Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Arduino Mega 2560
Uploaded by
GustavoMartinezOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Arduino Mega 2560
Uploaded by
GustavoMartinezCopyright:
Available Formats
Arduino Mega 2560
Ov er v i ew
The Arduino Mega 2560 is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega2560 (datasheet). It has 54 digital input/output
pins (of which 14 can be used as PWM outputs), 16 analog inputs, 4 UARTs (hardware serial ports), a 16 MHz crystal
oscillator, a USB connection, a power jack, an ICSP header, and a reset button. It contains everything needed to support
the microcontroller; simply connect it to a computer with a USB cable or power it with a AC-to-DC adapter or battery to
get started. The Mega is compatible with most shields designed for the Arduino Duemilanove or Diecimila.
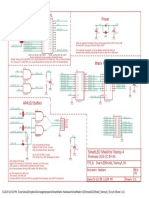
Sch emat i c & Ref er en ce Desi g n
EAGLE files: arduino-mega2560-reference-design.zip
Schematic: arduino-mega2560-schematic.pdf
Su mmar y
Microcontroller ATmega2560
Operating Voltage 5V
Input Voltage (recommended) 7-12V
Input Voltage (limits) 6-20V
Digital I/O Pins 54 (of which 14 provide PWM output)
Analog Input Pins 16
DC Current per I/O Pin 40 mA
DC Current for 3.3V Pin 50 mA
Flash Memory 256 KB of which 8 KB used by bootloader
SRAM 8 KB
EEPROM 4 KB
Clock Speed 16 MHz
Power
The Arduino Mega can be powered via the USB connection or with an external power supply. The power source is selected
automatically.
External (non-USB) power can come either from an AC-to-DC adapter (wall-wart) or battery. The adapter can be
connected by plugging a 2.1mm center-positive plug into the board's power jack. Leads from a battery can be inserted in
the Gnd and Vin pin headers of the POWER connector.
The board can operate on an external supply of 6 to 20 volts. If supplied with less than 7V, however, the 5V pin may supply
less than five volts and the board may be unstable. If using more than 12V, the voltage regulator may overheat and damage
the board. The recommended range is 7 to 12 volts.
The Mega2560 differs from all preceding boards in that it does not use the FTDI USB-to-serial driver chip. Instead, it
features the Atmega8U2 programmed as a USB-to-serial converter.
The power pins are as follows:
VIN. The input voltage to the Arduino board when it's using an external power source (as opposed to 5 volts from the
USB connection or other regulated power source). You can supply voltage through this pin, or, if supplying voltage via
the power jack, access it through this pin.
5V. The regulated power supply used to power the microcontroller and other components on the board. This can come
either from VIN via an on-board regulator, or be supplied by USB or another regulated 5V supply.
3V3. A 3.3 volt supply generated by the on-board regulator. Maximum current draw is 50 mA.
GND. Ground pins.
Memor y
The ATmega2560 has 256 KB of flash memory for storing code (of which 8 KB is used for the bootloader), 8 KB of SRAM
and 4 KB of EEPROM (which can be read and written with the EEPROM library).
I n p u t an d Ou t p u t
Each of the 54 digital pins on the Mega can be used as an input or output, using pinMode(), digitalWrite(), and
digitalRead() functions. They operate at 5 volts. Each pin can provide or receive a maximum of 40 mA and has an internal
pull-up resistor (disconnected by default) of 20-50 kOhms. In addition, some pins have specialized functions:
Serial: 0 (RX) and 1 (TX); Serial 1: 19 (RX) and 18 (TX); Serial 2: 17 (RX) and 16 (TX); Serial 3: 15
(RX) and 14 (TX). Used to receive (RX) and transmit (TX) TTL serial data. Pins 0 and 1 are also connected to the
corresponding pins of the ATmega8U2 USB-to-TTL Serial chip.
External Interrupts: 2 (interrupt 0), 3 (interrupt 1), 18 (interrupt 5), 19 (interrupt 4), 20 (interrupt
3), and 21 (interrupt 2). These pins can be configured to trigger an interrupt on a low value, a rising or falling edge,
or a change in value. See the attachInterrupt() function for details.
