Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Midterm1 Solution
Uploaded by
Sova ŽalosnaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Midterm1 Solution
Uploaded by
Sova ŽalosnaCopyright:
Available Formats
UC BERKELEY EECS 40, Spring 2007
Page 1 of 7
EECS 40, Spring 2007
Prof. Chang-Hasnain
Midterm #1
February 21, 2007
Total Time Allotted: 80 minutes
Total Points: 100
1. This is a closed book exam. However, you are allowed to bring one page (8.5 x
11), single-sided notes.
2. No electronic devices, i.e. calculators, cell phones, computers, etc.
3. SHOW all the steps on the exam. Answers without steps will be given only a small
percentage of credits. Partial credits will be given if you have proper steps but no
final answers.
4. Draw BOXES around your final answers.
5. Remember to put down units. Points will be taken off for answers without units.
Last (Family) Name:___Perfect_____________________________________________
First Name: ___Peter_____________________________________________________
Student ID: __00000000_________________ Discussion Session: ________________
Signature: _____________________________________________________________
Score:
Problem 1 (26 pts)
Problem 2 (28 pts):
Problem 3 (32 pts)
Problem 4 (14 pts)
Total
UC BERKELEY EECS 40, Spring 2007
Page 2 of 7
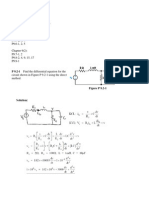
1. (26 pts) Circuit Analysis
(a) (4 pts) Express i
1
in terms of V
1
and constants given in this problem.
V
1
= 2 i
1
(b) (4 pts) Express i
2
in terms of V
1
AND V
2
and/or constants given in the problem.
i
2
= 3 V
1
/2
(c) (10 pts) Write two equations in V
1
and V
2
that can be used to solve the circuit (Hint: Use
KCL or KVL.).
10+V
1
V
2
=
0
2x(3 V
1
/2)+8x(V
1
/2) V
2
=0
(d) (8 pts) Solve for V
1
, V
2
, i
1
and i
2
.
V
1
= 2 V
V
1
= 12 V
i
1
= 1 A
i
2
= 2 A
UC BERKELEY EECS 40, Spring 2007
Page 3 of 7
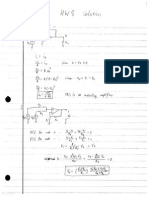
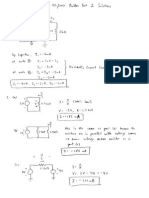
2. (27 pts) First-Order Circuit. Remember to put down units.
10_
4_
6_
C1=4!F
4!F
+
V
1
-
1A
i
1
i
2
30_
80_ 80_
50_
C3=1!F C
2
=2!F
30V
+
V
2
-
i
3
i
4
a) (12 pts) At t=0, the switch closes. Find the indicated current and voltages at t=0
-
s,
immediately BEFORE the switch closes. Note the current source has been active for a long
time before the switch closes.
Provide the steps or explanation for your answers, e.g. using KCL/KVL, etc.
i
1
1A
i
2
0A
i
3
0A
i
4
0A
V
1
10V
V
2
20V
All capacitors are open circuits, all currents but i
1
are 0. i
1
is the same as the current source.
Volts
A
V 10
2
1 * ) 6 4 10 (
1
=
!
"
#
$
%
& ' + ' + '
=
Volts A V 20 1 * ) 6 4 10 (
1
= ! + ! + ! =
b) (3 pts) At t=0
+
s, immediately AFTER the switch closes. Which quantities will be different?
All the currents may be different, so i
1
, i
2
, i
3
, and i
4
may change (in fact i
1
does not). Voltages
across capacitors cannot change instantaneously because this will result in infinite current flow.
UC BERKELEY EECS 40, Spring 2007
Page 4 of 7
c) (12 pts) Find the current and voltages after a very, very long time.
Provide the steps or explanation for your answers, e.g. using KCL/KVL, etc.
i
1
1.11A
i
2
0A
i
3
-0.11A
i
4
0A
v
1
11.11V
v
2
25.56V
UC BERKELEY EECS 40, Spring 2007
Page 5 of 7
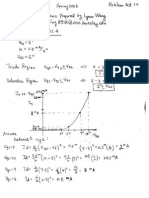
3. (32 pts) Second-Order Circuit. Remember to put down units.
3V
1_
1/6 F 2/3 H
+
V(t)
-
t=0
The switch is closed at t=0. The goal is to find the voltage across the capacitor, V(t).
a.) (2 pts) For t<0, assume that the switch was open and remained open for a very long time.
Find V(0-).
