Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Welding Vocabulary
Uploaded by
Anonymous LFgO4WbID0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
597 views2 pagesWelding Vocabulary
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentWelding Vocabulary
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
597 views2 pagesWelding Vocabulary
Uploaded by
Anonymous LFgO4WbIDWelding Vocabulary
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Welding Vocabulary
The following are common terms in welding.
Abrasive - A material, such as sand, silicon or crushed stone, used for surface cleaning.
Acetylene Gas - A chemical combination of two elements: carbon and hydrogen.
Alloy - A metal that is made by mixing two or more metals, or a metal and another substance.
Alternating Current (AC) - Is an electrical current in which magnitude and direction change in cycles,
as opposed to direct current, in which direction is constant.
Arc Welding (Shielded Metal Arc Welding) - A welding process where similar materials are joined
with a heating process caused by an electric arc. In the most common use, this process includes the use
of a fller metal.
Argon - Is a chemical element designated by the symbol Ar. Argon has atomic number 1 and is the
third element in group 1 of the periodic table !noble gases". Argon is present in the #arth$s atmosphere
at slightly less than 1%, ma&ing it the most common noble gas on #arth.
Brazing - A process where metals are joined by using a fller metal that melts at a temperature abo'e
()*+.
Butt Joint (Butt Weld) - A joint !or weld" where the two pieces being connected come directly
together in the same plane.
Buzz Box - Another term for a general,purpose arc welder. The name is deri'ed from the sound made
when the welder is running.
Consuable ! non-consuable electrodes - +onsumable electrodes pro'ide a path for the current.
They also supply fuller metal to the joint. -onconsumable electrodes are only used as a conductor for
the electrical current, such as in gas tungsten arc welding.
Cutting "i# - The part of an oxygen torch that directs the .ow of the gas.
Cutting "orch - The de'ice used in oxygen cutting to control and direct the .ow of the gasses used for
cutting and heating metal.
Cylinder - A container to store and transport compressed gas.
$e%ective Weld - A weld with one or more of the following defects: /orosity, undercut, slag inclusion
and improper weld si0e.
$irect Current ($C) - 1r 2continuous current,2 is considered as the constant .ow of electrons in the
single direction from low to high potential.
$o&n 'and Weld - A 'ertical weld where the welder starts at the top and wor&s downward.
(dge Weld - A weld where the edges of two pieces come together.
)(lectrode (Arc Welding) - A rod made up of fller metal with a coating on it designed to aid and
protect the bead during the welding process.
(lectrode 'older - The 2handle2 portion of the arc welder that holds the electrode in place.
*ace Shield ('elet) - A safety de'ice worn o'er the face to protect the eyes and face from the arc,
spar&s and molten metal. Arc welding without proper eye protection can lead !3uic&ly" to permanent
damage to the eyes.
*errous - +ontaining or relating to iron.
*illet Weld - A weld joining two pieces of metal that are more or less perpendicular to each other.
*iller etal - Is a metal added in the ma&ing of a joint through welding, bra0ing or soldering. 4arious
types of fller metals exist.
*ixture - A tool or de'ice used to hold pieces in place for welding.
*lat Weld - A weld where the pieces being joined come together hori0ontally in front of and below the
welder.
*lux - A substance that facilitates soldering, bra0ing and welding by chemically cleaning the metals to
be joined.
*orge - A de'ice used to heat metal for forming and bending. !5lac&smithing"
*uel Gases - 6ases mixed with oxygen in heating and cutting operations.
Gas "ungsten Arc Welding (G"AW) or ("+G) - +ommonly &nown as tungsten inert gas (TIG)
welding; an arc welding process that uses a non,consumable tungsten electrode to produce the weld.
'and Shield - 7imilar to a Face Shield or Helmet, but held in front of the face rather than worn.
+ron - A base element that is the primary substance in the ma&eup of steel, cast iron and wrought iron.
+nert gas,Shielding gas - A gas that does not normally combine chemically with materials. Their
purpose is to protect the weld area from atmospheric gases, such as oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide
and water 'apor.
-a# Joint - A joint where two pieces of metal lap o'er each other, allowing a bead to be placed
between the edge of one piece and the face of the other.
)M+G Welding (Metal +nert Gas) - Also &nown as wire,feed welding, although it is possible to do wire,
feed welding without the inert gas. 8etals that are di9cult to arc weld may be 8I6 welded.
Mild Steel - 7teel with less than *.1)% carbon. !Also called low carbon steel". 8ost steel in common
use is mild steel.
