Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electicity Exam As Edexcel PDF
Uploaded by
Ahmed HossainOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electicity Exam As Edexcel PDF
Uploaded by
Ahmed HossainCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
Three identical resistors are connected across a potential difference V so that one of them is
in parallel with the other two which are connected in series. The power dissipated through
the first one, compared to the power dissipated by each of the other two, is approximately
A
the same
B
half as much
C
twice as much
D
four times as much
(Total 1 mark)
2.
A circuit is set up as shown in the diagram.
10
40
20
When the switch is closed, the potential difference across the 20 resistor would
A
equal the potential difference across the 10 resistor
B
be twice the potential difference across the 10 resistor
C
equal the potential difference across the 40 resistor
D
be half the potential difference across the 40 resistor
(Total 1 mark)
3.
How much electrical energy is required to move 4.00 mC of charge through a potential
difference of 36.0 V?
A
1.11 104 J
B
C
D
4.
0.144 J
144 J
9000 J
(Total 1 mark)
Which of the following graphs gives the current-potential difference characteristic of an NTC
thermistor?
I
D
(Total 1 mark)
6.
A group of students is discussing why the resistance of the metal filament of a lamp and the
resistance of an NTC thermistor respond differently to changes in temperature.
One student says that the increased vibrations of the atoms affect the conduction process.
Another student says that as the temperature increases more electrons can break free of the
atoms and take part in conduction.
Both students are correct. Explain how these two effects apply to the lamp and the
thermistor.
...............................................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................................................
(Total 5 marks)
7.
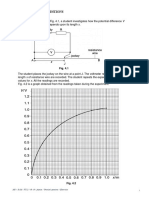
A student sets up the following circuit to measure the internal resistance of a cell.
(a)
What is wrong with his circuit diagram?
.....................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................ 1 mark
(b)
Using the correct circuit the student obtains the following results.
Current in the cell
Terminal potential difference
I/A
across the cell V/V
0.5
1.2
0.9
1.0
1.5
0.8
1.9
0.6
2.5
0.4
2.9
0.2
(i)
On the grid below, plot these results and draw the line of best fit through your
points.
V/V
1.4
1.2
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
0
3 I/A
(3)
(ii)
Use your graph to determine the e.m.f. of the cell.
e.m.f. = .........................................
(1)
(iii) Use your graph to determine the internal resistance of the cell.
Internal resistance = ...................
(2)
(c)
The experiment is repeated with two such cells connected in series. How does the
graph differ?
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 9 marks)
9.
(a)
Define resistivity.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(b)
(i)
The heating element used in a hairdryer consists of a long nichrome wire coiled
around an insulator. The hairdryer operates at 230 V and has a power of 1.0 kW.
Calculate the resistance of the heating element.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
Resistance = ..................................
(3)
(ii)
The wire has a cross-sectional area of 1.3 107 m2. The resistivity of nichrome is
1.1 106 m. Calculate the length of the nichrome wire.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
Length = ..................................
(3)
(iii)
The nichrome wire in this heating element has a diameter of 0.41 mm.
A manufacturer wishes to make a hairdryer of the same resistance but using half
the length of nichrome wire. What diameter wire must be used?
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
Diameter = ..................................
(2)
(Total 10 marks)
10.
(a)
Define the term electromotive force (e.m.f.).
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(b)
A battery of e.m.f. 3.0 V is connected to a 5.0 resistor with a very high resistance
voltmeter placed across the resistor.
(2)
3.0 V
5.0
(i)
The very high resistance voltmeter gives a reading of 2.8 V. Show that the internal
resistance of the battery is about 0.4 .
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(3)
(ii)
A voltmeter with a resistance of 10 is used instead of the original one. Calculate
the combined resistance of this voltmeter and the 5.0 resistor.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
Combined resistance = ..................................
(2)
(iii) Calculate the reading on this voltmeter.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
Voltmeter reading = ..................................
(3)
(c)
State and explain what the resistance of an ideal voltmeter should be.
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................................
(2)
(Total 12 marks)
11.
An experiment is set up to investigate how the current I in a filament lamp varies with the
potential difference V across it. The components used are shown below.
(a)
Readings are taken over the full range from 0 V to the cells maximum potential
difference. In the space below, draw a circuit diagram for this experiment.
(b)
(i)
(2)
Sketch on the axes below the shape of the graph you would expect the results to
give.
(2)
(ii)
Explain the shape of your graph. You may be awarded a mark for the clarity of
your answer.
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
...........................................................................................................................