V(0-) = 3 V
b.) (4 pts) What is V(0+)? Explain.
V(0+)=3V.
Because voltage across capacitor can not change abruptly.
c.) (10 pts) Derive the second-order differential equation for the circuit. (Hint: Use KVL/KCL)
Using KVL:
!
"3+ R(i
C
(t) + i
L
(t)) +V(t) = 0
!
"3+ R C
dV(t)
dt
+
1
L
V(t' )dt' +i
L
(0+)
0+
t
#
$
%
&
'
(
)
+V(t) = 0
!
RC
d
2
V(t)
dt
2
+
R
L
V(t) +
dV(t)
dt
= 0
or using KCL:
!
V(t) " 3
R
+ i
C
(t) + i
L
(t) = 0
!
V(t) " 3
R
+ C
dV(t)
dt
+
1
L
V(t' )dt' +i
L
(0+)
0+
t
#
= 0
!
C
d
2
V(t)
dt
2
+
1
L
V(t) +
1
R
dV(t)
dt
= 0
In standard form:
!
d
2
V(t)
dt
2
+
1
RC
dV(t)
dt
+
1
LC
V(t) = 0
!
d
2
V(t)
dt
2
+ 6
dV(t)
dt
+ 9V(t) = 0
UC BERKELEY EECS 40, Spring 2007
Page 6 of 7
d.) (3 pts) What is
!
"? What is
!
"
0
? Is this critically damped, underdamped, or overdamped?
!
" = 6/2 = 3rad / s
!
"
0
= 9 = 3rad / s
!
" =
#
$
0
=1
Critically damped.
e.) (3 pts) What is the particular solution?
v
p
(t)=0 V since after a long time, the inductor acts as a short circuit.
f.) (10 pts) Find the complementary (homogeneous) solution.
v
c
(t)=k
1
e
-3t
+ k
2
te
-3t
v(t)= v
p
(t)+ v
c
(t)= k
1
e
-3t
+ k
2
te
-3t
v(0)= 3 = k
1
dv(t)/dt |
t=0
=0=-3 k
1
+ k
2
=-9+ k
2
k
2
=9
v
c
(t)=3 e
-3t
+ 9 te
-3t
UC BERKELEY EECS 40, Spring 2007
Page 7 of 7
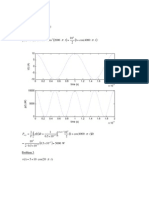
4. (14 pts) Equivalent Circuit. Remember to put down units.
a.) (5 pts) What is V
in
?
1500x1000/(1500+1000)=600 !
V
in
= 5 x 600/(600+400)=3 V
b.) (4 pts) What is V
ab
?
V
ab
= - g
m
V
in
x 5000 V
= - g
m
x3
x 5000 V
= - g
m
x15000 V
c.) (5 pts) What is the Thevenin equivalent circuit for terminals a-b? (Find R
Th
,V
Th
).
Answer in terms of g
m.
V
Th
=V
ab
= - g
m
x15000 V
R
Th
= V
Th
/I
sc
= - g
m
x15000 /(- g
m
x3) =5000 !
!
!
+
g
m
V
IN
5k"
V
IN
+
+
5V
a
b
1.5k"
400"
1k" !
!
+
g
m
V
IN
5k"
V
IN
+
+
5V
a
b
1.5k"
400"
1k"
You might also like
- Chapter 9 Homework SolutionDocument27 pagesChapter 9 Homework Solutionjoe100% (3)
- Solns 2cmosDocument18 pagesSolns 2cmosramprakash_rampelliNo ratings yet
- BentleyDocument8 pagesBentleymanaj_mohapatra204180% (5)
- ECE225Midterm2 SolDocument23 pagesECE225Midterm2 SolnonreplicaNo ratings yet
- EENG223 Final SolutionsDocument6 pagesEENG223 Final Solutionsercan952No ratings yet
- Electrotechnics 1b Outcome B Test 1 Memo 2021Document7 pagesElectrotechnics 1b Outcome B Test 1 Memo 2021spm0826722No ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering: Electrical and Electronic Engineering DepartmentDocument8 pagesFaculty of Engineering: Electrical and Electronic Engineering Departmentmurthy237No ratings yet
- Midterm Exam QuestionsDocument9 pagesMidterm Exam QuestionsShubhresh Kumar JhaNo ratings yet
- 6002x FinalReview S2012 CleanDocument80 pages6002x FinalReview S2012 CleanGemini GntNo ratings yet
- EENG 223 Final Exam S08-09 SolnDocument7 pagesEENG 223 Final Exam S08-09 SolnFredy AlbornozNo ratings yet
- ch10 PDFDocument39 pagesch10 PDFmri_leon100% (1)
- Tutorial 3Document6 pagesTutorial 3SYAFIQAH ISMAILNo ratings yet
- ExamDocument13 pagesExamHamed GhanbariNo ratings yet
- Principles of Matlab (Fall 07) Workout #1Document11 pagesPrinciples of Matlab (Fall 07) Workout #1Karim GaberNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Electric Circuit Variables: ExercisesDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - Electric Circuit Variables: ExercisesMinYong SungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Electric Circuit Variables: ExercisesDocument8 pagesChapter 1 - Electric Circuit Variables: ExercisesRulierNo ratings yet
