Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Force and Pressure 1
Uploaded by
Amrita KaurOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Force and Pressure 1
Uploaded by
Amrita KaurCopyright:
Available Formats
http://www.OnlineTuition.com.
my
Online Learning Resources for Malaysia Students
Pressure
Pressure
Pressure is defined as the force acting normally per unit area.
(Here, the word "normally" means perpendicularly.)
The SI unit of pressure is Pascal (Pa). 1 Pa is eaual to1 newton
per metre
2
(N/m
2
).
Factors that affect the pressure acting on a surface.
Magnitude of the force.
The larger the force, the higher the pressure.
Contact area.
The larger the contact area, the lower the pressure.
Examples of application of high pressure are:
a. Sharp Knife
b. Ice-Skate
c. Sole of shoes with spike
Examples of application of low pressure are
a. Foundation of Building
b. Snow Shoes
c. Tyre of Tractor
d. Feet of Elephant
Note
http://www.OnlineTuition.com.my
Online Learning Resources for Malaysia Students
Liquid Pressure
Pressure in Liquids
1. Pressure in liquid is owing to the weight of the
liquid acting on the surface of any objects in the
liquid.
2. Pressure of a liquid is directly proportional to
a. the gravitational field strength
b. the depth
c. density of the liquid.
Formulae:
Pressure caused by a liquid
P = hg
Pressure in a liquid
P = hg + P
atm
U-Tube
Usually, a U-tube is used to compare and measure density
of liquids.
The density of the 2 liquids is related by the equation:
Application of Liquid Pressure
1. Dam
2. Submarine
3. Measuring Blood Pressure
4. Intravenous Transfusion
5. Water Tower
http://www.OnlineTuition.com.my
Online Learning Resources for Malaysia Students
Gas & Atmospheric Pressure
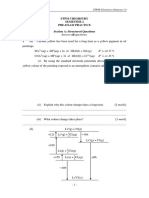
Q: Explain how gas pressure is produced in a closed
container?
A:
Gas molecules in the container are in constant
and random motion.
As a result, the gas molecules collide on the
inner wall of the container.
After colliding on the wall, the gas molecules
bounce off, and the direction change creating a
change of momentum to the molecule of the gas.
The change of momentum produces a force on
the wall.
The force per unit area is the pressure on the
wall.
Atmospheric Pressure
1. On the surface of the earth, there is a thick
layer of gas called the atmosphere. The
atmosphere consists of various types of gas
called the atmospheric gas.
2. The atmospheric gases collide on the surface
of the earth and hence exert a pressure on the
surface of the earth, called the atmospheric
pressure.
3. The atmospheric pressure can be measured in
the unit of atm, mmHg or Pa. The atmospheric
pressure at sea level is taken to be 1 atm,
which is approximately 760 mmHg or 101,000
Pa.
Characteristics of
Atmospherics Pressure
Decreases with altitude
The atmospheric pressure changes accordingly to the altitude. Altitude is
the height above sea level. The greater the altitude, the lower the
atmospheric pressure.
Act equally in all direction
The atmospheric pressure acts on every object in
the atmosphere. It acts equally in all direction.
Atmospheric pressure is ~ 100,000Pa at sea level
On the surface of the earth, the atmospheric pressure
can be as high as 101,000 Pa.
Proof of Existence of Atmospheric Pressure
The existence of the atmospheric pressure can be proved
by the following experiments.
a. Crushing can experiment
b. Water cover with cardboard does not flow out
c. Magdeburg Hemisphere
Instruments Used to Measure Atmospheric Pressure
Atmospheric pressure can be measured by either
a. a simple barometer,
b. a Fortin barometer
c. an Aneroid barometer.