.ut-.%-/osition Weld - Any weld where the wor& is not .at in front of the welder.
.verhead Weld - An in'erted weld where the pieces being joined are abo'e the welder.
.xy%uel - /ure oxygen combined with gas
/lasa - A gas that has been heated to the point where it will conduct electricity.
/lasa Cutting - A cutting process where the metal is heated to the melting point by an arc through
the plasma and then remo'ed by the pressure of the gas as directed by the no00le. +-+ !computer
numeric control" plasma cutters are used for precise cutting of complex patterns in metal.
/olarity - The polarity of a machine refers to direction of current .ow. /olarity can only be obtained on
a :+ machine.
0adiation - #nergy from heat or light that you cannot see.
Shielding Gas - ,,See Inert gas.
Slag +nclusion - -on,metallic material trapped in a weld.
Soldering - A method of joining metal parts using a fller material !solder" that has a melting
temperature below ()*;+ !(<;=".
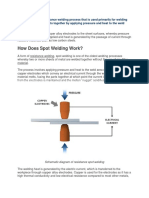
S#ot Weld - A weld between two o'erlapping pieces of material> normally used for sheet metal.
"ac1 Weld - A small weld used to hold pieces of an assembly in place prior to the fnal !continuous"
welding.
"+G Welding ("ungsten +nert Gas) - A welding process where an inert gas protects the molten metal
from the atmosphere to produce a high 3uality weld.
"ungsten - A non,consumable material used in TI6 welding to carry current to the weld puddle. !'ery
hard, hea'y, steel,grey,to,white transition metal> ? in the periodic table."
2# 'and Weld - A 'ertical weld where the welder starts at the bottom and wor&s upward.
3entilate - To cause fresh air to enter and mo'e around an enclosed space
Weave Bead - A welding pattern often used in butt welds where the welder mo'es the arc bac& and
forth across the joint while also mo'ing along it.
Weld - To join two pieces of metal together permanently by melting the parts that touch.
Welder (noun) - A person whose job is welding.
Welding /o&er Su##ly - A de'ice that pro'ides an electrical current to perform welding.
Welding 0od - A means of deli'ering fller metal to the weld. In arc welding, the rod is called an
electrode.
3oltage (3) - Is the pressure re3uired to mo'e the electric current.
An #@*<( electrode, for instance, will ha'e the following characteristics:
# , electrode !arc welding"
@* , multiplied by 1*** means @*,*** psi !pounds per s3uare inch" tensile strength.
< , .at position
( , A+ and :+ !straight and re'erse"
Basic Rules for SAW
1) Arc !ength: The distance between the tip of the electrode and the base metal being welded. The
correct distance must be kept.
2) Angle of electrode: :uring welding, the electrode must be held at the correct angle.
3) Speed of tra'el: If a good weld is to be made, the correct speed must be kept.
4) Amperage: Incorrect amperage heat) !ill result in a poor !eld.
7ome welders use the word AB,A,7,CD to remember these four points.
!engt" # Angle # S$eed # %eat (a&$erage)
You might also like
- Welders TerminologyDocument37 pagesWelders TerminologyNicolae Marin100% (2)
- Oxy-Acetylene Welding and Cutting: Electric, Forge and Thermit Welding together with related methods and materials used in metal working and the oxygen process for removal of carbonFrom EverandOxy-Acetylene Welding and Cutting: Electric, Forge and Thermit Welding together with related methods and materials used in metal working and the oxygen process for removal of carbonNo ratings yet
- WELD-Arc Welding - Maine Welding CompanyDocument7 pagesWELD-Arc Welding - Maine Welding CompanypeterNo ratings yet
- Technical Manual - The Blacksmith and the Welder - June 16, 1941From EverandTechnical Manual - The Blacksmith and the Welder - June 16, 1941No ratings yet
- WeldingDocument12 pagesWeldingChaudhry BrothersNo ratings yet
- SMAW Shielded Metal Arc Welding GuideDocument6 pagesSMAW Shielded Metal Arc Welding GuideJoseph BautistaNo ratings yet
- Welding BasicDocument31 pagesWelding BasicSNEHAL PATEL50% (2)