(4)
(Total 8 marks
You might also like
- Schaum's Outline of Basic Electricity, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Outline of Basic Electricity, Second EditionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (14)
- W 4 BookDocument55 pagesW 4 BookAdri De Udok100% (1)
- DC Electricity 1Document21 pagesDC Electricity 1heroictollNo ratings yet
- IB Physics Review - Electrostatics and FieldsDocument7 pagesIB Physics Review - Electrostatics and Fieldsballer5556No ratings yet
- Current and Potential Difference 1Document66 pagesCurrent and Potential Difference 1kyle toddNo ratings yet
- University of Geneva Introduction to Basic Electronic Concepts and Circuit TheoryDocument25 pagesUniversity of Geneva Introduction to Basic Electronic Concepts and Circuit TheoryDante FilhoNo ratings yet
- Bank of Questions - ElectricityDocument68 pagesBank of Questions - ElectricityAnonymous CommentatorNo ratings yet
- Electrical Quantities and Components-2Document66 pagesElectrical Quantities and Components-2Benny ZhongNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 STPM Trial 2014Document10 pagesPhysics 2 STPM Trial 2014Abdul Shariff100% (1)
- Electrical Science Transformers: DOE FundamentalsDocument25 pagesElectrical Science Transformers: DOE FundamentalsgebremariamNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Capacitors QPDocument19 pagesEdexcel Capacitors QPMehrabNo ratings yet
- Electric Field and CapacitorsDocument18 pagesElectric Field and CapacitorsTharushiNethmiNo ratings yet
- Thermal PhysicsDocument10 pagesThermal PhysicsAtulya BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24 - Electric PotentialDocument12 pagesChapter 24 - Electric PotentialVV CepheiNo ratings yet
- Electricity: 1. A Fuse Is One Form of Protection in An Electrical CircuitDocument14 pagesElectricity: 1. A Fuse Is One Form of Protection in An Electrical CircuitUsman AhmedNo ratings yet
- 42.4-Electrical Quantities-Cie Igcse Physics Ext-Theory-QpDocument11 pages42.4-Electrical Quantities-Cie Igcse Physics Ext-Theory-Qpdiyakrishna202010No ratings yet
- Variation of Conductance with Temperature in ElectrolytesDocument19 pagesVariation of Conductance with Temperature in ElectrolytesShantanu VermaNo ratings yet
- 2009 IB Physics - SL FieldsDocument17 pages2009 IB Physics - SL FieldsGajendraNo ratings yet
- Electricity Including Electrostatics: NameDocument93 pagesElectricity Including Electrostatics: Nameinaaya azamNo ratings yet
- U2-Electricity, Q&ADocument34 pagesU2-Electricity, Q&ALiang LuNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper ADocument8 pagesSample Paper ADeezNo ratings yet
- Madeley High School Q1 Physics Circuit and Resistance QuestionsDocument23 pagesMadeley High School Q1 Physics Circuit and Resistance QuestionsmadhujayanNo ratings yet
- EMFT BookDocument260 pagesEMFT BookSimonas GrubinskasNo ratings yet
- Types of ResistorDocument18 pagesTypes of ResistorSahil SharmaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Investigatory Project Chemistry Project ConductivityDocument19 pagesCBSE Investigatory Project Chemistry Project ConductivityAnushkaNo ratings yet
- Quantum and Solid State Physics: Aakash Jog 2015-16Document153 pagesQuantum and Solid State Physics: Aakash Jog 2015-16Anonymous zYmMPgsyVNo ratings yet
- Current, Potential Difference & Resistance 1Document17 pagesCurrent, Potential Difference & Resistance 1Juyeon NamNo ratings yet
- Current, Potential Difference - Resistance 1 QPDocument19 pagesCurrent, Potential Difference - Resistance 1 QPSheikhNo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuits and Internal ResistanceDocument64 pagesElectrical Circuits and Internal ResistancegeorgehenryandersonNo ratings yet
- IB Questionbank Physics 1Document5 pagesIB Questionbank Physics 1Uncharted FireNo ratings yet
- Report of PhysicsDocument21 pagesReport of PhysicsNafih ZebariNo ratings yet
- Electricity 1.: (Total 1 Mark)Document21 pagesElectricity 1.: (Total 1 Mark)mardel11No ratings yet
- 2024 April G10 First Term ExamDocument10 pages2024 April G10 First Term ExamboggaliveNo ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument14 pagesNew Text DocumentAnonymous JPOZdekNo ratings yet
