Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Blower Air Line
Uploaded by
Juan Pablo ApazaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Blower Air Line
Uploaded by
Juan Pablo ApazaCopyright:
Available Formats
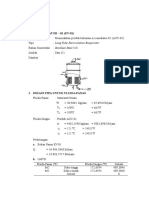
Blower air line
Height above sea level H = 2637.7 m.a.s.l. Flow per blower (2 + 1 ) at
Local atmospheric pressure P
atm
= 73.40 kPa blower discharge (Vendor data)
Blower discharge pressure P
blower_out
= 70 kPa(g) Q
blower
= 623
m
3
/min
(at silencer exit) P
blower_out
= 143.4 kPa Q
blower
= 37,380
m
3
/h
P
blower_out
= 143,399 Pa Q
total
= Q
blower
* 2
Maximum pressure drop AP
max
= 2 kPa Q
total
= 1,246.0
m
3
/min
Minimum required pressure P
disc_min
= 141.4 kPa Q
total
= 74,760
m
3
/h
(at inlet ring) P
disc_min
= 68.0 kPa(g)
Eq.1
P
in
Description Node Node
m
3
/h m
3
/s
Pa
kg/m
3
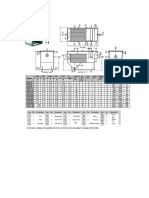
Enlargement 1 2 37,380 10.4 143,399 1.24
V. Butterfly 2 3 37,380 10.4 143,931 1.25
Elbow 45 (5 D) 3 4 37,380 10.4 143,399 1.24
Pipe with Tee branch 4 5 37,380 10.4 143,382 1.24
Manifold with Tee straight 5 6 37,380 10.4 143,354 1.24
Manifold 2 with Tee straight 6 7 74,760 20.8 143,039 1.24
Manifold with elbow 90 7 8 74,760 20.8 143,004 1.24
Pipe with elbow 90 8 9 74,760 20.8 142,887 1.24
Pipe 9 10 74,760 20.8 142,768 1.24
Pipe 10 11 74,760 20.8 142,657 1.24
Pipe 11 12 74,760 20.8 142,460 1.24
Pipe 12 13 74,760 20.8 142,325 1.23
Pipe 13 14 74,760 20.8 142,180 1.23
Pipe 14 15 74,760 20.8 142,035 1.23
Q
act
8
10
11
12
13
14
15. Discharge
point
1: Silencer discharge in a 24" pipe (lbatery limit) 8-9: Pipe with elbow 90|
1 -2: Enlargement 24" a 36" 9-10: Pipe with elbow 90|
2-3: Butterfly valve 10-11: Pipe with elbow 90|
3-4: Elbow 11-12: Pipe with elbow 90|
4-5: Pipe with T branch 12-13: Pipe with elbow 90|
5-5: 13-14: Pipe with elbow 90|
6-7: Manifold with tee straight 14-15: Pipe
7-8: Manifold wit5h elbow 90
12
Blower discharge temperature Carbon steel pipe P * v = R *T
t
blower_out
= 128.6 C Sch = STD
=
P / (R * T) Eq. 1
T = 401.75 K Rabs = 0.1 mm d
i
= Pipe_Imp_CS_Dint_Dn_SCH Eq. 2
Air properties Rabs = 0.0001 m hv = (/2) * v^2 [Pa] Eq. 3
R = 286.9 J/(kg*K) Rrel = Rabs / d Eq. 4
Air viscosity Re = v * d / v Eq. 5
=
2.31E-05 Pa s f = Pipe_Friction_Factor_Rrel_Re Eq. 6
=
1.24
kg/m
3
AP
f
= f * (L/d) * hv Eq. 7
v =
1.9E-05 m/s
Eq. 2 Eq. 3 Eq. 4 Eq. 5 Eq. 6 Eq. 7
dn di L A v hv Rrel Re f
AP
f
in m m m m/s Pa - - - Pa
24 0.59 0.00 0.274 37.9 891.6 0.00017 1E+06 0.0142 0.0
36 0.89 0.00 0.629 16.5 170.1 0.00011 8E+05 0.01386 0.0
36 0.89 0.00 0.629 16.5 169.5 0.00011 8E+05 0.01386 0.0
36 0.89 0.60 0.629 16.5 110.1 0.00011 8E+05 0.01386 1.0
40 1.00 6.05 0.781 13.3 110.0 0.00010 7E+05 0.01386 9.3
40 1.00 6.05 0.781 26.6 439.2 0.00010 1E+06 0.01306 34.8
40 1.00 5.00 0.781 26.6 439.0 0.00010 1E+06 0.01306 28.8
40 1.00 5.42 0.781 26.6 438.7 0.00010 1E+06 0.01306 31.2
40 1.00 4.00 0.781 26.6 438.3 0.00010 1E+06 0.01306 23.0
40 1.00 19 0.781 26.6 438.0 0.00010 1E+06 0.01306 109.0
40 1.00 8.35 0.781 26.6 437.4 0.00010 1E+06 0.01306 47.8
40 1.00 10 0.781 26.6 437.0 0.00010 1E+06 0.01306 57.3
40 1.00 10.00 0.781 26.6 436.5 0.00010 1E+06 0.01306 57.2
40 1.00 1 0.781 26.6 436.1 0.00010 1E+06 0.01306 5.7
3
5
6
7
8
9
4
2
42
36"
42"
Blower 2
Blower 3
Number of blowers: 2 + 1
8-9: Pipe with elbow 90| Aproximate equation for calculating the atmospheric
9-10: Pipe with elbow 90| pressure as a function of the height above sea level
10-11: Pipe with elbow 90| p = 101,325* (1 -2,25577E-5 * H)^5,25588
11-12: Pipe with elbow 90| The Engineering Toolbox
12-13: Pipe with elbow 90| http://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/air-altitude-pressure-d_462.html
13-14: Pipe with elbow 90|
14-15: Pipe g = 9.80665 m/s
2
Silencer 24"
42
24"
P
blower_ou
1
Blower 1
Unhide columns to see singular pressure
drop coefficients / Hide columns.