PWM: 0 to 13. Provide 8-bit PWM output with the analogWrite() function.
SPI: 50 (MISO), 51 (MOSI), 52 (SCK), 53 (SS). These pins support SPI communication using the SPI library.
The SPI pins are also broken out on the ICSP header, which is physically compatible with the Uno, Duemilanove and
Diecimila.
LED: 13. There is a built-in LED connected to digital pin 13. When the pin is HIGH value, the LED is on, when the
pin is LOW, it's off.
I
2
C: 20 (SDA) and 21 (SCL). Support I
2
C (TWI) communication using the Wire library (documentation on the
Wiring website). Note that these pins are not in the same location as the I
2
C pins on the Duemilanove or Diecimila.
The Mega2560 has 16 analog inputs, each of which provide 10 bits of resolution (i.e. 1024 different values). By default they
measure from ground to 5 volts, though is it possible to change the upper end of their range using the AREF pin and
analogReference() function.
There are a couple of other pins on the board:
AREF. Reference voltage for the analog inputs. Used with analogReference().
Reset. Bring this line LOW to reset the microcontroller. Typically used to add a reset button to shields which block
the one on the board.
Commu n i cat i on
The Arduino Mega2560 has a number of facilities for communicating with a computer, another Arduino, or other
microcontrollers. The ATmega2560 provides four hardware UARTs for TTL (5V) serial communication. An ATmega8U2
on the board channels one of these over USB and provides a virtual com port to software on the computer (Windows
machines will need a .inf file, but OSX and Linux machines will recognize the board as a COM port automatically. The
Arduino software includes a serial monitor which allows simple textual data to be sent to and from the board. The RX and
TX LEDs on the board will flash when data is being transmitted via the ATmega8U2 chip and USB connection to the
computer (but not for serial communication on pins 0 and 1).
A SoftwareSerial library allows for serial communication on any of the Mega2560's digital pins.
The ATmega2560 also supports I2C (TWI) and SPI communication. The Arduino software includes a Wire library to
simplify use of the I2C bus; see the documentation on the Wiring website for details. For SPI communication, use the SPI
library.
Pr og r ammi n g
The Arduino Mega can be programmed with the Arduino software (download). For details, see the reference and tutorials.
The ATmega2560 on the Arduino Mega comes preburned with a bootloader that allows you to upload new code to it
without the use of an external hardware programmer. It communicates using the original STK500 protocol (reference, C
header files).
You can also bypass the bootloader and program the microcontroller through the ICSP (In-Circuit Serial Programming)
header; see these instructions for details.
The ATmega8U2 firmware source code is available in the Arduino repository. The ATmega8U2 is loaded with a DFU
bootloader, which can be activated by connecting the solder jumper on the back of the board (near the map of Italy) and
then resetting the 8U2. You can then use Atmel's FLIP software (Windows) or the DFU programmer (Mac OS X and
Linux) to load a new firmware. Or you can use the ISP header with an external programmer (overwriting the DFU
bootloader). See this user-contributed tutorial for more information.
Au t omat i c ( Sof t war e) Reset
Rather then requiring a physical press of the reset button before an upload, the Arduino Mega2560 is designed in a way
that allows it to be reset by software running on a connected computer. One of the hardware flow control lines (DTR) of
the ATmega8U2 is connected to the reset line of the ATmega2560 via a 100 nanofarad capacitor. When this line is
asserted (taken low), the reset line drops long enough to reset the chip. The Arduino software uses this capability to allow
you to upload code by simply pressing the upload button in the Arduino environment. This means that the bootloader can
have a shorter timeout, as the lowering of DTR can be well-coordinated with the start of the upload.
This setup has other implications. When the Mega2560 is connected to either a computer running Mac OS X or Linux, it
resets each time a connection is made to it from software (via USB). For the following half-second or so, the bootloader is
running on the Mega2560. While it is programmed to ignore malformed data (i.e. anything besides an upload of new
code), it will intercept the first few bytes of data sent to the board after a connection is opened. If a sketch running on the
board receives one-time configuration or other data when it first starts, make sure that the software with which it
communicates waits a second after opening the connection and before sending this data.