Unit Used to Measure Atmospheric Pressure
1. Pascal (Pa)
2. Standard
Atmospheric
Pressure (atm)
3. mmHg (also
known as torr)
1 Pa = 1 N/m
2
1 atm = Atmospheric Pressure at
sea level ( = 101,325 Pa)
1 mmHg = 1/760 atm (roughly
equal to the liquid pressure
exerted by a millimetre of
mercury). In SPM, usually we use
the unit cmHg, instead of mmHg
http://www.OnlineTuition.com.my
Online Learning Resources for Malaysia Students
Gas & Atmospheric Pressure
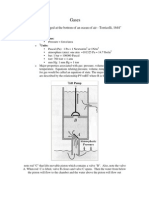
Simple Barometer
2 Cases
No air trapped in the tube Some air trapped in the tube
Pressure at A = x cmHg
Atmospheric pressure = h cmHg
Pressure at A = x cmHg + P
gas
Atmospheric pressure = h cmHg + P
gas
Characteristics of the Mercury Barometer
http://www.OnlineTuition.com.my
Online Learning Resources for Malaysia Students
Application of Atmospheric Pressure
Instruments Used to Measure Gas Pressure
The pressure of the gas in a container can be measured
by using
a. Bourdon gauge
b. Manometer
P
gas
= P
atm
+ P
liquid
.
http://www.OnlineTuition.com.my
Online Learning Resources for Malaysia Students
Pascals Principle
Pascal's principle states that in a
confined fluid, an externally
applied pressure is transmitted
uniformly in all directions.
Pascal's principle is also known as
the principle of transmission of
pressure in a liquid.
Experiment
When the plunger is pushed in, the water
squirts equally from all the holes. This
shows that the pressure applied to the
plunger has been transmitted uniformly
throughout the water.
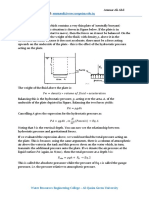
Hydraulic System
A hydraulic system applies Pascal's principle in its
working mechanism. It can be used as a force
multiplier.
According to Pascals principle,
Change of Oil Level in a Hydraulic System
In the diagram to the left, when piston-X is pressed
down, piston-Y will be push up. The change of the piston
levels of the 2 pistons is given by the following equation:
http://www.OnlineTuition.com.my
Online Learning Resources for Malaysia Students
Archimedes Principle
Archimedes Principle
1. Archimedes Principle states that when a body
is wholly or partially immersed in a fluid it
experiences an upthrust equal to the weight of
the fluid displaced.
2. Upthrust/Buoyant force is an upward force
exerted by a fluid on an object immersed in it.
F = Upthrust/Buoyant Force
= Density of the liquid
V = Volume of the displaced liquid
g = Gravitational field strength
Revision Note:
Density = mass per unit volume
Principle of Floatation
F = W
1. The principle of floatation states that when an
object floats in a liquid the buoyant
force/upthrust that acts on the object is equal
to the weight of the object.
2. If the weight of the object > upthrust, the
object will sink into the fluid.
Application of Archimedes Principle
1. Plimsoll Line
2. Airship
3. Hot Air Balloon
4. Hydrometers
5. Submarine
http://www.OnlineTuition.com.my
Online Learning Resources for Malaysia Students
Bernoullis Principle
Liquids flow from places with higer pressure to places
with lower pressure.
Q: Explain why the water level at B is the lowest.
A:
The pressure at B is the lowest because the liquid flow the
fastest at B. Therefore, the water level is the lowest at B.
Gases flow from places with higer pressure to places with
lower pressure.
Q: Explain why the water level at B is the highest.
A:
The pressure at B is the lowest because the gas flow the
fastest at B. Therefore, the atmospheric pressure will push he
water to the highest at B.
Bernoullis Principle
Bernoulli's Principle states that as the speed of a moving fluid (liquid or gas)
increases, the pressure within the fluid decreases.
Venturi Effect
The Venturi effect is the fluid pressure
that results when an incompressible
fluid flows through a constricted
section of a pipe.