- A Be Midterm Spring KeyDocument11 pagesA Be Midterm Spring KeyRex ChemNo ratings yet
- Inpho11 QPDocument28 pagesInpho11 QPAkshay PandeyNo ratings yet
- Sem1 1213 SolutionDocument17 pagesSem1 1213 SolutionThinesh StNo ratings yet
- EEE 133 1s2021 Problem Set 2Document3 pagesEEE 133 1s2021 Problem Set 2Roland Paul PrincipeNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory ECT1016 Assignment (05-06)Document3 pagesCircuit Theory ECT1016 Assignment (05-06)miindsurferNo ratings yet
- EMwavesLectureNotes 1 7Document149 pagesEMwavesLectureNotes 1 7Anonymous BWdaO1lNo ratings yet
- EECE 301 Note Set 13 FS DetailsDocument21 pagesEECE 301 Note Set 13 FS DetailsrodriguesvascoNo ratings yet
- LCA Assignment 1 Spring 2023Document6 pagesLCA Assignment 1 Spring 2023Huzaifa Pervaiz MayoNo ratings yet
- CKT Transients N Tellegen TheoremDocument32 pagesCKT Transients N Tellegen TheoremVSNo ratings yet
- Ec: Electronics and Communication Engineering: Duration: Three HoursDocument14 pagesEc: Electronics and Communication Engineering: Duration: Three HourspiyaloveNo ratings yet
- UNIVERSITI TUN HUSSEIN ONN MALAYSIA CIRCUIT ANALYSIS TOPICSDocument115 pagesUNIVERSITI TUN HUSSEIN ONN MALAYSIA CIRCUIT ANALYSIS TOPICSAzlin HazwaniNo ratings yet
- Ispitni Zadaci - ElektrotehnikaDocument14 pagesIspitni Zadaci - ElektrotehnikaAleksandar KrčuljNo ratings yet
- Gate EceDocument25 pagesGate Ecegreatbuddy2009No ratings yet
- Lecture #35: Analysis of Electrical Networks With Initial ConditionsDocument13 pagesLecture #35: Analysis of Electrical Networks With Initial ConditionsSaneesh KarayilNo ratings yet
- AC Circuit Analysis Using PhasorsDocument22 pagesAC Circuit Analysis Using PhasorsvsabioniNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJT) : NPN PNPDocument44 pagesBipolar Junction Transistors (BJT) : NPN PNPAli AhmadNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 ..2016Document8 pagesPaper 1 ..2016Dinesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Elec 2ND GradingDocument11 pagesElec 2ND GradingShaiNo ratings yet
- RepositoryDocument17 pagesRepositoryarefinhasib07No ratings yet
- Modeling and Simulation of RLC Circuit (Band Pass Filter)Document25 pagesModeling and Simulation of RLC Circuit (Band Pass Filter)elneelNo ratings yet
- New topics – energy storage elements capacitors inductorsDocument25 pagesNew topics – energy storage elements capacitors inductorsMuhammad AdeelNo ratings yet
- Edo - BoaDocument17 pagesEdo - BoaEdson Jansen MirandaNo ratings yet
- CH 01Document13 pagesCH 01SherifNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory - Solved Assignments - Spring 2006Document45 pagesCircuit Theory - Solved Assignments - Spring 2006Muhammad UmairNo ratings yet
- 07-Élec-A7 (Version Anglaise) - Novembre 2011Document5 pages07-Élec-A7 (Version Anglaise) - Novembre 2011andrytahiryNo ratings yet
- CEG 2136 - Fall 2008 - MidtermDocument20 pagesCEG 2136 - Fall 2008 - MidtermAmin DhouibNo ratings yet
- Final Exam ECE 1312 Question Sem-1 2013-2014Document9 pagesFinal Exam ECE 1312 Question Sem-1 2013-2014Fatihah AinaNo ratings yet
- EEEN 201 Lecture Notes-08Document10 pagesEEEN 201 Lecture Notes-08areeb ahmedNo ratings yet
- Solutions HWT ElectrostaticsDocument11 pagesSolutions HWT ElectrostaticsShubhamKhannaNo ratings yet
- Mid 2020 SDocument11 pagesMid 2020 Samedpv56No ratings yet
- Solutions To Exercises: Chapter 10: 10.1 Use The Chemical Potential of An Ideal Gas in (10.1.9) and Obtain The BarometricDocument6 pagesSolutions To Exercises: Chapter 10: 10.1 Use The Chemical Potential of An Ideal Gas in (10.1.9) and Obtain The BarometricSalomé TorresNo ratings yet
