Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IBwave Certification Course Syllabus
Uploaded by
SandroTrigoValdivia0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
241 views3 pagesIBwave certification Level 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIBwave certification Level 2
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
241 views3 pagesIBwave Certification Course Syllabus
Uploaded by
SandroTrigoValdiviaIBwave certification Level 2
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
COURSE PREREQUISITES:
(TO BE COMPLETED THROUGH THE E-LEARNING CENTRE)
3-part training videos
In-building review
Project deployment process
INTRODUCTION
The in-building wireless world
In-building wireless applications
Wireless technologies evolution
System architectures
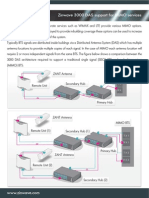
Passive DAS
Hybrid DAS
In-building design tools
In-building design components
Link budgets
Noise modeling
Propagation basics
PHASE 1: COLLECTING INFORMATION
Site visit preparation
Site survey
Signal measurement
PHASE 2: DESIGN, ENGINEERING & EQUIPMENT
SELECTION
Understanding project requirements
2D modeling
System architecture selection: - Vendor selection
- Cost optimization
- Design layout
Creating preliminary designs
Business case validation
Installation validation: - Real estate owner and
lease validation / negotiation
Creating nal designs
PHASE 3: SOLUTION IMPLEMENTATION
Equipment delivery and installation
System commissioning
System integration
System validation
System optimization
Acceptance and sign-off
iBWAVE DESIGN INTRODUCTION
In-building design challenges
What is iBwave Design?
iBwave Design features and benets
iBwave Design environment and navigation
Demonstration of utilities, tips and best practices
PROJECT SETTINGS
Creating and saving project properties
Page and print setup
Workspace customization and setting templates
Workshop to set up project properties (hands-on
exercices)
Demonstration of workshop solution
DESIGN PLANS
Acquire knowledge of the 3 types of plans in iBwave
Design
Procedures and tools to design on each plan
How to create various types of RF systems, add
components and scale and manipulate oor plans
How to design in-building networks using the 3 types of
plans, purpose and features
Understand design consistency and information display
Design Plan and mini quiz
Layout Plan and mini quiz
Picture Plan and mini quiz
Workshop for creating a project using the 3 types of plans
REPORTS
Purposes and functionalities of reports in iBwave Design
How to create, customize and change parameters in
reports
How to export reports
Reports workshop
PROBLEM BASED WORKSHOP
Common mistakes and pitfalls in designing
Workshop on project enhancement
DATABASE EDITOR
Network component database management
Database editor workspace features
How to create, edit, delete and share components
Troubleshooting component errors
Workshop to create components
PROJECT VALIDATION
Dene areas in a project that require validation to ensure
accuracy and consistency
Describe common methods to verify projects
How to use iBwave Design to troubleshoot errors in a
design
Workshop on project validation
DESIGNING A PROJECT FROM SCRATCH
Review of steps to design a project from start to nish
Demonstrations using sample les
Exercises for students to practice and refresh prior to exam
INTRODUCTION TO iBWAVE DESIGN MODULES
Overview of the key features available with iBwave Design
Modules (covered in more depth at the Expert Level):
- Propagation Module
- Optimization Module
- Collection Module
MULTIPLE CHOICE EXAM
(1 hour)
PRACTICAL EXAM
(2 hours)
PRODUCT PORTFOLIO OVERVIEW / CONCLUSION
(1 hour)
iBWAVE CERTIFICATION
COURSE SYLLABUS
LEVEL 1: iBWAVE DESIGN NETWORK PLANNING
iBWAVE
DESIGN
C E RT I F I E D
L E V E L 1
V
V
V
* Note: Course syllabus is subject to change
COURSE PREREQUISITES:
(TO BE COMPLETED THROUGH THE E-LEARNING CENTRE)
Radio wave propagation basics
Basic propagation models
Antenna characteristics
INTRODUCTION
PREREQUISITE: RADIO WAVE PROPAGATION
BASICS
Electromagnetic theory principles
The uniform plane wave
Effects of materials
Propagation mechanisms
Reection and refraction
Waveguiding
Scattering
PREREQUISITE: BASIC PROPAGATION MODELS
Path loss
Free space loss
PREREQUISITE: ANTENNA CHARACTERISTICS
