Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bs Codes For Pile
Uploaded by
ConciselyOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bs Codes For Pile
Uploaded by
ConciselyCopyright:
Available Formats
Delivered by ICEVirtualLibrary.
com to:
IP: 60.51.101.1
On: Fri, 29 Jul 2011 03:33:27
Black plate (237,1)
References
American Petroleum Institute Specication for Line Pipes 5L. 43rd
edition. API. 2004.
Arcelor RPS. Piling Handbook 8th ed. Arcelor. 2005.
Arcelor RPS. The impervious steel sheet pile wall Parts 1 and 2. Arcelor.
2006.
Arcelor RPS. Welding of Steel Sheet Piles. Arcelor. 2006.
ASTM D 4945-00. Standard test method for high-strain dynamic testing
for piles.
British Standards Institution. British Standard 144: Specication for coal
tar creosote for wood preservation. BSI, London. 1997.
British Standards Institution. British Standard 882: Specication for
aggregates from natural sources for concrete. BSI, London. 1983.
British Standards Institution. British Standard 450-1. Fly ash for concrete.
Denition, specication and conformity criteria. BSI, London. 2005.
British Standards Institution. British Standard 1047: Specication for air-
cooled blast furnace slag aggregate for use in construction. BSI, London.
1983.
British Standards Institution. British Standard 1282: Wood preservatives.
Guidance on choice, use and application. BSI, London. 1999.
British Standards Institution. British Standard 1305: Specication for
batch type concrete mixers. BSI, London. 1974.
British Standards Institution. British Standard 3892-1: Pulverised-fuel
ash. Specication for pulverised-fuel ash for use with Portland
cement. BSI, London. 1997.
British Standards Institution. British Standard 3900-E6 Paints and
varnishes. Cross-cut test. BSI, London. 1995.
British Standards Institution. British Standard 3963: Method testing the
mix performance of concrete mixers. BSI, London. 1974.
British Standards Institution. British Standard 4072: Copper/chromium/
arsenic preparations for wood preservation. BSI, London. 1999.
British Standards Institution. British Standard 4449: Steel for the re-
inforcement of concrete. Weldable reinforcing steel. Bar, coil and
decoiled product. Specication. BSI, London. 2005.
British Standards Institution. British Standard 4978: Specication for
visual strength grading of softwood. BSI, London. 1996.
British Standards Institution. British Standard 5228: Noise control on
construction and open sites, Part 4: code of practice for noise andvibra-
tion control applicable to piling operations. BSI, London. 1992.
British Standards Institution. British Standard 5328-4: Concrete. BSI,
London. 1997.
British Standards Institution. British Standard 5756: Specication for
visual strength grading of hardwood. BSI, London. 1997.
British Standards Institution. British Standard 5930: Code of practice for
site investigations. BSI, London. 1999.
British Standards Institution. British Standard 6682-1: Method for deter-
mination of bimetallic corrosion in outdoor exposure corrosion tests. BSI,
London. 1989.
British Standards Institution. British Standard 7079-A1: Preparation of
steel substrates before application of paints and related products.
Visual assessment of surface cleanliness. Rust grades and preparation
grades of uncoated steel substrates and of steel substrates after overall
removal of previous coatings. BSI, London. 1989.
British Standards Institution. British Standard 7385: Evaluation and
measurement for vibration in buildings. BSI, London. 1990.
Specication for piling and embedded retaining walls. Thomas Telford, London, 2007 237
Delivered by ICEVirtualLibrary.com to:
IP: 60.51.101.1
On: Fri, 29 Jul 2011 03:33:27
Black plate (238,1)
British Standards Institution. British Standard 7973-1: Spaces and chairs
for steel reinforcement and their specication, product performance
requirements. BSI, London. 2001.
British Standards Institution. British Standard 7973-2 Spaces and chairs
for steel reinforcement and their specication. Fixing and application
of spaces and chairs and tying of reinforcement. BSI, London. 2001.
British Standards Institution. British Standard 8102: Code of practice for
protection of structures against water from the ground, BSI, London,
1990.
British Standards Institution. British Standard 8110: Structural use of
concrete. BSI, London. 1997.
British Standards Institution. British Standard 8417: Preservation of
timber, recommendations. BSI, London. 2003.
