Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Answer PHYSIC STPM Trial Sem 1 2013
Uploaded by
Zuraini ArshadCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Answer PHYSIC STPM Trial Sem 1 2013
Uploaded by
Zuraini ArshadCopyright:
Available Formats
ANSWER TRIAL SEM 1 2013
Question Answer Explanation
1 C
Electric potential,
q
W
V = W(work done) and q (charge) are scalar
quantities
2 D L= rp= rmv = m(kgms
-1
)
3 A
4
B
u = 30 v =15 s = 75 a =?
S= ut +1/2at
2
v
2
= u
2
+ 2as
a =(15
2
30
2
)/2(75)
= -4.5
0 = 15
2
+2(-4.5)s
s = 25m
5 B
6 A
7 C
Linear momentum is conserved,
20 - 12 = -2 + momentum of Y
Momentum of Y = 10 Ns
8 D
m
F
g
mg
nal Gravitatio
=
=
2
r
Mm
G F
force
9 A
The force on each star is
-
+
=
=
7 N 3 N 4 N
7 N 3 N 10 N
F
W
F cos
W sin
ANSWER TRIAL SEM 1 2013
( )
2
2 2
4 2 R
GM
R
MM
G F = =
10 D
11 B
12 B
13 B
14 A
The change of momentum of gas molecules when they collide with the
wall cause the exertion of pressure and this cannot be neglected
15 D
Gradient of the graph
b
a
T
E
k
=
) 1 ......( NkT RT
N
N
nRt pV
A
= = =
k
k
E
N
NkT
E
N
c m
N
pV
c
V
Nm
c p
3
2
), 2 ( ) 1 (
) 2 .......(
3
2
2
1
3
2
3
1
3
1
2
2 2
= =
=
|
.
|
\
|
) ( =
) (
|
.
|
\
|
= ) ( =
Boltzman constant
b
a
T
E
k
k
3
2
3
2
= |
.
|
\
|
=
STRUCTURE
16
Mark
(a) Angular velocity is the rate of change of angular displacement
1
(b)
) ()
2
(c)
()
1
1
(d)
()()
1
1
ANSWER TRIAL SEM 1 2013
Structure
17
a
tionalarea cross
force
Stress
sec
=
ngth originalle
extension
Strain =
1
1
b
2
c
(i) Force on the wire, F = mg
Stress =
A
F
=
6
10 5 . 1
81 . 9 10
= 6.54 107 N m-2
1
1
(ii) Youngs Modulus,
Strain
Stress
E =
Strain =
E
Stress
=
11
7
10 2
10 54 . 6
= 3.27
10-4
Strain = Extension
Original length
Extension = (3.27 10-4)(2.5)
= 8.18 10-4 m
1
1
1
ESSAY
18a (i)
Principle of conservation of linear momentum states that total linear
momentum of a system of bodies is constant, if no external forces act on
the system
1
18a (ii)
For an elastic collision , the total kinetic energy is also conserved.
1
18b (i)
Gain in Grav. PE = 0.25(K)
0.031 = 0.25 K
1
1
ANSWER TRIAL SEM 1 2013
K = 0.124J
18(b) (ii)
1
3
2
75 . 4
10 11
124 . 0 2
2
2
1
=
=
=
ms
m
K
v
mv K
1
1
18 (b)
(iii)
After collision the kinetic energy = 0.75K
1
3
2
11 . 4
10 11
124 . 0 75 . 0 2
2
1
75 . 0
=
=
=
ms
v
mv K
1
1
18(c) (i)
Change in momentum= m(v-u)
= 11x 10
-3
(4.11- 4.75)
= -7.04 x 10
-3
kgms
-1
1
1
18(c) (ii)
N
in change
F
047 . 0
15 . 0
10 04 . 7
time
mometum
3
=
=
=
1
1
18(d) More energy is required.
The block becomes more stable//more difficult to be turned over//the new
C is lowered .
1
1
19(a) The resultant force is zero and the algebraic sum of the moments of the
force about any axis is zero.
