Professional Documents
Culture Documents
My Liver Enzyme Lab - 2013 2014
Uploaded by
api-256032840Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
My Liver Enzyme Lab - 2013 2014
Uploaded by
api-256032840Copyright:
Available Formats
Liver Enzyme Lab
Background Information:
Liver and other living tissues contain the enzyme catalase. This enzyme breaks down hydrogen peroxide, which is a
harmful by-product of the process of cellular respiration if it builds up in concentration in the cells. If we use liver or other
tissue containing this enzyme, we can measure the effect of varying temperature and pH on enzyme activity. The
reaction for the break-down of hydrogen peroxide (by catalase) into water and oxygen gas is given below.
2H
2
O
2
2H
2
O + O
2
Hypothesis: If we increase the temperature the efficiency of the catalase enzyme will go up until
we reach the temperature at which the enzyme denatures.
Materials:
7 test tubes
1 test tube rack
Hydrogen Peroxide (H
2
O
2
)
Distilled water (H
2
O)
Raw Calf Liver
Boiling water bath (Hot plate, water, beaker)
Ice Bath (ice, water, cooler)
Procedure:
1. You will prepare the contents as outlined below for each corresponding test tube:
a. Test tube #1- Water
b. Test tube #2- Water & Liver
c. Test tube #3- Water, Liver, & H
2
O
2
d. Test tube #4- Water, Liver (that has been boiled several minutes or strong acid) & H
2
O
2
e. Test tube #5- Water, Liver (that has been cooled on ice for several minutes or strong base) & H
2
O
2
2. Make a data table.
3. Record a hypothesis for each test tube set-up before beginning the lab.
4. The volume of water will always be 5mL.
5. The size of the piece of liver should be approximately the same and relatively small.
6. Place test tubes 4 & 5 in ice/water bath as soon as you prepare it.
7. Test one test tube at a time.
a. Set-up your test tube.
b. Add 5mL of H
2
O
2
c. Record your observations for 3 minutes.
d. Interpret what you think has happened to the enzyme.
8. Clean up
#5
Water,
Liver(cooled) ,
H
2
O
2
No reaction
will occur
Bubbling;
reaction
occured
Liver rose to top
and rapid
bubbling
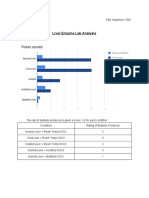
Methods Summary Chart:
Independent Variable
Temperature
Levels of the Independent Variable (if applicable)
Room temperature, Hot, Cold
Dependent Variable
Rate of oxygen production
Method for Measuring Changes in the Dependent
Variable
Amount of bubbles
Control Group (if applicable)
Room temperature and test tube #1 with just
water
Constants (factors that stay the same between your
control group and your experimental groups)
Amount of H
2
O
2,
type of liver, amount of water
Number of Trials 1 per treatment
Test Tube Contents Hypothesis Observation Interpretation
#1
Water
No Reaction Liver just sits
there
Its just water
#2
Water & liver
No reaction Liver just sits
in the water
Water is neutral
(pH 7)
#3
Water, Liver,
H
2
O
2
Reaction
occurs
Bubbles and
overflowed
out of tube
Hydrogen
peroxide is being
decomposed to
oxygen and water.
#4
Water,
Liver(boiled),
H
2
O
2
Reaction
occurs
Liver is
cooking; no
reaction
Liver enzymes
were denatured
in boiled water
No reaction occurred until H2O2 was added. Once the liver was boiled, no reaction
occurred. The hypothesis agreed with the results for all the tests except the tests that
included the boiled and cooled liver. For the boiled liver we hypothesized that a reaction
would occur, but none did. For the cooled liver, we hypothesized that a reaction would not
occur, but one did. Some potential errors could be timing procedures and another error could
have been that some solutions didnt have enough time for the reaction to actually occur. A
way to fix this would be by giving each at least thirty more minutes to react because some
reactions occur slower than others. To fix the timing procedures it would be best to start the
reactions all at the same time and have someone focus on each one of the test tubes so no
reaction occurs longer than the other ones.
