Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CSEC Biology 2014 Revision
Uploaded by
Nabeel Uddin89%(9)89% found this document useful (9 votes)
2K views44 pagesA few Biology topics based on CXC syllabus are included in this short presentation.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA few Biology topics based on CXC syllabus are included in this short presentation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
89%(9)89% found this document useful (9 votes)
2K views44 pagesCSEC Biology 2014 Revision
Uploaded by
Nabeel UddinA few Biology topics based on CXC syllabus are included in this short presentation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 44
Biology
Revision For 2014 CSEC Examination
Cells
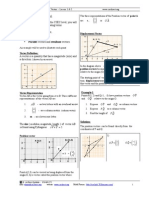
Diffusion
Definition:
Example:
Osmosis
Movement of water molecules
Across cell selectively permeable
membrane
E.g
Active Transport
Low to high concentration
Across cell membrane
Requires energy (ATP)
Food chain/web
You should be able to identify
Producer, primary consumer,
secondary consumer etc.
Herbivore, Carnivore, Omnivore
Main source of energy?
What limits the number of trophic
levels?
Pyramid of number
Pyramid of Energy
Symbiosis
Mutualism
Commensalism
Parasitism
Autotrophic Nutrition
Photosynthesis
Light stage: Light energy splits water
molecules ( H and O)
Dark Stage: H combine with CO2 forming
glucose
Word and chemical equation of photosynthesis
Photosynthesis
Cross section of leaf
Mutualism
Heterotrophic nutrition
Should be able to
Draw digestive system, and label parts
Know the function of macro and micro
nutrients
Deficiency disease: e.g. anemia, kwashiorkor,
Marasmus, and Obesity
Identify types of teeth and label parts correctly
Write dental formula
Care of teeth: e.g. brush with fluoride
toothpaste, Ca in diet
Role of enzymes
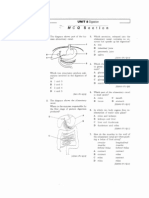
Digestive system
Where mechanical digestion
occurs?
Chemical digestion
Food products that are absorbed
into the small intestine (iluem)
Amino acids
Glucose
Fatty acids and glycerol
Enzymes
Amylase:
Pepsin
Rennin
Trypsin
Lipase
Maltase
Respiration
Draw respiratory system and
annotate structures
Breathing vs respiration
Aerobic vs anaerobic
Oxygen dept
Gas exchange in plants and single
cellular organisms
Plants: stomata, lenticels and root hairs
Breathing
Alveoli: gas exchange by diffusion
Bronchi into bronchiole
Trachea divides into two bronchi
Trachea, epiglottis opens
Nose: moisten air
Gas exchange
Plants gas exchange
Day: gives off oxygen
(photosynthesis occurs faster than
respiration)
Night: Gives off Carbon dioxide
Transport system
Types of blood cells
Role of platelets- Thrombocytes
Heart: structure and function
Blood vessels
Blood circulation
Transport in Plants-Dicots
Transport in Plants-Dicots
Excretion
Excretory products
Plants: O2 CO2, ,Nitrogenous
compounds
Animals: CO2, H2O, Ammonia, Urea
Excretory organs
Plants: Stomata, or some stored in
leaves and barks
Animals: Skin, Kidney, Lungs, Liver
(Bile)
Deamination
Nervous System
CNS and PNS
Stimulus, Receptors, Effectors
Types of Neurons
Reflex Action
Hormones are released from
glands/cells into the blood vessels
They travel to target organs, where
they cause a change
How does the Endocrine system works
Sense Organs
Should be able to label all (draw as
well)
The End
Nabeel Publication
You might also like