The Mega2560 contains a trace that can be cut to disable the auto-reset. The pads on either side of the trace can be
soldered together to re-enable it. It's labeled "RESET-EN". You may also be able to disable the auto-reset by connecting a
110 ohm resistor from 5V to the reset line; see this forum thread for details.
USB Ov er cu r r en t Pr ot ect i on
The Arduino Mega2560 has a resettable polyfuse that protects your computer's USB ports from shorts and overcurrent.
Although most computers provide their own internal protection, the fuse provides an extra layer of protection. If more
than 500 mA is applied to the USB port, the fuse will automatically break the connection until the short or overload is
removed.
Ph y si cal Ch ar act er i st i cs an d Sh i el d Comp at i b i l i t y
The maximum length and width of the Mega2560 PCB are 4 and 2.1 inches respectively, with the USB connector and
power jack extending beyond the former dimension. Three screw holes allow the board to be attached to a surface or case.
Note that the distance between digital pins 7 and 8 is 160 mil (0.16"), not an even multiple of the 100 mil spacing of the
other pins.
The Mega2560 is designed to be compatible with most shields designed for the Uno, Diecimila or Duemilanove. Digital
pins 0 to 13 (and the adjacent AREF and GND pins), analog inputs 0 to 5, the power header, and ICSP header are all in
equivalent locations. Further the main UART (serial port) is located on the same pins (0 and 1), as are external interrupts
0 and 1 (pins 2 and 3 respectively). SPI is available through the ICSP header on both the Mega2560 and Duemilanove /
Diecimila. Please note that I
2
C is not located on the same pins on the Mega (20 and 21) as the Duemilanove / Diecimila
(analog inputs 4 and 5).
ICSP
+5V
GND
+5V
GND
GND
+5V
GND GND
47u 47u
GND GND
G
N
D
GND
GREEN
G
N
D
+5V
M7
GND
MC33269D-5.0
MC33269ST-5.0T3
100n
GND
100n
100n
+3V3
+5V
+5V
ATMEGA1280-16AU
100n 100n
22p
+5V
GND
100n
GND
1
0
0
n
YELLOW
YELLOW
500mA
+5V
100n
GND
YELLOW
G
N
D
1
0
0
n
FDN340P
LM358D LM358D
GND
100n
GND
+5V
100n
+5V
GND
+5V
GND
1u
+5V
ATMEGA8U2-MU
ICSP
+5V
GND
GND
16MHz
G
N
D
GND
BLM21
P
G
B
1
0
1
0
6
0
4
P
G
B
1
0
1
0
6
0
4
16MHz
G
N
D
1M
1k
1k
1k
1k
1
0
K
1
0
K
1
0
K
10K
1
0
K
1
0
K
1
0
K
10K
1k
1k
1k
1k
22R
22R
22R
22R
GND
TS42
1M
1
6
M
H
z
1
6
M
H
z
2
2
p
2
2
p
2
2
p
2
2
p
G
N
D
G
N
D
GND
2
7
R
2
7
R
1 2
3 4
5 6
ICSP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
PWML