British Standards Institution. British Standard 8500: Concrete. Com-
plementary British Standard to BS EN 206-1. BSI, London. 2006.
British Standards Institution. British Standard 8500-1: Concrete. Com-
plementary British Standard to BS EN 206-1. Method of specifying
and guidance for the specier. BSI, London. 2006.
British Standards Institution. British Standard 8500-2: Concrete. Com-
plementary British Standard to BS EN 206-1. Specication for constitu-
ent materials and concrete. BSI, London. 2006.
British Standards Institution. British Standard 8666: Scheduling dimen-
sioning, bending of steel reinforcements for concrete specication. BSI,
London. 2005.
British Standards Institution. British Standard BS 4-1. Structural steel
sections. Specication for hot-rolled sections. BSI, London. 2005.
British Standards Institution. British Standard BS 450-1: Fly ash for
concrete. Denitions, specication and conformity criteria. BSI,
London. 2005.
British Standards Institution. British StandardBS 8102: Code of practice for
protection of structures against water fromthe ground. BSI, London. 1990.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 197-1: Cement.
Composition, specication and conformity criteria for common cements.
BSI, London. 2000.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 197-4: Cement. Com-
position specications and conformity criteria for low early strength
blastfurnace cements. BSI, London. 1998.
British Standards Institution. British Standard BS EN 206-1: Concrete.
Specication, performance, production and conformity. BSI, London.
2000.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 287-1: Qualication
test of welders. Fusion welding. Steels. BSI, London. 2004.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 287: Approval testing
of welders for fusion welding. Parts 1 and 2. 1992.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 350-1: Durability of
wood and wood based products. Natural durability of solid wood. Guide
to the principles of testing and classication of natural durability of
wood. BSI, London. 1994.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 350-2: Durability of
wood and wood-based products. Natural durability of solid wood.
Guide to natural durability and treatability of selected wood species of
importance in Europe. BSI, London. 1994.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 480-4: Admixtures for
concrete, mortar and grout. Test methods. Determination of bleeding in
concrete. BSI, London. 2005.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 934-2: Admixture for
concrete, mortar and grout. Concrete admixture. Denitions, require-
ments, conformity, marking and labelling. BSI, London. 2001.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 1008: Mixing water
for concrete. Specication for sampling, testing and assessing the suit-
ability of water, including water recovered from processes in the concrete
industry, as mixing water for concrete. BSI, London. 2002.
238 Specication for piling and embedded retaining walls. Thomas Telford, London, 2007
Delivered by ICEVirtualLibrary.com to:
IP: 60.51.101.1
On: Fri, 29 Jul 2011 03:33:27
Black plate (239,1)
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 1011-1: Welding
recommendations for welding of metallic materials, general guidance
for arc welding. BSI, London. 1998.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 1011-2: Welding
recommendations for welding of metallic materials. Arc welding of
ferretic steels. BSI, London. 2001.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 1536: Execution of
special geotechnical work piles. BSI, London. 2000.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 1561: Founding, grey
cast irons. BSI, London. 1997.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 1563: Specication,
cast iron sectional tanks (rectangular). Founding. Spheroidal graphite
cast iron. BSI, London. 1997.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 1583: Execution of
special geotechnical work diaphragm walls. BSI, London. 2000.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 1990: Eurocode basis
of structural design. BSI, London. 2002.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 1991-1-2: Eurocode 1:
Actions on structures, BSI, London. 2002.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 1992-1-1: Eurocode 2:
Design of concrete structures. General rules and the rules for buildings.
BSI, London. 2004.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 1992-3. Eurocode 2:
Design of concrete structures: concrete foundations. BSI, London.
1998.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 1993-5. Eurocode 3:
Design of steel structures, Part 5: Piling. BSI, London. 2006.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 1995-1-1. Eurocode 5:
Design of timber structures, General, common rules and rules for build-
ings. BSI, London. 2004.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 1997-1: 2004 Euro-
code 7: Geotechnical design, Part 1: General rules. BSI, London. 2004.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 1997-2: 2007 Euro-
code 7: Geotechnical design, Part 2: Ground investigation and testing.
BSI, London. 2007.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 5817: Welding.
