Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Things To Know For The Exam #1: (75 Points in Total) (40 Points) (3 Points) (10 Points)
Uploaded by
Huy PhamOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Things To Know For The Exam #1: (75 Points in Total) (40 Points) (3 Points) (10 Points)
Uploaded by
Huy PhamCopyright:
Available Formats
PrepForExam#1.doc 1 J.
Alampi
Things to Know for the Exam #1
1. CHAPTERS 1, 2, part of 4, 5, 6 and Appendix A
2. See Things to Know From Chapter 5 starting on page 2 of this
handout
3. Review all your notes on these Chapters and Labs from the 1
st
6 weeks
4. Review all Quiz Prep Documents from weeks 1 through 5
5. Format of the Exam (75 points in Total)
a. 40 Multiple Choice, Fill in the Blanks and Matching
Questions (40 points)
b. 3 questions on characteristics of Various Operating
Systems (3 points)
c. Questions on DOS Commands from Labs (10 points)
- Format
- Creating a Directory
- Removing a Directory
- Changing a Directory
- Changing from Drive to Drive
- Getting to the root directory from Anywhere
d. Questions on IRQ Tables, IRQ priorities [Now because of this second
chip the priority system becomes 0,1, (8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15), 3,4,5,6,7], Handout on
IRQs and information on IRQs in the textbook on pages
1208-1212 (8 points)
e. Number System Calculations (14 points)
- Binary to Decimal, Decimal to binary, Adding in binary,
Subtracting in Binary, Hex to Decimal, Decimal to Hex,
Adding in Hex, Subtracting in Hex, Hex to 4-bit Binary, 4-bit
Binary to Hex
PrepForExam#1.doc 2 J.Alampi
Things to Know from Chapters 5
Pgs 175-232
CHAPTER 5 Lectures 1 & 2
1. Know the Motherboard Form factor and that it drives the size
of the motherboard and its features: from Chapter 5 Lecture 1
notes and pages 176-177
2. Be able to name five main categories of form factors used for
motherboards from Chapter 5 Lecture 1 notes and pg 233
review question #1
3. Be able to name Four types of cargo carried by a bus: from
Chapter 5 Lecture 2 notes (Electric Power, control signals, memory addresses,
data)
4. Know how buses have evolved around data path and speed
from Chapter 5 Lecture 2 notes and page 185
5. Know the definitions of the following terms from Chapter 5
Lecture 2 notes: Synchronous, Asynchronous, Wait state.
6. Know the types of buses and the definitions of the following
terms from Chapter 5 Lecture 2 notes: Expansion bus, Local Bus,
Local I/O Bus, Local Video Bus.
7. Know the 3 Categories of PCI buses from Chapter 5 Lecture 2
notes: Conventional PCI, PCI-X, PCI Express
8. Know some characteristics of each of the following buses
from Chapter 5 Lecture 2 notes: Conventional PCI, PCI-X, PCI
Express
9. Know the four types of PCI Express buses and which holds the
PCIe video card from Chapter 5 Lecture 2 notes:
10. Know the Definitions of on-board ports and internal
connectors from Chapter 5 Lecture 2 notes
11. Know Three features used to configure the motherboard
(DIP switches, jumpers, CMOS RAM) from Chapter 5 Lecture 2 notes
12. Know some characteristics of DIP Switches, jumpers and
CMOS RAM from Chapter 5 Lecture 2 notes
13. Know how to document Configuration Settings from
Chapter 5 Lecture 2 notes and pages 230-231
14. Understand the concepts of Flashing ROM BIOS and
Motherboard Drivers from Chapter 5 Lecture 2 notes and
pages 211-214
PrepForExam#1.doc 3 J.Alampi
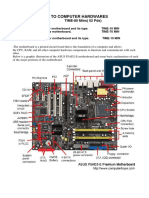
15. Review Figures on pages 176-183
16. Review Page 178 Table 5-1 to understand Sockets for Intel
processors used for desktop computers and Page 180 Table 5-
2 to understand Sockets for AMD processors used for desktop
computers
17. Review Page 186 Table 5-3 to understand Bus Types, Data
Path, Bus Frequency and Throughput of each bus type.
