Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Summary Sheet For Grade 11 Summer Exam - PDF Waves and Sounds
Uploaded by
Faadumomizankaahiye0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views3 pageslesson is free with out money
Original Title
Summary Sheet for Grade 11 Summer Exam.pdf Waves and Sounds
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentlesson is free with out money
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
40 views3 pagesSummary Sheet For Grade 11 Summer Exam - PDF Waves and Sounds
Uploaded by
Faadumomizankaahiyelesson is free with out money
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Waves
1. definition wave: energy is transmitted in the form of waves
2.types: transverse, longitudinal, mechanical, electromagnetic definitions and e.gs of each type
3.wave form: rest position, amplitude, wavelength, cycle, period, frequency
4.Reflection: waves bounce off from surface so that angle of reflection = angle of incidence,
5.Refraction(pg 42): waves pass across a boundary and change speed and wavelength (freq stays the same)
6.Diffraction (pg 42): bending of waves around corners or obstacles. Sharp diffraction if opening is small compared to
wavelength, slight diffraction if opening is large compared to wavelength
7.Interference: constructive and destructive
Sound
1.longitudinal waves produced when objects vibrate, mechanical needs a medium
2.bell jar expt, (pg 54)sound spectrum, human hearing range (20Hz 20KHz), ultra sound (above 20KHz),
3.echoes used to find speed of sound in air (pg 56), depth sounding (pg 57), sonar
4.speed of sound in media of different densities. Sound travels fastest through solids, then liquids and slowest through
air. Faster in cold air than in hot air.
5.loudness related to amplitude, pitch depends on frequency.
6.strings: thickness, tension, length of string and frequency. [Thicker the string, lower the freq], [longer the string, lower
the freq], [greater the tension, higher the freq]
7.acoustics guitar depends on reverberations/ electric guitar needs amplifier, buildings
Light
1.types of optical material: opaque, transparent, translucent, luminous, non luminous
2.locate the light spectrum in the electromagnetic spectrum, travels in straight lines, point and extended sources,
shadows umbra and pen umbra.
3.images description *size of image in relation to size of object, *real or virtual,* upright or inverted, *image distance in
relation to object distance.
Image in Pinhole camera-*real,* inverted, *diminished, *image dist smaller than object dist.
Image in Plane mirror: *upright, *virtual, *same size,* image dist=object dist.
4.Laws of reflection:* incident ray, reflected ray and normal are all in the same plane.
* Angle of reflection = angle of incidence.
5. mirrors: ray diagrams: Rules for constructing ray diagrams for mirrors:
*any ray parallel to the principal axis is reflected through the principal focus
*any ray through the principal focus is reflected parallel to the principal axis
*any ray through the center of curvature is reflected back along its own path
*any ray incident at the pole is reflected making the same angle with the principal axis.
concave, converging mirror (many ray diagrams- 1 is virtual when object between F and P, make up mirror),
convex, diverging mirror (only 1 image description for object placed anywhere on principal axis)image is diminished,
virtual, formed between F and P, upright- used for rear view mirror of cars gives a wide field of view.
6.lenses: ray diagrams: Rules for constructing ray diagrams for lenses:
*any ray parallel to the principal axis is refracted through the principal focus on the other side of lens
*any ray through the principal focus is refracted parallel to the principal axis on the other side
*any ray through the optical center goes straight through undeviated (not refracted)
convex, converging lenses (many ray diagrams-1 is virtual when object place between optical center and F, magnifying
glass), concave, diverging lenses (only 1 image description for object placed anywhere on the principal axis)image is
diminished, virtual, upright, formed between optical center and F
7. Mirror and lens formula (real is positive sign convention) 1/f = 1/v + 1/u where f= focal length, v = image distance, u
= object distance
8. Magnification means how many times bigger the image is than the object. A magnification of 2 means that the image
is 2 times the size of the object. A magnification of 0.5 means that the image is 0.5 times the size of the object.
*Magnification = image distance/ object distance *Magnification = image height / object height
9.Power of lens = 1/ (focal length in meters) Thicker a lens, shorter the focal length
10.Refractive index (n) equations *n= sin I / sin r *n= real depth/ apparent depth
*n= speed of light in air / speed of light in medium * n=1/sin C therefore C = (1/n) sin
-1
C=critical angle
11. Critical angle (C) is an angle of incidence for which the angle of refraction =90
0
(or refracted ray lies along the
boundary) Total internal reflection occurs when the angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle.
