Professional Documents
Culture Documents
III SEMESTER ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS AND MEASUREMENTS
Uploaded by
SriramOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
III SEMESTER ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS AND MEASUREMENTS
Uploaded by
SriramCopyright:
Available Formats
III SEMESTER - ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS (Core Subject 1)
UNIT-I
Rectifiers half wave rectifier, bridge rectifier, Inductor Capacitor-L type filters
ripple factor voltage regulator (series type) current limit over load production
Introduction to IC fixed and variable IC 723 ,78XX,79XX voltage regulators- formulas value
substitution problems.
UNIT-II
Amplifiers- general principle of operation classification of amplifiers classification
of distortion (amplitudes, frequency, phase) RC coupled amplifiers gain frequency
response input and output impedance- multistage amplifiers- transformer couple
amplifiers- frequency response formula value substitution problems.
UNIT-III
Introduction classification power amplifier class A power amplifier class A push
pull amplifier class B power amplifier class B push pull amplifier class C power
amplifiers- class C push pull amplifiers- power dissipation output power distributors
formula value substitution problems.
UNIT-IV
Feed back- basic concepts- characteristics- effect of negative feed back - on gain
stability distortion band width analysis of voltage and current feed back amplifier
circuits- formula value substitution problems.
UNIT-V
Classification of oscillators-use of positive feed back- barkhausen criterion for
oscillation colpitts oscillator Hartley oscillator wein bridge oscillator- phase shift
oscillator- crystal oscillator- frequency stability of oscillators- multivibrators
(mono,astable,bistable)- formula value substitution problems.
Books for study and references:
1. Electronic devices and circuits Millman & Halkias
2. Electronic devices and applications and integrated circuits-Mathu.
3. Basic Electronics B.L Theraja
4. Electronic devices and circuits G.K Mithal,Khanna publishers.
5. Electronic devices and circuits Allen mottershead
6. Problems and solutions of electronic devices and circuits- Experience Teachers
(CBS publication, New Delhi)
III SEMESTER
ELECTRONIC MEASUREMENTS AND CIRCUIT THEORY (Core Subject 2)
UNIT-I
Measurements, errors in measurements-standard, Classification characteristics of
Transducers, AC/DC Bridge measurements and their applications.
UNIT-II
A.F Spectrum Analyser Digital Voltmeters and Multimeters, AC voltmeter- vector
voltmeter- CRO Block Diagram single beam- dual trace- Sampling oscilloscope, Analog
Digital recorders and printers.
UNIT-III
Ohms Law Kirchoffs Laws and their applications Branch and loop cun mesh and
node analysis
UNIT-IV
Fundamental ideas of AC circuits impedance of RL, RC ,RLC circuits- Resonance
in AC circuits series and parallel single tuned and double tuned co circuits
UNIT-V
Network graph of a network concept of tree- branches and chords dual networks-
Networks theorems: Superposition, Thevenin Norton Maximum Pow transfer Theorem.
Books for Study and references:
1. C.S Rangan Instrumentation Devices and Systems Tata McGraw Hill
2. Copper Electronic Instrumentation and measurement Techniques PHI
3. A.J Bouwels Digital Instrumentation , McGraw Hill,1986
4. C.Barney Intelligent InstrumentationPHI,1985
5. Oliver and Cage Electronic Measurements and Instrumentation McGraw 1975
6. Deobelin Measurements Systems McGraw HILL,1990
7. Electronic Circuits Edminister (Schaum outline series- TMH)
8. Circuits and networks, Analysis and synthesis A.Sudakar & S.P Shyar (TMH)
9. Networks, analysis and synthesis Umesh sinha
10. Eltronic circuits theory Dr. M. Arumugam & Dr. N.Prem Kumaran
ELECTRICAL INSTRUMENTS AND MEASUREMENT (Skill based)
UNIT I
Principle of operation of maters- Essentials of indicating instruments-Deflecting controlling
Torque-Dampling Torque- Moving iron ammeter and voltmeter-Attracting moving iron
instrument Repulsion type moving iron instrument Extension of range.
UNIT II
Moving coil instruments- permanent magnet type instrument Advantages and
disadvantages of PMMC instrument- Extension of range Electrodynamometer type
instruments- Hot wire instruments.