Rev. cjc. 30.01.2014
Ksing = SUMPRODUCTO(range_A*range_B)
Eq.8
APs =
Ksing * hv Eq.9
APk: Pressure increment due to deceleration
(Sheet Tobera) Eq. 10
Eq. 8 Eq. 9 Eq. 10
AP =
P
out
=
Ksing
APs APk
AP
f
+AP
s
P
in
- AP
Pa Pa Pa Pa kPa(g)
1.13 190 -722 -532 143931 70.53
0.37 63 63 143869 70.47
0.10 17 17 143382 69.98
0.79 87 -59 29 143354 69.95
0.50 55 250.5 315 143039 69.64
0.00 0 35 143004 69.60
0.20 88 117 142887 69.49
0.20 88 119 142768 69.37
0.20 88 111 142657 69.26
0.20 88 197 142460 69.06
0.20 88 136 142325 68.93
0.20 88 145 142180 68.78
0.20 88 145 142035 68.64
0.00 0 6 142029 68.63
OK. Pexit > 68 kPa
3
4
5
2
1
Pressure increment in nozzle due to
area increment Expansion with central angl3 of 30
P
1
P
2
Singular pressure drop
calculated according Crane
15
K
2
= Function Pipe_Expansion_Theta30gr_beta(beta)
Q = 37,380 m
3
/h u = 30
Q = 10.38 m
3
/s b = 0.6603
K
2
= 1.13
d
n_1
= 24 in
Sch = STD h
v_2
=
(/2) * v^2
d
1
= 590.94 mm
=
1.24
d
1
= 0.591 m v
2
= 16.51
h
v_2
= 168.9
d
n_2
= 36 in
Sch = STD
AP =
K
2
* h
v_2
d
2
= 894.94 mm K
2
= 1.126
d
2
= 0.895 m h
v_2
= 168.9
AP = 190
A
2
= 0.629 m
v
2
= Q / A
2
Q = 10.38 m
3
/s Note 1
A
2
= 0.629 The coefficient K
2
corresponds to the conditions at
v
2
= 16.51 m/s the largest diameter, which is d
2
.
Since this value wil be calculated in the next step,
| =
d
1
/ d
2
an initial assumption need to be made.
d
1
= 0.591 m
d
2
= 0.895 m
| = 0.6603
P
2_0
- P
1
= (/2) * v
2
^2 * ( 1/|^4 -1 )
= 1.24 kg/m
3
v
2
= 16.51 m/s
| = 0.6603
P
2_0
- P
1
= 722 Pa
If u <= 45
( )
4
2
2
2
1
2
6 . 2
|
|
0
|
.
|
\
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
seno
K
K
2
=
(2.6 * ( seno(radianes(u)/2) ) * (1 - |^2)^2) / |^4
u = 30
| =
0.707 |
min
= 0.7
K
2
= 0.674
AP =
K
2
* h
v_2
K
2
= 0.674
h
v_2
= 891.6 Pa
AP = 601 Pa
Pipe_Expansion_Theta30gr_beta = 2.6 * Sin(30 / 2 * (Pi / 180)) * (1 - beta ^ 2) ^ 2 / beta ^ 4
End Function
( )
4
2
2
2
1
2
6 . 2
|
|
0
|
.
|
\
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
seno
K
Nozzle
Expansion with central angl3 of 30
Function Pipe_Expansion_Theta30gr_beta(beta)
[Pa]
kg/m OK (Note 1)
m/s
[Pa]
Pa
Pa
The coefficient K
2
corresponds to the conditions at
the largest diameter, which is d
2
.
Since this value wil be calculated in the next step,
an initial assumption need to be made.
P
2
- P
1
= P
2_0
- P
1
- AP
'20.- Pipe reductions and expansions
'20.a
Function Pipe_Reduction_Theta45gr_beta(beta)
Pipe_Reduction_Theta45gr_beta = 0.306147 * (1 - beta ^ 2) / beta ^ 4
End Function
h
g
v
g
P
Z
g
v
g
P
Z A +
+ =
+
2 2
2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
h
g
v
g
P
g
v
g
P
A +
+
2 2
2
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
h
g
v
g
P
g
v
g
P
A +
+
2 2
2
2 2
2
1 1
g h
v
P
v
P A +
+ =
+
2 2
2
2
2
2
1
1
g h
v v
P P A
=
2 2
2
2
2
1
1 2
( ) g h v v P P A =
2
2
2
1 1 2
2
( ) P v v P P A =
2
2
2
1 1 2
2
P v
v
P P A
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
2
2 2
2
2
1 2
2 |
P
v
P P A
|
|
.