1
ANSWER TRIAL SEM 1 2013
19(b)(i)
(b)(ii)
1
1
1
19(b)(iii) Total torque about the point B = 0
N R
R
75
0 )
2
5 . 1
200 ( ) 0 . 2 (
=
=
Resultant force in the vertical direction = 0
P 200 = 0
P = 200 N
Resultant force in the horizontal direction = 0
F R = 0
F = R
= 75 N
1
1
1
1
19(c)(i) Limiting static friction = the maximum value of static friction just before
an object starts to move.
Coefficient of limiting static friction =
tion normalreac
friction static limiting
1
1
19(c)(ii) Dynamic friction has constant value and is less than the limiting static
friction.
1
19(d) The 10.0 kg block and the 20.0 kg trolley both have the same acceleration
a.
Apply the Newtons second law of motion,
(i) for the load
100 - T = 10.0a ---------- (1)
(ii) for the block
a F T
k
20 =
But N mg R F
k k
80 10 20 4 . 0 = = = =
T - 80.0 = 20.0a ----------- (2)
Adding (1) and (2), we get
20 .0 = 30 .0 a
a = 0 .67 m s-2
From equation (1),
T = 93 .3 N
1
1
1
1
1
20(a-i)
Energy contained in a system ie the sum of potential and kinetic energies
(translational, rotational, vibrational )
1
ANSWER TRIAL SEM 1 2013
(a-ii)
The quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 mole of gas by
1K
1
(b)
For an ideal gas, the potential energy of the gaseous molecules can be
neglected and this means that the total kinetic energy is equivalent to the
internal energy.
Internal energy is directly proportional to absolute temperature and its
mass/number of molecule.
1
1
(c)
The molar heat capacity at constant pressure includes work done by the
gas expanding when heated
C
V
T = U and C
P
T = Q
But pV = RT =W
From Q = U + W
C
P
T = C
V
T + RT or C
P
= C
V
+ R
Since R> 0, C
P
> C
V
1
1
1
(d-i)
n = 0.200 mole, p
1
=1.04 x 10
5
Pa , T
1
= 300K
Ideal gas pV = nRT
3 3
5
1
10 79 . 4
10 04 . 1
300 31 . 8 200 . 0
m
V
=
=
1
1
(d-ii)
p
2
= 5.00 x 10
6
Pa , V
2
= V
1
/10
K
V p
V p
T
T
3 . 1442
10
1
10 79 . 4 10 00 . 5
10 79 . 4 10 04 . 1
300
3 6
3 5
2 2
1 1
1
2
=
=
=
1
1
(d-iii)
Q=6000J, p
3
= 5.00 x 10
6
Pa, T
3
= 2500K
(1) molar heat capacity
( )
1 1
4 . 28
3 . 1442 2500 2 . 0
6000
=
=
A
A
=
K Jmol
T n
Q
C
p
(2) final volume
3 4
6
10 31 . 8
10 00 . 5
2500 31 . 8 200 . 0
m
p
nRT
V
=
= =
1
1
1
1
You might also like
- Actual 2009 STPMDocument16 pagesActual 2009 STPMtweihuai100% (1)
- Marking Scheme: Answer All Questions in This SectionDocument7 pagesMarking Scheme: Answer All Questions in This SectionlllNo ratings yet
- STPM 2014 Physics Trial 2Document17 pagesSTPM 2014 Physics Trial 2choichiang100% (1)
- MATHEMATICS T Muar Marking SchemeTrialSem22021Document9 pagesMATHEMATICS T Muar Marking SchemeTrialSem22021ZurainiNo ratings yet
- IPTA Cut Off Point For PHYSICS STPM 2011 / 2012 University EntryDocument12 pagesIPTA Cut Off Point For PHYSICS STPM 2011 / 2012 University EntrySKNo ratings yet
- Physics Formula List STPM (Edu - Joshuatly.com)Document0 pagesPhysics Formula List STPM (Edu - Joshuatly.com)Choe Kok HuanNo ratings yet
- STPM Physics Sem 1 ThermodynamicsDocument8 pagesSTPM Physics Sem 1 ThermodynamicsChong Yin Ping0% (1)
- Maths T Coursework: Complex NumbersDocument38 pagesMaths T Coursework: Complex NumbersbendanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics T Trial Paper Semester 2Document5 pagesMathematics T Trial Paper Semester 2Loo Siaw Choon100% (1)