- Mater and Radiation TuteDocument8 pagesMater and Radiation TuteSahlo FolinaNo ratings yet
- Electricity Eou Test: Ial PhysicsDocument7 pagesElectricity Eou Test: Ial PhysicsefoneoNo ratings yet
- Notes Plasma PhysicsDocument83 pagesNotes Plasma PhysicsRocio BriceñoNo ratings yet
- Q1. The Diagram Below Shows Part of An Energy Level Diagram For A Hydrogen AtomDocument8 pagesQ1. The Diagram Below Shows Part of An Energy Level Diagram For A Hydrogen AtomTony CliftonNo ratings yet
- Inzenjerski Engleski JezikDocument6 pagesInzenjerski Engleski JezikAmel BegićNo ratings yet
- Electro Erf EffectsDocument246 pagesElectro Erf Effectsaeroseb1No ratings yet
- 4.4 E and M FieldsDocument145 pages4.4 E and M FieldsMozammel AnowarNo ratings yet
- 2 Synchrotron Radiation 56Document65 pages2 Synchrotron Radiation 56Aurélie MaillardNo ratings yet
- HW On Energy and PhotonDocument8 pagesHW On Energy and PhotonTony CliftonNo ratings yet
- FT 12 Gr10 P4 Qs (Electricity)Document8 pagesFT 12 Gr10 P4 Qs (Electricity)Kiron SheiqNo ratings yet
- Fields - QP IBDP PhysicsDocument9 pagesFields - QP IBDP PhysicsArham ShahNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Field Theory - Bo Thide PDFDocument202 pagesElectromagnetic Field Theory - Bo Thide PDFnacrosse100% (1)
- Antropov - Theoretical Electrochemistry - Mir - 1972Document569 pagesAntropov - Theoretical Electrochemistry - Mir - 1972daya100% (1)
- 2010 A ReviewofconductionphenomenainLi-IonbatteriesDocument26 pages2010 A ReviewofconductionphenomenainLi-IonbatteriesBruce LiNo ratings yet
- Quantum PhysicsDocument21 pagesQuantum PhysicsMartin DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Field TheoryDocument262 pagesElectromagnetic Field TheoryDuygu Nazan Gençoğlan100% (2)
- Applications of Quantum and Classical Connections in Modeling Atomic, Molecular and Electrodynamic SystemsFrom EverandApplications of Quantum and Classical Connections in Modeling Atomic, Molecular and Electrodynamic SystemsNo ratings yet
- Environmental Electrochemistry: Fundamentals and Applications in Pollution Sensors and AbatementFrom EverandEnvironmental Electrochemistry: Fundamentals and Applications in Pollution Sensors and AbatementNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Abc of Capacitors: Basic PrinciplesFrom EverandAbc of Capacitors: Basic PrinciplesWürth ElektronikNo ratings yet
- 60 SETS PhysicsDocument8 pages60 SETS PhysicsAhmed Hossain100% (1)
- Style Lecture 02 FinalDocument5 pagesStyle Lecture 02 FinalAhmed HossainNo ratings yet
- Question Paper 1Document55 pagesQuestion Paper 1Joshua Aaron Solomon100% (1)
- 0625 - s09 - Ms - 3documentation of PhysicsDocument13 pages0625 - s09 - Ms - 3documentation of PhysicsAhmed HossainNo ratings yet
- Full Name Telephone No. SchoolDocument1 pageFull Name Telephone No. SchoolAhmed HossainNo ratings yet
- 0625 - w10 - Ms - 22documentation of PhysicsDocument6 pages0625 - w10 - Ms - 22documentation of PhysicsAhmed HossainNo ratings yet
- 0625 - s15 - Msdocumentation of Physics - 31Document8 pages0625 - s15 - Msdocumentation of Physics - 31Ahmed HossainNo ratings yet
- 0625 - s09 - Ms - 2documentation of PhysicsDocument7 pages0625 - s09 - Ms - 2documentation of PhysicsAhmed HossainNo ratings yet
- Qubee ReportDocument14 pagesQubee ReportZahidur RezaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics equations motion problemsDocument3 pagesKinematics equations motion problemsAhmed HossainNo ratings yet
- Mock U2 Edexcel PDFDocument14 pagesMock U2 Edexcel PDFAhmed HossainNo ratings yet
- Implementation of An Adder Circuit With A Carry Look Ahead GeneratorDocument2 pagesImplementation of An Adder Circuit With A Carry Look Ahead GeneratorAhmed HossainNo ratings yet
- Software Categories and Youtube Links PDFDocument19 pagesSoftware Categories and Youtube Links PDFAhmed HossainNo ratings yet
- Mock U2 Edexcel PDFDocument14 pagesMock U2 Edexcel PDFAhmed HossainNo ratings yet
- Quark Charges and Particle MassesDocument7 pagesQuark Charges and Particle MassesAhmed HossainNo ratings yet
- Mock U1 Edexcel PDFDocument11 pagesMock U1 Edexcel PDFAhmed HossainNo ratings yet