UNIT III
Megger- Induction Ammeter Induction voltmeter Error in Induction Instruments-
advantages and disadvantages-Electrostatic Voltmeters-Attracted disc type voltr quadrant
voltmeter-kelvins Multicellular voltmeter-Advantages and Limitations of Electrostatic
Voltmeters-Range extension of electrostatic voltmeters.
UNIT IV
Wattmeter-Dynamometer wattmeter Wattmeter errors-Induction wattmeter- Advantages
and limitations of induction wattmeters- Energy meters-Electrolytic meter-Motor meter-
Errors in motor Meters-Induction type single phase watt hour meter Errors in induction
watthour meters
UNIT V
Ballastic Galvanometer Vibration Galvanometer- Vibrating reed frequency meter-
Electrodynamic Frequency meter- Moving iron frequency meter-Electrodynamic power
Factor meter-Moving iron Power Factor Meter-Instrument Transformers-Current
Transformer-Clip on type power Transformer-Potential Transformer.
TEXT BOOK
Electrical Technology-B.L.Theraja A.K.Theraja
Reference Book
Basic electrical engg-P.S.Dhogal TMH
DIGITAL DATA COMMUNICATION
UNIT I
Ray form coding techniques, Information in a communication system-low pass, band pass,
PCM, quantizing and encoding- companding-DM-ADM-comparison of PCM and DM on the
basics of speech signals-Telegraphy-Telex-FDM and TDM- coding speech at low bit rays-
typical telephone multiplexing scheme with details of bit, word and frame-
Sysnchornization.
UNIT II
Modulation techniques and codes- Band pass data transmission systems- PSK FSK-
DPSK-QPSK-MSK-receiver implementation-signal detection techniques definition of
codes- need for line shaping signals-RZ-NRZ-Shannons noiseless coding theorem-
Shannon coding Huffmans coding.
UNIT III
Discrete signals-information rate- Shannons theorem-channel capacity- symmetric
channels- deterministic and noiseless channels- entropy of continuous signals- rate of
transmission capacity of band limited channels-Shannon Hartely law- Band width- SNR
trade off- Bandwidth efficiency- Shannons llimit.
UNIT IV
Half duplex full duplex-synchronous and asynchronous communication- telephone
system- multiplexer- circuit, message and packet switching- concept of protocols- ISO-OSI
reference model- functions of each layers-RS 232C, RS422A, V.24-SDLC,HDLC
procedures.
UNIT V(LAN and Internet working)
TCP/IP APQ and protocols used in each layer-LAN topology and standards IEEE
802.3(CSMA/CD).IEEE 802.4(token bus), Token ring, purse ALOHA protocols,
conventional channel allocation methods, Radio and satellites networks, ISDN , Local Area
Network.
Ref.Books:
Digital communication-Simon Haykins
Communication Systems-Tauv and Schillling
Digital Communications - Prokis.
Introduction to Data communications and networking -M.Schwarts.
Computer Networks -Tanenbaum.
COMPUTER HARDWARE
III SEMESTER
UNIT I
CPU Essentials Processor modes Modern CPU Concepts Architectural
performance features the Intels CPU.
UNIT II
Essential memory concepts Memory organizations Memory packages Modules
Logical Memory Organizations Memory Considerations Memory types Memory
techniques Selecting and Installing memory.
UNIT III
Active motherboards sockets and slots Intel D8050GB Pentium board Mother
Board Expansion slots Form factor Upgrading a mother board Chipsets North
Bridge South Bridge.
UNIT IV
Power Suppliers and Power Management Concepts of switching regulation
potential Power Problems Power Management. The floppy drive The magnetic storage
Magnetic recording principles data and disk organization floppy drive hard drive data
organization and hard drive sector layout.
UNIT V
IDE drive standards and features Hard drive electronics CDROM drive
construction CDROM electronics DVD-ROM DVD media DVD drive and decoder.
TEXT BOOK
1. Stephen J.Bigelow, Trouble Shooting, Maintaining and Repairing PCs, Tata
McGraw-Hill, New Delhi, 2001.
REFERENCES
1. Craig Zacker & John Rourke , The Complete Reference : PC Hardware, Tata
McGraw-Hill, New Delhi, 2001.
2. Mike Mayers, Introduction to PC Hardware and Trouble Shooting , Tata
McGraw-Hill, New Delhi, 2003.