Antenna basics
Antenna parameters
Radiation patterns
Antenna types used for in-building
In-building antenna cases
Radiating cables
IN-BUILDING PROPAGATION MODELS
In-building propagation models
Empirical and physical models
Comparing models: measures of accuracy
Keenan & Motley empirical model
Cost 231 multi-wall empirical model
In-building dominant path model
Challenging environments
BUILDING MODELING
Acquire knowledge on how to model a building
Importing the walls from image les and AutoCAD,
selecting the right building material, scaling and exporting
it into a 3D model
Hands-on workshop to practice building modeling using
sample les from complex structures
PREDICTION PANEL & CONFIGURATION
Conducting a propagation study using iBwave Design
Features of the Propagation Module (panel and output
map conguration)
Compare differences of propagation results according to
the selected propagation models and the available
parameter settings
Color schemes
Prediction models
Compliancy area
PROPAGATION WORKSHOP
Conducting propagation exercises with different
compliancy areas and models
Compare accuracy of the model against measurement
IN-BUILDING PROPAGATION MEASUREMENT
GUIDELINES
Propagation measurement basics
Measurement equipment
Walk routes guidelines
Calibration and validation
COLLECTION MODULE
Importing collected survey data into iBwave Design
Manual data collection
Understanding le output of various data collection tools
Workshop to practice importing survey data and using the
data Collection Module
TUNING AND VALIDATION
Measurements for model tuning
Identication of disputable survey data
Walls, oors, and model tuning in iBwave Design
Propagation model validation example
Calibration model in iBwave Design
Workshop on model tuning and calibration
IMPORTING OUDOOR PREDICTION
How to dene building properties
How to import outdoor prediction into iBwave Design
How to display the imported outdoor maps
OPTIMIZATION MODULE
Setting network optimization parameters
Understanding the optimization output maps in iBwave
Design
Creating output maps (ex. SNIR & Ec/Nt Maps)
Optimal antenna placement
DESIGNING A PROJECT FROM SCRATCH
Review of steps to design a project from start to nish
using the iBwave Design Modules
Demonstrations using sample les
Exercises for students to practice and refresh prior to exam
ADVANCED PROJECT VALIDATION - COMMON
ERRORS
Dene areas in a project that require validation to ensure
accuracy and consistency
Highlight common pitfalls when working on complex
designs
Describe common methods to verify projects using iBwave
Design Modules
How to use iBwave Design to troubleshoot errors in a
design
Workshop on project validation
MULTIPLE CHOICE EXAM
(1 hour)
PRACTICAL EXAM
(2 hours)
PRODUCT PORTFOLIO OVERVIEW / CONCLUSION
(1 hour)
iBWAVE CERTIFICATION
COURSE SYLLABUS
LEVEL 2: PROPAGATION, DATA COLLECTION AND OPTIMIZATION
V
V
V
* Note: Course syllabus is subject to change
iBWAVE
DESIGN
C E RT I F I E D
L E V E L 2
MIMO
MIMO THEORY
Introduction
MIMO Operation Modes: - Diversity - Multiplexing
Open Loop vs. Closed Loop
MIMO Gains Compared to SISO Systems: - Diversity Gain
- Multiplexing Gain
MIMO Schemes: - WCDMA - HSDPA - LTE - WiMAX
MIMO IN iBWAVE DESIGN
MIMO Gain Conguration
Creating Output Maps with MIMO Parameters
Running MIMO Predictions
Analyzing MIMO Prediction Results: MIMO Gain
MIMO Gain Compared to SISO
MIMO Workshop
CAPACITY
CAPACITY PLANNING THEORY
Capacity Background
Subscriber Types and Mix
Capacity Limits
Example of Capacity Calculations: - GSM - UMTS - HSPA - LTE
CAPACITY PLANNING IN iBWAVE DESIGN
Capacity Analysis Algorithm
Subscriber Types and Different Technologies
Running a Capacity Analysis
Understanding Capacity Analysis Results
Capacity Analysis Workshop
STADIUM DESIGN
STADIUM DESIGN REQUIREMENTS
What makes a stadium environment special?:
- The differing needs of three communities visitors, stadium
operations and event personnel
- Radio challenges mix of pitch, seating and back of house, all
with different propagation environments
- Capacity intensity of demand compared with typical venues,
likelihood of high existing coverage, strong variation between
events compared to in-between, leading to challenges in
business case
- Mix of systems not only cellular, but broadcasting, Wi-Fi,
PMR, etc.