|
\
|
= 1
1
2
4
2
2
1 2
|
'20.b
Function Pipe_Expansion_Theta45gr_beta(beta)
Pipe_Expansion_Theta45gr_beta = (1 - beta ^ 2) ^ 2 / beta ^ 4
End Function
'20.c
Function Pipe_Reduction_Theta30gr_beta(beta)
Pipe_Reduction_Theta30gr_beta = 0.8 * Sin(0.523599 / 2) * (1 - beta ^ 2) / beta ^ 4
End Function
'20.d
Function Pipe_Expansion_Theta30gr_beta(beta)
Pi = 3.14159
Pipe_Expansion_Theta30gr_beta = 2.6 * Sin(30 / 2 * (Pi / 180)) * (1 - beta ^ 2) ^ 2 / beta ^ 4
End Function
2 2 1 1
v A v A Q = =
2
1
2
1
v
A
A
v =
2 2
1
2
2
1
v
d
d
v =
2
2
2
1
2
1
d
d
v
v =
2
2
1
2
1
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
d
d
v
v
2
1
d
d
= |
2
2
1
|
v
v =
4
2
2 2
1
|
v
v =
Abrupt and gradual expansion
If u <= 45
K
2
=
(2.6 * ( seno(radianes(u)/2) ) * (1 - |^2)^2) / |^4
u = 30
| =
0.707 |
min
= 0.7
K
2
= 0.674
Nota. Coefficients refered to the velocity of larger pipe (Index 2)
u
d
1
d
2
2
1
d
d
= |
( )
4
2
2
2
1
2
6 . 2
|
|
0
|
.
|
\
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
seno
K
For enlargements with u > 45
with | >= 0.7
K
2
= (1 - b^2) / b^4
| = 0.7
K
2
= 2.1241
If 45 < u <= 180
K
2
=
(1 - |^2)^2/ |^4
| =
0.66 |
min
= 0.7
K
2
= 1.679
( )
4
2
2
2
1
|
|
= K
Blower air net from silencers until discharge in distribution ring
Blower 1
Flotation
Flotation air system
11
12
13
14
15
Batery limit
Blower
Silencer
Manifold
Blower
Silencer
Blower
Silencer
Ing.
Vendor
Distribution ring
36"
42"
36"
42"
36"
Blower 1
5
6
7
8
9
10
4
2
Silencer 24"
36"
42"
P
1
Ing.
Vendor
1: Silencer discharge in a 24" pipe (batery limit)
1 -2: Enlargement 24" a 36"
2-3: Butterfly valve
3-4: Elbow
4-5: Pipe with T branch
5-5:
6: Discharge point of blower 2
6-7: Manifold with tee straight
7: Discharge point of blower 3 (Spare)
7-8: Manifold wit5h elbow 90
8-9: Pipe with elbow 90
9-10: Pipe with elbow 90
10-11: Pipe with elbow 90
11-12: Pipe with elbow 90
12-13: Pipe with elbow 90
13-14: Pipe with elbow 90
14-15: Pipe
15.- Discharge in distribution ring
3
4
42"
24"
P
blower_out
Batery limit
1: Silencer discharge in a 24" pipe (batery limit)
Total flow: Q
tot
= 1246 am/min
Pressure at inlet of ring P
ring
= 68 kPa
Blower discharge pressure t
blower_out
= 128.6 C
Blower discharge temperature P
blower_out
= 70 kPa(g)
Minimum pressure at ring inlet P
disc
= 68 kPa(g)
Maximum pressure loss between
Blower silencer and ring inlet AP
max
= 2 kPa
Actual flow rate, per blower, at discharge temperature and pressure
Q
blowerer
= 623
m
3
/min
stimado Carlos.
Reenvo la informacin que por error me fue copiada.
Slds sres.
Carlos Cruz Aquino
Electrical Engineer, PDG
Tel: +51 (1) 714 4000
Fax: +51 (1) 714 4001
Mobile: +51 981700214 / RPM #981700214
626 Conquistadores Av., San Isidro, Lima, Peru
www.hatch.ca
From: Alarcon, Carlos
Sent: Tuesday, September 06, 2011 5:50 PM
To: Cruz, Carlos; Munoz, Hugo; Loewe, Christian; Vejar, Eduardo; Morales, Carlos (Contractor)
Subject: PM-014: REQUERIMIENTO DE AIRE PARA LA TOTALIDAD DE LAS CELDAS DE FLOTACIN MMH.
Importance: High
Estimados Seores:
Reenvo informacin enviada por OUTOTEC respecto a los requerimientos de aire para las celdas.
Saluda atte.,
Carlos Alarcn F.
Senior Buyer
Tel: +56-2-430 2600 Anexo 5185
Torre Titanium
Av. Isidora Goyenechea 2800, Piso 39
Las Condes - Santiago
Chile
From: german.heufemann@outotec.com [mailto:german.heufemann@outotec.com]
Sent: Tuesday, September 06, 2011 5:02 PM
To: Alarcon, Carlos
Subject: ADJUNTA INFORMACIN DEL REQUERIMIENTO DE AIRE PARA LA TOTALIDAD DE LAS CELDAS DE FLOTACIN MMH.
Resumen.-
Caudal total: 1246 am3/min
Presin: 68 Kpa
Adjuntos antecedentes: (See attached file: ANTECEDENTES CONSUMO DE AIRE.pdf)
atte.,
German Heufemann
Outotec Chile
Tel: +56 2 3362062
Mob: + 56 9 93099302
German.Heufemann@Outotec.com
www.outotec.com
Subject: PM-014: REQUERIMIENTO DE AIRE PARA LA TOTALIDAD DE LAS CELDAS DE FLOTACIN MMH.
