Professional Documents
Culture Documents
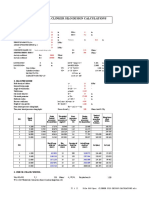
Silo and Hopper Pressure Calculations
Uploaded by
Nam Ngô DuyOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Silo and Hopper Pressure Calculations
Uploaded by
Nam Ngô DuyCopyright:
Available Formats
Fig_PC&P_5 Lecture Product Characterization and Processing of Pharmaceutical Particulate Solids, Silo pressure calculations , J rgen Tomas 29.05.
2013
Figure 5.0
Prof. Dr.-Ing. habil. J . Tomas chair for Mechanical Process Engineering
5. Silo and hopper pressure calculations
5.1 shaft and hopper pressures
5.2 Wall thickness
Fig_PC&P_5 Lecture Product Characterization and Processing of Pharmaceutical Particulate Solids, Silo pressure calculations , J rgen Tomas 29.05.2013
Figure 5.1
Prof. Dr.-Ing. habil. J . Tomas chair for Mechanical Process Engineering
5.1 shaft and hopper pressures
Vertikal and Horizontal Pressures at Mass Flow Silo
height level of flattened
free bulk surface
intersection between
shaft and hopper
height level of
discharge opening
filling
discharging
s
i
l
o
h
e
i
g
h
t
H
silo pressures p
v
and p
h
p
v
p
v
p
h
p
h
p
v
p
h
radial stress field r
F 5.1
Fig_PC&P_5 Lecture Product Characterization and Processing of Pharmaceutical Particulate Solids, Silo pressure calculations , J rgen Tomas 29.05.2013
Figure 5.2
Prof. Dr.-Ing. habil. J . Tomas chair for Mechanical Process Engineering
Fig_PC&P_5 Lecture Product Characterization and Processing of Pharmaceutical Particulate Solids, Silo pressure calculations , J rgen Tomas 29.05.2013
Figure 5.3
Prof. Dr.-Ing. habil. J . Tomas chair for Mechanical Process Engineering
Fig_PC&P_5 Lecture Product Characterization and Processing of Pharmaceutical Particulate Solids, Silo pressure calculations , J rgen Tomas 29.05.2013
Figure 5.4
Prof. Dr.-Ing. habil. J . Tomas chair for Mechanical Process Engineering
p
o
s
i
t
i
o
n
o
f
a
c
t
i
v
e
s
h
e
a
r
p
l
a
n
e
Active and Passive Rankine's Stress State Limits
Yield locus: = tan
i
+
c
= tan
i
( +
Z
)
or
R
= sin
i
(
M
+
Z
)
p
h,a
active
passive
s
h
e
a
r
s
t
r
e
s
s
tensile
strength
Z
cohesion
c
2,a
a
=
i
4 2
+
R ,a
2
a
p
v
1,a
y
i
e
l
d
l
o
c
u
s
p
h,p
1,p
p
=
i
4
-
2
M,p
=
1,p
+
2,p
2
p
o
s
i
t
i
o
n
o
f
p
a
s
s
i
v
e
s
h
e
a
r
p
l
a
n
e
R,p
=
1,p
2,p
2
-
active passive
principal stresses
lateral or
horizontal
stress ratio
2,a
=
1
+
c
1 - sin
i
1 + sin
i
2 cos
i
1 + sin
i
1,p
=
2,p
+
c
1 + sin
i
1 - sin
i
2 cos
i
1 - sin
i
lower limit for
c
= 0 upper limit for
c
= 0
p
h,p
p
v
= = = tan
2
1 + sin
i
1 - sin
i
(
4
+
i
2
p
p
h,a
p
v
= = = tan
2
1 - sin
i
1 + sin
i
(
4
-
i
2
active
i
4 2
+
p
v
p
h,a
p
v
p
h,p
passive
i
4 2
-
p
v
p
h,a
p
v
p
h,p
normal stress
given: p
v
=
1
=
b
.g y
c
,
i
searched: 2 stress states which meet the yield condition
y
x
2,p
F 5.4
Fig_PC&P_5 Lecture Product Characterization and Processing of Pharmaceutical Particulate Solids, Silo pressure calculations , J rgen Tomas 29.05.2013
Figure 5.5
Prof. Dr.-Ing. habil. J . Tomas chair for Mechanical Process Engineering
Fig_PC&P_5 Lecture Product Characterization and Processing of Pharmaceutical Particulate Solids, Silo pressure calculations , J rgen Tomas 29.05.2013
Figure 5.6