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
PWMH
PC1 PC2
ON
D1
1
1
2
2
3
3
VI
3
1
VO
2
IC2
ADJ
1
IN
3
OUT
4
2
IC1
1
2
3
4
5
6
POWER
C3
C6
C2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
ADCL
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
COMMUNICATION
(A8)PC0
53
(A9)PC1
54
(A10)PC2
55
(A11)PC3
56
(A12)PC4
57
(A13)PC5
58
(A14)PC6
59
(A15)PC7
60
(AD0)PA0
78
(AD1)PA1
77
(AD2)PA2
76
(AD3)PA3
75
(AD4)PA4
74
(AD5)PA5
73
(AD6)PA6
72
(AD7)PA7
71
(ADC0)PF0
97
(ADC1)PF1
96
(ADC2)PF2
95
(ADC3)PF3
94
(ADC4/TCK)PF4
93
(ADC5/TMS)PF5
92
(ADC6/TDO)PF6
91
(ADC7/TDI)PF7
90
(ALE)PG2
70
(CLKO/ICP3/INT7)PE7
9
(ICP1)PD4
47
(MISO/PCINT3)PB3
22
(MOSI/PCINT2)PB2
21
(OC0A/OC1C/PCINT7)PB7
26
(OC0B)PG5
1
(OC1A/PCINT5)PB5
24
(OC1B/PCINT6)PB6
25
(OC2A/PCINT4)PB4
23
(OC3A/AIN1)PE3
5
(OC3B/INT4)PE4
6
(OC3C/INT5)PE5
7
(RD)PG1
52
(RXD0/PCIN8)PE0
2
(RXD1/INT2)PD2
45
(SCK/PCINT1)PB1
20
(SCL/INT0)PD0
43
(SDA/INT1)PD1
44
(SS/PCINT0)PB0
19
(T0)PD7
50
(T1)PD6
49
(T3/INT6)PE6
8
(TOSC1)PG4
29
(TOSC2)PG3
28
(TXD0)PE1
3
(TXD1/INT3)PD3
46
(WR)PG0
51
(XCK0/AIN0)PE2
4
(XCK1)PD5
48
AGND
99
AREF
98
AVCC
100
GND
11
32
62
81
PH0(RXD2)
12
PH1(TXD2)
13
PH2(XCK2)
14
PH3(OC4A)
15
PH4(OC4B)
16
PH5(OC4C)
17
PH6(OC2B)
18
PH7(T4)
27
PJ0(RXD3/PCINT9)
63
PJ1(TXD3/PCINT10)
64
PJ2(XCK3/PCINT11)
65
PJ3(PCINT12)
66
PJ4(PCINT13)
67
PJ5(PCINT14)
68
PJ6(PCINT15)
69
PJ7
79
PK0(ADC8/PCINT16)
89
PK1(ADC9/PCINT17)
88
PK2(ADC10/PCINT18)
87
PK3(ADC11/PCINT19)
86
PK4(ADC12/PCINT20)
85
PK5(ADC13/PCINT21)
84
PK6(ADC14/PCINT22)
83
PK7(ADC15/PCINT23)
82
PL0(ICP4)
35
PL1(ICP5)
36
PL2(T5)
37
PL3(OC5A)
38
PL4(OC5B)
39
PL5(OC5C)
40
PL6
41
PL7
42
RESET
30
VCC
10
31
61
80
XTAL1
34
XTAL2
33
GND
GND
GND
VCC
VCC
VCC
IC3
C5 C4
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
ADCH
C1
C8
C
1
3
RX
TX
1
2
3
4 P
$
1
P
$
1
P
$
2
P
$
2
X2 F1
C9
L
C
7
T2
2
3
1
IC5A
6
5
7
IC5B
8
4
C12
C11
1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
9 10
11 12
13 14
15 16
XIOH
1 2
3 4
5 6
7 8
9 10
11 12
13 14
15 16
XIOL
1 JP1
1 JP2
1 JP3
1 JP4
2 1
RESET-EN
C10
(PCINT9/OC1B)PC5
25
(PCINT10)PC4
26
(INT4/ICP1/CLK0)PC7
22
(OC1A/PCINT8)PC6
23
(AIN2/PCINT11)PC2
5
(PCINT5)PB5
19
(T1/PCINT4)PB4
18
(PD0/MISO/PCINT3)PB3
17
(PDI/MOSI/PCINT2)PB2
16
(SCLK/PCINT1)PB1
15
(SS/PCINT0)PB0
14
(CTS/HWB/AIN6/TO/INT7)PD7
13
(RTS/AIN5/INT6)PD6
12
(XCK/AIN4/PCINT12)PD5
11
(INT5/AIN3)PD4
10
(TXD1/INT3)PD3
9
(RXD1/AIN1/INT2)PD2
8
(AIN0/INT1)PD1
7
(OC0B/INT0)PD0
6
GND
3
VCC
4
AVCC
32
UVCC
31
XTAL1
1
XTAL2(PC0)
2
RESET(PC1/DW)
24
UGND