- Business criticality if the radio system doesnt work a new
stadium cannot open and existing stadiums cannot operate
- KPI requirements for various wireless technologies:
GSM CDMA 1x/EVDO
UMTS/HSPA(+) LTE
Specic requirements:
Coverage levels
Frequency bands and technologies
Capacity for voice and data
Handover to surrounding network
Gathering project data:
- Environment classication, characteristics, building materials,
and challenges:
- Types of stadium: football, baseball and rugby stadiums; sport
arenas (basketball, ice hockey, etc.); car racing venues; use of
pitch/not etc.
- Trafc and capacity needs
- Existing network topology, trafc data and existing
measurements
- Creation of a three-dimensional building model in IBwave
STADIUM DESIGN ISSUES
Isolation from existing macrocell sites, including existing coverage
measurement issues and key points
Capacity considerations to support peak loading issues, load
sharing, dynamic channel assignment, etc.
Choice of radio system architecture:
- Low power DAS
- Highly directive overhead antennas
- Micro/pico/femtocells
- Base station hotel
- Business model considerations for stadium design
- Differing needs of each area:
Seating Pitch
VIP / Corporate boxes Broadcasters and press
Back of house public
Back of house operational
Ingress/egress and surrounding area
STADIUM DESIGN CAPACITY PLANNING
Special strategies to optimize network resources: sectorization,
zoning, antenna placement, optimization, etc.
Sectorization strategy
Motivations and benets
Ring
Wedge
Hybrid
Managing sector overlap
Optimizing performance
SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS FOR STADIUM DESIGN
Multi-operator design considerations for stadiums
Specic RF measurement requirements and issues for stadiums
Handover planning and optimization
Installation and other implementation constraints and
considerations
WI-FI DATA OFFLOAD
BACKGROUND AND MOTIVATIONS
Data growth: historical and projections for next 5-10 years
Nature of data: indoors vs. outdoor, work vs. home vs.
on-the-move
Devices: relative volumes between feature phones, smartphones,
tablets
Challenge: revenue growth vs. data growth. Cost per GB for
operator (very interesting).
Projected growth of 3G-enabled devices by category and Wi-Fi
enabled devices
Concept of data ofoad: how Wi-Fi and femtocells t together
(strong focus on Wi-Fi)
WI-FI TECHNOLOGY ISSUES
Wi-Fi basics
- History - Bodies: IEEE and Wi-Fi Alliance
- Decoding the standards: IEEE 802.11 a,b,g,n,
- How does the Wi-Fi air interface work?:
Modulation and coding CSMA
Radio issues
- Bands supported (with regional variations)
- 2.4 GHz and 5GHz spectrum (future 60 GHz spectrum,
licensed band operation)
- Device availability
Less than 2% of personal mobile devices support 5 GHz
- Wi-Fi channel numbering and bandwidth occupancy
- SINR performance:
Performance curves
Interference relative to collisions (impact of carrier
sensing)
Adjacent channel and out of band performance (NB
cordless phones in or adjacent to 2,.4 GHZ)
- Interference challenges
Channel planning, non Wi-Fi devices, automated
channel planning
- Link budgets with focus on coverage:
Expected range Role of antennas vs. licensing
- Capacity planning (also for APs) (for all the different layers, 2G,
3G, 4G and Wi-Fi) with differences between a, b, g and n
Users, contention, Tput, number of access points, too
many access points
Beacon packets and impact on interference or CS
backoff or collisions
Network issues
- Network architectures and implications (different vendors,
power over Ethernet, optical bers...)