Prof. Dr.-Ing. habil. J . Tomas chair for Mechanical Process Engineering
Fig_PC&P_5 Lecture Product Characterization and Processing of Pharmaceutical Particulate Solids, Silo pressure calculations , J rgen Tomas 29.05.2013
Figure 5.7
Prof. Dr.-Ing. habil. J . Tomas chair for Mechanical Process Engineering
Fig_PC&P_5 Lecture Product Characterization and Processing of Pharmaceutical Particulate Solids, Silo pressure calculations , J rgen Tomas 29.05.2013
Figure 5.8
Prof. Dr.-Ing. habil. J . Tomas chair for Mechanical Process Engineering
storage time t
L
= 22 h
m
Fill
= 11,5 t
b
= 0,8 t/m
3
e
= 33
w
= 23 steel sheet (CF)
w
= 18 steel sheet (MF)
mass flow, switch load p
n
= (c
4
- c
1
) p
n
cos ,
TGL 32274/09
mass flow, switch load p
n
=
b
g (H or D),
DIN 1055 part 6
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
wall normal pressures p
h
, p
n
in kPa
0
1
2
3
4
5
h
e
i
g
h
t
H
,
H
'
i
n
m
mass flow (MF)
core flow
flow
bondary
silo
G 807
p
n
Wall Normal Pressures p
h
, p
n
of Wheat
measured, filling
measured, discharging
calculated, filling
calculated, discharging,
load factors c
1
= 1,4, c
4
= 3,0
calculated, DIN 1055 part 6
c
3
= 1.8
(CF)
23
30
p
h
D = 2,4 m
measurements according to Scholz
F 5.8
Fig_PC&P_5 Lecture Product Characterization and Processing of Pharmaceutical Particulate Solids, Silo pressure calculations , J rgen Tomas 29.05.2013
Figure 5.9
Prof. Dr.-Ing. habil. J . Tomas chair for Mechanical Process Engineering
Maximum Normal Pressures (Discharging) versus
Effective Angle of Internal Friction
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
w
= 10
boundaries
rough wall
w
=10
20
30 40 50
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
p*
h
shaft
p*
n
hopper
20
30
40
50
60
p
*
h
,
m
a
x
,
p
*
n
,
m
a
x
12
e
in deg
Maximum Vertical Pressures (Filling) versus Effektive
Angle of Internal Friction
p
*
v
,
m
a
x
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
w
= 10
20
30
40
50
boundary
rough wall
= 10 mass flow
=0,725
= 2,414
A
U
H
D
shaft
hopper
w
=10
20
30 40
50
12
13
14
e
in deg
Maximum Vertical Pressures (Filling) versus
Wall Friction Angle
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
e
=30 40
50
12
13
isostatic pressure
boundary
rough wall
p
*
v
,
m
a
x
14
shaft
hopper
60
w
in deg
Maximum Normal Pressures (Discharging)
versus Wall Friction Angle
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
30
40
50
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
boundaries
rough wall
p
*
h
,
m
a
x
,
p
*
n
,
m
a
x
12
13
14
60
e
=30
w
in deg
60
50
40
p*
h
shaft
p*
n
hopper
Maximum Wall Friction Loads (Discharging)
versus Effective Angle of Internal Friction
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
w
=10
20
30
40
-50
p*
h
shaft
p*
n
hopper
20
10
30
20
40
50
-10
e
=30
1
2
1,5
2,5
0 0
0,5
0,6
0,7
0,4
0,3
0,2
0,1
p
*
w
,
m
a
x
boundaries
rough wall
0,5
60
40
50
p
*
w
,
m
a
x
e
in deg
p
*
w
,
m
a
x
p
*
w
,
m
a
x
Maximum Wall Friction Loads (Discharging) versus
Wall Friction Angle
e
=30
40
50
50
40
0
0,5
1
1,5
2
2,5
0
0,5
0,6
0,7
0,4
0,3
0,2
0,1
boundaries
rough wall
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
60
60
e
=
30
w
in deg
p*
w
shaft
p*
w
hopper
p* = p U
b
g A
.
. .