12. Laws of refraction: *Snells law of refraction: the ratio of sin I to sin r is a constant for a given pair of media.
*The normal ray, incident ray and the refracted rays are all in the same plane.
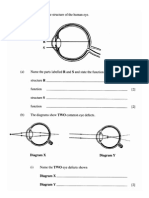
Eye (pg24)
1.compare the camera and eye, parts, function,
Short sightedness- light rays meet in front of the retina, correction: use concave, diverging lens.
Long sightedness- light rays meet behind the retina, correction: use convex, converging lens.
Colour (pg 27)
1.Dispersion of white light into its components (ROYGBIV)by prism,
2.Recombination of spectrum by prisms.
*Primary: red, blue, green *Secondary: magenta, cyan, yellow *Complimentary: [magenta,
green], [cyan, red], [yellow, blue]
Colours of the spectrum and relationship to wavelength and part of the electromagnetic
spectrum eg. Violet is closest to UV while Red is closest to IR.
Electromagnetic spectrum (pg 50)
1.complete spectrum in order of wavelengths or frequencies; gamma, x-rays, UV, infrared, , radio waves, (microwaves).
2.Properties of electromagnetic waves, learn at least 4: all electromagnetic waves *transfer energy from one place to
another * can be emitted and absorbed by matter *do not need a medium to travel through * travel at 3.0 x 10
8
m/s in a
vacuum * are transverse waves and can be polarized * can be superposed and produce interference effects
(constructive and destructive interference) *obey the laws of reflection and refraction * can be diffracted * carry no
charge
3.Uses and properties of individual electromagnetic waves
You might also like
- Gambool Properties of Mater 14Document13 pagesGambool Properties of Mater 14FaadumomizankaahiyeNo ratings yet
- Physics 3Document64 pagesPhysics 3FaadumomizankaahiyeNo ratings yet
- Gambool Properties of Matter.11Document14 pagesGambool Properties of Matter.11FaadumomizankaahiyeNo ratings yet
- Physics Word14Document5 pagesPhysics Word14FaadumomizankaahiyeNo ratings yet
- Cspap3 2007#1 EyeDocument2 pagesCspap3 2007#1 EyeFaadumomizankaahiyeNo ratings yet
- Physics 3Document64 pagesPhysics 3FaadumomizankaahiyeNo ratings yet
- Physics 4Document155 pagesPhysics 4FaadumomizankaahiyeNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Physics Summer Exams SummaryDocument2 pagesGrade 10 Physics Summer Exams SummaryFaadumomizankaahiyeNo ratings yet
- Lesson Topic: Wave Types and CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesLesson Topic: Wave Types and CharacteristicsFaadumomizankaahiyeNo ratings yet
- Form WotDocument1 pageForm WotFaadumomizankaahiyeNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Physics Summer Exams SummaryDocument2 pagesGrade 10 Physics Summer Exams SummaryFaadumomizankaahiyeNo ratings yet
- PDF Physics1Document2 pagesPDF Physics1FaadumomizankaahiyeNo ratings yet
- Physcics Form Two CajiibDocument36 pagesPhyscics Form Two CajiibFaadumomizankaahiyeNo ratings yet
- Aphyspap3 2011 #4 Machines, Energy, Work, PowerDocument2 pagesAphyspap3 2011 #4 Machines, Energy, Work, PowerFaadumomizankaahiyeNo ratings yet
- Aphyspap3 2011 #5 Heat SHCDocument3 pagesAphyspap3 2011 #5 Heat SHCFaadumomizankaahiyeNo ratings yet
- Aphyspap3 2011 #5 Heat SHCDocument3 pagesAphyspap3 2011 #5 Heat SHCFaadumomizankaahiyeNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics notes on charges, induction and Van de Graaff generatorDocument5 pagesElectrostatics notes on charges, induction and Van de Graaff generatorAbdiwahabSaedIbrahim67% (3)
- 03 - Description of Motion in Two and Three DimensionsDocument4 pages03 - Description of Motion in Two and Three DimensionsSuhaib_Faryad_5001No ratings yet
