Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Differences RAM ROM Given
Uploaded by
Fakir TajulCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Differences RAM ROM Given
Uploaded by
Fakir TajulCopyright:
Available Formats
Fakir Tajul Islam_UU_Intro Com_Diff ramrom riskcisk maop
Page | 1
Fakir Tajul Islam. Contact: 01687473922 or ftiprince_gb@yahoo.com
1.0. RAM vs ROM
Read-only memory or ROM is a form of data storage in computers and other electronic devices
that can not be easily altered or reprogrammed. RAM is referred to as volatile memory and is lost
when the power is turned off whereas ROM in non-volatile and the contents are retained even
after the power is switched off.
Random Access Memory or RAM is a form of data storage that can be accessed randomly at
any time, in any order and from any physical location in contrast to other storage devices, such
as hard drives, where the physical location of the data determines the time taken to retrieve it.
RAM is measured in megabytes and the speed is measured in nanoseconds and RAM chips can
read data faster than ROM.
Comparison chart
Type-1
RAM ROM
Definition: Random Access Memory or RAM is a
form of data storage that can be
accessed randomly at any time, in any
order and from any physical location.
Allowing quick access and
manipulation.
Read-only memory or ROM is also a
form of data storage that can not be easily
altered or reprogrammed.Stores
instuctions that are not nescesary for re-
booting up to make the computer operate
when it is switched off.They are
hardwired.
Stands for: Random Access Memory Read-only memory
Use: RAM allows the computer to read data
quickly to run applications. It allows
reading and writing.
ROM stores the program required to
initially boot the computer. It only allows
reading.
Volatility: RAM is volatile i.e. its contents are
lost when the device is powered off.
It is non-volatile i.e. its contents are
retained even when the device is powered
off.
Types: The two main types of RAM are static
RAM and dynamic RAM.
The types of ROM include PROM,
EPROM and EEPROM.
Picturial
difference
Fakir Tajul Islam_UU_Intro Com_Diff ramrom riskcisk maop
Page | 2
Fakir Tajul Islam. Contact: 01687473922 or ftiprince_gb@yahoo.com
Type-2
Options RAM ROM
Elaboration Random Access Memory Read Only memory
Accessibility In reference with the processor,
the information stored in the RAM
is easily accessed
The processor cannot directly access
the information that is stored in the
ROM. In order to access the ROM
information, first the information will
be transferred into the RAM and then
it gets executed by the processor
Working type Both the read and write operations
can be performed over the
information that is stored in the
RAM
The ROM memory only allows the
user to read the information. User
cannot make any changes to the
information.
Storage RAM memory is only used to
store the temporary information.
ROM memory is used to store
permanent information and cannot be
deleted.
Speed the accessing speed of RAM is
faster, it assist the processor to
boost up the speed
Speed is slower in comparison with
RAM, ROM cannot boost up the
processor speed
Data preserving Electricity is needed in RAM to
flow to preserving information
Electricity is not needed in ROM to
flow to preserving information
structure The RAM is an chip, which is in
the rectangle form and is inserted
over the mother board of the
computer
ROMs are generally the optical
drivers, which are made of magnetic
tapes.
Cost The price of RAMs are
comparatively high
The price of ROMs are comparatively
low
Chip size Physically size of RAM chip is
larger than ROM chip
Physically size of ROM chip is smaller
than RAM chip.