Subject: ADJUNTA INFORMACIN DEL REQUERIMIENTO DE AIRE PARA LA TOTALIDAD DE LAS CELDAS DE FLOTACIN MMH.
Degremon Tee. ESide entrance 45
Entrance of first blowers flow Q
2
= 0
Q
L
= 37,380.0
Q
P
= 37,380.0
0 10.4
0 0.78
13.3
10.4
m
3
/s
0.63 m
16.5 m/s
K
L
= 1 + (L25*P25)^2 - 2*(P25)*(1-L25)^2 - L27 * (P25) * (L25)^2 + L28
K
L
= 0.79
The decrease in velocity causes an increase in pressure
Q
2
= 37,380.0
Entrance of second blowers flow Q
L
= 37,380.0
Q
P
= 74,760
10.38
m
3
/s
Q
p
= 20.8
m
3
/s
0.78 m S
P
= 0.86 m
13.30 m/s V
P
= 24.1 m/s
o
Q
L
=
S
L
=
V
L
=
Q
2
=
S
2
=
V
2
=
Q
2
=
S
2
=
V
2
=
Q
P
=
S
P
=
V
P
=
o
L
P
L
L
P
P
L
L
P
L
P
P
L
L
C
Q
Q
S
S
B
Q
Q
S
S
S
S
Q
Q
K +
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
2 2 2
1 2 1
2
2 2
2
2 2
2
2
1 2 1 1 C
Q
Q
S
S
B
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
S
S
K
P
L
L
P
P
L P
P
L P
+
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
o =
45
10.4
m
3
/s
S
L
/S
P
=
0.27 m S
L
= 0.27
37.9 m/s S
P
= 0.86
S
L
/S
P
= 0.32
C
2
= 0.14
B = 1.41
K
2
= 1 + (S
P
/S
2
)^2 * (1 - Q
L
/Q
P
)^2 - 2 * (S
P
/S
2
) * (1 - Q
L
/Q
P
)^2 - B * (S
P
/S
L
) * (Q
L
/Q
P
)^2 +C
2
K
2
= 0.50
o
Q
L
=
S
L
=
V
L
=
V
2
=
o
K
L
= 1 + ((Q
L
/Q
P
) *( S
P
/S
L
))^2 - 2 * (Sp/SL) * (1-Q
L
/Q
P
)^2 - B * (S
P
/S
L
) * (Q
L
/Q
P
)^2 +C
L
K
L
= 0.790204907
m
3
/h
d
n_L
= 36 in d
n_P
= 40
m
3
/h
Sch = STD Sch = STD
m
3
/h
d
L
= 0.89 m d
P
= 1.00
S
L
= 0.63 m S
P
= 0.78
m
3
/s
Q
L
= 37,380.0
m
3
/h
Q
P
= 37,380.0
m Q
L
= 10.4
m
3
/s
Q
P
= 10.4
m/s v
L
= Q
L
/ S
L
v
P
= Q
L
/ S
L
Q
L
= 10.38
m
3
/s
Q
P
= 10.38
S
L
= 0.63 m S
P
= 0.78
v
L
= 16.5 m/s v
P
= 13.3
Q
L
/ Q
P
= S
P
/ S
L
=
Q
L
= 10.38
m
3
/s
S
P
= 0.78
Q
P
= 10
m
3
/s
S
L
= 0.63
Q
L
/ Q
P
= 1 S
P
/ S
L
= 1.24
B = 1.41 S
L
/ S
P
= 0.81
C
L
= 0
K
2
= 1 + (S
P
/S
2
)^2 * (1 - Q
L
/Q
P
)^2 - 2 * (S
P
/S
2
) * (1 - Q
L
/Q
P
)^2 - B * (S
P
/S
L
) * (Q
L
/Q
P
)^2 +C
2
K
2
= 0.50326473
m
3
/h
d
n_L
= 24 in d
n_P
= 42
m
3
/h
Sch = STD Sch = STD
m
3
/h
d
L
= 0.59 m d
P
= 1.05
S
L
= 0.27 m S
P
= 0.86
Q
L
=
37,380.0
m
3
/h
Q
P
=
74,760.0
Q
L
=
10.4
m
3
/s
Q
P
=
20.8
L
P
L
L
P
P
L
L
P
L
P
P
L
L
C
Q
Q
S
S
B
Q
Q
S
S
S
S
Q
Q
K +
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
2 2 2
1 2 1
2
2 2
2
2 2
2
2
1 2 1 1 C
Q
Q
S
S
B
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
S
S
K
P
L
L
P
P
L P
P
L P
+
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
v
L
= Q
L
/ S
L
v
P
= Q
L
/ S
L
Q
L
= 10.38
m
3
/s
Q
P
= 20.77
S
L
= 0.27 m S
P
= 0.86
v
L
= 37.9 m/s v
P
= 24.1
Q
L
/ Q
P
= S
P
/ S
2
=
Q
L
= 10.38
m
3
/s
S
P
= 0.86
Q
P
= 20.8
m
3
/s
S
2
= 0.78
Q
L
/ Q
P
= 0.5 L57 S
P
/ S
2
= 1.10
B = 1.41 L59 S
P
/ S
L
= 3.14
C
2
= 0.14 L60
1 + ((Q
L
/Q
P
) *( S
P
/S
L
))^2 - 2 * (Sp/SL) * (1-Q
L
/Q
P
)^2 - B * (S
P
/S
L
) * (Q
L
/Q
P
)^2 +C
L
in P
L
- P
P
= (/2) * (v
P
^2 - v
L
^2)
=
1.24 kg/m
m v
P
= 13.3 m/s
m v
L
= 16.5 m/s
P
L
- P
P
= -59.43 Pa
m
3
/h
m
3
/s
m
3
/s
m
m/s
m
m
1 + (S
P
/S
2
)^2 * (1 - Q
L
/Q
P
)^2 - 2 * (S
P
/S
2
) * (1 - Q
L
/Q
P
)^2 - B * (S
P
/S
L
) * (Q
L
/Q
P
)^2 +C
2
in P
2
- P
P
= (/2) * (v
P
^2 - v
2
^2)
=
1.24 kg/m
m v
P
= 24.1 m/s
m v
2
= 13.3 m/s
P
2
- P
P
= 250.47 Pa
m
3
/h
m
3
/s
( )
2
2
2
1 1 2
2
v v P P =
m
3
/s
m
m/s
m
m
P57
P59
Degremon
Cambio de presin en el ramal lateral Cambio de presin en tramo recto
En los dos casos la velocidad de En los dos casos la velocidad de
referencia es la del ramal principal referencia es la del ramal principal
despus de la unin (v
P
) despus de la unin (v
P
)
Prdida de presin Prdida de presin
Cambio de presin debido al cambio de Cambio de presin debido al cambio de
velocidades velocidades
Cambio total de presin Cambio total de presin
2
_
_
2
P L L loss
P L L loss
v K P
hv K P
= A
= A
( )
2 2
_
2
P L L Kinem
v v P
|
.