F 5.9
Fig_PC&P_5 Lecture Product Characterization and Processing of Pharmaceutical Particulate Solids, Silo pressure calculations , J rgen Tomas 29.05.2013
Figure 5.10
Prof. Dr.-Ing. habil. J . Tomas chair for Mechanical Process Engineering
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
p
*
v
,
m
a
x
9
10
11
w
= 10
20
30
40
50
boundary
rough wall
= 30 core flow
=0,725
= 2,414
A
U
H
D
shaft
hopper
w
=10
20
30 40
50
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
e
in deg
Maximum Vertical Pressures (Filling) versus Effektive
Angle of Internal Friction
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
e
=30 40
50
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
12
13
shaft
hopper
isistatic pressure
boundary
rough wall
p
*
v
,
m
a
x
60
w
in deg
Maximum Vertical Pressures (Filling)
versus Wall Friction Angle
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
w
= 10
boundaries
rough wall
w
=10
20
30
40
50
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
p*
h
shaft
p*
n
hopper
20
30
40
50
60
p
*
h
,
m
a
x
,
p
*
n
,
m
a
x
60
e
in deg
Maximum Normal Pressures (Discharging) versus
Effective Angle of Internal Friction
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
e
=30 40
50
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
e
=30
40
50
60
60
boundaries
rough wall
p
*
h
,
m
a
x
,
p
*
n
,
m
a
x
w
in deg
p*
h
shaft
p*
n
hopper
Maximum Normal Pressures (Discharging)
versus Wall Friction Angle
e
=30
40
50
50
40
e
=
30
0 0
I
p
*
w
,
m
a
x
0,5
0,6
0,7
0,8
0,9
1,0
0,4
0,3
0,2
0,1
0,5
1
1,5
2
2,5
3
p
*
w
,
m
a
x
boundaries
rough wall
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
60
60
w
in deg
p*
h
shaft
p*
n
hopper
Maximum Wall Friction Loads (Discharging)
versus Wall Friction Angle
3
w
=10
20
30
40
50
20
10
30
20
30
40
50
10
e
=60
1
2
1,5
2,5
0
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
0
0,5
0,6
0,7
0,8
0,9
1,0
0,4
0,3
0,2
0,1
I
p
*
w
,
m
a
x
boundaries
rough wall
0,5
e
in deg
p
*
w
,
m
a
x
p*
h
shaft
p*
n
hopper
Maximum Wall Friction Loads (Discharging)
versus Effective Angle of Internal Friction
p* = p U
b
g A
.
. .
F 5.10
Fig_PC&P_5 Lecture Product Characterization and Processing of Pharmaceutical Particulate Solids, Silo pressure calculations , J rgen Tomas 29.05.2013
Figure 5.11
Prof. Dr.-Ing. habil. J . Tomas chair for Mechanical Process Engineering
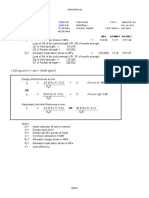
5.2 Wall thickness
Necessary Steel Reinforcement of Concrete A
St
D
i,1
p
n
A
St
H
D
i
D
i,2
p
n
D
i
=
D
i,1
+ D
i,2
2
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
cos
F,St
2
j
c
s i
D
n
p
A
St
=
H
A
2 cos /
i
D H
n
p 0 F
St
= =
(
(
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
i
D
H
w
tan
F
4 exp 1
F,St
cos
w
tan 8
j
c
s
2
i
D g
b
St
A
load factors according to TGL 32 274/09
( ) cos c c 1 c
1 4 or 3 j
+ =
c
j
= c
1
oder c
3
oder c
4
with c
1
= 1,2 ... 1,6
c
3
= 1,7 ... 2,1
c
4
= 2,1 ... 4,0
hopper
shaft
discharging
core flow
mass flow
F 5.11
Fig_PC&P_5 Lecture Product Characterization and Processing of Pharmaceutical Particulate Solids, Silo pressure calculations , J rgen Tomas 29.05.2013
Figure 5.12
Prof. Dr.-Ing. habil. J . Tomas chair for Mechanical Process Engineering
You might also like
- S 101 Sodium Chloride Silo Specification Sheet and DesignDocument8 pagesS 101 Sodium Chloride Silo Specification Sheet and DesignBenedick Jayson MartiNo ratings yet
- Silo Capacity CalculationDocument1 pageSilo Capacity Calculationlbc123No ratings yet
- Wind On SiloDocument7 pagesWind On SiloHgagselim SelimNo ratings yet
- Silo Initial CalculationDocument10 pagesSilo Initial CalculationAnonymous 7IDARRWNo ratings yet
