Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Classical Conditioning
Uploaded by
Dzul Azraai DzulkarnainCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Classical Conditioning
Uploaded by
Dzul Azraai DzulkarnainCopyright:
Available Formats
Behavioral Learning Theory
Ivan Pavlov
Used conditioning to gain a
predictable response from a stimulus
Famous for behavioral experiment
with dogs
(1849-1936) Physiologist
John B. Watson
Key researcher of behaviorism
Famous for infant research and Little
Albert experiment
(1878-1958): Psychologist
Pavlov Dog Conditioning
Pavlov presented food to dogs dogs mouths water
Pavlov rang bell the dogs mouths did not water
Pavlov presented food to dogs and rang bell dogs mouths water
Pavlov rang bell without food present dogs mouths water
Conditioned
Response
Watsons Little Albert
Before
Conditioning
Baby Albert is
allowed to play
with a pet rat.
Albert enjoys
petting the rat and
does not fear it.
Albert was scared
of loud noises.
During
Conditioning
When Albert tried
to pet or come
near the rat,
Watson would
make a loud noise.
This scared Albert.
This scaring when
coming close
situation was
repeated many
times.
Once
conditioned
When Albert was
presented with the
rat again, he
became scared,
cried, and tried to
move away from
the rat.
He had become
conditioned into
realizing that the
white rat was
related to the loud
noise.
Main Points
Classical conditioning deals with reflexes,
or responses that are evoked from a specific stimulus
People can be trained to perform a certain task or
response by providing some sort of trigger, which
may be a sound, picture, phrase, etc.
When you see this:
What do you think of?
Youve be conditioned to think of McDonalds after
seeing this picture! (Are you salivating?)
Classroom Implications
If the teacher is consistent and repetitive with these stimuli, eventually the students
will come to learn to behave properly through classical conditioning.
If the teacher Then the students
Before conditioning Counts down from twenty
Tells the class to clean up
Will not clean up.
Will clean up.
During conditioning Tells the class to clean up
and counts down from
twenty
Will clean up.
After conditioning Counts down from twenty Will clean up.
The students behavior has been conditioned!
Classroom Implications
If the teacher is consistent and repetitive with these stimuli, eventually the students
will come to learn to behave properly through classical conditioning.
If the teacher Then the students
Before conditioning Instructs the class to quiet down
Claps 3 times.
Will get quiet.
Will not get quiet.
During conditioning Claps 3 times and instructs the
class to quiet down.
Will get quiet.
After conditioning Claps 3 times. Will get quiet.
The students behavior has been conditioned!
Classroom Implications
Technology can be used too to help students be classically conditioned!
Music and computers are used here.
If the teacher Then the students
Before conditioning Plays the alphabet song
Instructs the students to go to
their assigned computers
Will not get setup up at
computers.
Will get setup at computers.
During conditioning Plays the alphabet song and
instructs students to go to their
assigned computers.
Will get setup at computers.
After conditioning Claps 3 times. Will get setup at computers.
The students behavior has been conditioned!
Classroom Implications
Technology can be used too to help students be classically conditioned!
Calculators can help students learn through this behavioral method.
If the teacher Then the students
Before conditioning Wants students to learn
multiplication tables
Use calculator to find answers
Will not know answers.
Will be able to find answers.
During conditioning Wants class to repeat using
calculators to learn
multiplication tables
Will be able to find answers
and slowly learn answers.
After conditioning Wants students to learn
multiplication tables
Will no longer need
calculators and will
know answer.
The students behavior has been conditioned!
Personal Applications
In the classroom, I hope to use classical conditioning to teach
my students expected behaviors for routine activities
without having to daily tell them what Im wanting.
Clapping 3 times to get class quiet
Counting down from twenty to get class to clean up
Have certain songs played representing where students
should be (ie: reading song playing means go to reading
corner)
Flashing the lights twice to get the class to return to their
seats.
Credits & Citations
Biographical pictures from biography.com
All other images from Microsoft Office Collections
Cherry, Kendra. "Pavlov's Dogs: How Ivan Pavlov Discovered Classical
Conditioning." 13 Nov. 2012.
<http://psychology.about.com/od/classicalconditioning/a/pavlovs-dogs.htm>.
Cherry, Kendra. John B. Watsons Biography (1878-1958)." 13 Nov. 2012.
