Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unite 2
Uploaded by
api-240050255Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unite 2
Uploaded by
api-240050255Copyright:
Available Formats
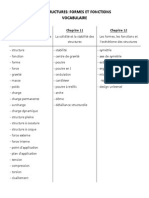
LA CHALEUR DANS L'ENVIRONNEMENT
Vocabulaire
Chapitre 7
Le rchauffement et le
refroidissement
Chapitre 8
Le transfert et la
conservation d'nergie
Chapitre 9
Les sources de chaleur dans
l'environnement
- thorie particulaire de la
matire
- chaleur
- nergie cintique
- temprature
- nergie thermique
- dilatation thermique
- contraction thermique
- conduction
- nergie gothermique
- roche igne
- roche mtamorphique
- convection
- nergie de
rayonnement
- rayonnement
- nergie solaire
- friction
- source d'nergie
classique
- source d'nergie
renouvelable
- sources d'nergie non
renouvelable
- combustibles fossiles
- bilan nergtique de la
Terre
- effet de serre
- gaz effet de serre
- rchauffement de la
plante
- source d'nergie
alternative
- chauffage solaire passif
- systme d'nergie solaire
active
- biocarburant
OVERVIEW
Heat energy plays a critical role in natural processes and in human life. Global warming has
also focused considerable attention on the processes that control temperatures at the earth's
surface. By acquiring a working understanding of the nature of heat, students will gain new
insights into the ways that heat affects our world. Students will learn about the causes and
effects of heat, investigate its properties, relate it to geological and meteorological processes,
and use their new-found knowledge to design a device to minimize heat transfer. They will
also use the particle theory to help them explain their observations.
Experiments with heat require that students identify and explain the importance of practices
that ensure their personal safety and the safety of others. This includes knowing why very hot
water should always be carried in a closed container (e.g., an insulated flask) and why they
should stand when heating things and hold objects that are being heated well away from
themselves.
Fundamental Concepts: Energy
Big Ideas:
Heat is a form of energy that can be transformed and transferred. These processes can
be explained using the particle theory of matter.
Fundamental Concepts: Sustainability and Stewardship
Big Ideas:
There are many sources of heat.
Fundamental Concepts: Systems and Interactions
Big Ideas:
Heat has both positive and negative effects on the environment.
OVERALL EXPECTATIONS
By the end of the unit, students will:
1. assess the cost and benefits of technologies that reduce heat loss or heat-related impacts
on the environment;
2. investigate the ways in which heat changes substances, and describe how heat is
transferred;
3. demonstrate an understanding of heat as a form of energy that is associated with the
movement of particles and is essential to many processes within the earth's system.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
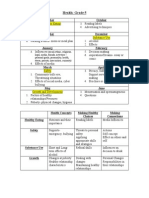
- Grade 8 Phe Annual PlanDocument2 pagesGrade 8 Phe Annual Planapi-240050255No ratings yet
- Grade 5 Health Annual PlanDocument1 pageGrade 5 Health Annual Planapi-240050255No ratings yet
- GR 5 Health Year PlanDocument1 pageGR 5 Health Year Planapi-240050255No ratings yet
- List of Drugs For PamphletDocument1 pageList of Drugs For Pamphletapi-240050255No ratings yet
- GR 7 Phe Annual PlanDocument2 pagesGR 7 Phe Annual Planapi-240050255No ratings yet
- Drug Pamphlet RubicsDocument2 pagesDrug Pamphlet Rubicsapi-240050255No ratings yet
- Grade 8 Phe Annual PlanDocument2 pagesGrade 8 Phe Annual Planapi-240050255No ratings yet
- Grade 6 Health Annual PlanDocument1 pageGrade 6 Health Annual Planapi-240050255No ratings yet
- Hpe Rubrics 2015-16Document2 pagesHpe Rubrics 2015-16api-240050255No ratings yet
- STD Brochure W RubricDocument2 pagesSTD Brochure W Rubricapi-240050255No ratings yet
- Questions Grande SeductionDocument2 pagesQuestions Grande Seductionapi-240050255No ratings yet
- Contraception PamphletDocument2 pagesContraception Pamphletapi-240050255No ratings yet
- Eleanor RigbyDocument1 pageEleanor Rigbyapi-240050255No ratings yet
- Traveling Through The DarkDocument1 pageTraveling Through The Darkapi-240050255No ratings yet
- Body Image and Media PT 1Document2 pagesBody Image and Media PT 1api-240050255No ratings yet
- Double DenotationDocument4 pagesDouble Denotationapi-240050255No ratings yet
- Sciences CH 1 ReviewDocument4 pagesSciences CH 1 Reviewapi-240050255No ratings yet
- The Highwayman PoemDocument4 pagesThe Highwayman Poemapi-240050255No ratings yet
- Body Image and The Media Ques and Poster RubricDocument2 pagesBody Image and The Media Ques and Poster Rubricapi-240050255No ratings yet