- Welding Assignment-Submitted by Fatima Fayyaz-PID-09Document4 pagesWelding Assignment-Submitted by Fatima Fayyaz-PID-09api-19753215No ratings yet
- Welding ShopDocument13 pagesWelding ShopAliNo ratings yet
- Engineering Practice: Assignment # 01Document8 pagesEngineering Practice: Assignment # 01Saad Ur Rehman AftabNo ratings yet
- Types of Welding ProcessesDocument7 pagesTypes of Welding Processesrohitme045No ratings yet
- PART 166 What Is Spot WeldingDocument4 pagesPART 166 What Is Spot Weldingravindra_jivaniNo ratings yet
- Welding Terms & Definitions GuideDocument42 pagesWelding Terms & Definitions GuidepchakkrapaniNo ratings yet
- Intro To Welding TechnologyDocument9 pagesIntro To Welding TechnologyOVURUTHO PIUSNo ratings yet
- Basic Welding GuideDocument2 pagesBasic Welding GuideJelena MitrovicNo ratings yet
- ESAB GlossaryDocument20 pagesESAB GlossaryGoanengineerNo ratings yet
- Metal JoiningDocument62 pagesMetal Joiningbhavna agarwalNo ratings yet
- Metal Joining Processes FLIPPED LEARNINGDocument2 pagesMetal Joining Processes FLIPPED LEARNINGreubenjamesstephensNo ratings yet
- Welding Electrode ClassificationsDocument18 pagesWelding Electrode ClassificationsMansukh KahlonNo ratings yet
- SMAWDocument4 pagesSMAWjerreyannNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Processes (Welding (BENG) HandoutDocument67 pagesManufacturing Processes (Welding (BENG) HandoutbananaNo ratings yet
- Breif Introduction To Joining Methord in EngineeringDocument13 pagesBreif Introduction To Joining Methord in EngineeringMuhammad Hammad UmerNo ratings yet
- Welding & Joining ProcessesDocument5 pagesWelding & Joining ProcessesKetan TiwariNo ratings yet
- What Is WeldingDocument5 pagesWhat Is WeldingJennie VicentaNo ratings yet
- Welding, Soldering and BrazingDocument11 pagesWelding, Soldering and BrazingAyush 100niNo ratings yet
- Welding Term Definitions and GlossaryDocument5 pagesWelding Term Definitions and GlossaryMac PatNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Technology: Tig Welding - Process AnalysisDocument8 pagesManufacturing Technology: Tig Welding - Process AnalysisshubhamNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4 Principle of Selected Joining and Assembling Process A Brief History of WeldingDocument12 pagesChapter-4 Principle of Selected Joining and Assembling Process A Brief History of WeldingFira tubeNo ratings yet
- Assigment WeldingDocument4 pagesAssigment WeldingAnonymous Co9r0PbNo ratings yet
- Physics of WeldingDocument3 pagesPhysics of WeldingKhurram RehmanNo ratings yet
- Welding TerminologiesDocument11 pagesWelding TerminologiesPankajabhangNo ratings yet
- Arc Welding GuideDocument229 pagesArc Welding GuideTilak MoundekarNo ratings yet
- 3 Unit 2 - Arc, Gas, Plastic Welding, LBW, EBW and Thermit WeldingDocument96 pages3 Unit 2 - Arc, Gas, Plastic Welding, LBW, EBW and Thermit WeldingAditya KumarNo ratings yet
- Welding Basics, Techniques & Safety-2020Document86 pagesWelding Basics, Techniques & Safety-2020Tayyaba RahimNo ratings yet
- Welding ShopDocument10 pagesWelding ShopAsifJavedNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Welding Techniques and Joint TypesDocument34 pagesAircraft Welding Techniques and Joint TypesJoshua BarteNo ratings yet
- Krishna Engineering College Department of Mechanical EngineeringDocument5 pagesKrishna Engineering College Department of Mechanical EngineeringVivek BajpaiNo ratings yet
- WeldingDocument169 pagesWeldingamarparimi100% (1)
- Aircraft Materials, Construction and RepairDocument34 pagesAircraft Materials, Construction and RepairJoshua BarteNo ratings yet
- Metal Joining Processes: List Types of Welding, Description With Sketches of Arc Welding, Soldering and Brazing and Their ApplicationsDocument21 pagesMetal Joining Processes: List Types of Welding, Description With Sketches of Arc Welding, Soldering and Brazing and Their ApplicationseldhosekjnitNo ratings yet
- Arc Welding ProjectDocument11 pagesArc Welding ProjectLeahNo ratings yet
- Welding WorkshopDocument11 pagesWelding WorkshopMuhammad Tauseef ZafarNo ratings yet