- Routing (back to switch)
- Access controllers
Managing Wi-Fi environment
- Proliferation of devices (both APs and phones, incl Mi,
iPhones personal hotspot, etc.)
- Ongoing monitoring and intrusion detection (example
products)
What does it mean (different vendors) for # of AP, switches...
- Radio dimensioning
- Network dimensioning
WI-FI BASED OFFLOAD
Status and future of data ofoading
Economics: how does ofoad reduce cost per GB?
Potential and perils:
- Wi-Fi ubiquity vs. ofoading the customer
- Battery life
- Customer experience
- Own networks vs. over-the-top
Distinction between carrier Wi-Fi and consumer Wi-Fi
Implementation challenges:
- (Seamless) Authentication (less focus)
- Mobility
- Hotspot 2.0
- Authentication schemes
EAP-SIM
- 802.11 initiatives
Market status
- Operators deployed
- Industry initiatives
PRACTICAL EXAM
(2 hours)
iBWAVE CERTIFICATION
COURSE SYLLABUS
LEVEL 3: MIMO, WI-FI, STADIUMS AND CAPACITY PLANNING
* Note: Course syllabus is subject to change
iBWAVE
DESIGN
C E RT I F I E D
L E V E L 3
You might also like
- How To Attain Success Through The Strength of The Vibration of NumbersDocument95 pagesHow To Attain Success Through The Strength of The Vibration of NumberszahkulNo ratings yet
- DAB SystemDocument44 pagesDAB SystemRio WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- Procurement Audit PlanDocument12 pagesProcurement Audit PlanMustafa Bilal100% (1)
- Propagation BasicsDocument76 pagesPropagation Basicsapi-3741610100% (3)
- Design and Test Technologies of A RepeaterDocument24 pagesDesign and Test Technologies of A Repeaternarges5058100% (1)
- CW Propagation Survey and Propagation Model TuningDocument4 pagesCW Propagation Survey and Propagation Model TuningSreeNo ratings yet
- Ion B SeriesDocument4 pagesIon B SerieszqandahNo ratings yet
- EMI-EMC - SHORT Q and ADocument5 pagesEMI-EMC - SHORT Q and AVENKAT PATILNo ratings yet
- Microwave Installation and CommisioningDocument54 pagesMicrowave Installation and CommisioningKrishna KnsNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam StatconDocument4 pagesMidterm Exam Statconlhemnaval100% (4)
- SPIE Oil & Gas Services: Pressure VesselsDocument56 pagesSPIE Oil & Gas Services: Pressure VesselsSadashiw PatilNo ratings yet
- DAS (Distributed Antenna System) Training: November 2018Document16 pagesDAS (Distributed Antenna System) Training: November 2018ekamal80No ratings yet
- BTS3911E Product DescriptionDocument31 pagesBTS3911E Product DescriptionSandroTrigoValdivia100% (1)
- Itu R Rec P.530 15Document53 pagesItu R Rec P.530 15Luc HenrykNo ratings yet
- GSM Network ComponentsDocument23 pagesGSM Network ComponentsShakeel AminNo ratings yet
- Microwave Filters for Communication Systems: Fundamentals, Design, and ApplicationsFrom EverandMicrowave Filters for Communication Systems: Fundamentals, Design, and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Passive DAS Vs Active DAS Vs Hybrid DAS ComparisonDocument2 pagesPassive DAS Vs Active DAS Vs Hybrid DAS ComparisonAbhay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Point To Point MicrowaveDocument81 pagesPoint To Point MicrowaveRicha BudhirajaNo ratings yet