- Assignment Viva f6Document11 pagesAssignment Viva f6Magendren Raman50% (2)
- MPM 3 Sample ADocument3 pagesMPM 3 Sample AmakoplNo ratings yet
- 2014 2 NSEMBILAN SMKStPaul Seremban MATHS QADocument7 pages2014 2 NSEMBILAN SMKStPaul Seremban MATHS QASK100% (1)
- Uppp2 Sem 1 2017Document9 pagesUppp2 Sem 1 2017WWZNo ratings yet
- STPM Physics Formulas (Derived)Document3 pagesSTPM Physics Formulas (Derived)Fu HongNo ratings yet
- Chem Sem 1 Q &A PDFDocument9 pagesChem Sem 1 Q &A PDFevacuate clashNo ratings yet
- STPM Physics QuestionDocument10 pagesSTPM Physics Questionmuhdsabri510% (1)
- STPM 2013 Section A and B Physics Exam Marking SchemeDocument6 pagesSTPM 2013 Section A and B Physics Exam Marking SchemeSaiful MaslulNo ratings yet
- Physics STPM Sem 3 DefinitionDocument2 pagesPhysics STPM Sem 3 DefinitionBen67% (3)
- SUGGESTED ANSWER STPM 2011 MATHEMATICS T Paper 2Document6 pagesSUGGESTED ANSWER STPM 2011 MATHEMATICS T Paper 2SKNo ratings yet
- STPM Physics Chapter 18 Alternating Current CircuitsDocument2 pagesSTPM Physics Chapter 18 Alternating Current CircuitsChris Lau100% (1)
- PENANG 2013 STPM TRIAL PAPERS For Mathematics T TERM 2Document8 pagesPENANG 2013 STPM TRIAL PAPERS For Mathematics T TERM 2SK100% (3)
- Math M Coursework - Doc3Document1 pageMath M Coursework - Doc3Chong Yin Ping100% (1)
- STPM Physics Chapter 12 ElectrostaticsDocument1 pageSTPM Physics Chapter 12 ElectrostaticsChris Lau100% (3)
- 02AAMathT - FWS - Chapter 02 PDFDocument18 pages02AAMathT - FWS - Chapter 02 PDFWei Chuan TanNo ratings yet
- Focus c.8Document22 pagesFocus c.8Nicholson NicholsonNo ratings yet
- Physic Experiment 6Document2 pagesPhysic Experiment 6JasonNo ratings yet
- Physics Coursework 2016/2017 STPMDocument13 pagesPhysics Coursework 2016/2017 STPMShi JieNo ratings yet
- 2016 2 KL SMK Methodist - Maths QADocument12 pages2016 2 KL SMK Methodist - Maths QAlingbooNo ratings yet
- 04 - AA - MathT - FWS - CH 10 - 1PP PDFDocument17 pages04 - AA - MathT - FWS - CH 10 - 1PP PDFWei Chuan TanNo ratings yet
- Maths T STPM Sem 1 Model Question Set 1-6 AnswerDocument12 pagesMaths T STPM Sem 1 Model Question Set 1-6 AnswerKenneth Chan100% (2)
- STPM Maths T Sem 1 Chapter 5 Past Year QuestionsDocument2 pagesSTPM Maths T Sem 1 Chapter 5 Past Year QuestionsKangJiaJiaNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 ProjectileDocument9 pagesExperiment 2 ProjectilevimalNo ratings yet
- 962 Chemistry (PPU - STPM) Semester 3 Topics-SyllabusDocument13 pages962 Chemistry (PPU - STPM) Semester 3 Topics-SyllabusJosh, LRTNo ratings yet
- Focus On Exam 7: Chapter 7 Limits and ContinuityDocument7 pagesFocus On Exam 7: Chapter 7 Limits and ContinuityChan KarlokNo ratings yet
- STPM Physics Earth Magnetic Field ExperimentDocument2 pagesSTPM Physics Earth Magnetic Field Experimenthonghong_LCHNo ratings yet
- Physics Definaition ListDocument10 pagesPhysics Definaition Listwanaizuddin80% (5)
- KH Pre-U STPM Term 1 Trial - Mathematics TDocument4 pagesKH Pre-U STPM Term 1 Trial - Mathematics THamzah benyehyaNo ratings yet
- STPM Physics Sem 3 Definition ListsDocument4 pagesSTPM Physics Sem 3 Definition ListsredroseNo ratings yet