3. B.Govindarajulu, IBM PC and Clones hardware trouble shooting and
Maintenance, Tata McGraw-Hill, New Delhi, 2002.
IV SEMESTER - LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
UNIT I
Differential amplifiers-dual input- balance output differential amplifier-current
monitor-level translator- block diagram representation of typical op amp interpreting a
typical set of data sheets- the ideal opamp-equivalent circuit of an op amp ideal voltage
transfer curve.
UNIT II
Input off set voltage input bias current input offset current total output offset
voltage input and output resistance thermal drift CMRR- voltage shunt and voltage
series feed back amplifiers.
UNIT III
Frequency response of iniatially compensated op amp open loop frequency
response- closed loop Frequency response circuit stability- slew rate.
Filters: low pass filters- high pass filters band pass filters- band reject filters- all pass
filters.
UNIT IV
Adder subtractor Integrator- differentiator- V to I and I to V converter. Oscillator:
Principles- types frequency stability phase shift oscillator- wein bridge oscillator-square
wave generator triangular wave generator.
UNIT V
Comparator- Schmitt trigger-clipper and clamper- peak detector-zero crossing
detectors IC 555 function block diagram mono stable operation astable operation
applications sawtooth wave generator.
Books for study and Reference:
1. Linear Integrated Circuit-D.Roychoudry & Shail jain( New age publications 1999).
2. Operational amplifiers and linear integrated circuits-F.Couglin & Drison(4
th
edition
prentice hall of India,1992).
3. Operational amplifiers and linear integrated circuits-Denton J. Dailey,Mc Graw Hill
1989.
4. Operational amplifiers and linear integrated circuits-Ramakant A. Gayakwad 3 rd
edition PHI.
5. second Edn. Operational amplifiers and Linear Ics-David A. Bell.
COMPUTER NETWORKS (Major Elective)
Unit I:
Data communication Concepts: Transmission media- data encoding- interface and
modems- multiplexing- error detection and correction- digital subscriber line-circuit
switching- packet switching- message switching.
Unit II:
Wide area networks: ISO-ISO layered architecture Function of the layers- Data link
protocols-HDLC, LAPB, LAPD, and Inter networking devices-Repeaters, Bridges,
Routers,Routing algorithms- Distance vector routing, link state routing ,x.25 protocol,
Congestion control.
Unit III:
Frame relay and ATM networks: Frame rely operation-layer and traffic control: ATM
networks-Architecture switching, layers services classes.
Unit IV:
Local Area Networks:
LAN Topology- Ethernet-Token bus-Token ring- FDDI-Wireless LAN,ATM LAN-IEEE 802
Medium access control layer standard-Random access protocols-ALOHA-slotted ALOHA.
Unit V:
OSI Layers:
Transport layer issue-session layer-synchronization-Presentationlayer-Encryption,
decryption, Application layer- message handling system, file transfer, virtual terminal-E-
mail.
Textbook:
1. William Stallings, Data and computer communication, Sixth edition, Pearson
education Asia 2002.
References:
1. Behrouz A,Forouzan, Data communication and networking, second edition, Tata
McGraw-Hill2000
2. Fred Halsall,Data communication, computer networks and open system, Fourth
edition, Addison Wesley, 1995.
3. Andrew S.Tanenbaum, Computer networks, Third Edition, PHI, 1996.
POWER CONVERTORS (Non Major Elective)
Unit 1
DC AC PWM inverters: Introduction Principle of operation Performance
parameters - Single phase bridge inverters.
Unit II
Three phase inverters Voltage control of single phase inverters Voltage control of
three phase inverters Current source inverters.
Unit III
Resonant pulse inverters; Introduction Series resonant inverters Paraller
resonant inverters Zero current switching resonant converter.
Unit IV
Zero voltage switching resonant converter Two quadrant ZVS resonant converter-
Resonant DC link inverter.
Unit V
Principle of phase controlled converter operation Single phase full converter
Single phase dual converter.
Text book:
Power Electronics Circuits ,Devices & Applications - Rashid M.H.
ALLIED- ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION
IV SEMESTER: COURSE II ADVANCED COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
UNIT I: Optical Fiber Transmission Media
Optical communication Advantages of optical fibres Block diagram of an
optical fiber communication system. Optical fiber construction, light propagation
Refraction, Refractive index, Snells law optical fiber configurations coupling
fibres fiber splicing optical fiber connections coupling losses; Optical sources
LEDs, ILD, Light Detectors PIN diodes.