- Training On Microwave Communcation: by Nilesh PatelDocument39 pagesTraining On Microwave Communcation: by Nilesh PatelKo AungNo ratings yet
- Network Field Tests: Walk & Drive Test GuideDocument23 pagesNetwork Field Tests: Walk & Drive Test Guide2000omotoNo ratings yet
- LTE Radio Link Budgeting and RF PlanningDocument7 pagesLTE Radio Link Budgeting and RF PlanningchuksrayNo ratings yet
- TRM Principles NSNDocument60 pagesTRM Principles NSNMustafa KamalNo ratings yet
- Network TopologiesDocument33 pagesNetwork TopologieskoneNo ratings yet
- Transmission CalculationDocument8 pagesTransmission Calculationapi-26989621No ratings yet
- Module Contents: Antenna SystemsDocument32 pagesModule Contents: Antenna SystemsFurqan Hamid100% (1)
- BSL-3 Training-1Document22 pagesBSL-3 Training-1Dayanandhi ElangovanNo ratings yet
- Massive MIMO: Fundamentals, Opportunities and Challenges: MM YSDocument45 pagesMassive MIMO: Fundamentals, Opportunities and Challenges: MM YSsetup.143No ratings yet
- SDR Link Budget PDFDocument49 pagesSDR Link Budget PDFSalah SalahNo ratings yet
- Understanding UMTS Radio Network Modelling, Planning and Automated Optimisation: Theory and PracticeFrom EverandUnderstanding UMTS Radio Network Modelling, Planning and Automated Optimisation: Theory and PracticeMaciej NawrockiNo ratings yet
- LTE Advanced Overview: Bong Youl (Brian) Cho, 조 봉 열Document22 pagesLTE Advanced Overview: Bong Youl (Brian) Cho, 조 봉 열yusufapw100% (1)
- Introduction To MicrowaveDocument13 pagesIntroduction To MicrowaveEmmanuel AlapNo ratings yet
- G-LII 202 Planning For Radio Coverage Capacity-20080312-A-2.1Document26 pagesG-LII 202 Planning For Radio Coverage Capacity-20080312-A-2.1naveedalishaNo ratings yet
- Link Budget TutorialDocument11 pagesLink Budget TutorialshaddiebitokNo ratings yet
- On Applied EthicsDocument34 pagesOn Applied Ethicsamanpatel78667% (3)
- WDM Technologies: Passive Optical ComponentsFrom EverandWDM Technologies: Passive Optical ComponentsAchyut K. DuttaNo ratings yet
- MP501 Mentum Planet 5.7 CoreDocument116 pagesMP501 Mentum Planet 5.7 CoreAnonymous iAYcAh100% (1)
- Ibwave Design Enterprise Product SheetDocument2 pagesIbwave Design Enterprise Product SheetindiomalignoNo ratings yet
- Ibwave Design SpecsheetDocument2 pagesIbwave Design SpecsheetmalamontagneNo ratings yet
- Link BudgetDocument15 pagesLink BudgetJayant VaishyaNo ratings yet
- Wireless Planning Wireless Planning FundamentalsDocument54 pagesWireless Planning Wireless Planning FundamentalstibebuNo ratings yet
- Microwave Radio Transmission Engineering Course OutlineDocument4 pagesMicrowave Radio Transmission Engineering Course OutlineneonetwirelessNo ratings yet
- The Value of Digital Transport in Distributed Antenna SystemsDocument4 pagesThe Value of Digital Transport in Distributed Antenna SystemsHiew KfNo ratings yet