- Klang High Trial STPM 2019 P3Document13 pagesKlang High Trial STPM 2019 P3Khang Ni 康妮 FooNo ratings yet
- STPM12Document18 pagesSTPM12Wei Chuan TanNo ratings yet
- STPM Physics Chapter 13 Capacitors PDFDocument1 pageSTPM Physics Chapter 13 Capacitors PDFChris LauNo ratings yet
- STPM Chemistry Practical Volumetric AnalysisDocument4 pagesSTPM Chemistry Practical Volumetric AnalysisUngHHNo ratings yet
- STPM Past Year QuestionDocument34 pagesSTPM Past Year QuestionChris Ng Kien Siong100% (2)
- STPM Physics Chapter 15 Direct Current CircuitsDocument1 pageSTPM Physics Chapter 15 Direct Current CircuitsChris Lau100% (1)
- STPM Chemistry 2001 - Paper 1Document15 pagesSTPM Chemistry 2001 - Paper 1Steve_Sam93No ratings yet
- Sem 1 2022 Manual ChemistryDocument9 pagesSem 1 2022 Manual ChemistryVZYFVVZHVMNo ratings yet
- Itmti Chemistry Term 2 STPM Chapter 7 Chemical EnergeticsDocument47 pagesItmti Chemistry Term 2 STPM Chapter 7 Chemical EnergeticsCherry T CYNo ratings yet
- Ace Ahead Mathematic T Exam Practise Chapter 5Document10 pagesAce Ahead Mathematic T Exam Practise Chapter 5James OoiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics (T) VIvaDocument11 pagesMathematics (T) VIvaJinJinKiraie0% (1)
- Math T STPM Sem 3 2021Document2 pagesMath T STPM Sem 3 2021tchinhuat82No ratings yet
- Answer Key (Test-6) PhysicsDocument20 pagesAnswer Key (Test-6) Physicssyuvarajno.1No ratings yet
- KEAM 2014 Physics Solutions For All Codes A1, A2, A3 & A4Document16 pagesKEAM 2014 Physics Solutions For All Codes A1, A2, A3 & A4Lokesh KumarNo ratings yet
- R A DeCarlo and P Lin Linear Circuit Analysis SDocument945 pagesR A DeCarlo and P Lin Linear Circuit Analysis STommyc102477% (13)
- Solutions To Home Work Test/Physics: Energy & Momentum HWT - 1Document11 pagesSolutions To Home Work Test/Physics: Energy & Momentum HWT - 1varunkohliinNo ratings yet
- 15-Chapter Problems SHM Frequency Period AmplitudeDocument4 pages15-Chapter Problems SHM Frequency Period AmplitudeBradley NartowtNo ratings yet
- Brilliant'S Full Syllabus Test 4: For Our Students Towards Joint Entrance Examination, 2013Document21 pagesBrilliant'S Full Syllabus Test 4: For Our Students Towards Joint Entrance Examination, 2013cshubham23No ratings yet
- Practice Exam - SolnsDocument5 pagesPractice Exam - SolnsbevinjNo ratings yet
- Pace Booklet Sol.Document27 pagesPace Booklet Sol.Akshay Sahai67% (3)
- NJC 2022 H2 Physics Prelim P1 AnsDocument7 pagesNJC 2022 H2 Physics Prelim P1 AnsYong JieNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Power Answers FinalDocument14 pagesWork Energy Power Answers FinalCealaNo ratings yet
- 2016 P1 Pahang State ADocument8 pages2016 P1 Pahang State AZuraini Arshad100% (1)
- 2016 P1 Pahang StateDocument3 pages2016 P1 Pahang StateZuraini ArshadNo ratings yet
- 2016 P1 SARAWAK ST Joseph ADocument8 pages2016 P1 SARAWAK ST Joseph AZuraini ArshadNo ratings yet
- STPM Math (M) Jit Sin 2015Document2 pagesSTPM Math (M) Jit Sin 2015Zuraini Arshad0% (1)
- Past Year Poligon IIDocument2 pagesPast Year Poligon IIZuraini ArshadNo ratings yet
- 2016 P1 ST JosephDocument2 pages2016 P1 ST JosephZuraini ArshadNo ratings yet
- Limit and Continuty (S)Document6 pagesLimit and Continuty (S)Zuraini ArshadNo ratings yet
