Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PMP Notes (In Progress)
Uploaded by
HmdecOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PMP Notes (In Progress)
Uploaded by
HmdecCopyright:
Available Formats
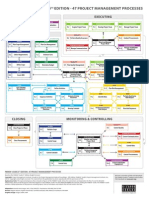
RISK MANAGEMENT
A risk is any uncertain event or condition that might affect your project +vely
or -vely.
Risk Mgmt plan:
The risk management plan is your guide to identifying and analyzing risks on you
r project.
It tells you who identifies and analyzes the risks, how they do it, and how ofte
n it happens.
Risk identification (P)
Risk analysis - Qual (P)
Risk analysis - Quant (P)
Risk response planning (P)
Risk monitoring and control (MC)
Sources of risk:
Technical
Resources
Critical path - schedule
Assumptions
Analysis:
Qualitative Risk Analysis helps you prioritize each risk and figure out its prob
ability and impact.
Quantitative analysis means taking measurements and coming up with exact numbers
to describe your risks.
Qualitative analysis focuses on the impact as the team judges it in planning.
Quantitative analysis focuses on getting the hard numbers to back up those judgm
ents.
Qualitative and quantitative analysis are all about ranking risks based on their
probability and impact.
Qualitative analysis is where you take the categories in your risk plan and assi
gn them to each of the
risks that youve identified.
Quantitative analysis focuses on gathering numbers to help evaluate risks and ma
ke the best
decisions about how to handle them.
Risk response planning: is figuring out what youll do if risks happen.
Avoid/Exploit, Mitigate/Enhance, Transfer/Enhance, Accept/Accept
Secondary risks are risks that come from a response you have to another risk.
If you dig a trench to stop landslides from taking out your camp, its always poss
ible for someone to fall
into the trench and get hurt.
Residual Risks are those that remain after your risk responses have been impleme
nted.
So even though you reinforce your tent stakes and get weatherproof gear, theres s
till a chance
that winds could destroy your camp if they are strong enough.
Risk Register:
Identified Risks
Potential Response
Root Cause Risk
Owner
Risk Category
Priority (H/M/L BASED on impact * probablity)
Urgency (H/M/L)
Risk monitoring and control process:
Risk monitoring should be done at every status meeting.
how to control risks:
Risk assessment
variance/Trend analysis
reserve analysis
technical performance measurement
risk audits
status meetings
management reserve: which is money set aside to handle any unknown costs that c
ome up on the project. Thats
a different kind of reserve than the one for controlling risks.
The kind of reserve used for risks is called a contingency reserve,because its u
se is contingent on a risk
actually materializing.
Project managers sometimes talk about both kinds of reserves together, because t
hey both have to show up on the same budget.
When they do, youll sometimes hear talk of known unknowns and unknown unknowns.
The management reserve is for unknown unknownsthings that you havent planned for
but could impact your project.
The contingency reserve is for known unknowns, or risks that you know about and
explicitly
planned for and put in your risk register.
--424 rita
COST MANAGEMENT
COst Planning (P)
Cost Estimation (P)
Cost Budgeting (P)
Cost Control (MC)
Cost Baseline: snapshot of planned budget
--386 oreily, 263 rita
COMMUNICATION MANAGEMENT
Communication planning (P)
Manage Communication (E)
Control Communication (MC)
Communication planning: documents how u manage and control communication
what is to be communicated
why
between whom
best method for communicating
responisiblity for sending
when & how often
STAKEHOLDER
Identify Stakeholder (I)
Plan Stakeholder management (P)
Manage Stakeholder (E)
Control Stakeholder management (MC)
identify ALL stakeholders
determine ALL their requirements
determine expectations
determine interests
determine level of influence
let stakeholders know what requirements will and what will not be met & why
Identify stakeholder:
Risk register-
ID
Name
Title
Supervisor
Contact
requirements
expectations
influence
role in prj
responsiiblity in project
classification
Manage stakeholder: is a communication functiont
Stakeholder should feel that thier needs & concerns are at least being considere
d even if not agreed to
why not prevent changes as much as possible by asking stakeholders what they exp
ect and clarifying any expectations that are not accurate. Manage stakeholde exp
ectations might involve walking them through what will occur to make sure they d
o not have unrealistic expectations. Requires attention to stakeholder needs whi
