Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Formulas For Gear Calculation - Internal Gears
Uploaded by
suna06m6403Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Formulas For Gear Calculation - Internal Gears
Uploaded by
suna06m6403Copyright:
Available Formats
Formulas for gears calculation internal gears
Contens
Internal spur gears with normal profile
Internal spur gears with corrected profile
Without center distance variation
With center distance variation
Internal helical gears with normal profile
Internal helical gears with corrected profile
Without center distance variation
With center distance variation
Length of contact and contact radius R
a
Interference
Dimension over pins and balls
Meaning of symbols
a Center distance m Module
Pressure angle Q Dimension over pins or balls
Helix angle r Radius
d Diameter R
a
Radius to start of active profile
g Length of contact s Tooth thickness on diameter d
g
1 Legth of recession
os
Chordal thickness
g
2
Length of approach t Pitch
h
f
Dedendum w Chordal thickness over z teeth (spur gears)
h
k
Addendum W Chordal thickness over z teeth (helical gears)
h
0
Corrected addendum z Number of teeth
h
r
Whole depth x Profile correction factor
l Tooth space
Meaning of indices
b Reffered to rolling diameter n Reffered to normal section
c Referred to roll diameter of basic rack o Reffered to pitch diameter
f
Reffered to root diameter
q
Reffered to the diameter throug balls center
g Reffered to base diameter r Reffered to balls
k
Refferred to outside diameter
s
Reffered to transverse section
i Refferred to equivalent w Reffered to tool
Internal spur gears with normal profile
cos
+2
cos
or
Fig.N1
Internal spur gears with corrected profile
a)- Without center distance variation
+ or
=
2
2 tan
b)- with center distance variation
+ 2tan
= 2 + 2
Internal helical gears with normal profile
cos
cos
cos
tan
=tan
cos
cos
or
+2
Internal helical gears with corrected profile
a)- Without center distance variation
or
2
2
tan
2
2
tan
b)- With center distance variation
+ 2tan
cos
2 +2
Contact length calculation
sin
sin
sin
Contact radius R
a
calculation
In the case of helical gears use transverse section values
instead of
.
Fig. N3
Interference
Primary interference
Minimum internal diameter without interference
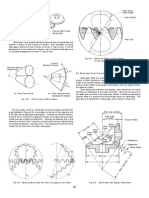
Secondary interference (figure N4)
cos =
cos =
cos =
When the points K
1
and K
2
on the pinion and gear move to K
1
and K
2
in time t
1
and t
2
,
the respective angles are:
for the gear: ;
for the pinion: + ;
To avoid interference, the points K
1
and K
2
should not coincide at K
1
and K
2
and should
satisfy the condition:
>
or
>
The diagram of figure N5 is used to determine the largest difference z
2
z
1
, which is a
function of the pressure angle
and the ratio
, where not interference exist.