Fusion-welded joints in steel, nickel, titanium and their alloys (beam
welding excluded). Quality levels for imperfection. BSI, London. 2003.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 10024: Hot rolled
taper ange I sections. Tolerances on shape and dimensions. BSI,
London. 1995.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 10025-1: Hot rolled
products of structural steels. General technical delivery conditions. BSI,
London. 2004.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 10034: Structural steel I
and H sections. Tolerances on shape and dimensions. BSI, London. 1993.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 10210-1: Hot nished
structural hollow sections of non-alloy and ne grain steels. Technical
delivery requirements. BSI, London. 2006.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 10210-2. Hot nished
structural hollow sections of non-alloy and ne grain steels. Tolerences,
dimensions and sectional properties. BSI, London. 2006.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 10219-1: Cold formed
welded structural hollow sections of non-alloy and ne grain steels.
Technical delivery requirements. London. 2006.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 10219-2. Cold
formed welded structural hollow sections of non-alloy and ne grain
steels. Tolerences, dimensions and sectional properties. BSI, London.
2006.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 10248-1. Hot rolled
sheet piling of non alloy steels. Technical delivery conditions. BSI,
London. 1996.
Specication for piling and embedded retaining walls. Thomas Telford, London, 2007 239
Delivered by ICEVirtualLibrary.com to:
IP: 60.51.101.1
On: Fri, 29 Jul 2011 03:33:27
Black plate (240,1)
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 10248-2. Hot rolled
sheet piling of non alloy steels. Tolerances on shape and dimensions.
BSI, London. 1996.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 10249-1: Cold formed
sheet piling of non alloy steels. Technical delivery conditions. BSI,
London. 1996.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 10249-2: Cold formed
sheet piling of non alloy steels. Tolerances on shape and dimensions. BSI,
London. 1996.
British Standards Institution. British Standard BS EN 10293: Steel cast-
ings for general engineering uses. BSI, London. 2005.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 12063: Execution of
special geotechnical work. Sheet pile walls. BSI, London. 1999.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 12350-1: Testing fresh
concrete. Sampling. BSI, London. 2000.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 12350-2: Testing fresh
concrete. Slump test. BSI, London, 2000.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 12350-5: Testing fresh
concrete. Flow table test. BSI, London. 2000.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 12390-1: Testing of
hardened concrete. BSI, London. 2000.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 12620: Aggregates for
concrete. BSI, London. 2002.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 12699: Execution of
special geotechnical work, displacement piles. BSI, London, 2001.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 12794: Precast
concrete products, foundations piles. BSI, London. 2005.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 14081-1: Timber struc-
tures. Strength graded structural timber with rectangular cross section.
General requirements. BSI, London. 2005.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 14199: Execution of
special geotechnical works. Micropiles. BSI, London. 2005.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN 15614-1: Specication
and qualication of welding procedures for metallic materials. Welding
procedure test. Arc and gas welding of steels and arc welding of nickel
and nickel alloys. BSI, London. 2004.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN ISO 2409: Paints and
varnishes. Cross-cut test. BSI, London. 1995.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN ISO 8501-1: Prepara-
tion of steel substrates before application of paints and related products.
Visual assessment of surface cleanliness. Rust grades and preparation
grades of uncoated steel substrates and of steel substrates after overall
removal of previous coatings. BSI, London. 2001.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN ISO 9001: Quality
management systems, requirements. BSI, London. 2000.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN ISO 12944: Paints and
varnishes. BSI, London. 2000.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN ISO 15607: Specica-
tion and qualication of welding procedures for metallic materials.
General rules. BSI, London. 2003.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN ISO 15609-1: Speci-
cation and qualication of welding procedures for metallic materials
building procedures. Specication arc welding. BSI, London. 2004.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN ISO 15613: Speci-
cation and qualication of welding procedures for metallic materials.
Qualication based on pre-production welding test. BSI, London. 2004.
British Standards Institution. British Standard EN ISO 22477-1. Pile
load test by static axially loaded compression. BSI, London. (In
production)
British Standards Institution. Published Document 6682-1 Aggregates.
Aggregates for concrete. Guidance on the use of BS EN12620. BSI,
London. 2003.
240 Specication for piling and embedded retaining walls. Thomas Telford, London, 2007
Delivered by ICEVirtualLibrary.com to:
IP: 60.51.101.1
On: Fri, 29 Jul 2011 03:33:27
Black plate (241,1)
Building Research Establishment. Working for Tracked Plant. BR 470.