18. Page 186 Figure 5-11 and page 187 Figure 5-12
19. Review Figure 5-14 on Page 188
20. Understand Figure 5-7 on Page 182 and Figure 5-9 on page
183
21. Review the various PCI Express Slots Page 189 Figure 5-15
22. Review the various AGP Standards on Page 191 Table 5-4
23. CNR Slot Page 193 Figure 5-20
24. Page 194 Figures 5-21 & 5-22
25. Page 195 Figures 5-23, 5-24 & 5-25
26. Page 197 Figures 5-27 & 5-28
27. Page 198 Figure 5-29
28. Understand the various CMOS Setup Menus by reviewing
Figures 5-59 through 5-65 on pages 227 - 231
29. Know all of the Key terms below
Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP): Ports developed specifically for video cards.
audio/modem riser (AMR): A specification for a small slot on a motherboard to
accommodate an audio or modem riser card. A controller on the motherboard
contains some of the logic for the audio or modem functionality.
CMOS battery: A lithium coin-cell battery enables CMOS RAM to hold
configuration data, even while the main power to the computer is off.
communication and networking riser (CNR): A specification for a small
expansion slot on a motherboard that accommodates a small audio, modem, or
network riser card.
CrossFire: ATI s technology for installing two video cards on a motherboard.
dual inline package (DIP) switch: A switch on a circuit board or other device
that can be set on or off to hold configuration or setup information.
front panel header: The corner of the motherboard for lights and switches.
I/O shield: The plate installed in the computer case to provide holes for I/O ports.
jumper: Two wires that stick up side by side on the motherboard and are used to
hold configuration information. The jumper is considered closed if a cover is over
the wires, and open if the cover is missing.
land grid array (LGA): Sockets that use lands rather than pins.
North Bridge: The faster hub in the Accelerated Hub Architecture.
On-board ports: Ports that are directly on the motherboard, such as a built-in
keyboard port or on-board serial port.
PrepForExam#1.doc 4 J.Alampi
PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect): Buses have been improved several
times. There are currently three major categories and within each category,
several variations of PCI. The PCI buses are used for many types of cards,
including video cards.
PCI Express (PCIe): PCI Express uses a serial bus, which is faster than a parallel
bus because it transmits data in packets similar to how an Ethernet network, USB,
and FireWire transmit data. A PCIe expansion slot can provide one or more of
these serial lanes.
pin grid array (PGA): Sockets aligned with pins aligned in uniform rows around
the socket. Used in earlier Pentiums.
power-on password: A password that a computer uses to control access during
the boot process.
riser card: A card that plugs into a motherboard and allows for expansion cards
to be mounted parallel to the motherboard. Expansion cards are plugged into slots
on the riser card.
SLI (Scalable Link Interface): NVIDIAs technology for installing two video
cards on a motherboard.
South Bridge: The slower hub in the Accelerated Hub Architecture.
Spacers: Another term for standoffs.
staggered pin grid array (SPGA): Having the pins staggered over the socket to
squeeze more pins into a small space.
standoffs: Round plastic or metal pegs that separate the motherboard from the
case, so that components on the back of the motherboard do not touch the case.
startup password: Another term for power-on password.
user password: A password enabling you to logon to the operating system.
wait state: A clock tick in which nothing happens. Used to ensure that the
microprocessor is not getting ahead of slower components. A 0-wait state is
preferable to a 1-wait state. Too many wait states can slow down a system.
zero insertion force (ZIF) sockets: Square or nearly square sockets so that even
force is applied when inserting the processor in the socket, all current processor
sockets have a lever on the side of the socket.