- Maths CXC Exam Notes CSECDocument169 pagesMaths CXC Exam Notes CSECTalisha April Mohammed100% (7)
- CSEC Study Guide - September 11, 2012Document11 pagesCSEC Study Guide - September 11, 2012ChantelleMorrisonNo ratings yet
- CXC CSEC HSB January 2017 P2 PDFDocument17 pagesCXC CSEC HSB January 2017 P2 PDFSayyid Muhammad Aqeed AabidiNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry June 2012 P1 (Specimen) PDFDocument10 pagesCSEC Chemistry June 2012 P1 (Specimen) PDFShanice Russell100% (4)
- CxcDirect Vectors TutorialDocument7 pagesCxcDirect Vectors TutorialMarshalee Francis0% (1)
- CSEC Biology January 2020 P2Document28 pagesCSEC Biology January 2020 P2Joy Boehmer67% (3)
- CSEC Biology MCQ Answers PDFDocument1 pageCSEC Biology MCQ Answers PDFJoy BoehmerNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology June 2002 P1 PDFDocument12 pagesCSEC Biology June 2002 P1 PDFLaimen Reveski100% (1)
- Csec Biology Work BookletDocument77 pagesCsec Biology Work BookletDevi Rambaran100% (4)
- CSEC Biology January 2013 P1 PDFDocument11 pagesCSEC Biology January 2013 P1 PDFCarl Agape Davis0% (3)
- Cape Communication Studies: Practical Exercises for Paper 02 EssaysFrom EverandCape Communication Studies: Practical Exercises for Paper 02 EssaysNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology Revision Guide AnswersDocument29 pagesCSEC Biology Revision Guide AnswersCharlobabooram50% (2)
- Csec BiologyDocument79 pagesCsec Biologysuggaball100% (4)
- Ms. D Rambaran 2018 FORM 4.2 Science Scheme of WorkDocument21 pagesMs. D Rambaran 2018 FORM 4.2 Science Scheme of WorksuggaballNo ratings yet
- Csec Bio. Digestion MCDocument8 pagesCsec Bio. Digestion MCShav Mad Swizz50% (4)
- CSEC Biology Paper 1 2007-13 SCBD Key ShareDocument4 pagesCSEC Biology Paper 1 2007-13 SCBD Key ShareShandarr Blades50% (12)
- CSEC Biology June 2009 P1Document12 pagesCSEC Biology June 2009 P1ANGELIA BURROWS100% (3)
- Carbon Dioxide Emissions in China and the USADocument13 pagesCarbon Dioxide Emissions in China and the USASolita Singh100% (3)
- CSEC Biology June 2015 P1 Specimen Paper PDFDocument48 pagesCSEC Biology June 2015 P1 Specimen Paper PDFJoy Boehmer100% (1)
- CSEC Chemistry January 2018 P1 PDFDocument11 pagesCSEC Chemistry January 2018 P1 PDFShalini K86% (7)
- Agricultural Science For Secondary School Book 1 PDFDocument124 pagesAgricultural Science For Secondary School Book 1 PDFFernando Matroo74% (43)
- CSEC Biology June 2013 P2 PDFDocument16 pagesCSEC Biology June 2013 P2 PDFJoy Boehmer100% (1)
- CSEC Physics Revision Guide AnswersDocument32 pagesCSEC Physics Revision Guide AnswersStudent Research100% (1)
- Csec BiologyDocument79 pagesCsec BiologysuggaballNo ratings yet
- Csec HSB January 2010 p2Document21 pagesCsec HSB January 2010 p2Sachin Bahadoorsingh50% (2)
- CSEC Chemistry Paper 1Document9 pagesCSEC Chemistry Paper 1Laimen ReveskiNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry June 2011 P1Document9 pagesCSEC Chemistry June 2011 P1Ajay Maharaj100% (1)
- Biology P2 2012 CSECDocument17 pagesBiology P2 2012 CSECshannee_lei75% (8)
- CSEC Chemistry June 2014 P1 PDFDocument9 pagesCSEC Chemistry June 2014 P1 PDFAlyssa Brown100% (2)
- F5 T1 HSB P1 2010-2011Document13 pagesF5 T1 HSB P1 2010-2011asjawolverine81% (27)
- CSEC Biology June 2005 P1 PDFDocument11 pagesCSEC Biology June 2005 P1 PDFCarl Agape Davis100% (7)
- CSEC Info Tech 1993-2003 SolutionsDocument68 pagesCSEC Info Tech 1993-2003 SolutionsVernon WhiteNo ratings yet