BRE. 2004.
Building Research Establishment. BRE Digest 330: AlkaliSilica reaction
in concrete. BRE. 2004.
Building Research Establishment. BRE Digest 479: Timber pile and
foundations. BRE. 2003.
Building Research Establishment. BRE Special Digest 1: Concrete in
aggressive ground. BRE. 2005.
Building Research Establishment. Information Paper 2005/17: Concrete
with high ggbs contents for use in hard/rm secant piling. BRE. 2005.
Building Research Establishment. Report BR470: Working platforms for
tracked plant. BRE. 2004.
Chin, F. K., (1970) Estimation of the ultimate load of piles from tests not
carried to failure. Proc. 2nd S E Asian Conf. Soil Engineering,
Singapore, 8192.
Construction (Design and Management) Regulations (CDM). Statutory
Instrument 1994 No. 3140. Crown Copyright. 1994. (Amended 2000)
Construction (Design and Management) Regulations (CDM). Statutory
Instrument 2007 No. 320. Crown Copyright. 2007.
Construction Industry Research and Information Association. CDM
Regulations work sector guidance for designers. CIRIA, Report 166.
1997.
Construction Industry Research and Information Association. Integrity
testing in piling practice. CIRIA, Report R144. 1997.
Construction Industry Research and Information Association. Water-
resisting basements. CIRIA, Report 139. 1995.
Construction Industry Research and Information Association. CIRIA,
Report PG3. The use and inuence of bentonite in bored pile construc-
tion. CIRIA. 1997.
Construction Industry Research and Information Association. CIRIA,
Report PG7. Pile load testing procedure. CIRIA. 1980.
Construction Industry Research and Information Association. DOE and
CIRIA piling development group report PG2: Review of problems
associated with the construction of cast-in-place concrete piles.
CIRIA. 1977.
Construction Industry Research and Information Association. Gaba,
A. R., Simpson, B. Powrie, W. and Beadman, D. R. Embedded
retaining walls guidance for economic design. CIRIA, Report C580.
2003.
Creosote Regulations 2003. Statutory Instrument 2003 No. 1511. The
Creosote (Prohibition on Use and Marketing) (No. 2) Regulations.
www-opsi.gov.uk
Environment Protection Regulations. 2003. Statutory Instrument 2003
No. 63. The Environment Protection (Duty of Care) (England)
(Amendment) Regulations. www-opsi.gov.uk
Federation of Piling Specialists. Bentonite support uids in civil engin-
eering in the UK. 2nd ed. www.fps.org.uk
Federation of Piling Specialists. Essential guide to the ICEspecication for
piling and embedded retaining walls. Thomas Telford, London. 1999.
Federation of Piling Specialists. Handbook on pile load testing. British
Standard. www.fps.org.uk 2006.
Fleming, M. and England W. G. K. (1994). Review of foundation testing
methods and procedures. Proc. ICE Geotechnical Engng, paper 10407.
Fleming, W. G. K. (1992) A New method for single pile settlement predic-
tion and analysis. Geotechnique, XLII, 3 411425.
Highways Agency. Specication for piling and embedded retaining walls.
HMSO. 1994.
Hutchinson, M. T, Daw, G. P. Shotton, P. G. andJames, A. N. The proper-
ties of bentonite slurries used in diaphragm wall and their control. Proc.
Conf. on diaphragm walls and anchorages. ICE, London. 1975, 3340.
Institution of Civil Engineers. Specication for piling and embedded
retaining walls. Thomas Telford, London. 1996.
Specication for piling and embedded retaining walls. Thomas Telford, London, 2007 241
Delivered by ICEVirtualLibrary.com to:
IP: 60.51.101.1
On: Fri, 29 Jul 2011 03:33:27
Black plate (242,1)
Institution of Civil Engineers. Specication for piling. Thomas Telford,
London. 2004.
Jeeris, S. (1992) Grout and Slurries. The Construction Materials Refer-
ence Book. Doran, D. K., Ed. Butterworth.
Leung, D. F., Tan, S. A. and Phoon, K. K. (1999) Proceedings of the
International symposium on eld measurements in geomechanics, 5,
Singapore, 13 Dec. 1999.