You might also like
- Unit 03 The MotherboardDocument17 pagesUnit 03 The MotherboardSneaky peteNo ratings yet
- Hard Ware Note BookDocument22 pagesHard Ware Note BookSrini VasuluNo ratings yet
- Ass 2Document8 pagesAss 2wudase solomonNo ratings yet
- A74010-B AMPRO Little Board Plus Technical Manual 1985Document142 pagesA74010-B AMPRO Little Board Plus Technical Manual 1985Pote DosNo ratings yet
- Understanding Motherboard ComponentsDocument9 pagesUnderstanding Motherboard ComponentsallamNo ratings yet
- The Quaid-e-Azam Group of Schools & Colleges, KP SLO Based Questions-AnswersDocument5 pagesThe Quaid-e-Azam Group of Schools & Colleges, KP SLO Based Questions-Answersyousafkhan9485No ratings yet
- The System Unit and The Motherboard: Technical Vocational Education (TVE) 9 First QuarterDocument10 pagesThe System Unit and The Motherboard: Technical Vocational Education (TVE) 9 First QuarterbogusbaikawNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of The MotherboardDocument4 pagesParts and Functions of The MotherboardIbrahim ObaidullahNo ratings yet
- Project Report: Prepared byDocument22 pagesProject Report: Prepared byumeshNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of The MotherboardDocument4 pagesParts and Functions of The MotherboardWilliam Paras InteNo ratings yet
- TVL CSS G11-Wlas-W1 - 2Document16 pagesTVL CSS G11-Wlas-W1 - 2Fern WehNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of The MotherboardDocument3 pagesParts and Functions of The MotherboardRodel Romero100% (2)
- Parts and Functions of The MotherboardDocument3 pagesParts and Functions of The MotherboardJohnPaulLlenticNo ratings yet
- Answer Lad d4 3 3 2Document6 pagesAnswer Lad d4 3 3 2Sang NiyomkhamNo ratings yet
- SeminarDocument30 pagesSeminarShweta Vishwakarma100% (1)
- The Motherboard Reference TermsDocument6 pagesThe Motherboard Reference TermsMax PowerNo ratings yet
- Parts of Mother BoardDocument17 pagesParts of Mother BoardJeza Estaura Cuizon100% (1)
- CHM SolvedDocument24 pagesCHM SolvedHod IfNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Personal Computer: IT Essentials 5.0Document44 pagesIntroduction To The Personal Computer: IT Essentials 5.0Amsalu SeteyNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware and ServicingDocument232 pagesComputer Hardware and ServicingrajeevNo ratings yet
- Module 4-Motherboard.18214342Document59 pagesModule 4-Motherboard.18214342Fercie Q. EngresoNo ratings yet
- Passing Package CSDocument20 pagesPassing Package CSbharathkumar900845No ratings yet
- G9-Css-Q2-Lesson 1-Parts-And-Functions-Of-MotherboardDocument10 pagesG9-Css-Q2-Lesson 1-Parts-And-Functions-Of-MotherboardElke EstandianNo ratings yet
- Motherboard Components & Functions ExplainedDocument13 pagesMotherboard Components & Functions Explainedjussan roaring100% (3)
- Identifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionDocument14 pagesIdentifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionBrenda Macanlalay Asuncion80% (5)
- EVGA Nforce 790i SLI FTW Motherboard User GuideDocument84 pagesEVGA Nforce 790i SLI FTW Motherboard User GuideryumacleodNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Typical Configuration of Computer SystemDocument29 pagesChapter 1 Typical Configuration of Computer SystemSohum VenkatadriNo ratings yet
- PCT (1)Document58 pagesPCT (1)ligasan.cjNo ratings yet
- Veriton x4620gDocument132 pagesVeriton x4620gmuer conconNo ratings yet
