Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problem Set Zener Diodes
Uploaded by
Siva PrasadOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Problem Set Zener Diodes
Uploaded by
Siva PrasadCopyright:
Available Formats
Dr.
Mark Andrews Microelectronic Circuits ELECTENG207
Problem Set
Zener Diodes
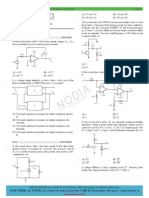
The model of a Zener diode is shown below. When forward biased (A more positive than K) the
Zener acts like an ideal diode
IDEAL
D . When reverse biased (K more positive than A) the Zener is
modelled as an ideal voltage source
Z
V in series with the resistance
Z
R .
D
K
A A
K
D
IDEAL
V
Z
R
Z
Question 1
For the circuit shown below calculate the Zener diode current
Z
I and the circuit output voltage
OUT
V assuming (a) 0 =
Z
R and (b) = 20
Z
R .
R
S
D V
OUT
V
IN
I
Z
V 12 =
IN
V
= 320
S
R
mA 5
) (
=
MIN Z
I
V 2 . 8 =
Z
V
Question 2
The circuit in Question 1 is connected to an unregulated voltage source
S
V that varies between
10.0 V and 20.0 V. Calculate the corresponding variation in output voltage assuming (a) = 0
Z
R
and (b) = 20
Z
R .
Question 3
The circuit below shows a simple Zener regulator with a permanently connected load
L
R .
Calculate the Zener diode current
Z
I and the circuit output voltage
OUT
V assuming (a) 0 =
Z
R and
(b) = 20
Z
R .
R
S
D
V
OUT
V
IN
I
Z
R
L
V 12 =
IN
V
= 75
S
R
mA 5
) (
=
MIN Z
I
V 2 . 8 =
Z
V
= 250
L
R
Dr. Mark Andrews Microelectronic Circuits ELECTENG207
Question 4
Design a Zener regulator to supply 8.2 V to a constant, permanently connected, 50 load. The
input to the circuit is an unregulated DC supply in the range 15.0 V to 24.0 V. Assume that the
Zener diode needs 5 mA to ensure operation and = 0
Z
R .
Notes:
1. The Zener diode must have 5 mA flowing through it at ALL times for the circuit to function
correctly.
2. You need to calculate the value and power rating of the source resistor together with the
power rating of the Zener diode.)
Question 5
With reference to your design in Question 4, calculate the power dissipated in the Zener diode if
the load is accidentally disconnected. Is this a problem?
Dr. Mark Andrews Microelectronic Circuits ELECTENG207
Outline Solutions
Question 1
(b) Sum the voltages around the loop to get
OUT
V
Z Z Z S Z IN
V R I R I V + + = .
Thus mA 176 . 11 =
+
=
Z S
Z IN
Z
R R
V V
I and V 424 . 8 = + =
Z Z Z OUT
V R I V .
Question 2
(b) V 0 . 10
) (
=
MIN S
V and V 0 . 20
) (
=
MAX S
V . Using the results of Question 1 we get
mA 294 . 5
) (
) (
=
+
=
Z S
Z MIN S
MIN Z
R R
V V
I giving V 306 . 8
) ( ) (
= + =
Z Z MIN Z MIN OUT
V R I V . Similarly,
V 894 . 8
) (
=
MAX OUT
V . The variation in the output is V 306 8 894 8 . . or V 588 . 0 or % 1 . 7 Note
that the input variation is V 0 . 10 or % 0 . 100 .
Question 3
(b) Replace the Zener diode with its equivalent circuit:
R
S
V
IN
V
OUT
V
Z
R
Z
R
L
N
Sum the currents leaving the node N to get 0 = +
L
OUT
Z
Z OUT
S
IN OUT
R
V
R
V V
R
V V
. Now solve for the
output voltage V 465 . 8
1 1 1
=
+ +
+
=
L Z S
Z
Z
S
IN
R R R
R
V
R
V
OUT
V . The Zener current is mA 267 . 13 =
=
Z
Z OUT
Z
R
V V
I .