UNIT II: Telephone instrument and signals
Introduction Carbon Granule transmitter, Receiving transducer, Simple local
battery telephone circuit Functions of Telephone Set, Block diagram of Telephone
set, Basic telephone call procedures, Call progress tones and signals Dial tone,
DTMF tone, Dial tone, Dial pulse, Station busy, Equipment busy, Ringing, Ring-
back, Receiver on/off Hook, Cordless telephones, Caller ID, Electronic Telephones.
UNIT III: Public Telephone Network and Switching
Instruments, Local Loops, Trunk circuits and Exchanges, Local central office
telephone Exchanges, Operator assisted local exchanges, Automated central office
switches and exchanges, Matrix Switching, Step by step switching.
UNIT IV: Cellular telephone Concept
Cellular telephone Fundamental concepts of cellular telephones
Frequency reuse, Interference Co-channel, Adjacent channel, Cell splitting,
Sectoring, Segmentation and Duplication, Cellular system topology, Roaming,
handoff, Cellular Telephone network components Electronic switching center, cell-
Site controller, Radio Transceiver, System interconnects, Mobile and Portable
Telephone units, Communication protocols.
UNIT V: Satellite Communications
Keplers laws, Satellite orbital pattern, Geosynchronous satellites, Satellite
classifications, Spacing and Frequency allocation, Satellite Antenna Radiation
patterns, Footprints, Satellite system link models Uplink, transponder, Downlink,
Cross-links.
Reference Books:
1. Advanced electronics communication systems, Wayne Tomasi, PHI, 6
th
Edition
2. Telecommunication Systems, P.H.Smale, Wheeler Publication, 2
nd
Edition
3. Optical Fibre Communications, Gerd Kaiser, TMH, 2
nd
Edition
Satellite Communications, Roddy, TMH, 4
th
Edition
Allied - Communication Laboratory
1. Suppressed carrier AM
2. Voltage to frequency converter.
3. Study of AGC(Automatic gain control)
4. Study of Mixer circuit
5. Study of IF amplifier
6. Study of analog signal sampling
7. Directional characteristics of micro phone and loud speakers
8. Time division MUX and DeXUX
9. PCM encoder
10. PCM detector
11. ASK modulator and detector
12. PSK modulator and detector
13. Low high power splitter using MATLAB
14. Band pass and Band stop filter using MATLAB
PERSONALITY DEVELOPMENT
Unit I
Evolution Life cycle Infancy Childhood,Adolescence,Adulthood,Old age.
Unit II
Concept of Personality Definition of personality Need for understanding personality
Nature of personality Formation of personality.
Unit III
Personality, Some characteristics Imagery, achievement, Affiliation,Extension,Power.
Self -meaning,Self- concept,Self esteem,Perceptions and attitudes and self development.
Unit IV
Theories of personality Heredity Theory Environmental theory - Family
,culture,Society and situation Psychoanalytic theory.
Unit V
Types of personalities,Type A,Type B,Introvert Extrovert- Locus of control,Styles-
authoritarian,democratic,problem solving. Skills- communication
skills,etiquette,Presentation skills ,interpersonal skills , leadership skills.
Books for study and reference:
1. John Aurther,Personality Development,Lotus Press,2009,New delhi.
2. Stephen P.Robbins Organizational Behaviour Ninth Edition,Ashok
k.Ghosh,Prentice Hall of India Pvt Ltd 2000,New Delhi.
3. Nirmal Singh,Organizational Behaviour,Deep & Deep Publications Pvt Ltd 2001,
New Delhi.
4. Gangadhar rao.M.V.S.P and Narayanan .P.S.,Organizational Behaviour,Konark
Publishers Pvt Ltd 1997,New Delhi.
5. Chandan.Jit S, Organizational Behaviour,Vikaas Publishing House
Pvt.Ltd,1996,New Delhi.
6. Aswathappa.K. Organizational Behaviour,Himalaya Publishing House
Pvt.Ltd,2004,Mumbai.
7. Rao.V.S.P Narayana.P.S. Organizational Theory and Behaviour 2
nd
edition,
Konark Publishers Pvt Ltd ,2000,New Delhi.