|
\
|
= A
( )
( )
L P L L
P L P L L
P L P L L
L loss L Kinem L
K v v P
v K v v P
v K v v P
P P P
+
|
.
|
\
|
|
.
|
\
|
= A
|
.
|
\
|
|
.
|
\
|
= A
|
.
|
\
|
= A
A A = A
1
2 2
2 2 2
2 2
2 2
2 2 2
2 2 2
_ _
2
2 2 _
2 2 _
2
P loss
P loss
v K P
hv K P
= A
= A
( )
2 2
2 2 _
2
P Kinem
v v P
|
.
|
\
|
= A
( )
( )
2
2 2
2 2
2
2
2 2
2 2
2
2
2 2
2 2
2 _ 2 _ 2
1
2 2
2 2 2
2 2
K v v P
v K v v P
v K v v P
P P P
P
P P
P P
loss Kinem
+
|
.
|
\
|
|
.
|
\
|
= A
|
.
|
\
|
|
.
|
\
|
= A
|
.
|
\
|
= A
A A = A
( )
( )
L P L L
P L P L L
P L P L L
L loss L Kinem L
K v v P
v K v v P
v K v v P
P P P
+
|
.
|
\
|
|
.
|
\
|
= A
|
.
|
\
|
|
.
|
\
|
= A
|
.
|
\
|
= A
A A = A
1
2 2
2 2 2
2 2
2 2
2 2 2
2 2 2
_ _
L
P
L
L
P
P
L
L
P
L
P
P
L
L
C
Q
Q
S
S
B
Q
Q
S
S
S
S
Q
Q
K +
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
2 2 2
1 2 1
2
2 2
2
2 2
2
2
1 2 1 1 C
Q
Q
S
S
B
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
S
S
K
P
L
L
P
P
L P
P
L P
+
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
( )
( )
2
2 2
2 2
2
2
2 2
2 2
2
2
2 2
2 2
2 _ 2 _ 2
1
2 2
2 2 2
2 2
K v v P
v K v v P
v K v v P
P P P
P
P P
P P
loss Kinem
+
|
.
|
\
|
|
.
|
\
|
= A
|
.
|
\
|
|
.
|
\
|
= A
|
.
|
\
|
= A
A A = A
o
B
0 0.1 0.2 0.33 0.5
15 1.94 C
L
0 0 0 0 0
C
2 0 0 0 0.14 0.4
30 1.74 C
L
0 0 0 0 0
C
2 0 0 0 0.17 0.4
45 1.41 C
L
0 0 0 0 0
C
2 0 0.05 0.14 0.14 0.3
60 1.0 C
L
0 0 0 0 0.1
C
2 0 0 0 0.1 0.25
S
L
/ S
P
Tabla 14
L
P
L
L
P
P
L
L
P
L
P
P
L
L
C
Q
Q
S
S
B
Q
Q
S
S
S
S
Q
Q
K +
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
2 2 2
1 2 1
Pressure loss coefficient for gas flow
a * AP^2 + b * AP + c = 0
a =
P
in
=
b =
b =
C = (SG*Q
m3h
^2) / (Kv
m3h,bar
^2*18.9^2) * (273+t
out
)/293.15
Fluid air
SG =
Q
m3h
=
t
out
=
Kv coefficient for a butterfly valve
From sheet Norris B.V.