- Design of HopperDocument18 pagesDesign of HopperJitendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Design of Silo: Presented by Shyamala.C M.Tech (Storage Engg.) 2015604605Document26 pagesDesign of Silo: Presented by Shyamala.C M.Tech (Storage Engg.) 2015604605Darshan PanchalNo ratings yet
- Concept of Silo DesignDocument6 pagesConcept of Silo Designv2299No ratings yet
- Silo PressureDocument4 pagesSilo PressureRNo ratings yet
- Stresses in SiloDocument12 pagesStresses in SiloENAENA187No ratings yet
- FEECO Complete OfferingsDocument8 pagesFEECO Complete OfferingsawfahNo ratings yet
- Calculation For D12m SiloDocument4 pagesCalculation For D12m SiloJuan Carlos Quispe Chara0% (1)
- Design of circular silo bunkerDocument24 pagesDesign of circular silo bunkerJames AugustineNo ratings yet
- Hopper Design Factors for Bulk Solids HandlingDocument49 pagesHopper Design Factors for Bulk Solids Handlingmhd badhrul bin baharNo ratings yet
- Analysis Strength of Scaffolding Structure On Stack HRSG For Cable TightDocument5 pagesAnalysis Strength of Scaffolding Structure On Stack HRSG For Cable TighthendraNo ratings yet
- ASME manual coil heating procedureDocument8 pagesASME manual coil heating procedurehgagNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Analysis of Steel Silo Using Wind Load As Per Indian Standard IJERTV8IS110206Document4 pagesDynamic Analysis of Steel Silo Using Wind Load As Per Indian Standard IJERTV8IS110206AliNo ratings yet
- API 650 Des PDFDocument13 pagesAPI 650 Des PDFDhakshina K100% (1)
- RO Tank Lifting Lug Design AnalysisDocument1 pageRO Tank Lifting Lug Design AnalysisSarfarazNo ratings yet
- L20 - Silos and TanksDocument22 pagesL20 - Silos and TanksVasil Georgiev GeorgievNo ratings yet
- Appendix A: Variable Ranges For Filter Cycle Calculations: Basic Properties of Solids, Solutes and FluidsDocument10 pagesAppendix A: Variable Ranges For Filter Cycle Calculations: Basic Properties of Solids, Solutes and FluidsBrendaline EnopiaNo ratings yet
- Potable Water Tank Calculation PDFDocument37 pagesPotable Water Tank Calculation PDFboysitumeangNo ratings yet
- API 650-Water SS Tank-060914Document84 pagesAPI 650-Water SS Tank-060914Hamou MelloulNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Calculations On VesselsDocument3 pagesWind Load Calculations On VesselssudhakarebvnNo ratings yet
- Steel Silo Quantity EstimationDocument4 pagesSteel Silo Quantity EstimationUttam Kumar Ghosh100% (1)
- 1200m3 Ash Silo Mechanical ReportDocument15 pages1200m3 Ash Silo Mechanical Reporttranceintt0% (1)
- 100cub API 650 STEEL SiloDocument19 pages100cub API 650 STEEL SiloUDayNo ratings yet
- Bunker StudyDocument20 pagesBunker StudySripara KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Tie Rod Support For Retangular TanksDocument11 pagesTie Rod Support For Retangular Tanksmiteshpatel191No ratings yet
- Add any change made in the sheet with new revision NoDocument16 pagesAdd any change made in the sheet with new revision Nochenfs27531No ratings yet
- Hopper Bottom DesignDocument2 pagesHopper Bottom DesignAnonymous ciKyr0tNo ratings yet
- SC Screw Conveyor Torque PDFDocument3 pagesSC Screw Conveyor Torque PDFQuality Tech AccessoriesNo ratings yet
- GLACIER LAr Tank Design (Deliverable 2.2)Document76 pagesGLACIER LAr Tank Design (Deliverable 2.2)atiqulaNo ratings yet
- SILODocument44 pagesSILOClezel MesaNo ratings yet
- Design and Study of Floating Roofs For Oil Storage TanksDocument12 pagesDesign and Study of Floating Roofs For Oil Storage TanksDavid RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Silo CalculationDocument10 pagesSilo CalculationSOURAVNo ratings yet
- OSHA standards for portable ladders, stairways and fixed laddersDocument45 pagesOSHA standards for portable ladders, stairways and fixed laddersAMITNo ratings yet