- STPM Math (M) Seremban 2015Document2 pagesSTPM Math (M) Seremban 2015Zuraini Arshad50% (2)
- Mathematics M Pre Test p1 2016Document2 pagesMathematics M Pre Test p1 2016Zuraini ArshadNo ratings yet
- Anwers Revision Exercise Mathematics MDocument4 pagesAnwers Revision Exercise Mathematics MZuraini ArshadNo ratings yet
- STPM Math (M) Jit Sin 2015Document2 pagesSTPM Math (M) Jit Sin 2015Zuraini Arshad0% (1)
- STPM Math (M) Seremban 2015Document2 pagesSTPM Math (M) Seremban 2015Zuraini Arshad50% (2)
- S K I L L Algebraic ExpressionsDocument24 pagesS K I L L Algebraic ExpressionsZuraini ArshadNo ratings yet
- Theorem PhagorasDocument3 pagesTheorem PhagorasZuraini ArshadNo ratings yet
- Linear Inequalities, Trigonometry Dan Line and Angles IIDocument4 pagesLinear Inequalities, Trigonometry Dan Line and Angles IIZuraini ArshadNo ratings yet
- (Q) - TRIAL CHEMISTRY SEM 3-Stpm 2013Document14 pages(Q) - TRIAL CHEMISTRY SEM 3-Stpm 2013Zuraini Arshad100% (1)
- Past Year Questions of Circle 1: PMR 2004 PMR 2005Document2 pagesPast Year Questions of Circle 1: PMR 2004 PMR 2005Zuraini ArshadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Ratios, Rates and ProportionsDocument6 pagesChapter 5 Ratios, Rates and ProportionsZuraini ArshadNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY STPM Trial First Term 2013Document12 pagesCHEMISTRY STPM Trial First Term 2013Zuraini Arshad100% (2)
- Intermediate AlgebraDocument6 pagesIntermediate AlgebraZuraini ArshadNo ratings yet
- 3P: Chapter 2 Squares, Square Roots, Cubes & Cube RootsDocument4 pages3P: Chapter 2 Squares, Square Roots, Cubes & Cube RootsZuraini ArshadNo ratings yet
- Revision Linear Equations IDocument1 pageRevision Linear Equations IZuraini ArshadNo ratings yet
- Quizzes of Direct NumbersDocument1 pageQuizzes of Direct NumbersZuraini ArshadNo ratings yet
- SCHEME TRIAL CHEMISTRY SEM 3-Stpm 2013Document11 pagesSCHEME TRIAL CHEMISTRY SEM 3-Stpm 2013Zuraini Arshad100% (1)
- TOPIC 11 PerimeterAreaDocument2 pagesTOPIC 11 PerimeterAreaZuraini ArshadNo ratings yet
- Physics 960 Constants and Fundamental QuantitiesDocument10 pagesPhysics 960 Constants and Fundamental QuantitiesZuraini Arshad0% (1)
- Name, NRIC, Chemistry Trial PaperDocument7 pagesName, NRIC, Chemistry Trial PaperZuraini ArshadNo ratings yet
- Mark scheme Trial Term 3 2013 exam solutionsDocument6 pagesMark scheme Trial Term 3 2013 exam solutionsZuraini ArshadNo ratings yet
- Trial Physics STPM Sem 3 2013 TerengganuDocument7 pagesTrial Physics STPM Sem 3 2013 TerengganuZuraini Arshad100% (1)
- SOP Healthcare Equipment Repair DisposalDocument2 pagesSOP Healthcare Equipment Repair DisposalJad HajjdeebNo ratings yet
- Spanish Colonial System in the PhilippinesDocument3 pagesSpanish Colonial System in the PhilippinesCathy RafolsNo ratings yet
- TVM - Time Value of Money ProblemsDocument1 pageTVM - Time Value of Money ProblemsperiNo ratings yet
- MC - Form MC:F002 - Tenant Interview v1.1 (18 Oct 2019)Document8 pagesMC - Form MC:F002 - Tenant Interview v1.1 (18 Oct 2019)Rohit DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- ManualDocument108 pagesManualSaid Abu khaulaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 - Basic Numbering System of Police ReportsDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 4 - Basic Numbering System of Police ReportsAilyne CabuquinNo ratings yet