le work is been done & making sure trust is built, conflicts resolved and proble
ms prevented
rita-379
, ore-519
HR
Plan HR management (P)
Acquire Project team (E)
Develop Project team (E)
Manage Project team (E)
Plan HR management:
u plan out exactly which resources u will need, how u will train ur team, how u
make sure that they stay motivated
o/p-
project organization chart - shows how team members relate with each other
staffing mgmt plan - who u need by type, resource count, where they will come fr
om, when u need and what skills they need, training needs, R&R, release criteria
, compliance, safety
roles & responsiiblity - shows who is responsible for what
--o reilly 459, rita 333
Acquire Project team:
staffing assignments
resource availablity/calendars
updated staffing mgmt plan - changes to hr plan & other components of PM plan r
esulting from acquiring additional staff
--o reilly 459, rita 336
Develop Project team:
decrease turnover
improve individual knowledge & skill
improve teamwork
tools->
team building activities-
holiday, birthday celebrations
milestone parties
taking classes together
out-of-office trips
creating WBS
getting everyone involved in some way in planning the project
training-
ground rules-
colocation-
R&R-
output->
team performance assessment- looking at team effectiveness
rita 340, oreilly 468
Manage Project team:
involves day-to-day management of people
observation & conversation
project performance appraisals
issue log-
Issue#
Issue
Date Added
Raised by
person assigned
resolution due date
status
date resolved
resolution
--rita 340, oreilly 473
TIME
Plan schedule mgmt (p)
Define Activities (P)
Sequence activities (P)
estimate activity resources (p)
estimate activity duration (p)
Develop Schedule (p)
Control schedule (MC)
Define Activities:
O/P-
ACTIVITY LIST
activity attributes
milestone list
Sequence Activities:
o/p-
Network diagram i.e. Project schedule network diagram
gives logical relationships between activities
estimate activity resources:
o/p-
RBS (resource breakdown structure) - category , type(people/equipment/materials)
, quantity
estimate activity durations:
o/p: estimate
estimate how much time each activity will take
In cases where there are many unknowns and information to clarify is not availab
le, potential need for additional time or funds should be addressed with reserve
s through risk mgmt process. In risk mgmt, uncertainties are turned into identif
iable opportunities and threat(risks )
one-point estimation-
based on expert judgement or historical info or guess
only to be used for projects that do not require a detailed, highly reliable sch
edule
Analogous estimating (Top down)-
uses expert judgement and historical info
it means overall project estimate given to project mgmt from management or spons
or
Parametric estimation-
looks at relationships between variables on activity to calculate estimates.
3 point estimates-
will give more accurate range
develop schedule:
get initial schedule followed by schedule n/w analysis
schedule n/w analysis-
critical path
schedule compression
what-if scenario
resource levelling
critical chain method
schedule compression-
fast tracking
crashing
resource levlling-
is used to produce a resource-limited schedule
Lenghtens the schedule and increases the cost in order to deal with limited amt
of resources, resource availability and other resource constraints
critical chain method-
takes
into account both activity & resource dependencies
involves managing duration buffers so that you meet each individual milestone da
te and thus project milestone completion date
o/p-
project schedule which can be shown as-
network diagram - to show interdependencies between activities
milestone chart - to report to senior mgmt
bar chart or Gantt chart - to track progress & to report to team
schedule baseline - version of schedule used to manage the project and that the
project team's performance is measured against. It can be only changed as a resu
lt of formally approved change
Control schedule:
control means measure which means measure against the plan
it also involves taking corrective, preventive action over & over again during t
he life of project to keep project in line with plan.Also means looking out for
things that are causing changes and influencing the sources of changes
--rita 229
QUALITY:
quality is degree to which project fulfills requirements
quality is also conformance to requirements
Quality mgmt consists of below and includes creating & following policies, proce
dures to ensure project meets the intended needs of customer
Plan quality (P)
perform QA (E)
control quality - perform QC (MC)
Plan quality:
focusses on defning quality for project and identifying how it can be achieved.