- S&S CombinedDocument55 pagesS&S Combinedzphil33No ratings yet
- GATE 2012 EE Electrical Engineering Question PaperDocument20 pagesGATE 2012 EE Electrical Engineering Question PaperSomesh SshNo ratings yet
- EE420 Problem Set 1: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering SolutionsDocument11 pagesEE420 Problem Set 1: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering SolutionsWingel LullabyNo ratings yet
- Circuits With Periodic SourcesDocument10 pagesCircuits With Periodic SourcesahmdNo ratings yet
- Electronics 3 Checkbook: The Checkbooks SeriesFrom EverandElectronics 3 Checkbook: The Checkbooks SeriesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Model Answers in Ordinary National Certificate Mathematics for EngineersFrom EverandModel Answers in Ordinary National Certificate Mathematics for EngineersNo ratings yet
- Logical progression of twelve double binary tables of physical-mathematical elements correlated with scientific-philosophical as well as metaphysical key concepts evidencing the dually four-dimensional basic structure of the universeFrom EverandLogical progression of twelve double binary tables of physical-mathematical elements correlated with scientific-philosophical as well as metaphysical key concepts evidencing the dually four-dimensional basic structure of the universeNo ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Electronic Systems: Study Topics in Physics Book 8From EverandElectronic Systems: Study Topics in Physics Book 8Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- HW 8Document1 pageHW 8Sova ŽalosnaNo ratings yet
- EE42/100 Spring 2006 Problem Set 12Document3 pagesEE42/100 Spring 2006 Problem Set 12Sova ŽalosnaNo ratings yet
- HW 11 SolDocument4 pagesHW 11 SolSova ŽalosnaNo ratings yet
- HW 8Document1 pageHW 8Sova ŽalosnaNo ratings yet
- HW 8Document1 pageHW 8Sova ŽalosnaNo ratings yet
- (Reading Assignment) : EE42/100-Spring 2006Document4 pages(Reading Assignment) : EE42/100-Spring 2006Sova ŽalosnaNo ratings yet
- HW 8 SolDocument4 pagesHW 8 SolSova ŽalosnaNo ratings yet
- HW 10 SolDocument6 pagesHW 10 SolSova ŽalosnaNo ratings yet
- HW 8Document1 pageHW 8Sova ŽalosnaNo ratings yet
- HW 9 SolDocument5 pagesHW 9 SolSova ŽalosnaNo ratings yet
- Problem 2) 2000 Cos (10) ( : T AvgDocument8 pagesProblem 2) 2000 Cos (10) ( : T AvgSova ŽalosnaNo ratings yet
- EECS Homework SolutionsDocument2 pagesEECS Homework SolutionsSova ŽalosnaNo ratings yet
- HW 5Document2 pagesHW 5Sova ŽalosnaNo ratings yet
- HW 7 SolDocument11 pagesHW 7 SolSova ŽalosnaNo ratings yet
- HW 8Document1 pageHW 8Sova ŽalosnaNo ratings yet
- HW 8Document1 pageHW 8Sova ŽalosnaNo ratings yet
- HW 4Document5 pagesHW 4Sova ŽalosnaNo ratings yet
- Homework 3Document1 pageHomework 3Sova ŽalosnaNo ratings yet
- EE42/100 Spring 2006 Problem Set 1Document3 pagesEE42/100 Spring 2006 Problem Set 1Sova ŽalosnaNo ratings yet
- EE42/100 Spring 2006 Problem Set 1Document2 pagesEE42/100 Spring 2006 Problem Set 1Sova ŽalosnaNo ratings yet
- Dave's Math TablesDocument43 pagesDave's Math TablesManuel F. Presnilla100% (2)
- Homework 2Document1 pageHomework 2Sova ŽalosnaNo ratings yet
- Homework 2Document1 pageHomework 2Sova ŽalosnaNo ratings yet
- HW 2 SolDocument4 pagesHW 2 SolSova ŽalosnaNo ratings yet
- Homework 2Document1 pageHomework 2Sova ŽalosnaNo ratings yet
- The Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) The Fast Fourier Transform (Document5 pagesThe Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) The Fast Fourier Transform (Shane MurrayNo ratings yet