8. Chandan.Jit S, Organizational Behaviour, 3
nd
edition Vikaas Publishing House
Pvt.Ltd,2005,New Delhi.
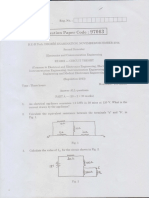
PRACTICAL II - ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS AND MEASUREMENTS LAB
(All experiments have to be carried out compulsorily)
Electronics circuits
1. Study and use of CRO
2. Half wave rectifier and Full wave rectifier
3. Fixed dual power supply construction using ICs
4. RC coupled amplifier two stage
5. FET amplifier
6. RC phase shift oscillator
7. Hartley oscillator
8. Colpitts oscillator
9. Clipping and Clamping circuits
10. Monostable multivibrator
11. Astable multivibrator
Measurements lab:
1.Wheatstone bridge
2.Kelvin double bridge
3.Maxwell bridge
4.Hay bridge
5.Schering bridge
6.LVDT
7.Displacement meter
8.Transducer applications and measurement
9.Extension of range of PMMC meter
10.Current measurement using sensors.
Students should be encouraged to do a mini project which should be submitter at the
end of the IV semester.
You might also like
- ELECTRICAL TNPSC Engineering Service ExamDocument3 pagesELECTRICAL TNPSC Engineering Service ExamM KumarNo ratings yet
- Tamil Nadu Public Service Commission: Code No.206Document4 pagesTamil Nadu Public Service Commission: Code No.206Kaviarasu ThangarajNo ratings yet
- Electric and InstrumentDocument3 pagesElectric and InstrumentjvigforuNo ratings yet
- 5TH Sem SyllabusDocument16 pages5TH Sem SyllabusHunter HarshaNo ratings yet
- Sub Engrr Electrical - KSEBDocument4 pagesSub Engrr Electrical - KSEBk keralaNo ratings yet
- Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering & Instrumentation and Control EngineeringDocument4 pagesElectronics and Instrumentation Engineering & Instrumentation and Control EngineeringSakthi Sekar CbiNo ratings yet
- S.V.University, Tirupati: Semester: IiDocument13 pagesS.V.University, Tirupati: Semester: IiMallikaNo ratings yet
- Degree Standard-Electrical and InstrumentationDocument3 pagesDegree Standard-Electrical and InstrumentationPrem KumarNo ratings yet
- MG University 5th Ece Full SyllabusDocument9 pagesMG University 5th Ece Full SyllabusJinu MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Ec SyllabusDocument51 pagesEc SyllabusAjith AreNo ratings yet
- Process Control Lab ManualDocument338 pagesProcess Control Lab ManualMichael Edwards75% (4)
- Electronics & Instrumentation CoursesDocument214 pagesElectronics & Instrumentation Coursessohaib_86No ratings yet
- IES Electrical Engg.Document2 pagesIES Electrical Engg.Anil BishnoiNo ratings yet
- MG University Ece Full SyllabusDocument66 pagesMG University Ece Full SyllabusA dominicNo ratings yet
- Prist University - Ece 2nd Year Detailed SyllabusDocument21 pagesPrist University - Ece 2nd Year Detailed SyllabusPrist UniversityNo ratings yet
- M.Tech. Entrance Exam Syllabus for Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument3 pagesM.Tech. Entrance Exam Syllabus for Electrical and Electronics EngineeringmjrsudhakarNo ratings yet
- Electronic InstrumentationDocument2 pagesElectronic InstrumentationcsjaisonNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis.: Unit I IntroductionDocument7 pagesPower System Analysis.: Unit I IntroductionJagadeesh MannivannanNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronics Engg. B.Tech. Semester-Vii: Course Code Course Title L T P CreditsDocument26 pagesElectrical and Electronics Engg. B.Tech. Semester-Vii: Course Code Course Title L T P CreditsAbhishek Kumar ChambelNo ratings yet
- Sastra Universiy: B.Tech (Eee) ProgrammeDocument13 pagesSastra Universiy: B.Tech (Eee) ProgrammeSriram VenkatachariNo ratings yet