- Magnetism&Motors - PDF Form 2Document30 pagesMagnetism&Motors - PDF Form 2FaadumomizankaahiyeNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument24 pagesElectromagnetic WavesAzula Ada100% (1)
- 6 Optics PDFDocument29 pages6 Optics PDFthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Bounds6Document12 pagesBounds6Jack NachamkinNo ratings yet
- Kaertner - 2010 - Fundamentals - of - PhotonicsKaertner 2010 Fundamentals of PhotonicsDocument361 pagesKaertner - 2010 - Fundamentals - of - PhotonicsKaertner 2010 Fundamentals of Photonicsstlsgrg17No ratings yet
- Snell's LawDocument7 pagesSnell's LawKatiaAlbiterNo ratings yet
- Sample of Industrial Attachment ReportDocument35 pagesSample of Industrial Attachment ReportMudzimai Wanhasi83% (30)
- Holt Physics Chapter 4Document4 pagesHolt Physics Chapter 4mariedot5100% (1)
- DH-SD52C225I-HC: 2MP 25x Starlight PTZ HDCVI CameraDocument3 pagesDH-SD52C225I-HC: 2MP 25x Starlight PTZ HDCVI CameraMarcelo VeraNo ratings yet
- AFCAT GK General ScienceDocument53 pagesAFCAT GK General Sciencerustam1rioNo ratings yet
- Brewsters Fringes Optical PhenomenonDocument2 pagesBrewsters Fringes Optical PhenomenonAlejandra Lemus Vega0% (1)
- Experiment Design in PhysicsDocument11 pagesExperiment Design in Physicsmedha0% (1)
- Faraday's LawDocument9 pagesFaraday's LawaliNo ratings yet
- CHM 301 - Instrumentation and Analytical Chemistry I: Lecturer: Prof. F. M. AdebiyiDocument8 pagesCHM 301 - Instrumentation and Analytical Chemistry I: Lecturer: Prof. F. M. AdebiyiEmmanuel OladeleNo ratings yet
- QUIRINO GENERAL HIGH SCHOOL HOME LEARNING PLANDocument4 pagesQUIRINO GENERAL HIGH SCHOOL HOME LEARNING PLANPau AbuenaNo ratings yet
- Matrix of MatrixDocument9 pagesMatrix of Matrixubi bhattNo ratings yet
- Isaac Newton: Father of Modern PhysicsDocument4 pagesIsaac Newton: Father of Modern Physicsomar cariño rojasNo ratings yet
- 03 Deflection of Beta Particles in A Magnetic Field PDFDocument4 pages03 Deflection of Beta Particles in A Magnetic Field PDFPriya RamkissoonNo ratings yet
- Course Description File PHY123 SampleDocument3 pagesCourse Description File PHY123 SampleSaadNo ratings yet
- College Physics Volume 2 11th Edition Serway Solutions ManualDocument5 pagesCollege Physics Volume 2 11th Edition Serway Solutions ManualHshsNo ratings yet
- Exam 3a Rev QuesDocument35 pagesExam 3a Rev QuesUmesh Reddy100% (1)
- EDFA Amplifier Raman Amplifier Semiconductor Amplifier: A Comparison Based StudyDocument61 pagesEDFA Amplifier Raman Amplifier Semiconductor Amplifier: A Comparison Based StudySanjay YadavNo ratings yet
- DayStar Filters Magnesium Quark User ManualDocument16 pagesDayStar Filters Magnesium Quark User ManualfredpbNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation. of UvDocument4 pagesInstrumentation. of UvPriya VagelaNo ratings yet
- Science Intervention MaterialDocument41 pagesScience Intervention MaterialGlenn LelinaNo ratings yet
- New Physics CurrDocument21 pagesNew Physics CurrJan B. DivinaNo ratings yet
- Electric Field Between Parallel PlatesDocument40 pagesElectric Field Between Parallel PlatesJamieNo ratings yet
- The Following Are The Scientist Who Discover The Big Bang TheoryDocument3 pagesThe Following Are The Scientist Who Discover The Big Bang TheoryFrances Nicole ArceNo ratings yet
- Unit Term 2 Energy Review QuestionsDocument57 pagesUnit Term 2 Energy Review QuestionsLissa Hannah100% (1)
- The Critical AngleDocument8 pagesThe Critical AngleleonNo ratings yet
- Camera Cheat SheetDocument9 pagesCamera Cheat Sheetapi-301878235No ratings yet