You might also like
- From "The Musician's Guide To Theory and Analysis," by Jane Piper Clendinning and Elizabeth Marvin, Second EditionDocument4 pagesFrom "The Musician's Guide To Theory and Analysis," by Jane Piper Clendinning and Elizabeth Marvin, Second EditionSiva PrasadNo ratings yet
- Diode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesFrom EverandDiode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- CalculationsDocument15 pagesCalculationsnho_OsakaNo ratings yet
- MV SWGR InspectionDocument10 pagesMV SWGR InspectionTHULASI RAM100% (1)
- A Kuthi - Nanosecond Pulse Generator Using A Fast Recovery DiodeDocument4 pagesA Kuthi - Nanosecond Pulse Generator Using A Fast Recovery Diodesebastian.gonczarekNo ratings yet
- 5V DC Power SupplyDocument6 pages5V DC Power SupplyTarik Imran100% (2)
- Electric Circuit and Fields QuestionsDocument38 pagesElectric Circuit and Fields Questionssamg270% (1)
- Analog and Digital Electronics PDFDocument34 pagesAnalog and Digital Electronics PDFJatinNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Sheet 2: Example 1: A 20 kVA, 2500/250 V, 50Hz, Single-Phase Transformer Gave TheDocument3 pagesSheet 2: Example 1: A 20 kVA, 2500/250 V, 50Hz, Single-Phase Transformer Gave Thetareq omar71% (7)
- Preboard Sept 2013 Set B SolutionDocument20 pagesPreboard Sept 2013 Set B Solutionmark ian100% (4)
- Lab Report - Zener DiodDocument34 pagesLab Report - Zener Diodانوارالدين محمد قاسم100% (1)
- Assignment 01Document6 pagesAssignment 01Z S PlaysNo ratings yet
- Special Purpose DiodesDocument30 pagesSpecial Purpose DiodesSumi GargiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 DiodesDocument52 pagesLecture 1 DiodesfaradeyisaheroNo ratings yet
- Yanbu University College: Electronics (CSE 252)Document6 pagesYanbu University College: Electronics (CSE 252)Raed AlRuwaili100% (1)
- 4d8f8analog 1, Tut SheetDocument19 pages4d8f8analog 1, Tut SheetmntykrNo ratings yet
- HW 1Document9 pagesHW 1Kyto_oNo ratings yet
- Ece 1001: Basic Electronics: Assignment Sheet - 1Document2 pagesEce 1001: Basic Electronics: Assignment Sheet - 1Deepanshu SehgalNo ratings yet
- = 6 V. (Ans. (a) 860 Ω; (b) 26.5 mW, 3.5 mW)Document2 pages= 6 V. (Ans. (a) 860 Ω; (b) 26.5 mW, 3.5 mW)Daudi Erasto MlangiNo ratings yet
- Electronics I Suggested Exercises 2: Problem 1Document3 pagesElectronics I Suggested Exercises 2: Problem 1Ibrahim Al-HusariNo ratings yet
- ECE101 Modules 9 Zener DiodesDocument34 pagesECE101 Modules 9 Zener DiodesGio AscanNo ratings yet
- bee-EXPERIMENT 5 ZenerDocument6 pagesbee-EXPERIMENT 5 ZenerKzenetteNo ratings yet
- CH2 Diode Ckts and AppsDocument7 pagesCH2 Diode Ckts and AppsCharles Adrian CervaniaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 (Modified)Document8 pagesExperiment 5 (Modified)Mark Sangalang100% (1)
- Tut SemiconductDocument3 pagesTut SemiconductLim Chieh ShingNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics Practice QuestionsDocument19 pagesAnalog Electronics Practice Questionssharma_rockstarNo ratings yet
- Sem 3 Module 1Document3 pagesSem 3 Module 1fczeroNo ratings yet
- HW 6Document3 pagesHW 6Miles GrubbsNo ratings yet
- Colour Coded ResistorsDocument28 pagesColour Coded ResistorsEd JudgeNo ratings yet
- Diode ProblemsDocument9 pagesDiode ProblemsAravind KarthikNo ratings yet