28
IC4
PAD
EXP
UCAP
27
D-
30
D+
29
(PCINT6)PB6
20
(PCINT7/OC0A/OC1C)PB7
21
1 2
3 4
5 6
ICSP1
Y2
2
1
U
B
O
O
T
L1
Z
1
Z
2
2 1
GROUND
Y1
R1
1 8
RN4A
2 7
RN4B
3 6
RN4C
4 5
RN4D
1
8
R
N
5
A
2
7
R
N
5
B
3
6
R
N
5
C
4 5
RN5D
1
8
R
N
1
A
2
7
R
N
1
B
3
6
R
N
1
C
4 5
RN1D
1 8
RN3A
2 7
RN3B
3 6
RN3C
4 5
RN3D
1 8 RN2A
2 7
RN2B
3 6
RN2C
4 5 RN2D
1 3
4 2
RESET
5
R2
2
1
Q
1
2
1
Q
2
C
1
4
C
1
5
C
1
6
C
1
7
IN
1
EN
3
NC/FB
4
OUT
5
GND
2
R
3
R
4
+5V
+5V
GND
AREF
AREF
AREF
RESET
RESET
RESET
RESET
RESET
VIN
VIN
VIN
M8RXD
M8RXD
M8TXD
M8TXD
PWRIN
ADC0
ADC2
ADC1
ADC3
ADC4
ADC5
ADC6
ADC7
+3V3
+3V3
+3V3
SDA
SDA
SCL
SCL
ADC9
ADC8
ADC10
ADC11
ADC12
ADC13
ADC14
ADC15
PB3
PB3
PB3
PB2
PB2
PB2
PB1
PB1
PB1
PB5
PB4
PE5
PE5
PE4
PE4
PE3
PE3
PE1 PE1
PE1
PE0 PE0
PE0
DTR
USBVCC
USBVCC
USBVCC
GATE_CMD
CMP
PB6
PH3
PH3
PH4
PH4
PH5
PH5
PH6
PH6
PG5
PG5
RXD1
TXD1
RXD2
RXD2
RXD3
RXD3
TXD2
TXD2
TXD3
TXD3
PC0
PC0
PC1
PC1
PC2
PC2
PC3
PC3
PC4
PC4
PC5
PC5
PC6
PC6
PC7
PC7
PB0
PB0
PG0
PG0
PG1
PG1
PG2
PG2
PD7
PD7
PA0 PA0
PA1
PA1
PA2
PA2
PA3
PA3
PA4
PA4
PA5
PA5
PA6
PA6
PA7
PA7
PL0
PL0
PL1
PL1
PL2
PL2
PL3
PL3 PL4
PL4
PL5
PL5
PL6
PL6
PL7
PL7
PB7
VUCAP
RD-
RD-
RD+
RD+
RESET2
RESET2
MISO2
MISO2
MOSI2
MOSI2
SCK2
SCK2
XVCC
RXL
TXL
D-
D+
U
G
N
D
UGND
U
S
H
IE
L
D
XTAL2
XTAL2
XTAL1
XTAL1
XT2
XT2
XT1
XT1
XTAL1R
XT1R
++
U
S
B
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
14
(SCK)
(MISO)
(MOSI)
pwm
pwm
pwm
pwm
pwm
pwm
pwm
pwm
pwm
pwm
pwm
pwm
pwm
pwm
pwm
(TX0)
(RX0)
51
52 53
pwm
pwm
pwm
pwm
pwm
(MISO)
(SCK)
(MOSI)
(SS)
(MOSI)
(SCK)
(MISO)
22 23
24 25
26 27
28 29
30
32
34
36
31
33
35
37
49
47
45
43
41
39
50
48
46
44
42
40
38
pwm
pwm
pwm
pwm
pwm
U
S
B
b
o
o
t E
n
Arduino Mega 2560 Reference Design
TM
Reference Designs ARE PROVIDED "AS IS" AND "WITH ALL FAULTS". Arduino DISCLAIMS ALL OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED,
Arduino may make changes to specifications and product descriptions at any time, without notice. The Customer must not
REGARDING PRODUCTS, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO, ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE
rely on the absence or characteristics of any features or instructions marked "reserved" or "undefined." Arduino reserves
these for future definition and shall have no responsibility whatsoever for conflicts or incompatibilities arising from future changes to them.
The product information on the Web Site or Materials is subject to change without notice. Do not finalize a design with this information.