- Arc Welding SessionalDocument13 pagesArc Welding Sessionalnehar shubheschaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Welding TechnologyDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Welding Technologyibnu.asad984No ratings yet
- Guide to basic welding techniquesDocument7 pagesGuide to basic welding techniquesJaveed A. KhanNo ratings yet
- Welding: Welding Is A Process of Metal Joining by Applying Heat and Sometime PressureDocument41 pagesWelding: Welding Is A Process of Metal Joining by Applying Heat and Sometime PressureJith Viswa100% (1)
- Welding Types of Welding Gas Welding (Oxy-Acetylene) Arc Welding (Metal Arc) Merits & Limitations of Welding Process Application ConclusionDocument14 pagesWelding Types of Welding Gas Welding (Oxy-Acetylene) Arc Welding (Metal Arc) Merits & Limitations of Welding Process Application ConclusionAjinkya MoreNo ratings yet
- Introduction Basic Welding TechnologyDocument17 pagesIntroduction Basic Welding TechnologyBenny Syahputra100% (1)
- Introduction To Arc WeldingDocument36 pagesIntroduction To Arc WeldingKetan VaghosiNo ratings yet
- WELDING Is A Fabrication or Sculptural Process That Joins Materials, Usually Metals or Thermoplastics, by CausingDocument8 pagesWELDING Is A Fabrication or Sculptural Process That Joins Materials, Usually Metals or Thermoplastics, by CausingNaeemrindNo ratings yet
- Soldering, Brazing and Welding BasicsDocument7 pagesSoldering, Brazing and Welding BasicsJerin CyriacNo ratings yet
- Welding WorkshopDocument29 pagesWelding WorkshopAnonymous h5OeGoX3MTNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document65 pagesLecture 4Ishtiaq AhmedNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Metal JoiningDocument44 pagesDifferent Types of Metal JoiningKentDemeterioNo ratings yet
- WeldingDocument28 pagesWeldingShahdan DahlanNo ratings yet
- WeldingDocument17 pagesWeldingMirxa UxmanNo ratings yet
- Arc Welding FundamentalsDocument2 pagesArc Welding FundamentalsDananjaya Yogie HartantoNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating Procedures For FS EquipmentsDocument24 pagesStandard Operating Procedures For FS EquipmentsAnonymous LFgO4WbIDNo ratings yet
- Cars Stutter As Water Leaks Into Fuel StationDocument2 pagesCars Stutter As Water Leaks Into Fuel StationAnonymous LFgO4WbIDNo ratings yet
- Search Again Home Page LogoutDocument1 pageSearch Again Home Page LogoutAnonymous LFgO4WbIDNo ratings yet
- MMH Manual Ver 1Document102 pagesMMH Manual Ver 1Anonymous LFgO4WbIDNo ratings yet
- Sri Sri Thakur by Dr. Rebati Mohan Biswas About LifeDocument51 pagesSri Sri Thakur by Dr. Rebati Mohan Biswas About LifeAnonymous LFgO4WbID80% (5)
- What Is A Job Safety AnalysisDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Job Safety AnalysisAnonymous LFgO4WbIDNo ratings yet
- Search Again Home Page LogoutDocument1 pageSearch Again Home Page LogoutAnonymous LFgO4WbIDNo ratings yet
- Diesel Fuel Contamination Causes Engine FailuresDocument8 pagesDiesel Fuel Contamination Causes Engine FailuresAnonymous LFgO4WbIDNo ratings yet
- Sri Sri Thakur by Dr. Rebati Mohan Biswas About LifeDocument51 pagesSri Sri Thakur by Dr. Rebati Mohan Biswas About LifeAnonymous LFgO4WbID80% (5)
- Find a match for Deepthy KrovvidiDocument1 pageFind a match for Deepthy KrovvidiAnonymous LFgO4WbIDNo ratings yet
- Search Again Home Page LogoutDocument1 pageSearch Again Home Page LogoutAnonymous LFgO4WbIDNo ratings yet
- 17512Document1 page17512Anonymous LFgO4WbIDNo ratings yet
- Safety DocumentsDocument11 pagesSafety DocumentsAnonymous LFgO4WbIDNo ratings yet
- Sling SafetyDocument24 pagesSling SafetyAnonymous LFgO4WbIDNo ratings yet
- Material HandlingDocument8 pagesMaterial HandlingAnonymous LFgO4WbIDNo ratings yet
- Mobile Crane Safety FactorsDocument3 pagesMobile Crane Safety FactorsAnonymous LFgO4WbIDNo ratings yet
- Material Handling SafetyDocument8 pagesMaterial Handling SafetyAnonymous LFgO4WbIDNo ratings yet
- Physical Hazards and Safety IssuesDocument2 pagesPhysical Hazards and Safety IssuesAnonymous LFgO4WbIDNo ratings yet