- 3 2 SyllabusDocument16 pages3 2 SyllabusRamNo ratings yet
- Syllabus 5th SemesterDocument5 pagesSyllabus 5th SemestersultangetinNo ratings yet
- Detailed Syllabus FOR 5 Semester: Anpat Niversity U. V. Patel College of Engineering Ganpat Vidyanagar, Kherva-382711Document10 pagesDetailed Syllabus FOR 5 Semester: Anpat Niversity U. V. Patel College of Engineering Ganpat Vidyanagar, Kherva-382711Maulik SharmaNo ratings yet
- EC1601 Semester VI Electronics MeasurementsDocument11 pagesEC1601 Semester VI Electronics MeasurementsDileepNo ratings yet
- s6 SyllabusDocument9 pagess6 SyllabusPrabith PradeepNo ratings yet
- New Syllabus Electrical Electrical and Electronics Engineering DiplomaDocument3 pagesNew Syllabus Electrical Electrical and Electronics Engineering DiplomadivyasatthishNo ratings yet
- Anna University 7th Sem SyllabusDocument5 pagesAnna University 7th Sem Syllabusamit8634No ratings yet
- 4th Sem SyllabusDocument10 pages4th Sem SyllabusAswin RaghavNo ratings yet
- M.Sc. Electronics & Communication PAPER - 1 Mathematical Methods Unit-IDocument16 pagesM.Sc. Electronics & Communication PAPER - 1 Mathematical Methods Unit-IgadeshaNo ratings yet
- bscelectronics (1)Document7 pagesbscelectronics (1)chinnuyadav523No ratings yet
- Ine 312:: Microprocessors and Interfacing: Course OutcomeDocument4 pagesIne 312:: Microprocessors and Interfacing: Course OutcomeVineeth KumarNo ratings yet
- B techecesyllabusOLDDocument61 pagesB techecesyllabusOLDNevil BastiansunnyNo ratings yet
- Aero MechDocument1 pageAero MechSathyanarayananNo ratings yet
- EX-701 Utilization of Electrical EnergyDocument10 pagesEX-701 Utilization of Electrical EnergyVikesh gondNo ratings yet
- 6th Semester Arrears Plus Current Subject's Syllabus: Arrear SubjectsDocument10 pages6th Semester Arrears Plus Current Subject's Syllabus: Arrear SubjectsRahul DawnNo ratings yet
- Be Ece 7th Semester Syllabus For Regulation 2008Document11 pagesBe Ece 7th Semester Syllabus For Regulation 2008tannamalaiNo ratings yet
- ElectronicsDocument5 pagesElectronicsriyasbasheerNo ratings yet
- Optimal Design of Electrical MachinesDocument10 pagesOptimal Design of Electrical MachinesShammi Shekhar ParmarNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Instruction and Examination B.Tech (Instrumentation Engineering)Document37 pagesScheme of Instruction and Examination B.Tech (Instrumentation Engineering)Jagabandhu KarNo ratings yet
- ECE Diploma StandardDocument3 pagesECE Diploma StandarddivyasatthishNo ratings yet
- Xee 701social Engineering 3 0 0 3Document7 pagesXee 701social Engineering 3 0 0 3jamesprabuwwfNo ratings yet
- RSMSSB JEN Electrical SyllabusDocument2 pagesRSMSSB JEN Electrical Syllabusashwinivema1980No ratings yet
- Syllabus EEE Semester-5Document6 pagesSyllabus EEE Semester-5Murali KrishnanNo ratings yet
- RGPV Syllabus Cbgs Ec 3 Sem All SubjectsDocument8 pagesRGPV Syllabus Cbgs Ec 3 Sem All SubjectsAyushNo ratings yet
- CUSAT B.TECH Degree Course – Scheme of Examinations & Syllabus 2006 EE Sem VIDocument7 pagesCUSAT B.TECH Degree Course – Scheme of Examinations & Syllabus 2006 EE Sem VIRohithnarayanNo ratings yet
- Anna University Coimbatore SyllabusDocument7 pagesAnna University Coimbatore SyllabuscyogalakshmiNo ratings yet
- EeeDocument391 pagesEeeGhulam AbbasNo ratings yet
- EeeDocument268 pagesEeeNajiruddin ShaikNo ratings yet
- Deputy Engineer ElectricalDocument3 pagesDeputy Engineer ElectricalSargi BeepumohanNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Copy M&IDocument1 pageSyllabus Copy M&Inuthal4uNo ratings yet