You might also like
- Arduino Microcontroller Processing For Everyone-Steven F. BarrettDocument358 pagesArduino Microcontroller Processing For Everyone-Steven F. BarrettPedro LimaNo ratings yet
- Arduino Mega 2560Document5 pagesArduino Mega 2560sivasankarchenna_014No ratings yet
- Electronics Today 1978 11Document138 pagesElectronics Today 1978 11cornel_24100% (1)
- I2c 1602 LCDDocument8 pagesI2c 1602 LCDnarwres barhoumiNo ratings yet
- Electronics Today International August 1994Document78 pagesElectronics Today International August 1994Mitchell CifuentesNo ratings yet
- Electronics Today 1977 10Document84 pagesElectronics Today 1977 10cornel_24100% (3)
- Silicon Chip 032022Document116 pagesSilicon Chip 032022CODE PowerNo ratings yet
- The 1974 RCA Triac SCR and Diacs Data BookDocument538 pagesThe 1974 RCA Triac SCR and Diacs Data BookEdd Whatley100% (1)
- Arduino Info Nrf24L01 2.4GHz HowToDocument23 pagesArduino Info Nrf24L01 2.4GHz HowToDirane MiguehNo ratings yet
- Esp32 DocumentatieDocument356 pagesEsp32 Documentatiesady1967No ratings yet
- Elektor (Nonlinear - Ir) 1979-09 - TextDocument57 pagesElektor (Nonlinear - Ir) 1979-09 - TextQuincheNo ratings yet
- Using The Hitachi HD44780 With The Arduin1Document10 pagesUsing The Hitachi HD44780 With The Arduin1winkyiNo ratings yet
- SparkFun Inventors Kit Guide V4.0a-1372082Document113 pagesSparkFun Inventors Kit Guide V4.0a-1372082James MurilloNo ratings yet
- Starting STM8 MicrocontrollersDocument126 pagesStarting STM8 MicrocontrollersTushar Shenoy100% (1)
- 1993 Motorola Linear Interface ICs Vol 2Document1,046 pages1993 Motorola Linear Interface ICs Vol 2matwan29No ratings yet
- Ubm Edn 20120202Document52 pagesUbm Edn 20120202David Felipe García Cadavid100% (1)
- Interfacing Numeric Keypad With MB90F387SDocument18 pagesInterfacing Numeric Keypad With MB90F387SMark VillamorNo ratings yet
- A Short and Simple Guide To Bootloading The Attiny-85 or 45Document4 pagesA Short and Simple Guide To Bootloading The Attiny-85 or 45StephanieAnnRosales100% (1)
- Wireless World 1995 08 S OCRDocument92 pagesWireless World 1995 08 S OCRMilton Nast50% (2)
- 433Mhz RF Remote Control System Based On Pic MicrocontrollerDocument7 pages433Mhz RF Remote Control System Based On Pic MicrocontrollerkinenNo ratings yet
- Neopixels For Attiny85Document1 pageNeopixels For Attiny85lvolders4833No ratings yet
- SmartLEDShield Teensy4 V0 SCHDocument1 pageSmartLEDShield Teensy4 V0 SCHpangymylyNo ratings yet
- HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor On An Atmel ATtiny13 at PDFDocument8 pagesHC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor On An Atmel ATtiny13 at PDFDr MukeshNo ratings yet
- 16 Key Keypad Decoding With An AVRDocument12 pages16 Key Keypad Decoding With An AVRAhmad KhotibNo ratings yet
- Arduino Mega 2560Document7 pagesArduino Mega 2560siddharthNo ratings yet
- Op Amp Using PspiceDocument18 pagesOp Amp Using PspiceSathish BalaNo ratings yet
- Adafruit - Feather m0 Wifi Atwinc1500Document67 pagesAdafruit - Feather m0 Wifi Atwinc1500Bobby100% (1)
- SCSI Internal Pinout Diagram at PinoutsDocument3 pagesSCSI Internal Pinout Diagram at PinoutsNabendu Ghosh0% (1)