Types The RAM memory is categorized
into two types they are the:
Statistic RAM (SRAM) and
Dynamic RAM (DRAM)
The ROM memory is categorized into
three types, they are: PROM
(Programmable Read Only memory),
EPROM (Erasable Programmable
Read Only memory) and EEPROM
(Electrically Erasable Programmable
Read Only memory)
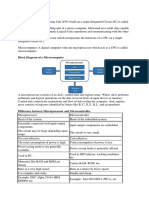
2.0. CISC and RISC processors
Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) and Complex Instruction Set Computer (CISC) are
two philosophies by which computer chips are designed. RISC became a popular technology
buzzword in the 1990s, and many processors used in the enterprise business segment were RISC-
based. Learning about how RISC and CISC differ can give you a better understanding of the
Fakir Tajul Islam_UU_Intro Com_Diff ramrom riskcisk maop
Page | 3
Fakir Tajul Islam. Contact: 01687473922 or ftiprince_gb@yahoo.com
computer hardware industry and how the personal computers of the future might operate. RISC
(Reduced I nstruction Set Computer)
RISC stands for Reduced Instruction Set Computer. To execute each instruction, if there is
separate electronic circuitry in the control unit, which produces all the necessary signals, this
approach of the design of the control section of the processor is called RISC design. It is also
called hard-wired approach.
Examples of RISC processors:
IBM RS6000, MC88100
DECs Alpha 21064, 21164 and 21264 processors
Features of RISC Processors:
The standard features of RISC processors are listed below:
RISC processors use a small and limited number of instructions.
RISC machines mostly uses hardwired control unit.
RISC processors consume less power and are having high performance.
Each instruction is very simple and consistent.
RISC processors uses simple addressing modes.
RISC instruction is of uniform fixed length.
CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computer)
CISC stands for Complex Instruction Set Computer. If the control unit contains a number of
micro-electronic circuitry to generate a set of control signals and each micro-circuitry is
activated by a micro-code, this design approach is called CISC design.
Examples of CISC processors are:
Intel 386, 486, Pentium, Pentium Pro, Pentium II, Pentium III
Motorolas 68000, 68020, 68040, etc.
Features of CISC Processors:
The standard features of CISC processors are listed below:
CISC chips have a large amount of different and complex instructions.
CISC machines generally make use of complex addressing modes.
Different machine programs can be executed on CISC machine.
CISC machines uses micro-program control unit.
CISC processors are having limited number of registers.
Fakir Tajul Islam_UU_Intro Com_Diff ramrom riskcisk maop
Page | 4
Fakir Tajul Islam. Contact: 01687473922 or ftiprince_gb@yahoo.com
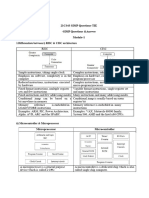
CISC and RISC processors - a comparison
CISC processors RISC processors
1 Complex Instruction Set
Computer (CISC) processors
has a bigger instruction set with
many addressing
modes.
1.Reduced Instruction Set
Computers (RISC) processors has
a smaller instruction set with few
addressing modes
2. It has to use a seperate micro-
programming unit with a control
memory to implement complex
instructions.
2. It has a hard-wired
programmed-unit without acontrol
memory, and seperate
hardware to implement each and
every instruction.
3. An easy compiler design 3. A complex compiler design.
4. The calculations are slower and
precise
4The calculations are faster and
precise
5. Decoding of instruction is
complex
5. Decoding of instruction is
6.The Execution time is very high. 6. It takes a very less execution
time.
7. It frequently needs the external
memory access to make
calculations.
7. Since it uses a hardwired
model, its not often, to take the
external memory access for
calculations.
8. Pipelining does not function
correctly here because of
complexity in instructions.
8. Pipeling is not a major problem
and this option speeds up the
processors.
9. These processors often stall
because of pipelining problem.
9. Since the instructions are not
complex, stalling is mostly
reduced.
10. Code Expansion is not a
problem in CISC processors.
10. Code expansion can be a
problem in some cases in RISC
processors.
11. Disc space is wasted. 11. Disc space is saved.
12. Used in low end applications
such us Security systems, Home
automation
12. Used in High end applications
such us video processing,
telecommunications, image
processing
CISC Computer RISC Computer
The acronym is variously used.
If it reads as above (i.e. as CISC
The acronym is variously used.