- Niyogis Are A Sect of Brahmins and Are Predominantly TeluguspeakersDocument38 pagesNiyogis Are A Sect of Brahmins and Are Predominantly TeluguspeakersAnonymous LFgO4WbIDNo ratings yet
- Do Marriage and Don'tDocument19 pagesDo Marriage and Don'tAnonymous LFgO4WbID100% (9)
- Mps Get MoneyDocument3 pagesMps Get MoneyAnonymous LFgO4WbIDNo ratings yet
- Astrological Combinations For Divorce & SeparationDocument16 pagesAstrological Combinations For Divorce & SeparationSaravana Kumar94% (17)
- Toll Free Numbers in IndiaDocument5 pagesToll Free Numbers in IndiaAnonymous LFgO4WbIDNo ratings yet
- Performance FailuresDocument25 pagesPerformance FailuresAnonymous LFgO4WbIDNo ratings yet
- HOT and Cold WorkingDocument22 pagesHOT and Cold WorkingRony Prayitno SimeonNo ratings yet
- Weld QualificationDocument16 pagesWeld QualificationAnonymous LFgO4WbIDNo ratings yet
- HyderabadDocument5 pagesHyderabadAnonymous LFgO4WbIDNo ratings yet
- Emission Norms For Passenger CarsDocument4 pagesEmission Norms For Passenger CarsAnonymous LFgO4WbIDNo ratings yet
- Prashna Jyotish Part 1Document279 pagesPrashna Jyotish Part 1Rohit Bose67% (3)
- BasicDocument36 pagesBasicAnonymous LFgO4WbIDNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper For ChemistryDocument23 pagesSample Paper For ChemistryAmit joshiNo ratings yet
- Hygroscopic and Nonhygroscopic MaterialDocument9 pagesHygroscopic and Nonhygroscopic Materialiresa_nuratNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Power: Pros, Cons and FutureDocument4 pagesNuclear Power: Pros, Cons and FutureSamarthNo ratings yet
- Paj-7e 201906Document2 pagesPaj-7e 201906Anum AkramNo ratings yet
- Rongalit ST LiqDocument11 pagesRongalit ST LiqMayank DhawanNo ratings yet
- Anderol General BrochureDocument12 pagesAnderol General BrochureepesanoNo ratings yet
- Science - Form 4 - Chapter 5Document12 pagesScience - Form 4 - Chapter 5Marcia PattersonNo ratings yet
- Modern Chemical Process SimulationDocument21 pagesModern Chemical Process SimulationWahab MaqboolNo ratings yet
- Boron FamilyDocument20 pagesBoron FamilyP. PARIS KATHERINE REBECCAH BCMBC2019No ratings yet
- LugalvanG35TechnicalInformation PDFDocument4 pagesLugalvanG35TechnicalInformation PDFJakin RookNo ratings yet
- Course Outline For 125:355, Physiological Systems For Biomedical EngineersDocument2 pagesCourse Outline For 125:355, Physiological Systems For Biomedical EngineersbillNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology IB ReviewerDocument28 pagesMolecular Biology IB ReviewerCeline Garin ColadaNo ratings yet
- PDS-POLYKEN-1027-V1-AUG17 - AARPS-0972 PrymerDocument2 pagesPDS-POLYKEN-1027-V1-AUG17 - AARPS-0972 PrymerJoel SaucedoNo ratings yet
- Msds - Marpozol W-505 (GHS) Eng 130409Document5 pagesMsds - Marpozol W-505 (GHS) Eng 130409Syafarul Mohammad100% (1)
- Paper 4 Jun 2001 PhysicsDocument2 pagesPaper 4 Jun 2001 Physicssolarixe100% (1)
- Astm A999a999mDocument12 pagesAstm A999a999mHammadNo ratings yet
- Metallurgical Defects of Cast Steel: SeminarDocument26 pagesMetallurgical Defects of Cast Steel: SeminarFacebookNo ratings yet
- Powder Metallurgy Process and ApplicationsDocument32 pagesPowder Metallurgy Process and ApplicationsChandan KumarNo ratings yet
- 2022-05-28 06 - 10 - 09.357.ScanFileDocument15 pages2022-05-28 06 - 10 - 09.357.ScanFileVamsi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table of ElementsDocument39 pagesThe Periodic Table of ElementsSamKris Guerrero Malasaga100% (1)
- Characterization of Raw Wastewater From TanneriesDocument9 pagesCharacterization of Raw Wastewater From TanneriesMaliha CheemaNo ratings yet
- UTP ABRADISC 6000 Offers Cost-Efficient Wear ProtectionDocument4 pagesUTP ABRADISC 6000 Offers Cost-Efficient Wear ProtectionpakhansNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Rate of EvaporationDocument22 pagesFactors Affecting Rate of EvaporationShimnu MoneNo ratings yet
- 12 Amadi TEOP Master-Ed2013-14 PDFDocument25 pages12 Amadi TEOP Master-Ed2013-14 PDFluis_seczonNo ratings yet