- Csec HSB June 2017 p2Document20 pagesCsec HSB June 2017 p2Sachin BahadoorsinghNo ratings yet
- CSEC Human & Social Biology January 2019 Past PaperDocument4 pagesCSEC Human & Social Biology January 2019 Past PaperDaniel Walsh64% (14)
- Biology 09 p2 CsecDocument15 pagesBiology 09 p2 CsecGiovanni Dubii Daba Hutton86% (7)
- Collins Csec Chemistry Practice Multiple Choice Questions WorkbookDocument121 pagesCollins Csec Chemistry Practice Multiple Choice Questions WorkbookAlvesia Weatherhead100% (2)
- GCSE Biology Revision GuideDocument113 pagesGCSE Biology Revision GuideFair Pisuttisarun50% (2)
- CSEC Chemistry Revision Guide Answers PDFDocument31 pagesCSEC Chemistry Revision Guide Answers PDFSimon PaulNo ratings yet
- HSB Past PapersDocument43 pagesHSB Past PapersAretha Dawes33% (6)
- CAPE Bio Mark SchemeDocument4 pagesCAPE Bio Mark Schemeron97150% (2)
- CSEC Chemistry June 2017 P2Document18 pagesCSEC Chemistry June 2017 P2Shan CampNo ratings yet
- CSEC-Chemistry-Past p2 Jan 2015 PDFDocument20 pagesCSEC-Chemistry-Past p2 Jan 2015 PDFdela20% (1)
- CSEC Chemistry 2002 - 2010 Past Papers PDFDocument25 pagesCSEC Chemistry 2002 - 2010 Past Papers PDFCandace Rodney79% (14)
- CSEC Biology ManualDocument132 pagesCSEC Biology ManualChelsea FrancisNo ratings yet
- TaxonomyDocument71 pagesTaxonomyNabeel Uddin100% (1)
- CSEC Biology June 2006 P1Document12 pagesCSEC Biology June 2006 P1Shotta Atkins100% (1)
- O Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Movement Of SubstancesFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Movement Of SubstancesNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology MCQ AnswersDocument1 pageCSEC Biology MCQ AnswersAshley kennedyNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Test #4: Mixtures & Separation TechniquesDocument1 pageGrade 7 Test #4: Mixtures & Separation TechniquesNabeel UddinNo ratings yet
- HSB Mock Paper 2Document17 pagesHSB Mock Paper 2Nadege Roach50% (2)
- General ChemistryDocument239 pagesGeneral Chemistrylaode100% (1)
- Communication Studies: Preparing Students for CapeFrom EverandCommunication Studies: Preparing Students for CapeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Jamaica Driver's Education Handbook: A Comprehensive Driver Training GuideFrom EverandJamaica Driver's Education Handbook: A Comprehensive Driver Training GuideNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry June 2003 P1Document10 pagesCSEC Chemistry June 2003 P1Laimen ReveskiNo ratings yet
- Human Body Systems Lesson Plan 1Document4 pagesHuman Body Systems Lesson Plan 1api-338430889100% (2)
- CXC CSEC Exam Human and Social BiologyDocument10 pagesCXC CSEC Exam Human and Social BiologyRiichad Mmed88% (8)
- Acute and Chronic InflammationDocument36 pagesAcute and Chronic Inflammationibnbasheer89% (18)
- Types, locations, symptoms and treatment of uterine fibroidsDocument4 pagesTypes, locations, symptoms and treatment of uterine fibroidsRomeo ReyesNo ratings yet
- Histology, Lecture 12, The Lymphatic System (LEcture Notes)Document6 pagesHistology, Lecture 12, The Lymphatic System (LEcture Notes)Ali Al-QudsiNo ratings yet
- Compound Microscope PartsDocument91 pagesCompound Microscope PartsAndy Alvarez100% (1)
- RossDocument436 pagesRossAna Ion100% (1)
- CSEC BIO MCQ Answers PDFDocument1 pageCSEC BIO MCQ Answers PDFKaydian AnnaRebel JouvieJoy WhyteGaribaldiNo ratings yet