If it reads as above (i.e. as RISC
Fakir Tajul Islam_UU_Intro Com_Diff ramrom riskcisk maop
Page | 5
Fakir Tajul Islam. Contact: 01687473922 or ftiprince_gb@yahoo.com
computer), it means a computer that
has a Complex Instruction Set Chip
as its cpu.
It is also referred to as CISC
computing.
It is sometimes called a CISC chip.
This could have a tautology in the
last two words, but it can be
overcome by thinking of it as a
Complex Instruction Set Computer
chip.
computer), it means a computer that
has a Reduced Instruction Set Chip
as its cpu.
It is also referred to as RISC
computing.
It is sometimes called a RISC chip.
This could have a tautology in the
last two words, but it can be
overcome by thinking of it as
Reduced Instruction Set Computer
chip.
CISC chips have an increasing
number of components and an ever
increasing instruction set and so are
always slower and less powerful at
executing common instructions
RISC chips have fewer components
and a smaller instruction set,
allowing faster accessing of
common instructions
CISC chips execute an instruction in
two to ten machine cycles
RISC chips execute an instruction in
one machine cycle
CISC chips do all of the processing
themselves
RISC chips distribute some of their
processing to other chips
CISC chips are more common in
computers that have a wider range of
instructions to execute
RISC chips are finding their way into
components that need faster
processing of a limited number of
instructions, such as printers and
games machines
3.0. Difference between Optical & Magnetic Storage
Magnetic storage Optical storage
Storage Magnetic storage uses disks
coated with a magnetic
material. Each tiny bit of the
disk carries a magnetic charge;
the direction of that charge
determines whether it
represents a 1 or a 0.
Optical storage, meanwhile,
uses disks made of reflective
material; how each bit
reflects light--or doesn't
reflect it--determines
whether it's a 1 or a 0.
Access Magnetic storage devices use
"read/write heads,"
electromagnets that detect
(read) or change (write) the
magnetization patterns on the
Optical storage devices use
lasers to read the reflections
in the disk or "burn" the data
pattern into the disks.
Fakir Tajul Islam_UU_Intro Com_Diff ramrom riskcisk maop
Page | 6
Fakir Tajul Islam. Contact: 01687473922 or ftiprince_gb@yahoo.com
disk.
Advantages In general, it's faster and easier
to write data to magnetic
storage media
In general, it's slower to
write data to optical storage
media
Advantages data stored on magnetic media
tends to be less durable
data stored on optical media
tends to be more durable
examples examples of magnetic storage
media include floppy disks,
magnetic recording tape, and
magnetic stripes on credit cards
CD ROM, DVD ROM, Blu
Ray etc..
Magnetic Storage
a) Stores data in magnetic form.
b) It is affected by magnetic field.
c) It has high storage capacity.
e) It doesn't use laser to read/write data.
f) Magnetic storage devices are ; Hard disk , Floppy disk, Magnetic tape etc
Optical Storage.
a) Stores data optically & used laser to read/write.
b) It is not affected by magnetic field.
c) It has less storage than hard disk.
e) Data accessing is high as compared to floppy.
f) Optical storage devices are ; CD-ROM,CD-R, CD-RW, DVD etc.