- Real Heat Engines and RefrigeratorsDocument11 pagesReal Heat Engines and RefrigeratorsMario MikulandraNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document2 pagesQuiz 1Carolyn Campita100% (1)
- B 193 - 02Document5 pagesB 193 - 02alanetn100% (1)
- Cell Biology and Membrane BiochemistryDocument106 pagesCell Biology and Membrane BiochemistryVijay Bhasker TekulapallyNo ratings yet
- Materials Used in Automotive Manufacture and Material Selection Using Ashby ChartsDocument15 pagesMaterials Used in Automotive Manufacture and Material Selection Using Ashby ChartsHanumantNo ratings yet
- UOP PX-Plus ™ XPDocument2 pagesUOP PX-Plus ™ XPana_dcz7154No ratings yet
- The Rights of Nature: A Legal Revolution That Could Save the WorldFrom EverandThe Rights of Nature: A Legal Revolution That Could Save the WorldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Art of Commenting: How to Influence Environmental Decisionmaking With Effective Comments, The, 2d EditionFrom EverandArt of Commenting: How to Influence Environmental Decisionmaking With Effective Comments, The, 2d EditionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Principles of direct and superior responsibility in international humanitarian lawFrom EverandPrinciples of direct and superior responsibility in international humanitarian lawNo ratings yet
- 3rd Grade Science: Life Sciences in Eco Systems | Textbook EditionFrom Everand3rd Grade Science: Life Sciences in Eco Systems | Textbook EditionNo ratings yet
- The Cyanide Canary: A True Story of InjusticeFrom EverandThe Cyanide Canary: A True Story of InjusticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Waste: One Woman’s Fight Against America’s Dirty SecretFrom EverandWaste: One Woman’s Fight Against America’s Dirty SecretRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Reduce, Reuse and Recycle : The Secret to Environmental Sustainability : Environment Textbooks | Children's Environment BooksFrom EverandReduce, Reuse and Recycle : The Secret to Environmental Sustainability : Environment Textbooks | Children's Environment BooksNo ratings yet
- Ecosystem Facts That You Should Know - The Forests Edition - Nature Picture Books | Children's Nature BooksFrom EverandEcosystem Facts That You Should Know - The Forests Edition - Nature Picture Books | Children's Nature BooksNo ratings yet
- Down to the Wire: Confronting Climate CollapseFrom EverandDown to the Wire: Confronting Climate CollapseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Environmental Education in Practice: Concepts and ApplicationsFrom EverandEnvironmental Education in Practice: Concepts and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Desperate: An Epic Battle for Clean Water and Justice in AppalachiaFrom EverandDesperate: An Epic Battle for Clean Water and Justice in AppalachiaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Land Divided by Law: The Yakama Indian Nation as Environmental History, 1840-1933From EverandLand Divided by Law: The Yakama Indian Nation as Environmental History, 1840-1933No ratings yet
- Exposure: Poisoned Water, Corporate Greed, and One Lawyer's Twenty-Year Battle against DuPontFrom EverandExposure: Poisoned Water, Corporate Greed, and One Lawyer's Twenty-Year Battle against DuPontRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (9)
- New Paradigms in Environmental Biomonitoring Using PlantsFrom EverandNew Paradigms in Environmental Biomonitoring Using PlantsSupriya TiwariNo ratings yet
- The Intersection of Intellectual Property Law and the “Green” Movement: RIPL’s Green Issue 2010From EverandThe Intersection of Intellectual Property Law and the “Green” Movement: RIPL’s Green Issue 2010Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Stand Up That Mountain: The Battle to Save One Small Community in the Wilderness Along the Appalachian TrailFrom EverandStand Up That Mountain: The Battle to Save One Small Community in the Wilderness Along the Appalachian TrailRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (3)