- Mahatma Gandhi University 5th Sem B.Tech Electrical Engineering Scheme & Syllabus 2002Document12 pagesMahatma Gandhi University 5th Sem B.Tech Electrical Engineering Scheme & Syllabus 2002Rajesh RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Asst Enggr Electrical KSEBDocument4 pagesAsst Enggr Electrical KSEBJibin PKNo ratings yet
- 5 Sem PDFDocument7 pages5 Sem PDFNikhil GurawaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Paper - I 1. EM TheoryDocument3 pagesElectrical Engineering Paper - I 1. EM TheorySumanth YalagandulaNo ratings yet
- 5th SEMDocument10 pages5th SEMChandra SekaranNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports: Volume 5: Measurement Circuits, Safeguards and Energy StorageFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports: Volume 5: Measurement Circuits, Safeguards and Energy StorageNo ratings yet
- EC8661 VLSI Design LaboratoryDocument53 pagesEC8661 VLSI Design LaboratorySriram100% (4)
- MeasurementsDocument12 pagesMeasurementsSriramNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory 2014 - Apr MayDocument6 pagesCircuit Theory 2014 - Apr MaySriramNo ratings yet
- What Determines The Color of An LED?: SemiconductingDocument1 pageWhat Determines The Color of An LED?: SemiconductingSriramNo ratings yet
- Ec 6501Document1 pageEc 6501SriramNo ratings yet
- 2014 - Apr May PDFDocument4 pages2014 - Apr May PDFSriramNo ratings yet
- VLSI Design Lab EC-6612-nDocument58 pagesVLSI Design Lab EC-6612-nSriramNo ratings yet
- Principles of Management: Lesson PlanDocument23 pagesPrinciples of Management: Lesson PlanSriram100% (1)
- EC6612 - VLSI Design Laboratory ManualDocument39 pagesEC6612 - VLSI Design Laboratory ManualSriramNo ratings yet
- Data Path Circuits - EC6601Document10 pagesData Path Circuits - EC6601SriramNo ratings yet
- Design Entry and Simulation of Sequential CircuitsDocument7 pagesDesign Entry and Simulation of Sequential CircuitsSriramNo ratings yet
- EC6702Document2 pagesEC6702SriramNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument18 pagesConcept MapSriramNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communication - EC 2401 - I - Answer KeyDocument9 pagesWireless Communication - EC 2401 - I - Answer KeySriramNo ratings yet
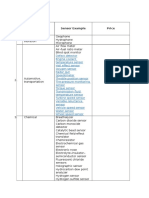
- Sensors: SL - N o Application Sensor Example PriceDocument6 pagesSensors: SL - N o Application Sensor Example PriceSriramNo ratings yet
- VerilogDocument12 pagesVerilogSriramNo ratings yet
- DSP WorkshopDocument2 pagesDSP WorkshopSriramNo ratings yet
- Ec6512 Communication Systems Laboratory ManuslDocument86 pagesEc6512 Communication Systems Laboratory ManuslSriram71% (24)
- Ece 2013Document14 pagesEce 2013SriramNo ratings yet
- ECE Department Course DetailsDocument151 pagesECE Department Course DetailsSriramNo ratings yet
- Verilog Course ManualDocument60 pagesVerilog Course ManualSriramNo ratings yet
- Ec6512 Communication Systems Laboratory ManuslDocument86 pagesEc6512 Communication Systems Laboratory ManuslSriram71% (24)
- EC2354 - VLSI DesignDocument2 pagesEC2354 - VLSI DesignSriramNo ratings yet
- Ece 2008Document27 pagesEce 2008SriramNo ratings yet
- Ec2357 - Vlsi Design LaboratoryDocument45 pagesEc2357 - Vlsi Design LaboratorySriramNo ratings yet
- Kalasalingam University ECE302 Analog Communication Question BankDocument6 pagesKalasalingam University ECE302 Analog Communication Question BankSriramNo ratings yet
- SEMESTER Requirements Lab EquipmentDocument29 pagesSEMESTER Requirements Lab EquipmentSriramNo ratings yet
- Verilog Lab ProgramsDocument25 pagesVerilog Lab ProgramsSriramNo ratings yet
- Analog DesignDocument4 pagesAnalog DesignSriramNo ratings yet
- VerilogDocument12 pagesVerilogSriramNo ratings yet