You might also like
- Nintendo 64 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #8From EverandNintendo 64 Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #8No ratings yet
- Micro-Controller: Emergers TechnologiesDocument21 pagesMicro-Controller: Emergers Technologiesprajun_kumar3No ratings yet
- Unit 1-ERTS QBDocument5 pagesUnit 1-ERTS QBBabuKannanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 COM101Document5 pagesChapter 2 COM101Christean Val Bayani ValezaNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture Interview Questions - Coding NinjasDocument12 pagesComputer Architecture Interview Questions - Coding NinjaseliyazNo ratings yet
- Computer ComponentsDocument32 pagesComputer ComponentsJSPAMoreNo ratings yet
- Assingment of ComputerDocument7 pagesAssingment of ComputerBurhan KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 EdDocument32 pagesUnit 1 Edsupraja tirumalasettiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Embedded MicrocontrollersDocument5 pagesChapter 2 Embedded MicrocontrollersyishakNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor & Random Access MemoryDocument4 pagesMicroprocessor & Random Access MemoryWaleed AnjumNo ratings yet
- On Chip Periperals tm4c UNIT-IIDocument30 pagesOn Chip Periperals tm4c UNIT-IIK JahnaviNo ratings yet
- Computer Basics: What Is A Computer?Document9 pagesComputer Basics: What Is A Computer?thripthiNo ratings yet
- Binder 1Document46 pagesBinder 1Hemalatha K.N.No ratings yet
- Unit 4 - L Notes - Introduction To MicrocontrollerDocument53 pagesUnit 4 - L Notes - Introduction To MicrocontrollerAKSHANSH MATHUR100% (1)
- computer lab 111Document21 pagescomputer lab 111Santosh BhandariNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1 Computer ArchitectureDocument34 pagesPresentation 1 Computer ArchitectureElw ayNo ratings yet
- Introduction to MicroprocessorsDocument24 pagesIntroduction to MicroprocessorsDeva RaguNo ratings yet
- EC303 - Chapter 1 Computer Architecture OrganizationDocument61 pagesEC303 - Chapter 1 Computer Architecture OrganizationChinNo ratings yet
- Lesson10 Registers - VonnNewmanArch 2Document13 pagesLesson10 Registers - VonnNewmanArch 2Cuadra Marzel louisNo ratings yet
- MCES-21CS43 Module-1 NotesDocument14 pagesMCES-21CS43 Module-1 NotesEdu techNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Understanding The Concept of Microprocessor and MicrocomputerDocument5 pagesChapter 1 - Understanding The Concept of Microprocessor and MicrocomputerFaizur FarihaNo ratings yet
- Hardware Interview QuestionsDocument5 pagesHardware Interview Questionssneha587No ratings yet
- 21CS43 SIMP Questions-TIEDocument60 pages21CS43 SIMP Questions-TIEVivek TgNo ratings yet
- Jan Marie Veatrice M. Pacia 4-ECE: What Are Cisc and Risc Architecture? How Do They Differ From Each Other?Document6 pagesJan Marie Veatrice M. Pacia 4-ECE: What Are Cisc and Risc Architecture? How Do They Differ From Each Other?Jan Marie Veatrice PaciaNo ratings yet
- UNIT-IVDocument72 pagesUNIT-IVfishatsion09No ratings yet
- CISC Is An Acronym For Complex Instruction Set ComputerDocument44 pagesCISC Is An Acronym For Complex Instruction Set ComputerVantharAlaNo ratings yet
- EST102 - M1 - Ktunotes - inDocument21 pagesEST102 - M1 - Ktunotes - inAthiraNo ratings yet
- Chapter#1-Part-B-For-First-Monthly TestDocument25 pagesChapter#1-Part-B-For-First-Monthly TestWasif QaziNo ratings yet
- System M6Document6 pagesSystem M6Lielanie NavarroNo ratings yet