- Digbeth Residents Association - ConstitutionDocument3 pagesDigbeth Residents Association - ConstitutionNicky GetgoodNo ratings yet
- Ristvet 2014 Ritual Performance and Politics in The Ancient Near East Final DraftDocument434 pagesRistvet 2014 Ritual Performance and Politics in The Ancient Near East Final Draftflanders_ned_No ratings yet
- Thread - o - Ring - Fittings (TD Williamson) PDFDocument4 pagesThread - o - Ring - Fittings (TD Williamson) PDFRahul RaghukumarNo ratings yet
- Tax RTP May 2020Document35 pagesTax RTP May 2020KarthikNo ratings yet
- Assignment Title: Professional Issues in ITDocument11 pagesAssignment Title: Professional Issues in IThemacrcNo ratings yet
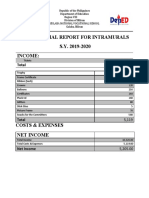
- Financial Report For IntramuralsDocument2 pagesFinancial Report For IntramuralsRosa Palconit0% (1)
- Civics Unit 3 Study Guide: Executive, Legislative, and Judicial BranchesDocument5 pagesCivics Unit 3 Study Guide: Executive, Legislative, and Judicial BranchesEmaya GillispieNo ratings yet
- List of Aces of AcesDocument4 pagesList of Aces of AcesJean-pierre NegreNo ratings yet
- Gorgeous Babe Skyy Black Enjoys Hardcore Outdoor Sex Big Black CockDocument1 pageGorgeous Babe Skyy Black Enjoys Hardcore Outdoor Sex Big Black CockLorena Sanchez 3No ratings yet
- Catalogueofsanfr00sanfrich PDFDocument310 pagesCatalogueofsanfr00sanfrich PDFMonserrat Benítez CastilloNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power in The United KingdomDocument188 pagesNuclear Power in The United KingdomRita CahillNo ratings yet
- Routing Slip: Document Tracking SystemDocument8 pagesRouting Slip: Document Tracking SystemJeffrey Arligue ArroyoNo ratings yet
- Work Without Your Laptop.: Samsung Dex ProductivityDocument2 pagesWork Without Your Laptop.: Samsung Dex ProductivityBtakeshi1No ratings yet
- Deuteronomy SBJT 18.3 Fall Complete v2Document160 pagesDeuteronomy SBJT 18.3 Fall Complete v2James ShafferNo ratings yet
- H.C.G. Paper 1 History & Civics examDocument5 pagesH.C.G. Paper 1 History & Civics examGreatAkbar1100% (1)
- BISU COMELEC Requests Permission for Upcoming SSG ElectionDocument2 pagesBISU COMELEC Requests Permission for Upcoming SSG ElectionDanes GuhitingNo ratings yet
- PDF 05 EuroMedJeunesse Etude LEBANON 090325Document28 pagesPDF 05 EuroMedJeunesse Etude LEBANON 090325ermetemNo ratings yet
- Inventories - : Methods For Inventory WritedownDocument5 pagesInventories - : Methods For Inventory WritedownBryan NatadNo ratings yet
- F3 Mock Answers 201603Document3 pagesF3 Mock Answers 201603getcultured69No ratings yet
- Navajo Silversmiths.: IllustrationsDocument18 pagesNavajo Silversmiths.: IllustrationsGutenberg.orgNo ratings yet
- What Is Leave Travel Allowance or LTADocument3 pagesWhat Is Leave Travel Allowance or LTAMukesh UpadhyeNo ratings yet
- Alphabet of Sirach: LilithDocument2 pagesAlphabet of Sirach: LilithNyx Bella Dark100% (1)
- Violence Against WomenDocument17 pagesViolence Against WomenkamalNo ratings yet
- J Alexander Kueng Cameras in CourtDocument3 pagesJ Alexander Kueng Cameras in CourtLaw&CrimeNo ratings yet