- Project - Convention On The Rights of The ChildDocument8 pagesProject - Convention On The Rights of The Childapi-240050255No ratings yet
- Unite 1Document2 pagesUnite 1api-240050255No ratings yet
- Unite 3Document3 pagesUnite 3api-240050255No ratings yet
- Cariboo Math Contest Infor 7 MayDocument1 pageCariboo Math Contest Infor 7 Mayapi-240050255No ratings yet
- Unite 4Document2 pagesUnite 4api-240050255No ratings yet
- PP 83 To 93Document12 pagesPP 83 To 93api-240050255No ratings yet
- Growth and Developement Diagram Quiz 1Document3 pagesGrowth and Developement Diagram Quiz 1api-240050255No ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Developing a Solar-Biomass Integrated Drying System for SpicesDocument30 pagesDeveloping a Solar-Biomass Integrated Drying System for SpicesSantosh AngadiNo ratings yet
- GEAS 1 - Chemistry - 2Document4 pagesGEAS 1 - Chemistry - 2Leoneil Angelo AbreuNo ratings yet
- Java Meets Numerical AnalysisDocument2 pagesJava Meets Numerical AnalysisbernasekNo ratings yet
- Precast BeamDocument8 pagesPrecast BeamMahmoud ShakerNo ratings yet
- Mousavi, Aliha, Imani - 2020 - On The Use of Edge Cracked Short Bend Beam Specimen For PMMA Fracture Toughness Testing Under Mixed-ModeDocument1 pageMousavi, Aliha, Imani - 2020 - On The Use of Edge Cracked Short Bend Beam Specimen For PMMA Fracture Toughness Testing Under Mixed-ModeMorteza AtaeiNo ratings yet
- LaminateDocument154 pagesLaminateAbhishek VaggarNo ratings yet
- Oversized Particles in Emulsified Asphalts (Sieve Test) : Standard Test Method ForDocument2 pagesOversized Particles in Emulsified Asphalts (Sieve Test) : Standard Test Method Forمحمد سليمان بن عمرNo ratings yet
- Datasheet MPX5100DPDocument16 pagesDatasheet MPX5100DPKemahyanto Exaudi SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Thermal Engineering PDFDocument76 pagesThermal Engineering PDFKartik KuriNo ratings yet
- F1223 1479757-1Document9 pagesF1223 1479757-1Thaweekarn ChangthongNo ratings yet
- TCL Air Conditioner Service ManualDocument138 pagesTCL Air Conditioner Service ManualFabian EtcheniqueNo ratings yet
- Stiffness of Cable-Based Parallel Manipulators With Application To Stability AnalysisDocument8 pagesStiffness of Cable-Based Parallel Manipulators With Application To Stability AnalysisNhật MinhNo ratings yet
- The D and F Block Elements PDFDocument8 pagesThe D and F Block Elements PDFTr Mazhar PunjabiNo ratings yet
- Curriculum-Of Mathematics Government College Women University, SialkotDocument119 pagesCurriculum-Of Mathematics Government College Women University, SialkotHuzaifa GurmaniNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Truss Using Abaqus SoftwareDocument7 pagesAnalysis of Truss Using Abaqus SoftwareKarthick NNo ratings yet
- HP Officejet Pro X476 X576 TroubleshootingDocument152 pagesHP Officejet Pro X476 X576 Troubleshootingjason7493No ratings yet
- Text - Anuario Cader 2018 INGLÉS PDFDocument57 pagesText - Anuario Cader 2018 INGLÉS PDFmicaelaNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 1st Quarter Module 1 ActivitiesDocument16 pagesGeneral Physics 1 1st Quarter Module 1 ActivitiesMica LopezNo ratings yet
- E-CAPS-28 - For CoE (XI) - Chemistry - (Que. - Answer Key)Document3 pagesE-CAPS-28 - For CoE (XI) - Chemistry - (Que. - Answer Key)darling deanNo ratings yet
- Calculating Energy: Complete These Questions in Your Exercise Books, With Full ESTAU Working OutDocument2 pagesCalculating Energy: Complete These Questions in Your Exercise Books, With Full ESTAU Working Outruby lillyNo ratings yet
- NNPC Recruitment Past Questions GuideDocument64 pagesNNPC Recruitment Past Questions GuidenwabukingzNo ratings yet
- Rocket PropulsionDocument41 pagesRocket PropulsionV DhinakaranNo ratings yet
- 1117 1 M-Ary Signals PART 1Document11 pages1117 1 M-Ary Signals PART 1PARKSANGWOOKNo ratings yet
- Schrodinger Equation DerivationDocument12 pagesSchrodinger Equation DerivationAndrés López Martínez100% (1)
- A Brief Overview of The Holographic TechnologyDocument5 pagesA Brief Overview of The Holographic TechnologyAltiel Ltd.No ratings yet
- Adrian Stan MFQMCourseHsL2006Document60 pagesAdrian Stan MFQMCourseHsL2006禿公No ratings yet
- FTTH Accessories PDFDocument10 pagesFTTH Accessories PDFdannyalcivarNo ratings yet
- Lilin Downhole MotorDocument35 pagesLilin Downhole MotorIAN.SEMUT100% (2)
- Additive Solutions For Low Sulphur Fuelsadditive Solutions For Low Sulphur Fuels July 10Document35 pagesAdditive Solutions For Low Sulphur Fuelsadditive Solutions For Low Sulphur Fuels July 10Mazhar HussainNo ratings yet
- DPP-1 QuantizationDocument1 pageDPP-1 QuantizationVikasNo ratings yet