Perfusion System 8000: A Flexible, Dependable, and Cost-Efficient Modular Blood Pumping SystemDocument4 pagesSarns Modular Perfusion System 8000: A Flexible, Dependable, and Cost-Efficient Modular Blood Pumping SystemAdvancemicronics MedicalsystemsNo ratings yet
- Mind Maps in Biochemistry - (Metabolism of Carbohydrates)Document23 pagesMind Maps in Biochemistry - (Metabolism of Carbohydrates)Gus LionsNo ratings yet
- Histology Guide: Tissues, Epithelial Types & FunctionsDocument40 pagesHistology Guide: Tissues, Epithelial Types & FunctionsStevenRafaelGarciaManingasNo ratings yet
- A Presentation On Pantothenic Acid or b5Document28 pagesA Presentation On Pantothenic Acid or b5jainsaketNo ratings yet
- 0 MnemonicsDocument133 pages0 MnemonicsAlex Ivan Chen TejadaNo ratings yet
- Fever PathophysiologyDocument9 pagesFever PathophysiologyNadya AzzahraNo ratings yet
- University of Phoenix Anatomy and Physiology Week 2 QuizDocument2 pagesUniversity of Phoenix Anatomy and Physiology Week 2 QuizSophia FHSNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument10 pagesNCPbabycheska08No ratings yet
- Heart Rate HomeostasisDocument2 pagesHeart Rate Homeostasisapi-332478778No ratings yet
- 24 Inner Ear Anatomy, Emberyology, Drugs Ototoxicity (Done)Document24 pages24 Inner Ear Anatomy, Emberyology, Drugs Ototoxicity (Done)osamaeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 The Foundations of BiochemistryDocument5 pagesChapter 1 The Foundations of BiochemistryghurapNo ratings yet
- Nptel: Biomechanics - Web CourseDocument2 pagesNptel: Biomechanics - Web CourseErin BarryNo ratings yet
- Hillside School: Biology For Grade 12 Note 2 Topic: The Structure and Function of Bacterial CellDocument8 pagesHillside School: Biology For Grade 12 Note 2 Topic: The Structure and Function of Bacterial Celloli JrNo ratings yet
- Module 1. General and Special Questions of Clinical Laboratory Diagnostics Text Test QuestionDocument229 pagesModule 1. General and Special Questions of Clinical Laboratory Diagnostics Text Test QuestionA.h.MuradNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument19 pagesCase Studywella goNo ratings yet
- Blueprint of LifeDocument42 pagesBlueprint of Lifesophiehee1234No ratings yet
- Nursing DictionaryDocument353 pagesNursing DictionaryEmmanuel BoadNo ratings yet