- Bio Papers AnswersDocument10 pagesBio Papers AnswersCarl Agape Davis75% (4)
- 2003 Csec Chem Paper 01Document10 pages2003 Csec Chem Paper 01Jesshaun Morris100% (6)
- CSEC Biology MCQ Answers PDFDocument1 pageCSEC Biology MCQ Answers PDFShanice RussellNo ratings yet
- CSEC Biology MCQ Answers from 2000-2014Document1 pageCSEC Biology MCQ Answers from 2000-2014Shannoi HindNo ratings yet
- FORM TP 2007061: Caribbean Examinations Council Secondary Education Certificate Examination ChemistryDocument8 pagesFORM TP 2007061: Caribbean Examinations Council Secondary Education Certificate Examination ChemistryJennifer ElliottNo ratings yet
- Bio NotesDocument18 pagesBio Notes185839No ratings yet
- Igcse Biology PlantsDocument3 pagesIgcse Biology PlantsNatalie BataNo ratings yet
- Digestive and Respiratory SystemDocument48 pagesDigestive and Respiratory Systemkenneth vergaraNo ratings yet
- Fossil Fuel Formation: Integrated Science Notes All Rights ReservedDocument2 pagesFossil Fuel Formation: Integrated Science Notes All Rights ReservedNabeel UddinNo ratings yet
- CXC Integrated Science Lab Manual All Rights ReservedDocument1 pageCXC Integrated Science Lab Manual All Rights ReservedNabeel UddinNo ratings yet
- ProctoringDocument2 pagesProctoringNabeel UddinNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science Grade 11: Air Masses and Weather FrontsDocument26 pagesIntegrated Science Grade 11: Air Masses and Weather FrontsNabeel UddinNo ratings yet
- Human and Social Biology Paper 1 (2011)Document11 pagesHuman and Social Biology Paper 1 (2011)Nabeel Uddin78% (58)
- Solar SystemDocument4 pagesSolar SystemNabeel UddinNo ratings yet
- Said, "Between Faith and Unbelief Is Abandoning The Prayer."Document4 pagesSaid, "Between Faith and Unbelief Is Abandoning The Prayer."Nabeel UddinNo ratings yet
- What You Need To KnowDocument6 pagesWhat You Need To KnowNabeel UddinNo ratings yet
- Integratred Science TestDocument2 pagesIntegratred Science TestNabeel UddinNo ratings yet
- UOPeople AssignmentDocument4 pagesUOPeople AssignmentNabeel Uddin100% (4)
- Tagore Memorial Secondary Easter Term Scheme, 2013 Integrated Science-Grade 9Document2 pagesTagore Memorial Secondary Easter Term Scheme, 2013 Integrated Science-Grade 9Nabeel Uddin100% (1)
- BioDocument4 pagesBioNabeel UddinNo ratings yet
- HSB Annual SchemeDocument2 pagesHSB Annual SchemeNabeel UddinNo ratings yet
- Night of PowerDocument6 pagesNight of PowerNabeel UddinNo ratings yet
- Biology Annual SchemeDocument3 pagesBiology Annual SchemeNabeel UddinNo ratings yet
- Muslim Scientific InventionsDocument5 pagesMuslim Scientific Inventionsebrohusaini100% (3)
- Uputstvo Za Obijanje Brava (Englseki)Document18 pagesUputstvo Za Obijanje Brava (Englseki)Nermin SelicNo ratings yet
- Life Cycle of MosquitoDocument19 pagesLife Cycle of MosquitoNabeel UddinNo ratings yet
- DeathDocument5 pagesDeathNabeel UddinNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 QuizDocument32 pagesGrade 7 QuizNabeel Uddin100% (1)
- Muhamad Nabeel Uddin Science Lab Manual: (2 Marks)Document1 pageMuhamad Nabeel Uddin Science Lab Manual: (2 Marks)Nabeel UddinNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Annual ExamDocument2 pagesGrade 7 Annual ExamNabeel UddinNo ratings yet
- Inclusive Education Research Shows Positive OutcomesDocument14 pagesInclusive Education Research Shows Positive OutcomesNabeel UddinNo ratings yet