Kv
m3h,bar
=
c =
[3]
http://detector-gas-systems.web.cern.ch/detector-gas-systems/downloads/kv_calc_doc.pdf
Joucomatic
Engineering information
Flow data
Flow factor and orifice size
15 . 293
273
9 . 18
2 2
, 3
2
3 out
bar h m
h m
t
Kv
Q SG
c
+
=
| |
| |
0 2
0 2
) 2 (
15 . 293
273
9 . 18
) 2 (
15 . 293
273
9 . 18
273
15 . 293
) 2 (
9 . 18
273
15 . 293
) 2 (
9 . 18
273
15 . 293 ) 2 (
9 . 18
) 2 (
9 . 18
____ __________
1
_
2
2
_
_
2 2
, 3
2
3
_ 2 2
, 3
2
3
_
, 3
3
_
, 3 3
3
3
= + A A
= A A
= A A
+
=
A A =
+
A A
=
A A
=
+
A A
=
A A
=
(
=
A
=
(
c P P P
c P P P
c P P P
t
Kv
Q SG
c
P P P
t
Kv
Q SG
t SG
P P P
Kv
Q
t SG
P P P
Kv Q
t SG
P P P
Kv Q
correction e temperatur with and
SG
bar P P P
Kv
h
Nm
Q
Gases
SG
SG
bar P
Kv
h
m
Q
Liquids
bar bar in bar
bar bar bar in
bar bar in bar
out
bar h m
h m
bar bar in bar
out
bar h m
h m
out
bar bar in bar
bar h m
h m
out
bar bar in bar
bar h m h m
out
in
in
water
0 2
_
2
= + A A c P P P
bar bar in bar
AP = (- b - (b^2 - 4 * a * c)^0.5 ) / (2 * a)
a = 1
b = -2.88
a * AP^2 + b * AP + c = 0 c = 0.00180
AP = 0.0006
1 AP = 63
1.44 bar From Sheet Air blown line
-2 * P
in
hv = 170.1
-2.88
Pressure loss coefficient
AP = K * hv
K = AP / hv
AP = 63
hv = 170.1
C = (SG*Q
m3h
^2) / (Kv
m3h,bar
^2*18.9^2) * (273+t
out
)/293.15 K = 0.37
This value will be used in the calculation table in sheet
1 - "Air blown line"
74,760 m/h
128.6 C Check of flow rate
Kv coefficient for a butterfly valve
From sheet Norris B.V.
109,112
0.0018
Q = Kv * 18.9 * (DP*(2*Pin-DP)/SG*293.15/(273 ))^0.5
Kv = 109,112
DP = 0.0006
http://detector-gas-systems.web.cern.ch/detector-gas-systems/downloads/kv_calc_doc.pdf Pin = 1.44
SG = 1
t
out
= 128.6
Engineering information Q = 74,760
Flow factor and orifice size
15 . 293
273
9 . 18
2 2
, 3
2
3 out
bar h m
h m
t
Kv
Q SG
c
+
=
0 2
_
2
= + A A c P P P
bar bar in bar
out
bar bar in bar
bar h m h m
t SG
P P P
Kv Q
+
A A
=
273
15 . 293 ) 2 (
9 . 18
_
, 3 3
(- b - (b^2 - 4 * a * c)^0.5 ) / (2 * a)
bar
Pa
Pa
Pa
Pa
This value will be used in the calculation table in sheet
Kv * 18.9 * (DP*(2*Pin-DP)/SG*293.15/(273 ))^0.5
bar
bar
C
m/h
out
bar bar in bar
bar h m h m
t SG
P P P
Kv Q
+
A A
=
273
15 . 293 ) 2 (
9 . 18
_
, 3 3
[2a] Norris butterfly valves
http://www.norriseal.com/files/comm_id_47/BV_HowTo_Brochure_120811.pdf
Kv
m3h,bar
=
Cv =
Kv
m3h,bar
=
Valve diameter (Air blown line)
dn = 36 in
From table, for 200 psi valves
Fully open valve value
Cv = 126,000
Kv-value
Relation Kv - Cv
Kv
m3h,bar
= 0.865972 * Cv
Cv = 126,000
Kv
m3h,bar
= 109112.5
Cv Kv
bar h m
= 864972 . 0
, 3
[1] Degremont
Manual notes
[2a] Norris butterfly valves
http://www.norriseal.com/files/comm_id_47/BV_HowTo_Brochure_120811.pdf
You might also like
- Tank Venting According API 2000Document34 pagesTank Venting According API 2000Youssef Lagrini50% (2)
- Calculation of Friction Losses, Power, Developed Head and Available Net Positive Suction Head of A Pump For A Non-Newtonian LiquidDocument5 pagesCalculation of Friction Losses, Power, Developed Head and Available Net Positive Suction Head of A Pump For A Non-Newtonian Liquidt_i_f_anoNo ratings yet
- Sludge Treatment: Total Solid in Raw Water 600 Kg/dayDocument12 pagesSludge Treatment: Total Solid in Raw Water 600 Kg/dayThava ThavaNo ratings yet
- Tolerance - E.O.T CranesDocument3 pagesTolerance - E.O.T CranesSriraghuraman Gopal RathnamNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pump CurvesDocument2 pagesCentrifugal Pump CurvesBesan LaduNo ratings yet
- Tube Rupture Relief CalculationDocument1 pageTube Rupture Relief CalculationAmin RoisNo ratings yet
- SizingAndSelectionOfHydrocyclones Rev2Document43 pagesSizingAndSelectionOfHydrocyclones Rev2RAVI1972100% (2)
- WTP CalculationsDocument10 pagesWTP CalculationsAngshuman Roy ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Line Size Calculation For Cooling Water Pipes: Pipe Size Provided Is OKDocument40 pagesLine Size Calculation For Cooling Water Pipes: Pipe Size Provided Is OKjitendra shindeNo ratings yet
- Sewer Pump Calculation ReportDocument4 pagesSewer Pump Calculation Reportarguteconsultants0% (1)
- Pipe Dimensions and Friction FactorDocument24 pagesPipe Dimensions and Friction FactorJuan Pablo ApazaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document13 pagesChapter 6Marco Luigi100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Biological Wastewater Treatment - PrefaceDocument4 pagesFundamentals of Biological Wastewater Treatment - Prefaceabhi_nddNo ratings yet