When the gears are corrected h
k
becomes:
Fig. N5
Dimension over pins and balls (figure N6)
Spur gear with even number of teeth
from which we have
Spur gear with odd number of teeth
and
are the same as for even teeth, but =
Helical gear with even number of teeth
Helical gear with odd number of teeth
and
are the same as for even teeth, but =
Fig.N6
You might also like
- Module IV: Gears and Gear TrainsDocument38 pagesModule IV: Gears and Gear TrainsSuraj VinayNo ratings yet
- Eugenics in The United StatesDocument14 pagesEugenics in The United StatesSnark Jacobs100% (1)
- A Short Guide To A Happy LifeDocument4 pagesA Short Guide To A Happy LifeHenry100% (1)
- Gearbox Design IitDocument25 pagesGearbox Design IitSrini VasanNo ratings yet
- Calculating Oee WorksheetDocument2 pagesCalculating Oee WorksheetAdriano Tiago EinsfeldNo ratings yet
- KPI and Supplier Performance Scorecard ToolDocument7 pagesKPI and Supplier Performance Scorecard ToolJayant Kumar JhaNo ratings yet
- Gear DesignDocument83 pagesGear DesignmuhammadaminjamalmutNo ratings yet
- APR11 Bearing Software BrochureDocument8 pagesAPR11 Bearing Software BrochureDagim GirmaNo ratings yet
- Spur Gear Design ProcedureDocument11 pagesSpur Gear Design ProcedureRamji RaoNo ratings yet
- GEAR TOOTH PROFILESDocument5 pagesGEAR TOOTH PROFILESpremnathgopinathanNo ratings yet
- Effect of Increased Center Distance on Gear Teeth Contact Ratio and StressDocument21 pagesEffect of Increased Center Distance on Gear Teeth Contact Ratio and StressDavide MaranoNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Planetary Gear Box For High Reduction RatioDocument12 pagesOptimization of Planetary Gear Box For High Reduction RatioNovriansyah BrianNo ratings yet
- 1.optimal Design of Two-Stage Speed ReducerDocument6 pages1.optimal Design of Two-Stage Speed Reducermlouredocasado100% (1)
- Gear DesignDocument5 pagesGear DesignKrishnadev Madhavan NairNo ratings yet
- Beam Deflection FormulaeDocument2 pagesBeam Deflection Formulae7575757575100% (6)
- Iso 1500 Iso 1000 Iso 680 Iso 460 Iso 320 Iso 220 Iso 150 Iso 100Document1 pageIso 1500 Iso 1000 Iso 680 Iso 460 Iso 320 Iso 220 Iso 150 Iso 100coleiroNo ratings yet
- Moment of Inertia ExplainedDocument18 pagesMoment of Inertia ExplainedSameOldHatNo ratings yet
- An Investigation of The Fatigue and Fretting PerformanceDocument19 pagesAn Investigation of The Fatigue and Fretting PerformanceKrishna PrasadNo ratings yet
- Gears - Engineering InformationDocument138 pagesGears - Engineering InformationGiang T LeNo ratings yet
- Design of Bevel GearDocument23 pagesDesign of Bevel Gearshahzadali078650% (2)
- Machine Design & Drawing - II - GEARSDocument12 pagesMachine Design & Drawing - II - GEARSSenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- Structure Dismantling JSADocument2 pagesStructure Dismantling JSAtnssbhaskar69% (13)
- Formulas For Gear Calculation - External GearsDocument10 pagesFormulas For Gear Calculation - External GearsJag WaramNo ratings yet
- A New Model in Rail-Vehicles Dynamics Considering Nonlinear Suspension Component BehaviorDocument11 pagesA New Model in Rail-Vehicles Dynamics Considering Nonlinear Suspension Component Behaviorjp220288No ratings yet
- Kisssoft Tut 006 E Shaft EditorDocument11 pagesKisssoft Tut 006 E Shaft EditorBeytullah AcarNo ratings yet
- Automotive BearingDocument29 pagesAutomotive BearingAhmed AbdelghanyNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis of Spur Gear Set PDFDocument85 pagesFinite Element Analysis of Spur Gear Set PDFCan CemreNo ratings yet