- MonkeyBoard DAB DAB FM Digital Radio Development Board Pro Mit SlideShowDocument3 pagesMonkeyBoard DAB DAB FM Digital Radio Development Board Pro Mit SlideShowDawid MleczkoNo ratings yet
- Acoustic 220 Service Manual PDFDocument17 pagesAcoustic 220 Service Manual PDFKevin Alfonso Rivera ParraNo ratings yet
- Electronics Today Magazine - January 1985 (ETI)Document76 pagesElectronics Today Magazine - January 1985 (ETI)crackintheshat100% (1)
- ca34b0592a1966a3cb9fc14674003749Document87 pagesca34b0592a1966a3cb9fc14674003749voin154No ratings yet
- LC22-24LE250 - 17MB95S SM - June2013 PDFDocument106 pagesLC22-24LE250 - 17MB95S SM - June2013 PDFAnonymous h80fVWNo ratings yet
- 70cms Simple Moxon 2el AntennaDocument3 pages70cms Simple Moxon 2el AntennaJosé Antonio MirandaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 USB To PIC Microcontroller InterfaceDocument8 pagesLecture 9 USB To PIC Microcontroller Interfaceaaaa100% (1)
- PIFA Planar Inverted F AntennaDocument4 pagesPIFA Planar Inverted F AntennaAhsan AltafNo ratings yet
- ATTINY13 Servo CTRLDocument1 pageATTINY13 Servo CTRLPusaka WigiNo ratings yet
- 500W 27MHz Class E Amplifier Using Single Plastic MOSFETDocument7 pages500W 27MHz Class E Amplifier Using Single Plastic MOSFETalekssmittNo ratings yet
- 1989 Analog Devices DSP Products DatabookDocument437 pages1989 Analog Devices DSP Products DatabookkgrhoadsNo ratings yet
- Tarjeta de Control Banners SeleccionDocument15 pagesTarjeta de Control Banners SeleccionWero SosaNo ratings yet
- Neopixel UberguideDocument69 pagesNeopixel UberguidedulcesinestesiaNo ratings yet
- X-Altra Moving Coil/Moving Magnet RIAA EQ Preamplifier RIAA EQ PreamplifierDocument7 pagesX-Altra Moving Coil/Moving Magnet RIAA EQ Preamplifier RIAA EQ PreamplifierbobannesicNo ratings yet
- Kit 90. 3 + 3 Watt Stereo Amplifier: ConstructionDocument3 pagesKit 90. 3 + 3 Watt Stereo Amplifier: ConstructionRiktam BasakNo ratings yet
- ALL 02 ManualDocument47 pagesALL 02 ManualmcabreratNo ratings yet
- CK701 1W AmplifierDocument3 pagesCK701 1W AmplifierFuad USNo ratings yet
- SiliconChipReview BitScope BS310Document4 pagesSiliconChipReview BitScope BS310FelipePerezNo ratings yet
- 1W STEREO KA2209 AMPLIFIER MODULEDocument3 pages1W STEREO KA2209 AMPLIFIER MODULEAlberto MoscosoNo ratings yet
- FirstWatt F5 Build GuideDocument56 pagesFirstWatt F5 Build GuideSébastien Mozzi100% (2)
- Compal AAL15 LA-D071P r1.0-1Document64 pagesCompal AAL15 LA-D071P r1.0-1Manishkumar JethvaNo ratings yet
- 89s52 Microcontroller TutorialDocument30 pages89s52 Microcontroller Tutorialm_adavoodi6479No ratings yet
- ELFADocument24 pagesELFAMayam AyoNo ratings yet
- ST Visual Develop (STVD)Document363 pagesST Visual Develop (STVD)api-3697475No ratings yet
- High-Speed Design TechniquesDocument28 pagesHigh-Speed Design TechniquesHemantkumarNo ratings yet
- Print Page - Ov7670 With Both Arduino Uno and Now MegaDocument60 pagesPrint Page - Ov7670 With Both Arduino Uno and Now MegaAhmad Arif Sakti100% (1)
- DX DiagDocument37 pagesDX Diagkonvar666No ratings yet
- Setup LogDocument185 pagesSetup Logelvis056No ratings yet
- Basic Pipelining: CS2100 - Computer OrganizationDocument83 pagesBasic Pipelining: CS2100 - Computer OrganizationamandaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four Input Output Systems in 40 CharactersDocument30 pagesChapter Four Input Output Systems in 40 CharacterssileNo ratings yet