- Presentation Construction Sequence of Silos 1503761554 305716Document44 pagesPresentation Construction Sequence of Silos 1503761554 305716MOHAMMED MOHSINNo ratings yet
- 9178 2 PDFDocument39 pages9178 2 PDFvivekNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Calibration Procedure For Weigh BridgeDocument1 page1.0 Calibration Procedure For Weigh BridgeMechanical ShauryaNo ratings yet
- Kuenz TRCMDocument9 pagesKuenz TRCMklcy1987No ratings yet
- Foundation Design Philosophy For Horizontal VesselDocument6 pagesFoundation Design Philosophy For Horizontal VesselKeaten ClaneyNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Tank Ring Wall Fo PDFDocument3 pagesDesign and Analysis of Tank Ring Wall Fo PDFsatyakamNo ratings yet
- Cone Bottom Thickness & Structure Calculation For Elevated Supported Bottom Cone Tank Document NameDocument1 pageCone Bottom Thickness & Structure Calculation For Elevated Supported Bottom Cone Tank Document NameSachin5586No ratings yet
- Tube Properties PDFDocument19 pagesTube Properties PDFjamoneoNo ratings yet
- Efficient silo designDocument21 pagesEfficient silo designAkhilprasad Sadige100% (1)
- Storage Silo, Bolting Silo, Mild Steel Silo, Lime Storage Silo, Manufacturers, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, IndiaDocument2 pagesStorage Silo, Bolting Silo, Mild Steel Silo, Lime Storage Silo, Manufacturers, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, Indiaaarticleseansmo50% (2)
- Impact of New Codes in Silos DesignDocument7 pagesImpact of New Codes in Silos DesignKhaled EidNo ratings yet
- Floating Roof DesinDocument5 pagesFloating Roof Desindimdaliak_985662241No ratings yet
- Min. Nozzles Spacing API-650Document1 pageMin. Nozzles Spacing API-650jojo_323No ratings yet
- CFD ApplicationsDocument5 pagesCFD ApplicationsavailmeNo ratings yet
- D12M Off-Spec. Clinker Silo Design CalculationsDocument1 pageD12M Off-Spec. Clinker Silo Design Calculationssami stelNo ratings yet
- GB 50077-2003-Code For Design of Reinforced Concrete SilosDocument86 pagesGB 50077-2003-Code For Design of Reinforced Concrete SilosGerardo Becker100% (1)
- Folien SFPS 5Document13 pagesFolien SFPS 5psiunia974No ratings yet
- PHYWE - Hall Effect - Experiments N and P Germanium - P2530116e PDFDocument11 pagesPHYWE - Hall Effect - Experiments N and P Germanium - P2530116e PDFMarco Antonio RH100% (1)
- Mathcad - 539900-050-130 Padeye Pulling Skid 9.5 TDocument7 pagesMathcad - 539900-050-130 Padeye Pulling Skid 9.5 TPablo Diego Didoné100% (1)
- Mathcad - Case-4 (22 OD) HYDDocument4 pagesMathcad - Case-4 (22 OD) HYDAdvisNo ratings yet
- Soil Constitutive ModelDocument36 pagesSoil Constitutive ModelMohamed YousufNo ratings yet
- HES2120 Lab2 2012 Sem1Document9 pagesHES2120 Lab2 2012 Sem1Anthony NguyenNo ratings yet
- Lab. 2 - Thin Wall Cylinder-2015 Sem. 2Document13 pagesLab. 2 - Thin Wall Cylinder-2015 Sem. 2harinder100% (1)
- 4b - IPO GL DesignDocument53 pages4b - IPO GL Designmrjohnston37No ratings yet
- TECHNICAL DESIGN-Calculation Report-Clinker SiloDocument128 pagesTECHNICAL DESIGN-Calculation Report-Clinker SiloNam Ngô DuyNo ratings yet
- Silos with stepped wall thickness on local supportsDocument12 pagesSilos with stepped wall thickness on local supportsNam Ngô DuyNo ratings yet
- Silo Pressure Predictions Using Discrete-ElementDocument28 pagesSilo Pressure Predictions Using Discrete-ElementNam Ngô DuyNo ratings yet
- ASME UG 37 Nozzles PDFDocument6 pagesASME UG 37 Nozzles PDFlatif.deNo ratings yet
- Pre Stressed Modal Analysis Using FiniteDocument8 pagesPre Stressed Modal Analysis Using Finitegreat2008No ratings yet