You might also like
- Pressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Physics NoteDocument8 pagesPhysics NotePoul GonaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Module Pressure ExplainedDocument15 pagesFluid Mechanics Module Pressure ExplainedGabriel CortesNo ratings yet
- 5.0 PressureDocument82 pages5.0 PressureKalkien CtNo ratings yet
- Fluid - Is A Substance That ContinuallyDocument8 pagesFluid - Is A Substance That ContinuallybenjerickNo ratings yet
- Understanding Pressure: Applications of Pressure in Everyday LivingDocument9 pagesUnderstanding Pressure: Applications of Pressure in Everyday Livingredz45No ratings yet
- Fluid-Mechanics (1)Document7 pagesFluid-Mechanics (1)Jim Bryan Wabina VergaraNo ratings yet
- Abe 106 - 04Document42 pagesAbe 106 - 04emmanuelNo ratings yet
- Pressure Measuring DevicesDocument11 pagesPressure Measuring DevicesKevin HiralalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Lecture Notes: P GH P GH +P F (A /A B W Q V/ T Av A V A V P V Gy + (1/2) V Gy F Av/lDocument13 pagesChapter 10 Lecture Notes: P GH P GH +P F (A /A B W Q V/ T Av A V A V P V Gy + (1/2) V Gy F Av/lvijayabharathi_vijivijiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Force & Pressure (Form 4)Document30 pagesChapter 3: Force & Pressure (Form 4)ruslawati100% (7)
- Pressure Physics Form 4Document47 pagesPressure Physics Form 4Hairul Akmal100% (2)
- Fluidi MaturskiDocument25 pagesFluidi MaturskiFarisNo ratings yet
- Sub Unit 1.2 - Fluid ForceDocument24 pagesSub Unit 1.2 - Fluid ForceAd Man GeTigNo ratings yet
- 6 Hydro Static DynamicDocument15 pages6 Hydro Static DynamiclundNo ratings yet
- GP6; PressureDocument5 pagesGP6; Pressuredinakempho3No ratings yet
- HYDROSTATICDocument8 pagesHYDROSTATICryan valerioNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 4Document10 pagesPhysics Form 4Woody CysNo ratings yet
- Presentation-Selected Topics of Physics-Stage 1Document23 pagesPresentation-Selected Topics of Physics-Stage 1diego reyesNo ratings yet
- Pressure 130723134649 Phpapp02Document76 pagesPressure 130723134649 Phpapp02Syazwana ElleasNo ratings yet
- Pressure: Force Area Perpendicular Gauge PressureDocument6 pagesPressure: Force Area Perpendicular Gauge PressureSyed Rameez MohiuddinNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 FORCES AND PRESSUREDocument57 pagesCHAPTER 3 FORCES AND PRESSURENor RasyidahNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project BernoullisDocument21 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project BernoullisvujayjananiNo ratings yet
- Fluids: Phys101 Lectures 23-27Document46 pagesFluids: Phys101 Lectures 23-27Raymund Dante CorderoNo ratings yet
- IY472 - Hydrostatics LabDocument2 pagesIY472 - Hydrostatics Labafatima paintingNo ratings yet
- Unit 7,8,9Document23 pagesUnit 7,8,9Adalbert MugambiraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 FluidsDocument51 pagesChapter 4 FluidsshahrulNo ratings yet
- Name: Salsadila Safitri Nim: 1805124208 Class: 6B Prodi: Pendidikan FisikaDocument8 pagesName: Salsadila Safitri Nim: 1805124208 Class: 6B Prodi: Pendidikan FisikaSalsadilaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1-Fluid Statics 2003Document6 pagesLecture 1-Fluid Statics 2003Leonardo LibresNo ratings yet
- PressureDocument6 pagesPressuredemetri lanezNo ratings yet