- Micro 1Document8 pagesMicro 1Zuhaib AyazNo ratings yet
- PC FileDocument19 pagesPC FileSameer khanNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Embedded SystemsDocument5 pagesIntroduction to Embedded SystemssreedeepuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Embeded SystemsDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Embeded Systemsatraw2004No ratings yet
- Memory Chips: Types, Modules, and Instruction CyclesDocument10 pagesMemory Chips: Types, Modules, and Instruction Cyclesfaris daboolNo ratings yet
- UNIT I - Day-2Document13 pagesUNIT I - Day-2V VizNo ratings yet
- MICROPROCESSORSDocument10 pagesMICROPROCESSORSKELVIN MUTHININo ratings yet
- Types of ComputersDocument48 pagesTypes of Computersnaveed321100% (5)
- PC Hardware Assignment: By: M.Shamrin Sofia 18COAE049Document28 pagesPC Hardware Assignment: By: M.Shamrin Sofia 18COAE049Sofia ShamrinNo ratings yet
- Katani Kalan, Ludhiana: Project Report On Computer HardwareDocument33 pagesKatani Kalan, Ludhiana: Project Report On Computer HardwareVijayinder Singh PatialNo ratings yet
- Architecture Part 2Document3 pagesArchitecture Part 2araik.gevorgyan.20021907No ratings yet
- Memory and Storage SystemDocument10 pagesMemory and Storage SystemPranjal ParmarNo ratings yet
- Computer MemoryDocument34 pagesComputer MemoryAlice GuarinNo ratings yet
- CC C CCC ! "#!$%Document28 pagesCC C CCC ! "#!$%Suresh PatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22Document23 pagesChapter 22Midhun LNo ratings yet
- Arm Processor: by Neha Dewangan Guest Faculty Sos in Electronics & Photonics, PrsuDocument14 pagesArm Processor: by Neha Dewangan Guest Faculty Sos in Electronics & Photonics, PrsuNeha DewanganNo ratings yet
- PYE 422 Lecture NoteDocument11 pagesPYE 422 Lecture Notecoker yusufNo ratings yet
- BCE Unit 1 Part 3Document42 pagesBCE Unit 1 Part 3AbhiraNo ratings yet
- CCT Notes UnitDocument11 pagesCCT Notes Unitlalansingh549No ratings yet
- I2C Lab ManualsDocument60 pagesI2C Lab ManualsInstructor KoNo ratings yet
- MemoryDocument6 pagesMemorykevinkingili450No ratings yet
- Types of Computer: It Is A Midsize Multi-Processing System Capable of Supporting Up To 250 Users SimultaneouslyDocument5 pagesTypes of Computer: It Is A Midsize Multi-Processing System Capable of Supporting Up To 250 Users SimultaneouslyMunim RajpootNo ratings yet
- Interview Questions On Embedded ProcessorsDocument5 pagesInterview Questions On Embedded ProcessorsKALYANNo ratings yet
- Prepared by Dasun Nilanjana ForDocument24 pagesPrepared by Dasun Nilanjana ForKeshila JayasooriyaNo ratings yet
- Computer HardwareDocument56 pagesComputer HardwareKenneth BautistaNo ratings yet
- Computer OrganizationDocument5 pagesComputer OrganizationSARFRAZNo ratings yet
- Processor DesignDocument4 pagesProcessor Designapi-3760571No ratings yet
- DERTS Lec4Document32 pagesDERTS Lec4quNo ratings yet
- Different RAM Types and Its Uses: IntroDocument6 pagesDifferent RAM Types and Its Uses: Introkittu423No ratings yet
- As Chapter 3 HardwareDocument60 pagesAs Chapter 3 Hardwareasheralt3791No ratings yet
- Unit 1 - ARM7Document67 pagesUnit 1 - ARM7Makrand KakatkarNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management Practices in A Local Organization of BangladeshDocument12 pagesHuman Resource Management Practices in A Local Organization of BangladeshisanNo ratings yet
- Liquidity StatementDocument10 pagesLiquidity StatementFakir TajulNo ratings yet