Myrovoll, F. (2003) Proceedings of the International symposium on eld
measurements in geomechanics, 6, Oslo, 1518 Sept. 2003.
North American Steel Sheet Piling Association. Sheet Piling TESPA
Installation Guide. NASSPA. 2005.
Proceedings of the International symposium on eld measurements in
geomechanics, 4, Bergamo, 1012 Apr. 1995.
Publication no 163 (1988). Drilling Fluid Materials. The Engineering
Equipment and Material Users Association. www.eemua.org
Puller, M. J. (1994) The Waterproofness of Structural Diaphragm Wall.
Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng, 107, pp. 4757.
So rum, G. (1991) Proceedings of the International symposium on eld
measurements in geomechanics, 3, Oslo, 911 Sept. 1991 vol. 12.
The marketing and use of dangerous substance regulations 2003 SR 2003/
105. www-opsi.gov.uk
242 Specication for piling and embedded retaining walls. Thomas Telford, London, 2007
You might also like
- BS - 6031 Code of Practice For Earthworks PDFDocument90 pagesBS - 6031 Code of Practice For Earthworks PDFAishwarya Kumar100% (2)
- Hip, Valley, & Jack Rafters: Chapter ObjectivesDocument26 pagesHip, Valley, & Jack Rafters: Chapter ObjectivesdamindaNo ratings yet
- BS EN 14490-2010 Execution of Special Geotechnical Works - Soil NailingDocument72 pagesBS EN 14490-2010 Execution of Special Geotechnical Works - Soil Nailingjadrichem50% (2)
- Method Statement For Grouting Sonic Tubes of Bored PilesDocument16 pagesMethod Statement For Grouting Sonic Tubes of Bored PilesYay B. Gico67% (3)
- Bs 85972015Document21 pagesBs 85972015谢兆岩No ratings yet
- BS 5328 Part1 PDFDocument28 pagesBS 5328 Part1 PDFtss13723100% (10)
- Prediction of Ground Movements and Assessment of Risk of Building Damage Due To Bored Tunnelling PDFDocument7 pagesPrediction of Ground Movements and Assessment of Risk of Building Damage Due To Bored Tunnelling PDFMartin Griffin100% (2)
- Appendix B SettlementDocument24 pagesAppendix B SettlementVince26100% (1)
- TR 26-Deep Excavation - 2010Document59 pagesTR 26-Deep Excavation - 2010Rajesh KyasanipalleyNo ratings yet
- Technical Note-Water Seepage Through PilesDocument5 pagesTechnical Note-Water Seepage Through PilesLijo Joseph100% (2)
- Pile Design To BS EN 1997-1:2004 (EC7) and The National AnnexDocument68 pagesPile Design To BS EN 1997-1:2004 (EC7) and The National AnnexSewGuanNo ratings yet
- A Misconception of EC On Structural Design of Foundation Bored PilesDocument58 pagesA Misconception of EC On Structural Design of Foundation Bored Pilesedward the iii100% (3)
- ICE Specification For Piling and Embedded Retaining WallsDocument12 pagesICE Specification For Piling and Embedded Retaining WallsAws100% (2)
- Analysis of Roof Truss Design DataDocument32 pagesAnalysis of Roof Truss Design DataARSENo ratings yet
- How To Use BS8500 With BS8110Document8 pagesHow To Use BS8500 With BS8110Marty AndersonNo ratings yet
- HA and HB Type Loading DesignDocument16 pagesHA and HB Type Loading DesignHilman Netjibvute100% (1)
- Implementing BS 8500-1 for Durable Concrete StructuresDocument13 pagesImplementing BS 8500-1 for Durable Concrete StructuresJimmy Lopez100% (1)
- Control Temp in Mass ConcreteDocument9 pagesControl Temp in Mass ConcretechrtromNo ratings yet
- Design pile foundations Eurocode 7Document10 pagesDesign pile foundations Eurocode 7정진교100% (1)
- Install Electrical Metallic - Nonmetallic (PVC Conduit)Document13 pagesInstall Electrical Metallic - Nonmetallic (PVC Conduit)Rex Chambers LadaoNo ratings yet