- Ap Physics B Lesson 64 76 Fluid MechanicsDocument58 pagesAp Physics B Lesson 64 76 Fluid MechanicsTammy SelaromNo ratings yet
- Fluids Assignment 2-1Document5 pagesFluids Assignment 2-1Cedric Arcel CruzNo ratings yet
- 1.8 Notes On Subtopic Pressure 5054 O Level PhysicsDocument11 pages1.8 Notes On Subtopic Pressure 5054 O Level Physicsmeyote4831No ratings yet
- Outcome 1 Static Fluid Systems Tutorial 1 Hydrostatics PDFDocument20 pagesOutcome 1 Static Fluid Systems Tutorial 1 Hydrostatics PDFMehdi SoltaniNo ratings yet
- Pressure Concept Derivation Sample ProblemsDocument22 pagesPressure Concept Derivation Sample ProblemsAyumi QuiomNo ratings yet
- CIE IGCSE Physics (0625) Pressure NotesDocument22 pagesCIE IGCSE Physics (0625) Pressure Notes9322483% (53)
- Hydrostatic Pressure: Ammarali@wrec - Uoqasim.edu - IqDocument13 pagesHydrostatic Pressure: Ammarali@wrec - Uoqasim.edu - IqCristopher SaldañaNo ratings yet
- Ap Physics B Lesson 64 76 Fluid MechanicsDocument58 pagesAp Physics B Lesson 64 76 Fluid MechanicslizaNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric PressureDocument12 pagesAtmospheric Pressureanwar9602020No ratings yet
- Basic Hydraulics Engineering ConceptsDocument125 pagesBasic Hydraulics Engineering ConceptsClaire Rizsha QuilonNo ratings yet
- Abe 106 - 01Document6 pagesAbe 106 - 01emmanuelNo ratings yet
- Pressure: A Force Per Unit AreaDocument11 pagesPressure: A Force Per Unit AreaToretto100% (1)
- JESSICA M. NAVOR - Pressure and Fluid StaticDocument34 pagesJESSICA M. NAVOR - Pressure and Fluid StaticJessica Manawes NavorNo ratings yet
- Lec. 1Document31 pagesLec. 1Ali. AboudNo ratings yet
- Part - 2Document81 pagesPart - 2aryanneet9599No ratings yet
- Presentation-4 (Pressure Its Measurement)Document45 pagesPresentation-4 (Pressure Its Measurement)Ali Al AbdullahNo ratings yet
- chapter 3Document37 pageschapter 3Moaaz AshrafNo ratings yet
- Physics Bernoulis Theorem Project CBSE Class 12Document21 pagesPhysics Bernoulis Theorem Project CBSE Class 12Faaiz100% (3)
- Fluid Mechanics Lab Manual IntroductionDocument50 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab Manual IntroductionpaniuatuiNo ratings yet
- PRESSURE AND (Repaired)Document138 pagesPRESSURE AND (Repaired)NitishNo ratings yet
- Fluid Dynamics Chapter SummaryDocument12 pagesFluid Dynamics Chapter SummaryLorenzo Miguel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- PressureDocument17 pagesPressurePrashant sapkota100% (1)
- Fluid MechanicsDocument45 pagesFluid MechanicsSean Eric CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1a GasesDocument12 pagesChapter 1a GasesKarunakarNo ratings yet
- Fluid-Pressure-and-Pressure-GaugesDocument47 pagesFluid-Pressure-and-Pressure-GaugesSin Za DolaNo ratings yet
- Diapositivas 2da UnidadDocument47 pagesDiapositivas 2da UnidadRuben Edhino Vicente DueñasNo ratings yet
- Lipids Biologial Membrane Transport Part II PDFDocument24 pagesLipids Biologial Membrane Transport Part II PDFJia HuiNo ratings yet
- Development and Implementation of VLSI Reconfigurable Architecture For Gabor Filter in Medical Imaging Application - ZenodoDocument6 pagesDevelopment and Implementation of VLSI Reconfigurable Architecture For Gabor Filter in Medical Imaging Application - ZenodoJia HuiNo ratings yet