- TCIL 17 Microwave Link DesignDocument68 pagesTCIL 17 Microwave Link Designapi-3723064100% (6)
- Contact Me: In-Building SolutionDocument7 pagesContact Me: In-Building SolutionhamidrezaNo ratings yet
- DAS Support For MIMO AntennasDocument2 pagesDAS Support For MIMO AntennasIhab A OsmanNo ratings yet
- FRIISDocument9 pagesFRIISBindia HandaNo ratings yet
- 06 GSM Link Balance and Coverage Distance Estimation ToolsDocument8 pages06 GSM Link Balance and Coverage Distance Estimation ToolsIrwan WahyudiNo ratings yet
- Microwave Planning and DesignDocument236 pagesMicrowave Planning and DesignAbu MuscabNo ratings yet
- Radio Propagation ModelingDocument24 pagesRadio Propagation Modelingcoolboy_usamaNo ratings yet
- RF & Transmission Survey: MD Shams TouhidDocument22 pagesRF & Transmission Survey: MD Shams TouhidshamstouhidNo ratings yet
- Channel Selective Repeaters Manual, Rev B-1 (GSM+UMTS)Document370 pagesChannel Selective Repeaters Manual, Rev B-1 (GSM+UMTS)Дима ВерхотуровNo ratings yet
- IBS Intergration Service V100R002 Technical Guide LTE Link Budget 01-ZHDocument48 pagesIBS Intergration Service V100R002 Technical Guide LTE Link Budget 01-ZHOgg SilverlemoneNo ratings yet
- Rudiments of Transmission NetworkDocument30 pagesRudiments of Transmission NetworkAtanda Babatunde MutiuNo ratings yet
- BBU-Baseband Unit-In TelecomDocument4 pagesBBU-Baseband Unit-In Telecomfelly mutuakashalaNo ratings yet
- Telecom Installation - BTS Installation - BTS Commissioning PreprationDocument2 pagesTelecom Installation - BTS Installation - BTS Commissioning Preprationfaiz_2010No ratings yet
- 3.3G Cellular, WMAN (WIMAX), WLAN (WIFI), WPAN (Bluetooth and UWB), Mobile Ad Hoc Networks (MANET), and Wireless Sensor NetworksDocument36 pages3.3G Cellular, WMAN (WIMAX), WLAN (WIFI), WPAN (Bluetooth and UWB), Mobile Ad Hoc Networks (MANET), and Wireless Sensor Networksekhy29No ratings yet
- MSC Thesis ProposalDocument11 pagesMSC Thesis ProposalGirma Abebe BNo ratings yet
- SNMP Alarms For Omu II Mbf-20 Mbf-40 00007si Rev 1.1Document18 pagesSNMP Alarms For Omu II Mbf-20 Mbf-40 00007si Rev 1.1carlosf_6No ratings yet
- Electrical and Mechanical Downtilt Effect On Pattern PerformanceDocument15 pagesElectrical and Mechanical Downtilt Effect On Pattern PerformanceNauman AliNo ratings yet
- 3G Radio Network Planning & Optimization V2Document11 pages3G Radio Network Planning & Optimization V2Pongpang ObNo ratings yet
- Outdoor Directional Tri-Band Antenna: ODP-065R12M14JJ-G ODP-065R12M14JJ-GQDocument3 pagesOutdoor Directional Tri-Band Antenna: ODP-065R12M14JJ-G ODP-065R12M14JJ-GQSandroTrigoValdiviaNo ratings yet
- PS-Rx-ON500C (H) DS 3-0-2Document1 pagePS-Rx-ON500C (H) DS 3-0-2SandroTrigoValdiviaNo ratings yet
- Outdoor Directional Dual-Band Antenna: ODP-065R12M14J-GDocument2 pagesOutdoor Directional Dual-Band Antenna: ODP-065R12M14J-GSandroTrigoValdiviaNo ratings yet