- CIP Procedure of RO MembraneDocument2 pagesCIP Procedure of RO MembraneTanzila SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Hydro-Flo Technologies DAF Sizing CalculatorDocument6 pagesHydro-Flo Technologies DAF Sizing CalculatorJuan Pablo ApazaNo ratings yet
- Cal. Dew PointDocument1 pageCal. Dew PointJuan Pablo ApazaNo ratings yet
- Cal. Dew PointDocument1 pageCal. Dew PointJuan Pablo ApazaNo ratings yet
- Control of Flow Rates at Startup: GAT2004-GKP-2010.009 September, 2010Document2 pagesControl of Flow Rates at Startup: GAT2004-GKP-2010.009 September, 2010Enyerberht Castañeda BritoNo ratings yet
- Pump CalcDocument1 pagePump CalcMoch WildanNo ratings yet
- Annex 29 Area Calculation For Extended AerationDocument1 pageAnnex 29 Area Calculation For Extended AerationPradeep DavuluriNo ratings yet
- Pid Engtech Pilot Plants v04pdfDocument20 pagesPid Engtech Pilot Plants v04pdfFaizan SarangNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties ExplainedDocument26 pagesColligative Properties ExplainedYAWAR SAEED100% (1)
- Qaverage Phase-1 Phase-2 Qpeak Phase-1 Phase-2 m3/d m3/d m3/hr m3/hr M3/sec M3/secDocument7 pagesQaverage Phase-1 Phase-2 Qpeak Phase-1 Phase-2 m3/d m3/d m3/hr m3/hr M3/sec M3/secHemantk8731100% (1)
- L.3.1. EVAPORATOR - 01 (EV-01) : 1 o o o oDocument9 pagesL.3.1. EVAPORATOR - 01 (EV-01) : 1 o o o omedias indah monica sariNo ratings yet
- Selection Criteria For DampersDocument4 pagesSelection Criteria For Dampersmarlon168No ratings yet
- PH Control Using CO2Document38 pagesPH Control Using CO2Bob SmithNo ratings yet
- SHELL AND TUBE HEAT EXCHANGER DESIGNDocument16 pagesSHELL AND TUBE HEAT EXCHANGER DESIGNSarvagyaNo ratings yet
- Reactor Geometry and Agitator SizingDocument26 pagesReactor Geometry and Agitator SizingNeeraj BhallaNo ratings yet
- Physical, Chemical & Biological: Design of Facilities For Treatment of Waste WaterDocument118 pagesPhysical, Chemical & Biological: Design of Facilities For Treatment of Waste Waterdrsalazar13No ratings yet
- MicrofilterDocument17 pagesMicrofilterArrianne Jaye MataNo ratings yet
- Psychrometric Functions - Resume: Max Max Max MaxDocument5 pagesPsychrometric Functions - Resume: Max Max Max MaxJuan Pablo ApazaNo ratings yet
- Spray Nozzles Total STDDocument3 pagesSpray Nozzles Total STDDylan RamasamyNo ratings yet
- Vapor Line Sizing-Mpp6Document10 pagesVapor Line Sizing-Mpp6Nitin KurupNo ratings yet
- Design 3Document2 pagesDesign 3JOY NATHNo ratings yet
- Packed Column Calculation Results: Packing Details System DetailsDocument1 pagePacked Column Calculation Results: Packing Details System Detailsdinakaranpatel100% (1)
- Calculating siphon discharge and design parametersDocument6 pagesCalculating siphon discharge and design parametersdzari6738100% (1)
- App 6 CalculationsDocument2 pagesApp 6 CalculationsNizarHamrouniNo ratings yet
- Calculation For Backpressure by Liquid SealDocument2 pagesCalculation For Backpressure by Liquid SealDodiya NikunjNo ratings yet
- C3 Recovery StudyDocument15 pagesC3 Recovery StudyengmohosmanNo ratings yet
- DP Calc 1Document3 pagesDP Calc 1Manjunath HardcheeseNo ratings yet
- Activated carbon columns designDocument21 pagesActivated carbon columns designnurrahman.auliaNo ratings yet
- Brosur - UF Membrane (A) PDFDocument8 pagesBrosur - UF Membrane (A) PDFigo badr100% (1)
- Tower SizingDocument6 pagesTower SizingNagwa MansyNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Conveying Spreadsheet-ContentDocument27 pagesPneumatic Conveying Spreadsheet-Contentaladdin4dNo ratings yet
- Modeling Mineral Size Reduction in The Closed-Circuit Ball Mill at The Pine Point Mines Concentrator (1981)Document18 pagesModeling Mineral Size Reduction in The Closed-Circuit Ball Mill at The Pine Point Mines Concentrator (1981)Ryan Cunningham100% (1)
- Paddle FlocculatorsDocument12 pagesPaddle FlocculatorsBinyam KebedeNo ratings yet
- Spreadsheet Based Scaling Calculations and Membrane PerformanceDocument16 pagesSpreadsheet Based Scaling Calculations and Membrane PerformanceWaleed EmaraNo ratings yet
- Frictional Head Loss Calculation in Pumping SystemsDocument1 pageFrictional Head Loss Calculation in Pumping Systemsaman vermaNo ratings yet
- Volume 3 Section 2 Process Requirements-FINAL 10062010Document63 pagesVolume 3 Section 2 Process Requirements-FINAL 10062010Pavle DimitrijevicNo ratings yet