- Manual Abit AB-PX5Document90 pagesManual Abit AB-PX5daniel mihaiNo ratings yet
- Aim: Introduction To Computer Hardwares Steps:-: TIME-80 Mins (02 PDS)Document15 pagesAim: Introduction To Computer Hardwares Steps:-: TIME-80 Mins (02 PDS)VanessaNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Motherboard: Ashley Abogado Computer 10Document4 pagesParts of The Motherboard: Ashley Abogado Computer 10DeathNo ratings yet
- PC Hardware Basics & Troubleshooting GuideDocument43 pagesPC Hardware Basics & Troubleshooting GuideBhavin Joshi100% (39)
- Motherboard Major Parts and FunctionDocument3 pagesMotherboard Major Parts and FunctionVic Picar0% (1)
- Contoh Makalah Dalam Bahasa InggrisDocument6 pagesContoh Makalah Dalam Bahasa InggrisMerry ErawatiNo ratings yet
- Super 7: SY-5EHM/5EH5Document71 pagesSuper 7: SY-5EHM/5EH5Polo HksNo ratings yet
- COA Practical FileDocument39 pagesCOA Practical FileDeepak MishraNo ratings yet
- How Motherboard WorksDocument12 pagesHow Motherboard Worksrez hablo100% (1)
- Unit-II: Accessory BoardDocument39 pagesUnit-II: Accessory BoardNavi KaurNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of MotherboardDocument4 pagesParts and Functions of MotherboardJimmySyNo ratings yet
- Ebook PDF Comptia A Core 1 220 1001 and Core 2 220 1002 Cert Guide 5th Edition Certification Guide 5th Edition PDFDocument44 pagesEbook PDF Comptia A Core 1 220 1001 and Core 2 220 1002 Cert Guide 5th Edition Certification Guide 5th Edition PDFelizabeth.leon66697% (31)
- Tugas Kelompok 6Document8 pagesTugas Kelompok 6Rika ElsiaNo ratings yet
- Tle TVL 9-12ia Css q1 Wk2day1 4Document5 pagesTle TVL 9-12ia Css q1 Wk2day1 4Rose FloresNo ratings yet
- BIOS InstallationDocument5 pagesBIOS InstallationArif ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Motherboard and Its Component (11813705)Document10 pagesMotherboard and Its Component (11813705)DeePäk YädävNo ratings yet
- Parts of MotherboardDocument86 pagesParts of MotherboardKurt BalaniNo ratings yet
- The Essential Guide to MotherboardsDocument5 pagesThe Essential Guide to MotherboardsElleera RemorerasNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Motherboard Its FunctionDocument42 pagesModule 2 Motherboard Its FunctionManilyn NunezNo ratings yet
- 5mvp3 v4Document75 pages5mvp3 v4Manuel CartagenaNo ratings yet
- Labeling The MotherboardDocument6 pagesLabeling The MotherboardKaan Knight OznacarNo ratings yet
- Practical No 3 - Motherboard Components and TypesDocument10 pagesPractical No 3 - Motherboard Components and TypesAshish SethiNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument25 pagesMotherboardsumitangiraNo ratings yet
- MotherboardDocument14 pagesMotherboardPalash Jain100% (1)
- Motherboard. CompDocument16 pagesMotherboard. Compfrp60658No ratings yet
- IEEE 1394 PortDocument4 pagesIEEE 1394 PortPRincess ScarLetNo ratings yet
- WPC Practical No. 10Document3 pagesWPC Practical No. 10rambaranyadav9224No ratings yet
- 6 ZX 85Document28 pages6 ZX 85keyvan cryptoNo ratings yet
- A+ Hardware Tutorial Topic 1: Installation, Configuration, and Up GradationDocument40 pagesA+ Hardware Tutorial Topic 1: Installation, Configuration, and Up GradationLindasharon AwourNo ratings yet
- 7521 ServiceManualDocument122 pages7521 ServiceManualRicardo Alexis Fuentes LufittNo ratings yet
- Borang KWLDocument2 pagesBorang KWLjp siaNo ratings yet