ANSWERS the q - what is quality and how we will ensure it
perform QA:
its focus is on work being done in project and ensure that team is following the
processes/procedures as planned to produce the project deliverables
ANSWERS the q - r we following the procedures & processes as planned
can we improve the way we are doing
perform QC:
examines the actual deliverables produced on project. its purpose is to ensure t
hat the deliverables are correct and they meet planned level of quality
ANSWERS the q - r the results of work meeting the standards
plan quality:
tools:
control chart
flowchart
benchmarking
sampling
DOE
perform QA:
Tools
As used in Plan quality, perform QC +
Quality audits
process analysis - focus on identifying improvements that might be needed in pro
cesses
SCOPE
Scope Mgmt plan
Collect requirements (P)
Define scope (P)
Create WBS (P)
verify scope (MC)
Control Scope (MC)
Scope Mgmt plan: contains
how scope will be planned, executed and controlled
it answers the q of-
how scope will be achieved
what tool to use for planning
what org assets to use
Collect reqmts:
o/p-
requirements
reqmt mgmt plan
requirements traceability matrix - links reqmts to strategic objectives or/and o
ther reqmts
define scope: is primarily concerned with what is and is not included in project
and its deliverables
Project scope statement might include
Prjoect scope
product scope
deliverables
product acceptnce criteria
what is not part of the project
assumptions
constraints
Create WBS:
creation of WBS is topdown effort to decompose the deliverables and work require
d to produce them into smaller pieces called work packages
work package = noun = things not actions. WBS is deliverable oreiented.
Includes complete scope of project including product scope, project scope and pM
efforts
task= activity
baselines = simply approved version of certain pieces of project'
verify scope:
involves frequent, planned-in meetings with customer or sponsor to gain formal a
cceptance of deliverables during project
monitoring and controlling
verify scope is done to ensure that prj is on track from customer point of view
during the project rather than just hoping to get the final acceptance in projec
t closure. Customer will either accept deliverables or make change requests.
o/ps:
accepted deliverables
change requests
prj doc updates - updated to reflect completion or changes
verify scope results in formal acceptance by customer of interim deliverables
close project = gets acceptance or sign-off from customer for project or phase a
s whole
verify scope can be done at end of each project phase in project life cycle.
difference between verify scope and perform qc-
perform QC is generally done first to make sure the deliverable meets the requir
ement before it is shown to customer
QC deplt checks this.
In vrfy scope the customer checks and hopefully accepts the deliverables
Control Scope:
involves measuring project and product scope performance and managing scope base
line changes
need to have scope baseline, org reqmts, RTM.
U then have to measure scope performance (work completed) against scope baseline
to analyze any variances and decide if
corrective/preventive action is required.
it includes thinking abt where changes to scope are coming from proj, what can b
e done to prevent or remove the need for any more changes from source
--rita 156
You might also like
- Ricardo Vargas Simplified Pmbok Flow 5ed Color enDocument0 pagesRicardo Vargas Simplified Pmbok Flow 5ed Color enAhmad Altarawneh Mba100% (5)
- Ricardo Vargas Simplified Pmbok Flow 5ed Color enDocument0 pagesRicardo Vargas Simplified Pmbok Flow 5ed Color enAhmad Altarawneh Mba100% (5)
- Kanban Vs ScrumDocument41 pagesKanban Vs ScrumJayab JunkNo ratings yet
- PMP Sample Test Questions (Correct Answers Are Bolded)Document1 pagePMP Sample Test Questions (Correct Answers Are Bolded)CKJJ55@hotmail.cmNo ratings yet
- PMP Sample Test Questions (Correct Answers Are Bolded)Document1 pagePMP Sample Test Questions (Correct Answers Are Bolded)CKJJ55@hotmail.cmNo ratings yet