- Smart Home Security Access System Using Field Programmable Gate ArraysDocument9 pagesSmart Home Security Access System Using Field Programmable Gate ArraysJia HuiNo ratings yet
- Russell C. Hibbeler: Chapter 5: TorsionDocument30 pagesRussell C. Hibbeler: Chapter 5: TorsionJia HuiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Functional Electrical StimulationDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Functional Electrical StimulationJia HuiNo ratings yet
- Dcug 5Document14 pagesDcug 5Nguyen Le HungNo ratings yet
- Sta 9 1Document125 pagesSta 9 1Jayaprakash Polimetla100% (1)
- Carbohydrates-Monosaccharide DerivativesDocument7 pagesCarbohydrates-Monosaccharide DerivativesJia HuiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Linear Models For Classification PDFDocument32 pagesLecture 6 Linear Models For Classification PDFJia HuiNo ratings yet
- A Real-Time QRS Detection AlgorithmDocument7 pagesA Real-Time QRS Detection AlgorithmHoang ManhNo ratings yet
- Synopsysi PDKDocument1 pageSynopsysi PDKJia HuiNo ratings yet
- Formula Solid MechanicsDocument4 pagesFormula Solid MechanicsJia HuiNo ratings yet
- Icc Saed32 Patcp10 PDFDocument16 pagesIcc Saed32 Patcp10 PDFJia HuiNo ratings yet
- Synopsys Class 2 5 1Document67 pagesSynopsys Class 2 5 1prashanth kumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 - Glucose Biosensor - Lim Jia HuiDocument7 pagesAssignment 2 - Glucose Biosensor - Lim Jia HuiJia HuiNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilator: Nur Aina Athiraa Binti Azman Wan Sabrina Binti Wan Safuan Azkiyyah Wahida Binti DzulkifliDocument35 pagesMechanical Ventilator: Nur Aina Athiraa Binti Azman Wan Sabrina Binti Wan Safuan Azkiyyah Wahida Binti DzulkifliJia HuiNo ratings yet
- Kidney Injury, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Abnormalities in AlcoholicsDocument15 pagesKidney Injury, Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Abnormalities in AlcoholicsJia HuiNo ratings yet
- Lim Jia Hui - Protein Misfolding (Alzheimer's Disease)Document5 pagesLim Jia Hui - Protein Misfolding (Alzheimer's Disease)Jia HuiNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment - TitrationDocument3 pagesIndividual Assignment - TitrationJia HuiNo ratings yet
- Maintainance of The Body Part 2Document26 pagesMaintainance of The Body Part 2Jia Hui100% (1)
- Maintenance of The BodyDocument34 pagesMaintenance of The BodyJia HuiNo ratings yet
- 3-Lead ECG Acquisition - Information SheetDocument3 pages3-Lead ECG Acquisition - Information SheetMarcelo PinottiNo ratings yet
- O2 and Co2 PDFDocument73 pagesO2 and Co2 PDFJia HuiNo ratings yet
- Types of CirculationDocument19 pagesTypes of CirculationJia HuiNo ratings yet
- Chem Sem 2 STRDocument44 pagesChem Sem 2 STRJia Hui50% (2)
- Flame Test (Group 2 Metals)Document2 pagesFlame Test (Group 2 Metals)Jia HuiNo ratings yet
- Trial Term 2 2014 Graphs and Differential EquationsDocument3 pagesTrial Term 2 2014 Graphs and Differential EquationsJia HuiNo ratings yet
- (Edu - Joshuatly.com) N9 STPM Trial 2010 Biology (W Ans) (7D789A37) PDFDocument34 pages(Edu - Joshuatly.com) N9 STPM Trial 2010 Biology (W Ans) (7D789A37) PDFJia HuiNo ratings yet
- HivDocument4 pagesHivJia HuiNo ratings yet
- (Edu - Joshuatly.com) N9 STPM Trial 2010 Biology (W Ans) (7D789A37) PDFDocument34 pages(Edu - Joshuatly.com) N9 STPM Trial 2010 Biology (W Ans) (7D789A37) PDFJia HuiNo ratings yet