- Qubee ReportDocument14 pagesQubee ReportZahidur RezaNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelDocument16 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelHubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- Physics 2010 Summer Review Midterm 5Document16 pagesPhysics 2010 Summer Review Midterm 5Erickson AbiolNo ratings yet
- Eigenvectors-Wolfram Mathematica 9 Documentation PDFDocument6 pagesEigenvectors-Wolfram Mathematica 9 Documentation PDFMahfudz ShodiqNo ratings yet
- Von Neumann AnalysisDocument16 pagesVon Neumann AnalysisakkansalNo ratings yet
- PHY - Unit 0 - Lessons 1 2 3 - Class PPT RevDocument61 pagesPHY - Unit 0 - Lessons 1 2 3 - Class PPT RevclemesgNo ratings yet
- List of Dynamical Systems and Differential Equations TopicsDocument6 pagesList of Dynamical Systems and Differential Equations TopicsSteeven AlquingaNo ratings yet
- Bahir Dar Academy Department of Physics Physics Worksheet V For Grade 11 (Rotational Motion)Document2 pagesBahir Dar Academy Department of Physics Physics Worksheet V For Grade 11 (Rotational Motion)Michael AmareNo ratings yet
- Uht-56 Asme Viii Div 1 2010Document1 pageUht-56 Asme Viii Div 1 2010Germán Lobo Clavijo100% (1)
- Bifilar SuspensionDocument9 pagesBifilar SuspensionUmer ZamanNo ratings yet
- Carsten Tschierske - Micro-Segregation, Molecular Shape and Molecular Topology - Partners For The Design of Liquid Crystalline Materials With Complex Mesophase MorphologiesDocument25 pagesCarsten Tschierske - Micro-Segregation, Molecular Shape and Molecular Topology - Partners For The Design of Liquid Crystalline Materials With Complex Mesophase MorphologiesDremHpNo ratings yet
- Cutler-Hammer Instructions For Installation, Operation and Maintenance of Type DHP-VR Vaccum Replacement Circuit Breakers For DHP SwitchgearDocument49 pagesCutler-Hammer Instructions For Installation, Operation and Maintenance of Type DHP-VR Vaccum Replacement Circuit Breakers For DHP Switchgearfafejaya13No ratings yet
- Vector Mechanics Engineers: Tenth EditionDocument5 pagesVector Mechanics Engineers: Tenth EditionSofia UmañaNo ratings yet
- Senior SolutionDocument2 pagesSenior Solutionminhtue90No ratings yet
- Homework 3 Vector Algebra and CalculusDocument3 pagesHomework 3 Vector Algebra and CalculusSwathi BDNo ratings yet
- Wind Power PlantDocument12 pagesWind Power PlantMohamad SaadNo ratings yet
- Quantum Bhabna Safalyagatha 0Document226 pagesQuantum Bhabna Safalyagatha 0mamunngsNo ratings yet
- PV NRT: PM RT DRT PDocument19 pagesPV NRT: PM RT DRT PRyle ArbonNo ratings yet
- NCCI: Mono-Symmetrical Uniform Members Under Bending and Axial CompressionDocument15 pagesNCCI: Mono-Symmetrical Uniform Members Under Bending and Axial CompressionhapsinteNo ratings yet
- Exercises ArchimedesDocument4 pagesExercises ArchimedesAnonymous UypCttW100% (2)
- Tutorial Sheet 1: Force Resolution, Resultant and EquilibriumDocument5 pagesTutorial Sheet 1: Force Resolution, Resultant and EquilibriumJahnavi JanuNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Rigid Body KinematicsDocument4 pagesAssignment On Rigid Body KinematicsKaveesh KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Loka-The Buddha's Formulation of The Universe Rick CrutcherDocument12 pagesLoka-The Buddha's Formulation of The Universe Rick CrutcherjonrcrowleyNo ratings yet
- Atomic ModelsDocument12 pagesAtomic ModelsDr Siva Kumar0% (1)
- Experiment 3.Document6 pagesExperiment 3.tracyymendozaNo ratings yet
- The Quantum Harmonic OscillatorDocument19 pagesThe Quantum Harmonic OscillatorSean MortaraNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Composite Materials and LaminatedDocument139 pagesMechanics of Composite Materials and LaminatedKhoi Le100% (1)
- Analize de Aciditate Si Isocianat La Fabricarea - The Plastics PDFDocument6 pagesAnalize de Aciditate Si Isocianat La Fabricarea - The Plastics PDFCorina StanculescuNo ratings yet
- CH 29Document13 pagesCH 29CristianNo ratings yet
- Calibration Curve of MBDocument140 pagesCalibration Curve of MBSandip KadoliNo ratings yet
- BSNL JTO Sample Paper-3Document100 pagesBSNL JTO Sample Paper-3ramesh_balakNo ratings yet
- ProblemSet3 SolutionsDocument8 pagesProblemSet3 SolutionsnormanNo ratings yet