- Sleeve Vs Antifriction Bearings Selection of The Optimal BearingDocument13 pagesSleeve Vs Antifriction Bearings Selection of The Optimal BearingKamal Arab0% (1)
- Spline Design Using KISSSoftDocument8 pagesSpline Design Using KISSSoftAllan John Sala Limson0% (1)
- Bevel Gear: Bevel Gears Are Gears Where The Axes of The Two Shafts Intersect and The ToothDocument3 pagesBevel Gear: Bevel Gears Are Gears Where The Axes of The Two Shafts Intersect and The ToothVetri VelNo ratings yet
- Cycloid Drive - Replaced by Planocentric Involute GearingDocument6 pagesCycloid Drive - Replaced by Planocentric Involute GearingMax GrandeNo ratings yet
- Cycloid Drive - Replaced by Planocentric Involute Gearing PDFDocument6 pagesCycloid Drive - Replaced by Planocentric Involute Gearing PDFMax GrandeNo ratings yet
- SpokenEnglish Section1 TheSoundSystemOfEnglishDocument132 pagesSpokenEnglish Section1 TheSoundSystemOfEnglishRaj Yash100% (1)
- Design and Analysis of Planetary Gearbox For All-Terrain VehicleDocument10 pagesDesign and Analysis of Planetary Gearbox For All-Terrain VehicleIJRASETPublications100% (1)
- How Calculate The Press Fit ForceDocument3 pagesHow Calculate The Press Fit ForceAuloma Holding Industrial AutomationNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Plant BreedingDocument190 pagesFundamentals of Plant BreedingDave SubiyantoNo ratings yet
- Klein Technical GuidelineDocument21 pagesKlein Technical GuidelinePeter100% (2)
- Flat Belt CalculationDocument19 pagesFlat Belt CalculationAstri NgentNo ratings yet
- Steering Universal JointsDocument11 pagesSteering Universal JointsAman JainNo ratings yet
- Civil-Engineering-Final-Year-Project-Quarry Dust As A Substitute of River Sand in Concrete Mixes PDFDocument75 pagesCivil-Engineering-Final-Year-Project-Quarry Dust As A Substitute of River Sand in Concrete Mixes PDFVEERKUMAR GNDEC100% (1)
- The Application of Bevel GearsDocument6 pagesThe Application of Bevel GearsPrasanth ThiagarajanNo ratings yet
- Design of Bevel and Worm Gear: Machine Element IIDocument60 pagesDesign of Bevel and Worm Gear: Machine Element IIkibromgidey12No ratings yet
- Boston Gear Helical GearsDocument14 pagesBoston Gear Helical GearssandchiNo ratings yet
- Spur and Helical Gear Modeling in Pro-EDocument13 pagesSpur and Helical Gear Modeling in Pro-Ek_udhay100% (1)
- Gleason LTCA ExampleDocument8 pagesGleason LTCA ExamplereddykvsNo ratings yet
- Shaft LayoutDocument21 pagesShaft LayoutAmmar SafwtNo ratings yet
- Gear Box Design: Mech 420 Major ProjectDocument62 pagesGear Box Design: Mech 420 Major ProjectAtul DahiyaNo ratings yet
- Approximate Equation For The Addendum Modification Factors For Tooth Gears With Balanced Specific SlidingDocument11 pagesApproximate Equation For The Addendum Modification Factors For Tooth Gears With Balanced Specific SlidingCan CemreNo ratings yet
- Gear Trains - Lecture 10Document22 pagesGear Trains - Lecture 10priyankar007No ratings yet
- Stress Reduction in Spur Gears Using Aero-Fin Shaped HolesDocument11 pagesStress Reduction in Spur Gears Using Aero-Fin Shaped HolesJojee MarieNo ratings yet
- Principle of Epicyclic GearingDocument11 pagesPrinciple of Epicyclic GearingAnuj AwasthiNo ratings yet
- Final ReportDocument45 pagesFinal ReportKuppu Raj100% (1)
- Design and Analysis Procedures For Shafts and Splines: Paul E. BurkeDocument21 pagesDesign and Analysis Procedures For Shafts and Splines: Paul E. BurkeBalasrinivasan Murugan100% (3)
- Rack and Pinion Gear DesignDocument32 pagesRack and Pinion Gear DesignSrini KumarNo ratings yet