<http://psychology.about.com/od/profilesofmajorthinkers/p/watson.htm>
Learning Theories Knowledgebase (2012, November). Classical Conditioning
(Pavlov) at Learning-Theories.com. Retrieved November 15th, 2012 from
http://www.learning-theories.com/classical-conditioning-pavlov.html
Shelly, Gary, Glenda Gunter, and Randolph Gunter. Teachers Discovering
Computers: Integrating Technology in a Connected World, Seventh Edition. Page
258. Boston: Cengage Learning, 2012.
You might also like
- Observing The Outer Person: Behavioral PerspectiveDocument7 pagesObserving The Outer Person: Behavioral PerspectiveLyanna MormontNo ratings yet
- BehaviorismDocument23 pagesBehaviorismCherry Calfoforo AbaoNo ratings yet
- BehaviorismDocument8 pagesBehaviorismjal67No ratings yet
- The Psychology of Learning: An Introduction for Students of EducationFrom EverandThe Psychology of Learning: An Introduction for Students of EducationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- BehaviorismDocument16 pagesBehaviorismKurt AcacioNo ratings yet
- Social Learning Theory - A Bandura Edited - FinalDocument25 pagesSocial Learning Theory - A Bandura Edited - FinalAnne RiveraNo ratings yet
- BehaviorismDocument10 pagesBehaviorismAbindra Raj Dangol100% (2)
- Operant ConditioningDocument11 pagesOperant ConditioningJoi JenozNo ratings yet
- BF Skinner and Operant ConditioningDocument26 pagesBF Skinner and Operant ConditioningjogiedejesusNo ratings yet
- Social Learning Theory PaperDocument5 pagesSocial Learning Theory Paperapi-346876019100% (1)
- BehaviorismDocument20 pagesBehaviorismSyuhada Ramli100% (3)
- Classical ConditioningDocument46 pagesClassical ConditioningRay Nante AcayanNo ratings yet
- Operant ConditioningDocument18 pagesOperant Conditioningkariverma100% (2)
- BehaviorismDocument19 pagesBehaviorismJanesa Roque0% (1)
- Behavioral TheoryDocument8 pagesBehavioral Theoryapi-286619177No ratings yet
- Operant ConditioningDocument18 pagesOperant ConditioningjanahfNo ratings yet
- Classical and Operant Conditioning ExamplesDocument6 pagesClassical and Operant Conditioning ExamplesPersephone355100% (1)
- Cognitive Learning TheoryDocument23 pagesCognitive Learning TheoryNi Wayan Sri Santika Dewi100% (1)
- Behaviorism TheoryDocument34 pagesBehaviorism TheoryL.s. YanNo ratings yet
- B. F. SkinnerDocument33 pagesB. F. SkinnerUmi Kalsum100% (1)
- Albert Bandura - Social Learning TheoryDocument2 pagesAlbert Bandura - Social Learning TheorygayyerNo ratings yet
- Bobo Doll ExperimentDocument5 pagesBobo Doll ExperimentShabir Ahmad Khan100% (1)
- Social Learning Theory of Albert BanduraDocument3 pagesSocial Learning Theory of Albert BanduraSyed Talha Kamal0% (1)
- What Is Behaviorism?Document23 pagesWhat Is Behaviorism?Mosedeil Herbert Tabios100% (1)
- Child Growth and DevelopmentDocument11 pagesChild Growth and DevelopmentMarvin Yebes ArceNo ratings yet
- Classical Vs Operant ConditioningDocument6 pagesClassical Vs Operant Conditioningmichelle gomez100% (2)
- BehaviorismDocument6 pagesBehaviorismamsaldi kristian100% (2)
- Cognitive Development Theory and Its Effects On Human DevelopmentDocument54 pagesCognitive Development Theory and Its Effects On Human DevelopmentArvella AlbayNo ratings yet
- Bandura's Social Learning TheoryDocument18 pagesBandura's Social Learning TheoryJames Ngu100% (7)
- Information Processing TheoryDocument14 pagesInformation Processing Theoryapi-276414713No ratings yet
- Social Cognitive Theory - BanduraDocument9 pagesSocial Cognitive Theory - BanduraJiss Palelil100% (1)
- BehaviorismDocument22 pagesBehaviorismOlcay Sanem SipahioğluNo ratings yet