- Earthq Engng Struct Dyn - 2023 - Hamilton - Seismic Excitation of Offshore Wind Turbines and Transition Piece ResponseDocument24 pagesEarthq Engng Struct Dyn - 2023 - Hamilton - Seismic Excitation of Offshore Wind Turbines and Transition Piece ResponseBridge&StructureNo ratings yet
- Nigel Priestley Publications To 2000Document41 pagesNigel Priestley Publications To 2000MunyaNo ratings yet
- Rao 기계진동학 6판_Chapter 4Document146 pagesRao 기계진동학 6판_Chapter 4hbinnn29No ratings yet
- Metcar Physical Characteristics GuideDocument3 pagesMetcar Physical Characteristics GuideJavad AmnianNo ratings yet
- Pile Capacity PrecastDocument38 pagesPile Capacity Precastbasum matNo ratings yet
- Effect of Hydrogen Diffusion on Steel EmbrittlementDocument6 pagesEffect of Hydrogen Diffusion on Steel EmbrittlementmohammadpniNo ratings yet
- Modified Cam Clay Modell (MCCM)Document15 pagesModified Cam Clay Modell (MCCM)Jorge Hernan LopezNo ratings yet
- Euler Bernoulli PDFDocument2 pagesEuler Bernoulli PDFJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Silo BucklingDocument14 pagesSilo BucklingrahilmlNo ratings yet
- Understanding ship bending stressesDocument85 pagesUnderstanding ship bending stressesS. Dinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Interview QuestionsDocument4 pagesCivil Engineering Interview QuestionsDivyang PatelNo ratings yet
- Structural steel design guide contentsDocument1 pageStructural steel design guide contentsNeeraj DubeyNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Soil Structure Interaction Analysis of Building On Clayey and Sandy Soil-IJRASETDocument11 pagesComparative Study of Soil Structure Interaction Analysis of Building On Clayey and Sandy Soil-IJRASETIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Design of Structure For Earthquake Resistance Part 1Document53 pagesDesign of Structure For Earthquake Resistance Part 1Ng JialinNo ratings yet
- A Review of Elastic-Plastic Contact MechanicsDocument30 pagesA Review of Elastic-Plastic Contact MechanicspeaceshadyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-Bending AnnotatedDocument52 pagesChapter 6-Bending AnnotatedOsvaldo IzataNo ratings yet
- Full Download Solution Manual For Mechanics of Materials Beer Johnston Dewolf Mazurek 6th Edition PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Solution Manual For Mechanics of Materials Beer Johnston Dewolf Mazurek 6th Edition PDF Full Chaptermooneye.beeve.r572100% (19)
- Design of Precast and Prestressed Double Tee Beam CalculationDocument20 pagesDesign of Precast and Prestressed Double Tee Beam CalculationLim Wee BengNo ratings yet
- Word Design of ProjectDocument381 pagesWord Design of ProjectSantosh Basnet100% (1)
- Ce 481 Shear Strength 3Document103 pagesCe 481 Shear Strength 3phan phucNo ratings yet
- Experimental Stress Analysis 1986 PDFDocument624 pagesExperimental Stress Analysis 1986 PDFHassan AlaaNo ratings yet
- TCC42 Post Tensioned Analysis & DesignDocument17 pagesTCC42 Post Tensioned Analysis & Designhala_azhariNo ratings yet
- CV of Prof M L SharmaDocument54 pagesCV of Prof M L SharmabbbbbbNo ratings yet
- GeoGuide1 RetainingWallDocument259 pagesGeoGuide1 RetainingWallClaireNgok100% (1)
- Buckling of Woven Fabric - NewDocument27 pagesBuckling of Woven Fabric - NewShovan Das100% (3)
- Richard J. Aquino, Msce, MSCM Assoc. Prof. Ii Ce and Enp: Design Process Limit States Design Codes Design PhilosophyDocument78 pagesRichard J. Aquino, Msce, MSCM Assoc. Prof. Ii Ce and Enp: Design Process Limit States Design Codes Design PhilosophySelf SevNo ratings yet
- Storage Tank DesignDocument21 pagesStorage Tank Designravi456compNo ratings yet
- Advanced beam bendingDocument2 pagesAdvanced beam bendingsarathkumarNo ratings yet
- Mathcad - C06-C10 PDFDocument7 pagesMathcad - C06-C10 PDFKrish ChandNo ratings yet