- Road Performance PDFDocument8 pagesRoad Performance PDFwanawNo ratings yet
- A Method to Optimize Brass Synchronizer RingDocument6 pagesA Method to Optimize Brass Synchronizer RingaravindhNo ratings yet
- Thermal and efficiency characterization of a low-backlash planetary gearboxDocument10 pagesThermal and efficiency characterization of a low-backlash planetary gearboxra maNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Trochoids and Their Application To Determining Gear Teeth Fillet ShapesDocument14 pagesCharacteristics of Trochoids and Their Application To Determining Gear Teeth Fillet ShapesJohn FelemegkasNo ratings yet
- Gearsand GearingDocument57 pagesGearsand Gearingcamohunter71No ratings yet
- Bevel Gear Transmission AnglesDocument6 pagesBevel Gear Transmission AnglesNabende UmarNo ratings yet
- A Crowning Achievement For Automotive ApplicationsDocument10 pagesA Crowning Achievement For Automotive ApplicationsCan CemreNo ratings yet
- Gear-Designing Parametric PDFDocument15 pagesGear-Designing Parametric PDFpichaidv100% (1)
- Design of A Planetary Gear System For A Small Scale Wind Turbine NewDocument19 pagesDesign of A Planetary Gear System For A Small Scale Wind Turbine NewanthonyNo ratings yet
- Spur Gear Design 1Document16 pagesSpur Gear Design 1Nagu SriramaNo ratings yet
- Tseng 2004 Mechanism and Machine TheoryDocument15 pagesTseng 2004 Mechanism and Machine TheoryKhanh VqNo ratings yet
- Kisssoft Tutorial 14 Compression SpringsDocument11 pagesKisssoft Tutorial 14 Compression SpringsNguyễnVănLăngNo ratings yet
- Formulas For Gear Calculation - Internal Gears PDFDocument7 pagesFormulas For Gear Calculation - Internal Gears PDFloosenutNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 CascadesDocument25 pagesChapter 6 Cascadesramamurthy123No ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials #6Document10 pagesMechanics of Materials #6siguaNo ratings yet
- Sukanta Mandal Pcme602Document11 pagesSukanta Mandal Pcme602Sukanta MandalNo ratings yet
- The Value ChainDocument6 pagesThe Value ChainFabio Hernan TorresNo ratings yet
- Final Program MM&FGM2014 0Document21 pagesFinal Program MM&FGM2014 0suna06m6403No ratings yet
- Ana 004Document9 pagesAna 004suna06m6403No ratings yet
- Taguchi Orthogonal ArraysDocument3 pagesTaguchi Orthogonal Arrayssuna06m6403No ratings yet
- Pricelist Complete 2014Document4 pagesPricelist Complete 2014suna06m6403No ratings yet
- G and M Codes - Turning and MillingDocument4 pagesG and M Codes - Turning and MillingmettayugeshreddyNo ratings yet
- LinkedIn Top 10 Job Search Blog Posts March 2013Document30 pagesLinkedIn Top 10 Job Search Blog Posts March 2013Kuppam BalagangadharaNo ratings yet
- 5S Workplace OrganizationDocument4 pages5S Workplace Organizationsuna06m6403No ratings yet
- Fried Rice, Gravy & ChutneyDocument1 pageFried Rice, Gravy & Chutneysuna06m6403No ratings yet
- Art:10.1007/s00158 008 0293 9Document2 pagesArt:10.1007/s00158 008 0293 9suna06m6403No ratings yet
- Strategic Dimensions of Maintenance Management: Albert H.C. TsangDocument33 pagesStrategic Dimensions of Maintenance Management: Albert H.C. Tsangsuna06m6403No ratings yet
- Tpi 008 de enDocument116 pagesTpi 008 de enRoberto Perez100% (1)
- Impact of Tooth Friction and Its Bending Effect On Gear DynamicsDocument25 pagesImpact of Tooth Friction and Its Bending Effect On Gear Dynamicssuna06m6403No ratings yet
- Free Body Diagrams of Gears and Gear TrainsDocument13 pagesFree Body Diagrams of Gears and Gear TrainsSelva KumarNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli's Principle DemosDocument8 pagesBernoulli's Principle Demossuna06m6403No ratings yet