- Lab A - 02 - 2022Document2 pagesLab A - 02 - 2022Vishvan VarmaNo ratings yet
- Azure Strategy and Implementation Guide: Fourth EditionDocument223 pagesAzure Strategy and Implementation Guide: Fourth EditionYue ZhaoNo ratings yet
- PSP 1000 Ta-081 Service Manual PW SceaDocument30 pagesPSP 1000 Ta-081 Service Manual PW SceaMaricel SinsayNo ratings yet
- ETI Micro Project 1Document10 pagesETI Micro Project 1Moin ShaikhNo ratings yet
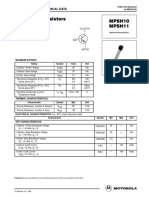
- MPSH10 11 (VHF UHF Transistor)Document5 pagesMPSH10 11 (VHF UHF Transistor)joelpalzaNo ratings yet
- 1000 Python MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) - SanfoundryDocument24 pages1000 Python MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) - Sanfoundrysrinivasa reddyNo ratings yet
- Model No.: M270Hge Suffix: L20: Product SpecificationDocument28 pagesModel No.: M270Hge Suffix: L20: Product SpecificationRaul AlfaroNo ratings yet
- RabbitMQ SuccinctlyDocument108 pagesRabbitMQ SuccinctlynbrindicNo ratings yet
- Cloud ArchitectureDocument32 pagesCloud ArchitectureKushal Kamra100% (1)
- Chapter 4 - SQADocument15 pagesChapter 4 - SQAsheilaabad8766No ratings yet
- Telon PsDocument5 pagesTelon Pssati1987No ratings yet
- Andrew ResumeDocument4 pagesAndrew ResumeAnonymous blqN8zpfNo ratings yet
- How To Install POSROGDocument3 pagesHow To Install POSROGMuhammad ZulfikarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Iteration StructuresDocument3 pagesLesson 7 Iteration StructuresRoanne ArcegaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Analog Circuits - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument60 pagesUnit 3 - Analog Circuits - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inRahul kumar singhNo ratings yet
- Atari 130XE Machine Language For The Absolute BeginnerDocument164 pagesAtari 130XE Machine Language For The Absolute Beginnerglia100% (1)
- Service Manual: D-NF420/NF421Document38 pagesService Manual: D-NF420/NF421Cristhian CrisantoNo ratings yet
- Creating an Active/Active SQL Cluster using Hyper-VDocument58 pagesCreating an Active/Active SQL Cluster using Hyper-VpraveenmpkNo ratings yet
- CDS - RoadmapDocument26 pagesCDS - RoadmapmariusrenardNo ratings yet
- Master Thesis - Observer Based Fault Detection in DC-DC Power Converter - Levin - KieranDocument97 pagesMaster Thesis - Observer Based Fault Detection in DC-DC Power Converter - Levin - KieranhieuhuechNo ratings yet
- Spss ExampleDocument458 pagesSpss Examplegautamabhishek4No ratings yet
- Exam Questions 2018Document3 pagesExam Questions 2018naveen g cNo ratings yet
- RJ45 Cable Tester: Bhaskar PandeyDocument3 pagesRJ45 Cable Tester: Bhaskar PandeyAleksandar RistićNo ratings yet
- Manual de Instrucciones CCM-200Document16 pagesManual de Instrucciones CCM-200Celeynes RTNo ratings yet
- Huawei HoloSens SDC M2120-EVL (7-35mm) DatasheetDocument4 pagesHuawei HoloSens SDC M2120-EVL (7-35mm) DatasheetDavincho SarangoNo ratings yet
- 2011-02!22!1 PC Zone Computer TradingDocument10 pages2011-02!22!1 PC Zone Computer Tradingv@r0_5No ratings yet
- Raspberry Pi Kiosk Using Chromium - Pi My Life UpDocument34 pagesRaspberry Pi Kiosk Using Chromium - Pi My Life UplecarNo ratings yet
- Skybox Virtual Appliance Quick Start GuideDocument45 pagesSkybox Virtual Appliance Quick Start GuideTấn VTrNo ratings yet
- Agile Slides PowerPoint TemplateDocument20 pagesAgile Slides PowerPoint TemplateNancy CenicerosNo ratings yet
- Informatica PowerCenter Connect 8.1.1 For SAP NetWeaver User GuideDocument452 pagesInformatica PowerCenter Connect 8.1.1 For SAP NetWeaver User GuideDipankarNo ratings yet