- Design of Piles Under Cyclic Loading: SOLCYP RecommendationsFrom EverandDesign of Piles Under Cyclic Loading: SOLCYP RecommendationsAlain PuechNo ratings yet
- Technical Report TR43Document120 pagesTechnical Report TR43José Atalaya Villanueva100% (1)
- BS en 14487-2-2006Document20 pagesBS en 14487-2-2006Thanh Hai QB50% (2)
- CV-0013-002 - Method Statement For Soil Improvement WorkDocument14 pagesCV-0013-002 - Method Statement For Soil Improvement Work한상호No ratings yet
- EC7 Briefing on Ground InvestigationDocument32 pagesEC7 Briefing on Ground Investigationjohnkoh99100% (1)
- ICE Manual of Geotechnical EngineeringDocument3 pagesICE Manual of Geotechnical Engineeringhcpingpui25% (12)
- Ciria Report 91 1981 PDFDocument19 pagesCiria Report 91 1981 PDFimranmehfoozNo ratings yet
- Why The BS 8500 Durability Tables Are The Way They Are-Concrete June2016Document4 pagesWhy The BS 8500 Durability Tables Are The Way They Are-Concrete June2016Vipin Kumar ParasharNo ratings yet
- SS 544-2-2014+Corr1+Amd1 - Preview PDFDocument13 pagesSS 544-2-2014+Corr1+Amd1 - Preview PDFPTchong0% (1)
- Method Statement For Installation of Soil Nails With For Slope StabilizationDocument11 pagesMethod Statement For Installation of Soil Nails With For Slope StabilizationDelon Yau100% (2)
- Joints in Steel Construction - Simple Connections - Part 11 PDFDocument4 pagesJoints in Steel Construction - Simple Connections - Part 11 PDFkakem61No ratings yet
- NA To BS EN 1997-2 2007.aspx PDFDocument16 pagesNA To BS EN 1997-2 2007.aspx PDFDang Thanh TuanNo ratings yet
- Concrete Formwork and FinishesDocument15 pagesConcrete Formwork and FinishesIm Chinith100% (1)
- Reuse of FoundationsDocument35 pagesReuse of Foundationspetrohasan100% (1)
- BS 1377part4 90 PDFDocument49 pagesBS 1377part4 90 PDFADENIYI DAPONo ratings yet
- Attachment 07 - Subcontractor's Quality Management RequirementsDocument6 pagesAttachment 07 - Subcontractor's Quality Management Requirementsum erNo ratings yet
- A Brief Guide To Design of Bored Piles Under Axial CompressionDocument15 pagesA Brief Guide To Design of Bored Piles Under Axial Compressiondanielsu87No ratings yet
- Ground AnchorDocument79 pagesGround AnchorLaughlikesiao HeheNo ratings yet
- BS 5328 - 2Document12 pagesBS 5328 - 2Sundeep Reddy100% (3)
- Shotcrete Design GuidelinesDocument36 pagesShotcrete Design GuidelinesJose MartinezNo ratings yet
- RCP Lighting PlansDocument47 pagesRCP Lighting PlansSalama ShurrabNo ratings yet
- Gabbion Wall PresentationDocument32 pagesGabbion Wall PresentationUsman Ilyas100% (1)
- Civil Bridge Design Exam Study GuideDocument1 pageCivil Bridge Design Exam Study GuidechrisjballNo ratings yet
- Ground Improvement Case Histories: Embankments with Special Reference to Consolidation and Other Physical MethodsFrom EverandGround Improvement Case Histories: Embankments with Special Reference to Consolidation and Other Physical MethodsNo ratings yet
- Concrete Formwork SpecsDocument6 pagesConcrete Formwork Specsclive_2201No ratings yet
- ASME Standard & Code ListingDocument7 pagesASME Standard & Code ListingMyron CampbellNo ratings yet
- Sprayed ConcreteDocument41 pagesSprayed ConcreteLemmy MulandiNo ratings yet
- BS 5328-3 1990 PDFDocument13 pagesBS 5328-3 1990 PDFSoham MaityNo ratings yet
- Installation of Steel Sheet PilesDocument2 pagesInstallation of Steel Sheet PilesAdam Lim100% (1)
- BS 8297 2017Document64 pagesBS 8297 2017MOHAMMAD100% (2)
- Design Calculation for Merdeka PNB 118 ProjectDocument1 pageDesign Calculation for Merdeka PNB 118 ProjectUma Selladurai100% (1)