- Biology Paper 2Document2 pagesBiology Paper 2Nabeel UddinNo ratings yet
- Grade 9Document2 pagesGrade 9Nabeel UddinNo ratings yet
- Short Biology TestDocument2 pagesShort Biology TestNabeel UddinNo ratings yet
- Excretory Products and Their Elimination - UnacademyDocument79 pagesExcretory Products and Their Elimination - UnacademyDEVENDRA kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- RADIO-IMAGISTICA PULMONARA SI MEDIASTINALA-finalDocument106 pagesRADIO-IMAGISTICA PULMONARA SI MEDIASTINALA-finalCarciuc DragosNo ratings yet
- Nur112: Anatomy and Physiology ISU Echague - College of NursingDocument14 pagesNur112: Anatomy and Physiology ISU Echague - College of NursingWai KikiNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonography of Gravid Uterus (Anomaly Scan) : Foetal BiometryDocument3 pagesUltrasonography of Gravid Uterus (Anomaly Scan) : Foetal BiometrypriyaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Human Physiology 6th Edition Ebook PDFDocument61 pagesPrinciples of Human Physiology 6th Edition Ebook PDFbilly.sparks463100% (40)
- Control and Coordination: One Mark QuestionsDocument7 pagesControl and Coordination: One Mark QuestionsJillianne JillNo ratings yet
- Physical Exam Vital SignsDocument4 pagesPhysical Exam Vital SignsmickeyNo ratings yet
- Vet Electives Zoology Course GuideDocument3 pagesVet Electives Zoology Course GuideRaymund AmbrocioNo ratings yet
- Physical Examination Head Neck Chest Breast and AbdomenDocument116 pagesPhysical Examination Head Neck Chest Breast and AbdomenSiva RamanNo ratings yet
- Prevent Hemolyzed SpecimensDocument1 pagePrevent Hemolyzed SpecimensQaiser ZamanNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 19 Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseDocument7 pagesLECTURE 19 Gestational Trophoblastic DiseaseCharisse Angelica MacedaNo ratings yet
- How Do We Take Care of Our Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesHow Do We Take Care of Our Endocrine SystemAndrei CunananNo ratings yet
- Special HistologyDocument64 pagesSpecial HistologyElijah KamaniNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Subfertile CoupleDocument12 pagesNursing Care of Subfertile CoupleSalea Fleur TaverronNo ratings yet
- ThyroidDocument96 pagesThyroidNimer Abdelhadi AliNo ratings yet
- Histology - Male Reproductive SystemDocument46 pagesHistology - Male Reproductive SystemKim AcostaNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4&5Document16 pagesBiology Form 4&5Ka Mun LeongNo ratings yet
- Understanding Hypothyroidism: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument14 pagesUnderstanding Hypothyroidism: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentMari IllustriousNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Health Guide Matches Key PartsDocument2 pagesReproductive Health Guide Matches Key Partsalan patinoNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal TissuesDocument7 pagesPlant and Animal Tissueskapil100% (1)
- Protozoa StructuresDocument2 pagesProtozoa StructuresKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Bio Exp 2 Hanis HaidaDocument10 pagesBio Exp 2 Hanis HaidaӇⱭӀƊⱭ ƘӇⱭlӀՏƳⱭ ՏƲƑƳⱭNo ratings yet
- Suprarenal GlandDocument19 pagesSuprarenal GlandKay BristolNo ratings yet
- READING PRACTICE TEST 3Document9 pagesREADING PRACTICE TEST 3Cao Son Dang Vu0% (1)