You might also like
- Prac ReportDocument3 pagesPrac ReporttomsaikssNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Catalase Lab ReportDocument2 pagesEnzyme Catalase Lab ReportRizziel Nemes50% (2)
- Lab: Effect of Temperature On Enzymes: 2H O 2H O + ODocument2 pagesLab: Effect of Temperature On Enzymes: 2H O 2H O + Okathryn_bruyèreNo ratings yet
- Liver LabDocument6 pagesLiver Labtensai-sama100% (5)
- CatalaselabDocument3 pagesCatalaselabJaime TerrazoNo ratings yet
- FormallabreportenzymesDocument15 pagesFormallabreportenzymesapi-267590857No ratings yet
- Catalase Liver Enzyme Lab SB1b: BackgroundDocument2 pagesCatalase Liver Enzyme Lab SB1b: BackgroundTosin Abiola100% (1)
- AP Catalase Enzyme LabDocument4 pagesAP Catalase Enzyme LabAesthetic LoverNo ratings yet
- Biology Enzyme LabDocument4 pagesBiology Enzyme LabMaya PlewniaNo ratings yet
- Catalase Enzyme LabDocument3 pagesCatalase Enzyme LabBruce0% (1)
- Investigation - Enzymes and Hydrogen Peroxide - CERDocument5 pagesInvestigation - Enzymes and Hydrogen Peroxide - CERMathias CronqvistNo ratings yet
- Liver Enzyme Lab Report - Dylon FreerksenDocument6 pagesLiver Enzyme Lab Report - Dylon Freerksenapi-593477553No ratings yet
- Bio Lab 9 - Enzymes and TemperatureDocument2 pagesBio Lab 9 - Enzymes and TemperatureRuqayyah KhanNo ratings yet
- Catalase Enzyme Lab: Effect of Disc QuantityDocument4 pagesCatalase Enzyme Lab: Effect of Disc QuantityJJ GoorbarryNo ratings yet
- Catalase Enzyme Lab RevisedDocument4 pagesCatalase Enzyme Lab RevisedIda FaridaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Enzyme LabDocument7 pagesLab Report Enzyme LabrualrightNo ratings yet
- Efe Lance Enoch - Student Sheet - Investigation Enzymes and Hydrogen PeroxideDocument3 pagesEfe Lance Enoch - Student Sheet - Investigation Enzymes and Hydrogen Peroxideapi-701777795No ratings yet
- Enzyme LabDocument6 pagesEnzyme Labjoshua.yuNo ratings yet
- Liver Enzyme LabDocument2 pagesLiver Enzyme LabskeltenboiNo ratings yet
- Lab LiverenzymeskiyahnaberniceDocument2 pagesLab Liverenzymeskiyahnaberniceapi-296931788No ratings yet
- Liver Lab ReportDocument7 pagesLiver Lab Reportapi-591481733No ratings yet
- BIO121 - Experiment 4Document7 pagesBIO121 - Experiment 4Tan Ri ShenNo ratings yet
- Enzymes 2222222Document5 pagesEnzymes 2222222Anne KaoNo ratings yet
- Effect of Temperature On Enzyme ActivityDocument1 pageEffect of Temperature On Enzyme ActivityTy HawkesNo ratings yet
- EnzymesDocument6 pagesEnzymesBenedique Valdez0% (1)
- B1a06 HomeostasisDocument3 pagesB1a06 HomeostasisTom MaguireNo ratings yet
- 4 t2.5 Comp EnzymesDocument4 pages4 t2.5 Comp EnzymessushantNo ratings yet
- Enzyme LabDocument4 pagesEnzyme Labapi-542562922No ratings yet
- Enzyme Performance Affected by TemperatureDocument5 pagesEnzyme Performance Affected by TemperatureJeannete Claudia WulandariNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: EnzymesDocument6 pagesLab Report: EnzymesJim Goetz80% (25)
- Potato Enzyme Lab HonorsDocument2 pagesPotato Enzyme Lab HonorsCrisa ChinaNo ratings yet
- Bio 101 Sample Lab ReportDocument3 pagesBio 101 Sample Lab ReportRavinderenPichan67% (3)
- Investigate Effects of Environmental Factors on Enzyme ActivityDocument13 pagesInvestigate Effects of Environmental Factors on Enzyme ActivityIsland VitalNo ratings yet