- Bennett, Charles - A New Latin CompositionDocument299 pagesBennett, Charles - A New Latin CompositionfsolomonNo ratings yet
- Pilates For Core StrengthDocument150 pagesPilates For Core StrengthCindy Leung75% (4)
- R. Pasnau - Divisions of Epistemic LaborDocument42 pagesR. Pasnau - Divisions of Epistemic LaborMarisa La BarberaNo ratings yet
- Miscellanea: Arab-Sasanian Copper P Esents Varie Ypo OgyDocument24 pagesMiscellanea: Arab-Sasanian Copper P Esents Varie Ypo Ogy12chainsNo ratings yet
- Shwebo District ADocument280 pagesShwebo District AKyaw MaungNo ratings yet
- Quantum Dot PDFDocument22 pagesQuantum Dot PDFALI ASHRAFNo ratings yet
- Basic French ConversationDocument7 pagesBasic French Conversationeszti kozmaNo ratings yet
- VE With CLE 10-Module 22-4th Quarter - CASTRODocument5 pagesVE With CLE 10-Module 22-4th Quarter - CASTRORojan ClarkNo ratings yet
- General and Local AnesthesiaDocument1 pageGeneral and Local Anesthesiaahmedhelper300No ratings yet
- 1814 d01 PDFDocument20 pages1814 d01 PDFteletrabbiesNo ratings yet
- 19 G15 - Polycystic Ovary Syndrome v12.22.2021 1Document3 pages19 G15 - Polycystic Ovary Syndrome v12.22.2021 1decota.sydneyNo ratings yet
- FulfillerDocument8 pagesFulfillermanojeil1No ratings yet
- How To Make Nano Silica From Extracted Silica Rice Husk (Discussion)Document1 pageHow To Make Nano Silica From Extracted Silica Rice Husk (Discussion)MohdhafizFaiz MdAliNo ratings yet
- Information Pack: Creative Media EducationDocument26 pagesInformation Pack: Creative Media EducationDaniel VladimirovNo ratings yet
- Well Plug and Abandonment Using HwuDocument1 pageWell Plug and Abandonment Using HwuJuan Pablo CassanelliNo ratings yet
- Disaccharides and PolysaccharidesDocument17 pagesDisaccharides and PolysaccharidesAarthi shreeNo ratings yet
- Polysemy Types ExplainedDocument13 pagesPolysemy Types ExplainedнастяNo ratings yet
- The Dilemma of Recognition Experienced Reality of Ethnicised Politics in Rwanda and BurundiDocument192 pagesThe Dilemma of Recognition Experienced Reality of Ethnicised Politics in Rwanda and BurundiShenandoa LeãoNo ratings yet
- SPEC 2 - Module 1Document21 pagesSPEC 2 - Module 1Margie Anne ClaudNo ratings yet
- 5G Americas Advanced Antenna Systems For 5G White PaperDocument59 pages5G Americas Advanced Antenna Systems For 5G White PaperArpitha HsNo ratings yet
- Cazul Cyril Burt 3Document3 pagesCazul Cyril Burt 3Cosmina MihaelaNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance Committees in India: Key Reports and RecommendationsDocument39 pagesCorporate Governance Committees in India: Key Reports and Recommendationskush mandaliaNo ratings yet
- BTechSyllabus EC PDFDocument140 pagesBTechSyllabus EC PDFHHNo ratings yet
- Chapter-12 Direct and Inverse ProportionsDocument22 pagesChapter-12 Direct and Inverse ProportionsscihimaNo ratings yet
- D820-93 (2009) Standard Test Methods For ChemicalDocument10 pagesD820-93 (2009) Standard Test Methods For Chemicalobis8053No ratings yet
- Contineous Assessment 2 Group BDocument11 pagesContineous Assessment 2 Group BMasnoon MidhatNo ratings yet
- Dec50103 PW2 F1004Document14 pagesDec50103 PW2 F1004Not GamingNo ratings yet
- Ant Amb452000 1502 Datasheet PDFDocument2 pagesAnt Amb452000 1502 Datasheet PDFIwan Arinta100% (1)
- 74HCT00Document8 pages74HCT00Sadikul FuadNo ratings yet
- azezew(1)Document48 pagesazezew(1)temesgen AsmamawNo ratings yet
- 302340KWDocument22 pages302340KWValarmathiNo ratings yet
- Operation ManualDocument83 pagesOperation ManualAn Son100% (1)