- Albert BanduraDocument3 pagesAlbert BanduraAimee Belle OliverosNo ratings yet
- BehaviourismDocument4 pagesBehaviourismSujatha Menon100% (1)
- Skinner - Operant Conditioning PDFDocument12 pagesSkinner - Operant Conditioning PDFArnt van HeldenNo ratings yet
- Learning TheoriesDocument95 pagesLearning TheoriesMuhammad Irfan100% (5)
- Key Issues in Developmental PsychologyDocument34 pagesKey Issues in Developmental Psychologydistant dreamer100% (25)
- GENERAL PsychologyDocument54 pagesGENERAL PsychologyRasalyn Cericos Valois100% (1)
- Piaget - Cognitive DevelopmentDocument17 pagesPiaget - Cognitive DevelopmentDaniel RangaNo ratings yet
- Psy 301 - Classical Conditioning in The Classroom - PresentationDocument16 pagesPsy 301 - Classical Conditioning in The Classroom - Presentationapi-537649077No ratings yet
- Theories of LearningDocument25 pagesTheories of LearningsiaieiaiNo ratings yet
- Social Learning TheoryDocument23 pagesSocial Learning TheoryJacqueline Lacuesta100% (2)
- Social Learning Theory by Albert BanduraDocument2 pagesSocial Learning Theory by Albert BanduraDENNIS AFABLE100% (1)
- Social Learning TheoryDocument18 pagesSocial Learning Theorynasyratul100% (4)
- Ecological Systems TheoryDocument4 pagesEcological Systems TheoryJuvee Lyne Timay100% (4)
- Classical ConditioningDocument8 pagesClassical Conditioninganon-140609100% (2)
- Bandura's Social Learning TheoryDocument5 pagesBandura's Social Learning TheoryTamamaNo ratings yet
- CH 9 Socio Cultural Perspective 1Document17 pagesCH 9 Socio Cultural Perspective 1Sadiq AliNo ratings yet
- Social Learning TheoryDocument7 pagesSocial Learning TheoryNemwel QuilonioNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Learning Theory and Behavioral PsychologyDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Learning Theory and Behavioral PsychologyKaruna RajiahNo ratings yet
- Social Learning TheoryDocument2 pagesSocial Learning TheoryAlice Mendeleyeva100% (1)
- Gestalt PsychologyDocument14 pagesGestalt PsychologyJoyce Anne RenacidoNo ratings yet
- 4 Behavioral AssessmentDocument69 pages4 Behavioral AssessmentGabrelle Ogayon100% (1)
- Stimulus Response TheoryDocument5 pagesStimulus Response TheoryAS0% (1)
- Nature of PsychologyDocument32 pagesNature of PsychologyTanveer KhanNo ratings yet
- 3 Adlerian Theory of PersonalityDocument38 pages3 Adlerian Theory of Personalityhyacinth jumao-asNo ratings yet
- F2 - RPT Form 2 PDFDocument32 pagesF2 - RPT Form 2 PDFAmalin sufiaNo ratings yet
- Topic1a PDFDocument20 pagesTopic1a PDFDzul Azraai DzulkarnainNo ratings yet
- The Journal of Writing AssessmentDocument9 pagesThe Journal of Writing AssessmentDzul Azraai DzulkarnainNo ratings yet
- The Destructiveness of A Love That Never ChangesDocument5 pagesThe Destructiveness of A Love That Never ChangesDzul Azraai Dzulkarnain100% (1)
- Introduction On BF Skinner and His TheoryDocument17 pagesIntroduction On BF Skinner and His TheoryDzul Azraai DzulkarnainNo ratings yet
- Mean DefinitionsDocument2 pagesMean DefinitionsDzul Azraai DzulkarnainNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan (KSSR 2016) TemplateDocument3 pagesLesson Plan (KSSR 2016) TemplateDzul Azraai DzulkarnainNo ratings yet
- Date: Subject/Time/Cl ASS Content Focus:Grammar Theme: NumbersDocument3 pagesDate: Subject/Time/Cl ASS Content Focus:Grammar Theme: NumbersDzul Azraai DzulkarnainNo ratings yet
- Future EducationDocument10 pagesFuture EducationDzul Azraai DzulkarnainNo ratings yet
- TG Perform Clerical Procedurese RefinedDocument98 pagesTG Perform Clerical Procedurese RefinedRidho Taufiq KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Result Roll NoDocument31 pagesResult Roll NoShafayet UddinNo ratings yet