- Liver Enzyme Lab Bio g10 2Document2 pagesLiver Enzyme Lab Bio g10 2api-462851756No ratings yet
- Lab Catalase 2Document2 pagesLab Catalase 2Siddharth KumraNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Substrate Concentration On The Activity of EnzymesDocument7 pagesThe Effect of Substrate Concentration On The Activity of Enzymesjosephine100% (1)
- Lap Report 2Document5 pagesLap Report 2api-340415931No ratings yet
- The Effect of Temperature On The Reaction Time of The Enzyme Peroxidase - Lab ReportDocument5 pagesThe Effect of Temperature On The Reaction Time of The Enzyme Peroxidase - Lab ReportAnonymous aZEERFhvNo ratings yet
- Effect of Temp & pH on EnzymeDocument3 pagesEffect of Temp & pH on Enzymejuliakang03No ratings yet
- Pengaruh Suhu Terhadap Kerja EnzimDocument6 pagesPengaruh Suhu Terhadap Kerja EnzimAlfrilin PadjaoNo ratings yet
- Practical 1 Biology (FINAL)Document3 pagesPractical 1 Biology (FINAL)Thet WinNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Activity FactorsDocument7 pagesEnzyme Activity FactorsIntan ZhofirNo ratings yet
- Catalase Lab 2014 Key 23Document6 pagesCatalase Lab 2014 Key 23kyungsoo studiesNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 BIO121Document12 pagesExperiment 4 BIO121Pui Ling ChanNo ratings yet
- Catalase enzyme reaction rateDocument4 pagesCatalase enzyme reaction rateNati ShitayeNo ratings yet
- Activity 6. Catalase EnzymeDocument6 pagesActivity 6. Catalase EnzymeBrian James BurtonNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Lab ResultsDocument13 pagesCellular Respiration Lab ResultsAlyona Booth100% (1)
- Homeostasis: The Enzyme CatalyseDocument4 pagesHomeostasis: The Enzyme CatalyseMonica Paris SisourathNo ratings yet
- The Potato LabDocument7 pagesThe Potato Labapi-31744529950% (2)
- Enzyme LabDocument5 pagesEnzyme LabJane ChongNo ratings yet
- Department of Other Natural Science Lab Activity 3 Course Code Biol 1012Document12 pagesDepartment of Other Natural Science Lab Activity 3 Course Code Biol 1012Aysheshim NegaNo ratings yet
- Bio Project (Enzymatic Reaction) by Sayan MukherjeeDocument20 pagesBio Project (Enzymatic Reaction) by Sayan Mukherjee9994739572sayanNo ratings yet
- Lab - Clock ReactionDocument3 pagesLab - Clock Reactiondxfvdm2zg8No ratings yet
- LabReport20 01Document9 pagesLabReport20 01Hania SwachaNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Lab Two: Enzyme CatalysisDocument4 pagesAP Biology Lab Two: Enzyme CatalysisCoolAsianDude95% (37)
- Water LabDocument4 pagesWater Labapi-317634731No ratings yet
- Labs CorretDocument27 pagesLabs CorretJayden NoelNo ratings yet
- Denature, or Unravel, Until It No Longer Has The Shape Necessary For Proper FunctioningDocument3 pagesDenature, or Unravel, Until It No Longer Has The Shape Necessary For Proper FunctioningRiccardo CatalanoNo ratings yet
- Liver Enzyme Lab Analysis: Fah Kasintorn 1001Document3 pagesLiver Enzyme Lab Analysis: Fah Kasintorn 1001api-441461742No ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolytes for Nursing StudentsFrom EverandFluid and Electrolytes for Nursing StudentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (12)
- Integrated Science2Document3 pagesIntegrated Science2Davies MasumbaNo ratings yet