- Homework SolutionsDocument46 pagesHomework SolutionsKashif AmjadNo ratings yet
- Dechassa - Retta - Lemma - 3189815 - 22577354 - BEE 332# Due Nov 2 From Abraham.aDocument33 pagesDechassa - Retta - Lemma - 3189815 - 22577354 - BEE 332# Due Nov 2 From Abraham.ajoe.kurina3194No ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document5 pagesTutorial 1Pasindu PramodNo ratings yet
- 1519292487one Indian Girl by Chetan BhagatDocument32 pages1519292487one Indian Girl by Chetan Bhagatabhishek kumarNo ratings yet
- UNSW Sydney Australia: Question DA1Document18 pagesUNSW Sydney Australia: Question DA1Marquee BrandNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document3 pagesTutorial 3miindsurferNo ratings yet
- Tutorial #1Document3 pagesTutorial #1Greenhearthazel Varma PdgNo ratings yet
- Linear Circuits Formal Lab ReportDocument7 pagesLinear Circuits Formal Lab ReportNishant JalgaonkarNo ratings yet
- Tipuri de TranzistoriDocument39 pagesTipuri de Tranzistorisokyb2004No ratings yet
- Mohit Jetani 1270404 0Document32 pagesMohit Jetani 1270404 0ronajoj120No ratings yet
- Tutorials Sheet No 1 Phys 2054 Nasey Fev 2022Document5 pagesTutorials Sheet No 1 Phys 2054 Nasey Fev 2022Arthur MoloNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode Problem SetDocument2 pagesZener Diode Problem SetManprit SinghNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode Problem Set PDFDocument2 pagesZener Diode Problem Set PDFfree5050No ratings yet
- Homework Assignment 02 Question 1 (Short Takes), 2 Points Each. 1Document14 pagesHomework Assignment 02 Question 1 (Short Takes), 2 Points Each. 1WoodchuckNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document2 pagesChapter 3William ZhuangNo ratings yet
- LAB 9 EE NewDocument9 pagesLAB 9 EE NewtengyanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Preliminary Report: ELEC3307 Electronics LaboratoryDocument5 pagesExperiment 1 Preliminary Report: ELEC3307 Electronics LaboratoryArda Deniz EryiğitNo ratings yet
- Analog CircuitsDocument33 pagesAnalog Circuitsafireon80% (1)
- Sem1 1213 SolutionDocument17 pagesSem1 1213 SolutionThinesh StNo ratings yet
- 3 - Zener Diod VI Characteristic.Document4 pages3 - Zener Diod VI Characteristic.BBA UniversityNo ratings yet
- Diode Characteristics PDFDocument16 pagesDiode Characteristics PDFJOECELLE ABLEGINANo ratings yet
- ELET1500 BJT Tutorial: E C E B C E B CDocument5 pagesELET1500 BJT Tutorial: E C E B C E B CCadane CodnerNo ratings yet
- ELET1500 BJT Tutorial: E C E B C E B CDocument5 pagesELET1500 BJT Tutorial: E C E B C E B CCadane CodnerNo ratings yet
- Lab3 ManualDocument12 pagesLab3 Manualdlat94No ratings yet
- ECE320 HW3 SolutionDocument3 pagesECE320 HW3 Solutiondigital2000No ratings yet
- SolutionDocument8 pagesSolutionPallavi SahuNo ratings yet
- Tutorial DiodeDocument15 pagesTutorial DiodeAravind KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Highlights Aug 20Document12 pagesHighlights Aug 20Siva PrasadNo ratings yet
- MA Sociology C. No. 102 28-9-20Document312 pagesMA Sociology C. No. 102 28-9-20Siva PrasadNo ratings yet
- APCFSSDocument1 pageAPCFSSSiva PrasadNo ratings yet
- Requirment of CCTV CAMERA1Document2 pagesRequirment of CCTV CAMERA1Siva PrasadNo ratings yet