- MS1314 2004 Pile SpecificattionDocument28 pagesMS1314 2004 Pile SpecificattionmaNo ratings yet
- ICE SPDocument3 pagesICE SPtehNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ICE Piling SpecsDocument1 pageIntroduction To ICE Piling SpecsT NgNo ratings yet
- British Standards 2006 PDFDocument21 pagesBritish Standards 2006 PDFYongsub JungNo ratings yet
- Bs Codes For PileDocument6 pagesBs Codes For PileConcisely0% (2)
- Local Pile Foundation Design GuideDocument30 pagesLocal Pile Foundation Design GuideEmily Shum100% (1)
- BS en 1536-1999 - Execution of Special Geotechnical Work-Bored PilesDocument84 pagesBS en 1536-1999 - Execution of Special Geotechnical Work-Bored PilesBeth Hteb50% (2)
- ASSESSING IN-SITU CONCRETE STRENGTHDocument4 pagesASSESSING IN-SITU CONCRETE STRENGTHMark WilliamsNo ratings yet
- BS 4550 3.4 PDFDocument17 pagesBS 4550 3.4 PDFMatt IkhramNo ratings yet
- En 14490 After CEN Enquiry (Soil Nailing)Document59 pagesEn 14490 After CEN Enquiry (Soil Nailing)Abraham FIgueroa ARevaloNo ratings yet
- Reinforcement Standard en 10080 and The ECDocument1 pageReinforcement Standard en 10080 and The ECLeed ENNo ratings yet
- BS 2499-2 1992Document14 pagesBS 2499-2 1992kunjal_radiaNo ratings yet
- (BS 1881-124) - Testing Concrete. Part 124. Methods For Analysis of Hardened Concrete PDFDocument45 pages(BS 1881-124) - Testing Concrete. Part 124. Methods For Analysis of Hardened Concrete PDFsidiq733% (3)
- References - Manual For The Design of Timber BuildingDocument6 pagesReferences - Manual For The Design of Timber Buildingrenuvenkat0070% (1)
- CE40008 - 50017 - T2S1 - Standards and TerminologyDocument16 pagesCE40008 - 50017 - T2S1 - Standards and TerminologyBashar ToshtashNo ratings yet
- Karst Topography Features: Stalactites, Sinkholes & MoreDocument1 pageKarst Topography Features: Stalactites, Sinkholes & MoreConciselyNo ratings yet
- Settlement DataDocument1 pageSettlement DataConciselyNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Weight of Product: RD GroupDocument2 pagesCalculation of Weight of Product: RD GroupConciselyNo ratings yet
- Er Ip (1-) B P/ S: Applied Pressure, P (KN/M)Document1 pageEr Ip (1-) B P/ S: Applied Pressure, P (KN/M)ConciselyNo ratings yet
- Correlation Between Soil Bearing Capacity and Modulus of Subgrade ReactionDocument5 pagesCorrelation Between Soil Bearing Capacity and Modulus of Subgrade ReactionCristian Camilo Londoño PiedrahítaNo ratings yet
- Pile Load Settlement ChartDocument1 pagePile Load Settlement ChartConciselyNo ratings yet
- Correlations Between Soil Plasticity and Strength ParametersDocument10 pagesCorrelations Between Soil Plasticity and Strength ParametersConciselyNo ratings yet
- Correlations Between Soil Plasticity and Strength ParametersDocument10 pagesCorrelations Between Soil Plasticity and Strength ParametersConciselyNo ratings yet
- Length of Sound Core Pieces 4 INCHES (100mm.) Total Core Run LengthDocument1 pageLength of Sound Core Pieces 4 INCHES (100mm.) Total Core Run LengthConciselyNo ratings yet
- Steel MaterialDocument12 pagesSteel MaterialConciselyNo ratings yet
- Pile Load Settlement ChartDocument1 pagePile Load Settlement ChartConciselyNo ratings yet
- Soil Nail Wall Design and Construction GuideDocument2 pagesSoil Nail Wall Design and Construction GuideConciselyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Lesson2 2DDocument22 pagesTutorial Lesson2 2DConciselyNo ratings yet
- Standpipe PiezoDocument2 pagesStandpipe PiezoConciselyNo ratings yet