- How To Resurrect An Intel SSD Locked by The Intel SSD Toolbox - NotebookReviewDocument4 pagesHow To Resurrect An Intel SSD Locked by The Intel SSD Toolbox - NotebookReviewIman Teguh PNo ratings yet
- A Seminar On Virtual KeyboardDocument30 pagesA Seminar On Virtual KeyboardpradeepdeceNo ratings yet
- CIS 5100 Homework Assignment #3 Solutions Fall 2020, Dr. Song XingDocument6 pagesCIS 5100 Homework Assignment #3 Solutions Fall 2020, Dr. Song XingOliver BaileyNo ratings yet
- STM32F103C8T6 PDFDocument68 pagesSTM32F103C8T6 PDFfebri kurniaNo ratings yet
- Multicore Cache EnergyDocument19 pagesMulticore Cache EnergyAniket MasalkhambNo ratings yet
- CX4 Series ArraysDocument67 pagesCX4 Series ArraysSrikanth KadiyalaNo ratings yet
- Toshiba e STUDIO 166 Digital Copier BrochureDocument2 pagesToshiba e STUDIO 166 Digital Copier BrochuretheesarNo ratings yet
- IBM BIOS POST Error Code ListDocument4 pagesIBM BIOS POST Error Code ListPoljkanNo ratings yet
- ICIT Unit 1 (Lecture 4)Document49 pagesICIT Unit 1 (Lecture 4)Nidhi JainNo ratings yet
- Brosur 2004N DadfDocument4 pagesBrosur 2004N DadfwicoroNo ratings yet
- Second Periodical Test in Information and Communications Technology (For Grade 8 and 10)Document3 pagesSecond Periodical Test in Information and Communications Technology (For Grade 8 and 10)DennisEstrellosoAlbisoNo ratings yet
- DSEA Technical Note: #040: Updated HQ RIP Plug-In InstallerDocument4 pagesDSEA Technical Note: #040: Updated HQ RIP Plug-In InstallerodelaineNo ratings yet
- Section 26 Codeguard SecurityDocument52 pagesSection 26 Codeguard SecurityG30nyNo ratings yet
- Komputer: Bagian Utama dan FungsinyaDocument2 pagesKomputer: Bagian Utama dan FungsinyaSimbah Lagi Simbah LagiNo ratings yet
- DraftDocument4 pagesDraftKas HNo ratings yet
- Xapp1079 Amp Bare Metal Cortex A9Document32 pagesXapp1079 Amp Bare Metal Cortex A9Whats app TAMIL statusNo ratings yet
- CSS Ict11 Q2Document14 pagesCSS Ict11 Q2Franz Lawrenz De TorresNo ratings yet
- FRAM Memory With A Unique Read-Only IDDocument1 pageFRAM Memory With A Unique Read-Only IDratata ratataNo ratings yet
- Guideline For Pharmaceutical Equipment Vendors - Appendix BOM v3.3Document69 pagesGuideline For Pharmaceutical Equipment Vendors - Appendix BOM v3.3Nguyễn Đình PhúNo ratings yet
- Computer Architecture Test 1Document6 pagesComputer Architecture Test 1gbland100% (1)
- Ds 00173 Gd5f4gq4xcxig Rev1.4Document45 pagesDs 00173 Gd5f4gq4xcxig Rev1.4xiliantonioNo ratings yet
- HP Pavilion DV2000 (965GM) WISTRON PAMIRS UMA 06228 REV SB SchematicsDocument41 pagesHP Pavilion DV2000 (965GM) WISTRON PAMIRS UMA 06228 REV SB SchematicsBlade Bla BlaNo ratings yet
- Task Switching:: JMP Call JMP Call Iret JMP Call IretDocument19 pagesTask Switching:: JMP Call JMP Call Iret JMP Call IretAshish PatilNo ratings yet
- Mixed Signal Microcontroller: FeaturesDocument119 pagesMixed Signal Microcontroller: FeaturesGradimir LjubibraticNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PDA: What's A Handheld PC (H/PC) ?Document19 pagesIntroduction To PDA: What's A Handheld PC (H/PC) ?dash_bani36No ratings yet
- Cs TestDocument12 pagesCs Testzain ahmadNo ratings yet