- Classification of Computers GivenDocument5 pagesClassification of Computers GivenFakir TajulNo ratings yet
- Uu Co MacroeconomicsDocument3 pagesUu Co MacroeconomicsFakir TajulNo ratings yet
- Mod Te Ha Ge Liaison Office of BDDocument37 pagesMod Te Ha Ge Liaison Office of BDFakir TajulNo ratings yet
- Chronic Condition Self-Management Approaches Research and EvaluationDocument50 pagesChronic Condition Self-Management Approaches Research and EvaluationFakir TajulNo ratings yet
- Service Quality Bank v1 Sent 2Document12 pagesService Quality Bank v1 Sent 2Fakir TajulNo ratings yet
- Assignment FormatDocument7 pagesAssignment FormatFakir TajulNo ratings yet
- Fund Management Practices of Nationalized Bangladeshi BanksDocument13 pagesFund Management Practices of Nationalized Bangladeshi BanksFakir TajulNo ratings yet
- Profitability An v1 Sent 2Document9 pagesProfitability An v1 Sent 2Fakir TajulNo ratings yet
- Just For UploadDocument1 pageJust For UploadFakir TajulNo ratings yet
- Differences RAM ROM GivenDocument6 pagesDifferences RAM ROM GivenFakir TajulNo ratings yet
- Carers in Partnership Mental Health CommissioningDocument6 pagesCarers in Partnership Mental Health CommissioningFakir TajulNo ratings yet
- 5 BP White Paper Engagement 2Document10 pages5 BP White Paper Engagement 2Fakir TajulNo ratings yet
- Jahid e Business Jan5 SentDocument6 pagesJahid e Business Jan5 SentFakir TajulNo ratings yet
- Irr SolveDocument1 pageIrr SolveFakir TajulNo ratings yet
- Rumki - Managing Finance in Public Sector 3500 - April 13 Sent Plaz SolveDocument12 pagesRumki - Managing Finance in Public Sector 3500 - April 13 Sent Plaz SolveFakir TajulNo ratings yet
- What Is CRR & SLR Position and What Are The Components of CRR & SLR?Document8 pagesWhat Is CRR & SLR Position and What Are The Components of CRR & SLR?Fakir TajulNo ratings yet
- Rumki - Vision and Strategic Direction 3500 - April 13 - Sent Black Plaz SolvedDocument16 pagesRumki - Vision and Strategic Direction 3500 - April 13 - Sent Black Plaz SolvedFakir Tajul100% (1)
- Rex Research ProposalDocument20 pagesRex Research ProposalFakir TajulNo ratings yet
- MTB Millionaire PlanDocument5 pagesMTB Millionaire PlanFakir TajulNo ratings yet
- Rex - Research Proposal SentDocument15 pagesRex - Research Proposal SentFakir TajulNo ratings yet
- Unit 8Document1 pageUnit 8Fakir TajulNo ratings yet
- MTB Millionaire PlanDocument5 pagesMTB Millionaire PlanFakir TajulNo ratings yet
- Subject CoverageDocument1 pageSubject CoverageFakir TajulNo ratings yet
- UnusedDocument2 pagesUnusedFakir TajulNo ratings yet
- GK - Headquaters of OrganizationsDocument1 pageGK - Headquaters of OrganizationsFakir TajulNo ratings yet
- CFA Exam Calendar and FeesDocument12 pagesCFA Exam Calendar and FeesFakir TajulNo ratings yet
- Management skills and organizational behaviorDocument1 pageManagement skills and organizational behaviorFakir TajulNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Study of Different Image Denoising Methods: Afreen Mulla, A.G.Patil, Sneha Pethkar, Nishigandha DeshmukhDocument6 pagesA Comparative Study of Different Image Denoising Methods: Afreen Mulla, A.G.Patil, Sneha Pethkar, Nishigandha DeshmukherpublicationNo ratings yet
- Marketing Assignment (Cool Air India)Document10 pagesMarketing Assignment (Cool Air India)Mandira PantNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Muscle Response Testing MRTDocument14 pagesAn Introduction To Muscle Response Testing MRTJuan Aguilar HernándezNo ratings yet