- Buoyant Force CalcDocument4 pagesBuoyant Force CalcConciselyNo ratings yet
- Soft SoilDocument1 pageSoft SoilConciselyNo ratings yet
- Strip FootingDocument16 pagesStrip FootingConciselyNo ratings yet
- Design of Piled Raft Foundation On Soft Final)Document20 pagesDesign of Piled Raft Foundation On Soft Final)rajudeenNo ratings yet
- Hand Auger (2m Depth)Document8 pagesHand Auger (2m Depth)ConciselyNo ratings yet
- Secant Pile Seawall Protects SR A1A in Flagler BeachDocument40 pagesSecant Pile Seawall Protects SR A1A in Flagler Beachsantanu mukherjeeNo ratings yet
- IIT Delhi Short Course on Recent Advances in Highway Design and ConstructionDocument4 pagesIIT Delhi Short Course on Recent Advances in Highway Design and ConstructionMohammed ShahbazNo ratings yet
- Bostik Seal N Flex (Technical Data Sheet)Document6 pagesBostik Seal N Flex (Technical Data Sheet)dep_vinNo ratings yet
- Detail & Abstract Estimate NewDocument6 pagesDetail & Abstract Estimate NewSAE/SO Damudya MahbubNo ratings yet
- Method Statement of Storage TankDocument49 pagesMethod Statement of Storage Tankengbilal.qaqc786No ratings yet
- Answer: Option CDocument4 pagesAnswer: Option CpransuNo ratings yet
- HMC Safety&health SowDocument2 pagesHMC Safety&health SowRoy Richard MacabodbodNo ratings yet
- Company Profile QCSDocument29 pagesCompany Profile QCSsachinNo ratings yet
- Datasheet: ULO Pipeline SupportDocument1 pageDatasheet: ULO Pipeline SupportSanjeevi ParthasarathiNo ratings yet
- Specification for Street Lighting SystemsDocument103 pagesSpecification for Street Lighting SystemsJaf FruminguezNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study On Self-Healing Concrete Using GGBS and MetakaolinDocument9 pagesExperimental Study On Self-Healing Concrete Using GGBS and MetakaolinIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
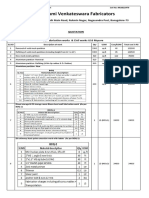
- All Fabrication Works & Civil Works QuotationDocument3 pagesAll Fabrication Works & Civil Works QuotationSai JaganNo ratings yet
- The Wafflemat™ Foundation Forming System: On-Grade Mat Foundation For Expansive, Collapsible and Rocky SoilsDocument25 pagesThe Wafflemat™ Foundation Forming System: On-Grade Mat Foundation For Expansive, Collapsible and Rocky Soilshumbert14000100% (1)
- Trenching SafetyDocument1 pageTrenching SafetyAldrien CabinteNo ratings yet
- Sub: Price Structure For 80mm and 100mm Interlock PaversDocument1 pageSub: Price Structure For 80mm and 100mm Interlock PaversDeepNo ratings yet
- 40X60 East DuplexDocument1 page40X60 East DuplexPhaniraj RamachandrulaNo ratings yet
- Scottish Land Tour 00 Fy FeDocument524 pagesScottish Land Tour 00 Fy FeargyllforumNo ratings yet
- TJ 4000 PDFDocument32 pagesTJ 4000 PDFkirubaNo ratings yet
- InterviewDocument2 pagesInterviewJhames Marck AblanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6 Civil Engineering Project & Cost ManagementDocument3 pagesTutorial 6 Civil Engineering Project & Cost ManagementFearless HeroNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: Prefabricated Construction - Part 2 Methods and UsesDocument46 pagesUnit 4: Prefabricated Construction - Part 2 Methods and Usesadit guptaNo ratings yet
- DPIEH - DPO - TDOB 12-16kW - Installation Manual - ENGDocument43 pagesDPIEH - DPO - TDOB 12-16kW - Installation Manual - ENGszekelyendre.klimaNo ratings yet
- CV and Portofolio Cretu BogdanDocument16 pagesCV and Portofolio Cretu BogdanCretu BogdanNo ratings yet
- Jabas, Aaron Qarl M.: ObjectivesDocument2 pagesJabas, Aaron Qarl M.: ObjectivesRome GalosoNo ratings yet