- Orifice SizingDocument1 pageOrifice SizingMarco D'OnofrioNo ratings yet
- Porous Sparger SizingDocument4 pagesPorous Sparger Sizingprav.saradaNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Flow Rate For Orifice Venturi or Flow Nozzle Meter Si UnitsDocument18 pagesCalculation of Flow Rate For Orifice Venturi or Flow Nozzle Meter Si UnitsPrakash WarrierNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument77 pagesNew Microsoft Word Documenthamza A.laftaNo ratings yet
- Stacks: Ammonia Injection: A Route To CleanDocument8 pagesStacks: Ammonia Injection: A Route To CleanZEN MA100% (1)
- (EDITED-FINAL) Sludge - Storage CalculationDocument17 pages(EDITED-FINAL) Sludge - Storage CalculationIftikhar KamranNo ratings yet
- 6 Crystallizer Design and Operation1Document22 pages6 Crystallizer Design and Operation1Dhrumil GandhiNo ratings yet
- Scale Up of Paddle DryerDocument4 pagesScale Up of Paddle DryerRavindra V. Lakhapati100% (1)
- Air CalculationsDocument4 pagesAir CalculationsSerkan YukselNo ratings yet
- Line Sizing Single Phase Fluid Flow: Chemical Engineering CalculationsDocument2 pagesLine Sizing Single Phase Fluid Flow: Chemical Engineering CalculationsRawlinson TolentinoNo ratings yet
- C 100 PDFDocument6 pagesC 100 PDFZeeshan TalibNo ratings yet
- Dykewall CalculationDocument4 pagesDykewall CalculationVipul GandhiNo ratings yet
- Two-Phase Flow Discharge in Nozzles and Pipes - A Unified ApproachDocument6 pagesTwo-Phase Flow Discharge in Nozzles and Pipes - A Unified ApproachAksheyNo ratings yet
- Blower and Compressor Selection for Membrane AerationDocument42 pagesBlower and Compressor Selection for Membrane AerationSuryaprakashNo ratings yet
- C 5 - 79 R97 - Qzutukve PDFDocument4 pagesC 5 - 79 R97 - Qzutukve PDFJuan Pablo ApazaNo ratings yet
- Steel Pipe Vessel1Document272 pagesSteel Pipe Vessel1Juan Pablo ApazaNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficient Compressed AirDocument25 pagesEnergy Efficient Compressed AirocchityaNo ratings yet
- Simulations of Dense-Phase Pneumatic ConveyingDocument7 pagesSimulations of Dense-Phase Pneumatic ConveyingMadan YadavNo ratings yet
- Quicklime For Structural PurposesDocument2 pagesQuicklime For Structural PurposesAlejandro Valdés RojasNo ratings yet
- D 5628 - 96 R01 - Rdu2mjg - PDFDocument10 pagesD 5628 - 96 R01 - Rdu2mjg - PDFJuan Pablo ApazaNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Wax in Paper: Standard Test Method ForDocument3 pagesPetroleum Wax in Paper: Standard Test Method ForJuan Pablo ApazaNo ratings yet
- Sampling and Accepting A Single Lot of Paper, Paperboard, Fiberboard, and Related ProductDocument5 pagesSampling and Accepting A Single Lot of Paper, Paperboard, Fiberboard, and Related ProductfrostestNo ratings yet
- Chap1 2Document60 pagesChap1 2Juan Pablo ApazaNo ratings yet
- A 501 - 01 Qtuwmq - PDFDocument6 pagesA 501 - 01 Qtuwmq - PDFJuan Pablo ApazaNo ratings yet
- E 527 - 83 R97 Rtuyny04m1i5n0ux PDFDocument7 pagesE 527 - 83 R97 Rtuyny04m1i5n0ux PDFJuan Pablo ApazaNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic ConveyingDocument8 pagesPneumatic ConveyingAstri NgentNo ratings yet
- Engineering Letter: SystemcalculationDocument4 pagesEngineering Letter: SystemcalculationjmartinezmoyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Letter: IntegralmotorsforcentrifugalfansDocument4 pagesEngineering Letter: IntegralmotorsforcentrifugalfansjameeloNo ratings yet
- FANS AND BLOWERS FOR COMBUSTIONDocument4 pagesFANS AND BLOWERS FOR COMBUSTIONnedduc20No ratings yet
- Engineering Letter: Fanperformance-ThesystemeffectDocument4 pagesEngineering Letter: Fanperformance-ThesystemeffectJuan Pablo ApazaNo ratings yet
- El 25Document8 pagesEl 25Juan Pablo ApazaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Letter: ElectricmotorcodesandstandardsDocument4 pagesEngineering Letter: Electricmotorcodesandstandardsnedduc20No ratings yet
- El GDocument8 pagesEl GJuan Pablo ApazaNo ratings yet
- EL-00 IndexDocument1 pageEL-00 IndexJuan Pablo ApazaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Steam Heating Systems ExplainedDocument2 pagesFundamentals of Steam Heating Systems ExplainedJuan Pablo ApazaNo ratings yet
- Ideal gas law application to air propertiesDocument12 pagesIdeal gas law application to air propertiesJuan Pablo ApazaNo ratings yet