- Mitigating arc ash hazards design constraintsDocument6 pagesMitigating arc ash hazards design constraintswaqas_a_shaikh4348No ratings yet
- Obeid Specialized Hospital - Riyadh: Inpatient DeptsDocument4 pagesObeid Specialized Hospital - Riyadh: Inpatient DeptsLovelydePerioNo ratings yet
- Plyometric Training Programs For Young Soccer Players: A Systematic ReviewDocument7 pagesPlyometric Training Programs For Young Soccer Players: A Systematic ReviewsteNo ratings yet
- Department of Education Region IV-A Business Plan GuideDocument4 pagesDepartment of Education Region IV-A Business Plan GuideSEAN DANIEL AGUARESNo ratings yet
- Grupo Stoncor Description - Stonhard Carboline Fibergrate PDFDocument22 pagesGrupo Stoncor Description - Stonhard Carboline Fibergrate PDFAndres OsorioNo ratings yet
- Kunduz Tutor Job Apply Question 1Document2 pagesKunduz Tutor Job Apply Question 1anirbanNo ratings yet
- Educ 1301 Field Experience 1 ThielenDocument4 pagesEduc 1301 Field Experience 1 Thielenapi-610903961No ratings yet
- CanReg5 InstructionsDocument150 pagesCanReg5 InstructionsdiyafersanNo ratings yet
- As Biology Revision L3 Cells Microscopes and IAM PPQ 2Document7 pagesAs Biology Revision L3 Cells Microscopes and IAM PPQ 2Anonymous fFKqcYNo ratings yet
- Check List of MossesDocument319 pagesCheck List of MossesAshen NirodyaNo ratings yet
- Atpl Formula MergedDocument74 pagesAtpl Formula Mergeddsw78jm2mxNo ratings yet
- CA 1 - Đề thi AV5 - CLC - Made - efDocument5 pagesCA 1 - Đề thi AV5 - CLC - Made - efQuang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Designing of 3 Phase Induction Motor Blackbook DoneDocument30 pagesDesigning of 3 Phase Induction Motor Blackbook Donetryd0% (1)
- Eccsa Five Year (2014 15 - 2018 19) Strategic PlanDocument95 pagesEccsa Five Year (2014 15 - 2018 19) Strategic Planyayehyirad100% (1)
- GulliverDocument8 pagesGulliverCris LuNo ratings yet
- IIT BOMBAY RESUME by SathyamoorthyDocument1 pageIIT BOMBAY RESUME by SathyamoorthySathyamoorthy VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Facts & Figures of Nepalese HydroDocument11 pagesFacts & Figures of Nepalese Hydromark bingNo ratings yet
- +GF+ Pressure Retaining Valve Type 586Document4 pages+GF+ Pressure Retaining Valve Type 586ROMNANo ratings yet
- Druckabschaltventil enDocument4 pagesDruckabschaltventil enSakthi Sekar CbiNo ratings yet
- Exoskeleton Power Requirements Based on Human BiomechanicsDocument54 pagesExoskeleton Power Requirements Based on Human Biomechanicsja2ja1No ratings yet
- Explosive Ordnance DisposalDocument13 pagesExplosive Ordnance DisposalZelwisNo ratings yet
- Sensor Guide: Standard Triaxial Geophones Specialty Triaxial Geophones Standard Overpressure MicrophonesDocument1 pageSensor Guide: Standard Triaxial Geophones Specialty Triaxial Geophones Standard Overpressure MicrophonesDennis Elias TaipeNo ratings yet
- Forensic Pharmacy: Dr. Zirwa AsimDocument35 pagesForensic Pharmacy: Dr. Zirwa AsimZirwa AsimNo ratings yet
- CH - 1Document4 pagesCH - 1Phantom GamingNo ratings yet
- CP QB PT-3 Harish KumarDocument3 pagesCP QB PT-3 Harish KumarVISHNU7 77No ratings yet
- Veiga Et Al. 2015 - Composition, Structure and Floristic Diversity in Dense Rain Forest inDocument8 pagesVeiga Et Al. 2015 - Composition, Structure and Floristic Diversity in Dense Rain Forest inYakov Mario QuinterosNo ratings yet