- PMP Sample Test Questions (Correct Answers Are Bolded)Document1 pagePMP Sample Test Questions (Correct Answers Are Bolded)CKJJ55@hotmail.cmNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5782)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Cost of QualityDocument14 pagesCost of QualitySreenath HtaneersNo ratings yet
- Folded PlateDocument14 pagesFolded PlateTanvi Yadav100% (3)
- Timing Relay, Stairwell Time Switch, Impulse Relay (6 FCT No.) Part No. TLK Catalog No. 101066Document2 pagesTiming Relay, Stairwell Time Switch, Impulse Relay (6 FCT No.) Part No. TLK Catalog No. 101066soufienne b.yahmedNo ratings yet
- VAYHAN AIR CONTROLS PRIVATE LIMITED Air Washer Unit SpecificationsDocument2 pagesVAYHAN AIR CONTROLS PRIVATE LIMITED Air Washer Unit SpecificationsSaleem BashaNo ratings yet
- Pyrometric ConesDocument1 pagePyrometric Coneslhoffman3No ratings yet
- Well Cementation: SynopsisDocument18 pagesWell Cementation: SynopsisHolger PinzonNo ratings yet
- Elevator Inspections FINALDocument17 pagesElevator Inspections FINALrkarlinNo ratings yet
- Preparing Ni-Ti Wire Samples for MicroscopyDocument8 pagesPreparing Ni-Ti Wire Samples for MicroscopyLevent öncelNo ratings yet
- LCA Training PackageDocument57 pagesLCA Training PackageSilvia PolliniNo ratings yet
- Performa EngineDocument26 pagesPerforma EngineAndri SetiyawanNo ratings yet
- Power King Tractor Owners ManualDocument54 pagesPower King Tractor Owners ManualBryan Potter100% (2)
- Damaging Effect of Moving Military Vehicles On Asphalt Pavement - Experimental StudyDocument8 pagesDamaging Effect of Moving Military Vehicles On Asphalt Pavement - Experimental StudyS. A. SultanNo ratings yet
- Technical Assessment - Sample Questions: Correct Answer: 1Document5 pagesTechnical Assessment - Sample Questions: Correct Answer: 1Shruti PNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Skipfish - ClubHACK MagazineDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Skipfish - ClubHACK MagazineAulia Haq AqobyNo ratings yet
- WS A25 Connecting Rod Types Guidelines For Assessment at Bottom End TB00-3301-16Document4 pagesWS A25 Connecting Rod Types Guidelines For Assessment at Bottom End TB00-3301-16DPNo ratings yet
- 76 5500 1 I1Document152 pages76 5500 1 I1shawn allen100% (4)
- Purchasing and Supply ManagementDocument78 pagesPurchasing and Supply Managementbilm100% (2)
- LR24A-MF 1 2 enDocument8 pagesLR24A-MF 1 2 enSasa RisticNo ratings yet
- GHS - Liquid (KOH Liquid)Document12 pagesGHS - Liquid (KOH Liquid)Yeniffer Geraldine guerra quispeNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Properties of Lithium Bromide Water Solutions at High TemperaturesDocument17 pagesThermodynamic Properties of Lithium Bromide Water Solutions at High TemperaturesAnonymous 7IKdlmNo ratings yet
- Ov2640 DS PDFDocument47 pagesOv2640 DS PDFpiramidon100% (1)
- WordPress For Beginners, The Missing GuideDocument85 pagesWordPress For Beginners, The Missing GuideNicoJulius50% (2)
- Paper tube adhesive composition increases strengthDocument4 pagesPaper tube adhesive composition increases strengthProduction SHVPMNo ratings yet
- HeatPipe WrapAroundDocument2 pagesHeatPipe WrapAroundJohnson ChuaNo ratings yet
- CE8395 QB - by WWW - Easyengineering.net 1Document18 pagesCE8395 QB - by WWW - Easyengineering.net 1sureshkumarNo ratings yet
- JSS - Reshaping Data with the reshape PackageDocument20 pagesJSS - Reshaping Data with the reshape PackagewhyawhaNo ratings yet
- Digestive Chamber: Scale NTSDocument1 pageDigestive Chamber: Scale NTSRomeo Beding Densen Jr.No ratings yet
- Comparative Study of MP Birla Cement and Other Brands Marketing MixDocument122 pagesComparative Study of MP Birla Cement and Other Brands Marketing MixduTyah seerionNo ratings yet
- Biotech. Facility DesignDocument17 pagesBiotech. Facility Designابُوالبَتُول ڈاکٹر صفدر علی قادری رضوی100% (1)
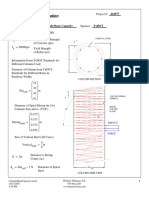
- ColumnShearCapacity 1Document4 pagesColumnShearCapacity 1Azhar PLNo ratings yet