- Relaxation 1 PDFDocument1 pageRelaxation 1 PDFSiva PrasadNo ratings yet
- Grade 2 Music Theory TermsDocument1 pageGrade 2 Music Theory TermsSiva PrasadNo ratings yet
- EE 141 Electromagnetic Field Theory: Professor K. E. OughstunDocument12 pagesEE 141 Electromagnetic Field Theory: Professor K. E. OughstunSiva PrasadNo ratings yet
- RJ11 RS-232 InterfaceDocument6 pagesRJ11 RS-232 InterfaceDrew AlbaneseNo ratings yet
- PN 15384 Fire-Lite Device Compatibility Document PDFDocument22 pagesPN 15384 Fire-Lite Device Compatibility Document PDFJuan CastilloNo ratings yet
- PEC Reviewer 4Document5 pagesPEC Reviewer 4JmNo ratings yet
- PsocDocument1 pagePsocGayan ShashiNo ratings yet
- 300B0000 IQT Basic StandardDocument2 pages300B0000 IQT Basic StandardSri67% (3)
- Wireless DC Moor Speed and Direction ControlDocument2 pagesWireless DC Moor Speed and Direction ControlJoseph JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Water Level Indicator PersentationDocument13 pagesWater Level Indicator Persentationakshay warghadeNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 2Document6 pagesLesson Plan 2nandhakumarmeNo ratings yet
- P.E - 16MDocument16 pagesP.E - 16M20EUEE053- MADHUBALAN.SNo ratings yet
- Panasonic TX-29pn1d F P TX-28pn1d F PDocument23 pagesPanasonic TX-29pn1d F P TX-28pn1d F POnde Onde Mbok Tie PonorogoNo ratings yet
- Dol1 5Document1 pageDol1 5Jusuf ElQudsyNo ratings yet
- Seminar PPT Manisha Gawale (ROBOTICS MOTORS)Document24 pagesSeminar PPT Manisha Gawale (ROBOTICS MOTORS)Nehul PatilNo ratings yet
- LM 533 PDFDocument43 pagesLM 533 PDFGilberto Grandini BitencourtNo ratings yet
- 4 Pin Dip Phototransistor Photocoupler EL817-G Series: FeaturesDocument14 pages4 Pin Dip Phototransistor Photocoupler EL817-G Series: FeaturesGilson3DNo ratings yet
- MFM - 2012 ABB Adda PresentationDocument69 pagesMFM - 2012 ABB Adda PresentationMr.SonerNo ratings yet
- Electrical Systems PDFDocument17 pagesElectrical Systems PDFJehan MohamadNo ratings yet
- Cip 0976Document2 pagesCip 0976limadacarlosNo ratings yet
- Design Metrics CMOS InverterDocument40 pagesDesign Metrics CMOS InverterPramod SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Phoenix Contact 0305080 enDocument4 pagesPhoenix Contact 0305080 enDGNo ratings yet
- Advance Electrical MachinesDocument32 pagesAdvance Electrical MachinessonuNo ratings yet
- Eng - Ademco Accord XPCDocument62 pagesEng - Ademco Accord XPCAdam ChalklyNo ratings yet
- EC2201 - Electrical EngineeringDocument5 pagesEC2201 - Electrical EngineeringrgramachandranNo ratings yet
- Ffle 2022 MW 2Document14 pagesFfle 2022 MW 2dan themanNo ratings yet
- Lun Masla Aquaculture: Technical Specification Electrical Panel BoardDocument5 pagesLun Masla Aquaculture: Technical Specification Electrical Panel BoardRobert TiinNo ratings yet
- DR Zen2 BLD MNLDocument15 pagesDR Zen2 BLD MNLRafael Frederico TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - DC - Machines - Lsn28 - S12Document13 pagesMathcad - DC - Machines - Lsn28 - S12Balaji DDNo ratings yet
- Induction Motors Faults and ProtectionDocument2 pagesInduction Motors Faults and ProtectionMuhammad Ali Khan AwanNo ratings yet
- Single Phase Rectifier Bridge: Standard and Avalanche TypesDocument2 pagesSingle Phase Rectifier Bridge: Standard and Avalanche TypesBatta CesarNo ratings yet