- Diagrama Eletrico Caterpillar 416 eDocument31 pagesDiagrama Eletrico Caterpillar 416 eJoão Basilio da Roza MartinsNo ratings yet
- I. Objective III. Problem Solving. Show Your SolutionsDocument1 pageI. Objective III. Problem Solving. Show Your SolutionsYsmael Alongan B. MangorsiNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Section (H) (Lab Report 3)Document9 pagesGroup 3 Section (H) (Lab Report 3)Shoaib KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Understanding Stress and StrainDocument17 pagesChapter 2: Understanding Stress and StrainMohammed IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab Report 1Document4 pagesPhysics Lab Report 1Rosalina ColetoNo ratings yet
- PERMA E-622 ElectrodeDocument1 pagePERMA E-622 Electrodepedromiguel20No ratings yet
- Science 9 Q2 Week 1Document11 pagesScience 9 Q2 Week 1Sofia ErruaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 The Behavior of GasesDocument59 pagesChapter 14 The Behavior of GasesHeather Wright100% (2)
- Grade 7 Q1 M4B Elements and CompoundsDocument17 pagesGrade 7 Q1 M4B Elements and CompoundsGia AbongNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium 1582Document21 pagesChemical Equilibrium 1582mohammadalirizwan423No ratings yet
- NORM in SaudiDocument30 pagesNORM in SaudiRosa MendozaNo ratings yet
- Flow Performance ObjectivesDocument18 pagesFlow Performance ObjectivesStanley EkechukwuNo ratings yet
- Sick BuildingsyndromeDocument11 pagesSick BuildingsyndromeAvipsha MohantyNo ratings yet
- Low Temperature Distillation (Ltdis) : Make The Right Choice..Document4 pagesLow Temperature Distillation (Ltdis) : Make The Right Choice..LexNo ratings yet
- 0620 - w16 - Ms - 32 Paper 3 Chemistry MArk SchemeDocument9 pages0620 - w16 - Ms - 32 Paper 3 Chemistry MArk SchemeCHANDREN ARUMUGAM100% (1)
- AmplifyDocument2 pagesAmplifyİsmail YakinNo ratings yet
- Corrosion ResistanceDocument36 pagesCorrosion ResistanceSamnang HangNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Biomolecules: LessonDocument28 pagesStructure and Function of Biomolecules: Lessonkim leNo ratings yet
- Creep FailureDocument21 pagesCreep FailureJericho HernanNo ratings yet
- B567 PDFDocument9 pagesB567 PDFCarlos Alberto Oviedo100% (1)
- Toxic Gas Exposure Limits and Alarm Levels, Portable Gas DetectionDocument1 pageToxic Gas Exposure Limits and Alarm Levels, Portable Gas DetectionwisnukerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3rd GASES MCQsDocument7 pagesChapter 3rd GASES MCQsbushra3ansari25% (4)
- Effluent Treatment Plant PhilosophyDocument2 pagesEffluent Treatment Plant PhilosophyLeonardo IndraNo ratings yet
- Alloys MGDocument16 pagesAlloys MGJuan Diego Ospina FlorezNo ratings yet
- Coagulation-Flocculation Mechanisms in Wastewater Treatment Plants Through Zeta Potential MeasurementsDocument11 pagesCoagulation-Flocculation Mechanisms in Wastewater Treatment Plants Through Zeta Potential MeasurementsAbiodun GbengaNo ratings yet
- Platinum Electroplating BathsDocument9 pagesPlatinum Electroplating Bathsm_f_deathNo ratings yet
- Weathering Process Breaks Down RocksDocument22 pagesWeathering Process Breaks Down RocksThev RubanNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Potassium TrisDocument3 pagesPreparation of Potassium TrisAndile ManyoniNo ratings yet