- Notes For B.EdDocument20 pagesNotes For B.EdratabNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan English 8 2020-2021Document19 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan English 8 2020-2021RHYSLYN RUFIN SALINASNo ratings yet
- Glorya H. Suk: PlacementDocument2 pagesGlorya H. Suk: Placementapi-254430460No ratings yet
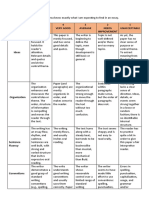
- Essay Writing RubricsDocument4 pagesEssay Writing RubricsTamudmud RicaNo ratings yet
- Current and Future Trends in Media and Information Literacy: Reported By: Group 8Document19 pagesCurrent and Future Trends in Media and Information Literacy: Reported By: Group 8Aphole SorianoNo ratings yet
- CyberBully Lesson Plan PDFDocument4 pagesCyberBully Lesson Plan PDFDiana Orfanides Moore100% (1)
- Education System TunisiaDocument20 pagesEducation System TunisiaIngYassineNo ratings yet
- A Critical Study of The Impact of Teacher-Student Relationship On Academic SuccessDocument6 pagesA Critical Study of The Impact of Teacher-Student Relationship On Academic SuccessInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 5th Grade - Technology Integration Lesson PlanDocument10 pages5th Grade - Technology Integration Lesson PlanemmaNo ratings yet
- Name: Messy Gustiani Class: 3.IA Lesson: Bahasa Inggris Lecturer: Beni WijayaDocument2 pagesName: Messy Gustiani Class: 3.IA Lesson: Bahasa Inggris Lecturer: Beni WijayaUwais HidayatullahNo ratings yet
- Effects of Technology-Enhanced Language Learning On Reducing EFL Learners Public Speaking AnxietyDocument26 pagesEffects of Technology-Enhanced Language Learning On Reducing EFL Learners Public Speaking AnxietyNurefşan DokgözNo ratings yet
- FIX English Olympiad Questions 2019Document16 pagesFIX English Olympiad Questions 2019Amalia Rahma100% (1)
- Chapter IDocument6 pagesChapter IHany Al AlmNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report in Reading 2018-2019Document3 pagesAccomplishment Report in Reading 2018-2019Rhona Luna100% (1)
- Brain GymDocument44 pagesBrain GymRaghu NadhNo ratings yet
- Changing School Culture - FinalDocument8 pagesChanging School Culture - FinalAura TabaraNo ratings yet
- LS1 Eng. LAS (Print-Non Print Materials)Document15 pagesLS1 Eng. LAS (Print-Non Print Materials)Rodge RufinNo ratings yet
- Iep (Ppi)Document26 pagesIep (Ppi)Robiansyah SetiawanNo ratings yet
- English Grade-10 Q2 LP-1-2Document7 pagesEnglish Grade-10 Q2 LP-1-2Trizh Nicole CastilloNo ratings yet
- Moral Responsibility of Students Gonzaleseljhay RDocument11 pagesMoral Responsibility of Students Gonzaleseljhay Rapi-592837323No ratings yet
- Module 1 - NC 1 - Receiving and Responding To Workplace Communication - FinalDocument82 pagesModule 1 - NC 1 - Receiving and Responding To Workplace Communication - Finalyunno adingNo ratings yet
- Health 4 Quarter 3Document8 pagesHealth 4 Quarter 3Lobmosgam HaileyhanaelaineNo ratings yet
- 75 Reading Has A Strong Influence On AcademicDocument2 pages75 Reading Has A Strong Influence On Academicsaifulazwan_19No ratings yet
- Grade 9 PETA Third QuarterDocument8 pagesGrade 9 PETA Third QuarterAnn HurbodaNo ratings yet
- SECNCI Module COED ENGLISH VERSIONDocument9 pagesSECNCI Module COED ENGLISH VERSIONAhnton AzuelaNo ratings yet
- E-Portfolio ResumeDocument1 pageE-Portfolio Resumeapi-481213890No ratings yet
- The Lexical ApproachDocument24 pagesThe Lexical ApproachSyed Anwer ShahNo ratings yet
- Muslim Rule in India (712-1526)Document40 pagesMuslim Rule in India (712-1526)Muhammad Rashid ShahNo ratings yet