- 3 Fatigue: 3.1 Endurance LimitDocument24 pages3 Fatigue: 3.1 Endurance LimitNeha KulkarniNo ratings yet
- NI Tutorial 4278 enDocument12 pagesNI Tutorial 4278 ensuna06m6403No ratings yet
- 8 Stress ConcentrationDocument15 pages8 Stress ConcentrationPRASAD326100% (3)
- Ana 004Document9 pagesAna 004suna06m6403No ratings yet
- CavallaroDocument6 pagesCavallarosuna06m6403No ratings yet
- Turbo Planetary Gear Technology OverviewDocument5 pagesTurbo Planetary Gear Technology Overviewsuna06m6403No ratings yet
- Friedman PDFDocument2 pagesFriedman PDFsuna06m6403No ratings yet
- 15e Moment of Inertia 03-03-09Document6 pages15e Moment of Inertia 03-03-09suna06m6403No ratings yet
- Advantages of Involute Splines over Straight Sided SplinesDocument3 pagesAdvantages of Involute Splines over Straight Sided Splinessuna06m6403No ratings yet
- Food Sample Test For Procedure Observation InferenceDocument2 pagesFood Sample Test For Procedure Observation InferenceMismah Binti Tassa YanaNo ratings yet
- Oxyprobe PDFDocument16 pagesOxyprobe PDFSrinivasa RNo ratings yet
- Three Little PigsDocument9 pagesThree Little PigsrNo ratings yet
- Meditation ProjectDocument2 pagesMeditation Projectapi-411448305No ratings yet
- SinogramDocument2 pagesSinogramNguyễn Thành CôngNo ratings yet
- PRC 2017 Annual Report ENDocument88 pagesPRC 2017 Annual Report ENmuhammad suryadiNo ratings yet
- Personal and Group Trainer Juan Carlos GonzalezDocument2 pagesPersonal and Group Trainer Juan Carlos GonzalezDidier G PeñuelaNo ratings yet
- Corn Genetics and Chi Square AnalysisDocument2 pagesCorn Genetics and Chi Square AnalysisBonifacius Budi NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Manual Murray 20Document28 pagesManual Murray 20freebanker777741No ratings yet
- Product Bulletin - Menopause Balance Complex Cooling LotionDocument2 pagesProduct Bulletin - Menopause Balance Complex Cooling Lotionshaklee480No ratings yet
- Dladla Effect 2013Document231 pagesDladla Effect 2013TheDreamMNo ratings yet
- Read The Following Text. A Day in The Life of Paula Radcliffe - Marathon RunnerDocument2 pagesRead The Following Text. A Day in The Life of Paula Radcliffe - Marathon RunnerAldo JimenezNo ratings yet
- Adrv9008 1Document68 pagesAdrv9008 1doubleNo ratings yet
- Carte Tehnica Partea IDocument22 pagesCarte Tehnica Partea IadrianNo ratings yet
- Companies Directory Alternative Fuels and Smart Transportation June 20Document82 pagesCompanies Directory Alternative Fuels and Smart Transportation June 20Mbamali Chukwunenye100% (1)
- Brian Cody Mcgonegal ResumeDocument2 pagesBrian Cody Mcgonegal Resumeapi-348833348No ratings yet
- Trinidad and Tobago Budget 2022 focuses on resilience amid pandemicDocument167 pagesTrinidad and Tobago Budget 2022 focuses on resilience amid pandemicAliyah AliNo ratings yet
- Rorschach y SuicidioDocument17 pagesRorschach y SuicidioLaura SierraNo ratings yet
- 6th Class EM All LessonsDocument33 pages6th Class EM All LessonsSathish PurushothamNo ratings yet
- Oplan Nena (Violation of RA 10364 Expanded Anti-Trafficking in Person Act of 2012)Document3 pagesOplan Nena (Violation of RA 10364 Expanded Anti-Trafficking in Person Act of 2012)Jhunary MunarNo ratings yet
- Tracking SARDO StudentsDocument2 pagesTracking SARDO StudentsLean ABNo ratings yet
- Kathrein Antenna Dual BandDocument4 pagesKathrein Antenna Dual BandAmine AchrafNo ratings yet
- Un Primer Acercamiento A La Escritura Científica: OPI LabDocument66 pagesUn Primer Acercamiento A La Escritura Científica: OPI LabLolaNo ratings yet