- Outdoor Directional Dual-Band Antenna: ODP-065R09M12J-G (2J)Document2 pagesOutdoor Directional Dual-Band Antenna: ODP-065R09M12J-G (2J)SandroTrigoValdivia100% (1)
- Indoor Omni-Directional Ceiling Mounted Antenna: IXD-360V03NNDocument1 pageIndoor Omni-Directional Ceiling Mounted Antenna: IXD-360V03NNSandroTrigoValdiviaNo ratings yet
- MS-6.3DB90 Datashee V10282020Document2 pagesMS-6.3DB90 Datashee V10282020SandroTrigoValdiviaNo ratings yet
- Fact Pack Financial Services KenyaDocument12 pagesFact Pack Financial Services KenyaCatherineNo ratings yet
- Surge Arrester: Technical DataDocument5 pagesSurge Arrester: Technical Datamaruf048No ratings yet
- Shares and Share CapitalDocument50 pagesShares and Share CapitalSteve Nteful100% (1)
- Solutions To Questions - Chapter 6 Mortgages: Additional Concepts, Analysis, and Applications Question 6-1Document16 pagesSolutions To Questions - Chapter 6 Mortgages: Additional Concepts, Analysis, and Applications Question 6-1--bolabolaNo ratings yet
- Grace Strux Beton PDFDocument33 pagesGrace Strux Beton PDFmpilgirNo ratings yet
- Project 1. RockCrawlingDocument2 pagesProject 1. RockCrawlingHằng MinhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Walter Nicholson Microcenomic TheoryDocument15 pagesChapter 11 Walter Nicholson Microcenomic TheoryUmair QaziNo ratings yet
- IIBA Academic Membership Info-Sheet 2013Document1 pageIIBA Academic Membership Info-Sheet 2013civanusNo ratings yet
- T&B Detailed Plan: Ceiling LineDocument1 pageT&B Detailed Plan: Ceiling LineKuthbert NoceteNo ratings yet
- Sigma Valve 2-WayDocument2 pagesSigma Valve 2-WayRahimNo ratings yet
- Perpetual InjunctionsDocument28 pagesPerpetual InjunctionsShubh MahalwarNo ratings yet
- TENDER DOSSIER - Odweyne Water PanDocument15 pagesTENDER DOSSIER - Odweyne Water PanMukhtar Case2022No ratings yet
- Tech Mahindra Sample Verbal Ability Placement Paper Level1Document11 pagesTech Mahindra Sample Verbal Ability Placement Paper Level1Madhav MaddyNo ratings yet
- MDC PT ChartDocument2 pagesMDC PT ChartKailas NimbalkarNo ratings yet
- SEBI Circular Dated 22.08.2011 (Cirmirsd162011)Document3 pagesSEBI Circular Dated 22.08.2011 (Cirmirsd162011)anantNo ratings yet
- BS As On 23-09-2023Document28 pagesBS As On 23-09-2023Farooq MaqboolNo ratings yet
- CE5215-Theory and Applications of Cement CompositesDocument10 pagesCE5215-Theory and Applications of Cement CompositesSivaramakrishnaNalluriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.4Document11 pagesChapter 1.4Gie AndalNo ratings yet
- NCR Minimum WageDocument2 pagesNCR Minimum WageJohnBataraNo ratings yet
- WhatsNew 2019 enDocument48 pagesWhatsNew 2019 enAdrian Martin BarrionuevoNo ratings yet
- 11 TR DSU - CarrierDocument1 page11 TR DSU - Carriercalvin.bloodaxe4478100% (1)
- A Study On Effective Training Programmes in Auto Mobile IndustryDocument7 pagesA Study On Effective Training Programmes in Auto Mobile IndustrySAURABH SINGHNo ratings yet
- Opel GT Wiring DiagramDocument30 pagesOpel GT Wiring DiagramMassimiliano MarchiNo ratings yet