- 1.MIL 1. Introduction To MIL (Part 2) - Characteristics of Information Literate Individual and Importance of MILDocument27 pages1.MIL 1. Introduction To MIL (Part 2) - Characteristics of Information Literate Individual and Importance of MILMargerie Fruelda50% (2)
- Harvard Style-1Document6 pagesHarvard Style-1Pamornwan NanNo ratings yet
- ADRs Applicability Summary for TrailersDocument4 pagesADRs Applicability Summary for TrailersjohncolalanciaNo ratings yet
- Solid Works Tutorial-Making Wind Turbine BladeDocument26 pagesSolid Works Tutorial-Making Wind Turbine Bladeمحمد جواد100% (1)
- 20 09 25 Pristina Dose White Paper - JB73643XXDocument10 pages20 09 25 Pristina Dose White Paper - JB73643XXMerab KvintradzeNo ratings yet
- Diesel Engine Workshop Manual TitleDocument106 pagesDiesel Engine Workshop Manual Titleiori yagami100% (1)
- Introduction of Online Music Portal - FreeProjectzDocument1 pageIntroduction of Online Music Portal - FreeProjectzTasleem ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Difference between engineers and technologists rolesDocument2 pagesDifference between engineers and technologists roleshunter20031No ratings yet
- Resonant Automation Company Overview and Areas of ExpertiseDocument2 pagesResonant Automation Company Overview and Areas of ExpertiseJohan ConradieNo ratings yet
- 901 User ManualDocument23 pages901 User ManualHappy DaysNo ratings yet
- 308E CR Excavador Electrical SystemDocument20 pages308E CR Excavador Electrical SystemRuddy RalNo ratings yet
- Trello DojoDocument73 pagesTrello DojoSully StewartNo ratings yet
- RCMRD Recruiting Short-Term Research Assistants KenyaDocument2 pagesRCMRD Recruiting Short-Term Research Assistants KenyaAlvine KNo ratings yet
- Art of Theatre On New Media Platform & Audience Viewing ExperienceDocument20 pagesArt of Theatre On New Media Platform & Audience Viewing ExperienceYvonne KayNo ratings yet
- Mat Piping ComponentsDocument49 pagesMat Piping Componentsnsr2tNo ratings yet
- 8051 Memory Map PDFDocument6 pages8051 Memory Map PDFCh'ng ShufenNo ratings yet
- Session13 Henkel SoritaDocument41 pagesSession13 Henkel Soritahsaini19762387No ratings yet
- Power Semiconductor Devices ThyristorsDocument140 pagesPower Semiconductor Devices ThyristorsNomanNo ratings yet
- Brochure OMS - CP4-CPN5-DFP3-DFP6 Parts - 14.06.23Document10 pagesBrochure OMS - CP4-CPN5-DFP3-DFP6 Parts - 14.06.23Michele GuerriniNo ratings yet
- Diagram AsDocument46 pagesDiagram AsHector Sepulveda OrellanaNo ratings yet
- E Airbus Skywise Contracts Keep Coming inDocument2 pagesE Airbus Skywise Contracts Keep Coming inSeenu CnuNo ratings yet
- June 2014 Question Paper 22 PDFDocument8 pagesJune 2014 Question Paper 22 PDFelafNo ratings yet
- CH 11Document50 pagesCH 11Donna Mae HernandezNo ratings yet
- Project Dossier Structure and Contents GuideDocument31 pagesProject Dossier Structure and Contents GuideSaravanan Varadarajan100% (1)
- Security of The Network and Reduces The Size of The Broadcast DomainDocument2 pagesSecurity of The Network and Reduces The Size of The Broadcast Domainflash driveNo ratings yet
- Excel Opening From VB6Document1 pageExcel Opening From VB6Sachin DhawadNo ratings yet
- Keys and Couplings: Definitions and Useful InformationDocument10 pagesKeys and Couplings: Definitions and Useful InformationRobert Michael CorpusNo ratings yet
- GSM Analysis Lab ExerciseDocument3 pagesGSM Analysis Lab ExerciseDramane BonkoungouNo ratings yet