Professional Documents
Culture Documents
IAETSD-Identifying and Preventing Resource Depletion Attack in
Uploaded by
iaetsdiaetsdOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
IAETSD-Identifying and Preventing Resource Depletion Attack in
Uploaded by
iaetsdiaetsdCopyright:
Available Formats
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON CURRENT INNOVATIONS IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
ISBN: 378 - 26 - 138420 - 5
Identifying And Preventing Resource Depletion Attack In
Mobile Sensor Network
V.Sucharitha
Associate Professor
jesuchi78@yahoo.com
Audisankara college of engineering and technology
M.Swapna M.Tech
swapna.12b2@gmail.com
ABSTRACT:
Ad-hoc low-power wireless networks are inspiring research direction in sense
and enveloping computing. In previous security work in this area has focused primarily
on inconsistency of communication at the routing or medium access control levels. This
paper explores resource depletion attacks at the navigation protocol layer, which
permanent disable networks by quickly draining nodes battery power. The Vampire
attacks are not specific protocol, but rather rely on the properties of many popular classes
of routing protocols. We find that all examined protocols are vulnerable to Vampire
attacks, which are demolish and difficult to detect, and easy to carry out using as few as
one malicious insider send only protocol compliant messages.
near future, such as omnipresent ondemand computing power, continuous
connectivity, and instantly-deployable
communication for military and first
responders. Such networks already
monitor
environmental
conditions,
factory
performance,
and
troop
deployment, to name a few applications.
As WSNs become more and more
crucial to the everyday functioning of
people and organizations, availability
faults become less tolerable lack of
availability can make the difference
between business as usual and lost
productivity,
power
outages,
environmental disasters, and even lost
lives; thus high availability of these
1.INTRODUCTION:
the last couple of years wireless
communication has become of such
fundamental importance that a world
without is no longer imaginable for
many of using. Beyond the establish
technologies such as mobile phones and
WLAN, new approaches to wireless
communication are emerging; one of
them are so called ad hoc and sensor
networks. Ad hoc and sensor networks
are formed by autonomous nodes
communicating via radio without any
additional backbone infrastructure. Adhoc wireless sensor networks (WSNs)
promise exciting new applications in the
INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY FOR SKILL DEVELOPMENT
155
www.iaetsd.in
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON CURRENT INNOVATIONS IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
networks is a critical property, and
should hold even under malicious
conditions. Due to their ad-hoc
organization, wireless ad-hoc networks
are particularly vulnerable to denial of
service (DoS) attacks, and a great deal of
research has been done to enhance
survivability.
While these schemes can prevent
attacks on the short-term availability of a
network, they do not address attacks that
affect long-term available the most
permanent denial of service attack is to
entirely deplete nodes batteries. This is
an instance of a resource depletion
attack, with battery power as the
resource of interest. this paper we
consider how routing protocols, even
those designed to be secure, lack
protection from these attacks, which we
call Vampire attacks, since they drain
the life from networks nodes. These
attacks are distinct from previouslystudied DoS, reduction of quality (RoQ),
and routing infrastructure attacks as they
do not disrupt immediate availability,
but rather work over time to entirely
disable a network. While some of the
individual attacks are simple, and powerdraining and resource exhaustion attacks
have been discussed before, prior work
has been mostly confined to other levels
of the protocol stack, e.g. medium access
control (MAC) or application layers, and
to our knowledge there is little
discussion, and no thorough analysis or
mitigation, of routing-layer resource
exhaustion attacks.
Vampire attacks are not protocolspecific, in that they do not rely on
design properties or implementation
faults of particular routing protocols, but
rather exploit general properties of
protocol classes such as link-state,
distance-vector, source routing and
geographic and beacon routing. Neither
ISBN: 378 - 26 - 138420 - 5
do these attacks rely on flooding the
network with large amounts of data, but
rather try to transmit as little data as
possible to achieve the largest energy
drain, preventing a rate limiting solution.
Since Vampires use protocol-compliant
messages, these attacks are very difficult
to detect and prevent.
This paper makes three primary
contributions. First, we thoroughly
evaluate the vulnerabilities of existing
protocols to routing layer battery
depletion attacks. We observe that
security measures to prevent Vampire
attacks are orthogonal to those used to
protect routing infrastructure, and so
existing secure routing protocols such as
Ariadne, SAODV, and SEAD do not
protect against Vampire attacks. Existing
work on secure routing attempts to
ensure that adversaries cannot cause path
discovery to return an invalid network
path, but Vampires do not disrupt or
alter discovered paths, instead using
existing valid network paths and
protocol compliant messages. Protocols
that maximize power efficiency are also
inappropriate, since they rely on
cooperative node behavior and cannot
optimize out malicious action. Second,
we show simulation results quantifying
the
performance
of
several
representative protocols in the presence
of a single Vampire (insider adversary).
Third, we modify an existing sensor
network routing protocol to provably
bound the damage from Vampire attacks
during packet forwarding.
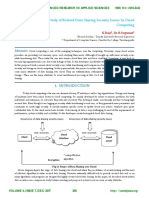
1.1.Wireless Adhoc Network:
An ad hoc wireless network is a
collection of wireless mobile nodes that
self-configure to form a network without
the aid of any established infrastructure,
as shown in without an inherent
infrastructure, the mobiles handle the
INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY FOR SKILL DEVELOPMENT
156
www.iaetsd.in
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON CURRENT INNOVATIONS IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
necessary control and networking tasks
by themselves, generally through the use
of distributed control algorithms.
Multihop
connections,
whereby
intermediate nodes send the packets
toward their final destination, are
supported to allow for efficient wireless
communication between parties that are
relatively far apart. Ad hoc wireless
networks are highly appealing for many
reasons. They can be rapidly deployed
and reconfigured. They can be tailored
to specific applications, as implied by
Oxfords definition. They are also highly
robust due to their distributed nature,
node redundancy, and the lack of single
points of failure.
ISBN: 378 - 26 - 138420 - 5
necessary to determine the time factor,
economy n company strength. Once
these things r satisfied, ten next steps are
to determine which operating system and
language can be used for developing the
tool.
Once
the
programmers
start
building the tool the programmers need
lot of external support. This support can
be obtained from senior programmers,
from book or from websites. Before
building
the
system
the
above
consideration r taken into account for
developing the proposed system.
A wireless sensor network (WSN)
consists
of
spatially
distributed
autonomous sensors to monitor physical
Fig:Adhoc Network Structure
or environmental conditions, such as
Existing work on secure routing
attempts to ensure that adversaries
cannot cause path discovery to return an
invalid network path, but Vampires do
not disrupt or alter discovered paths,
instead using existing valid network
paths and protocol compliant messages.
Protocols
that
maximize
power
efficiency are also inappropriate, since
they rely on cooperative node behavior
and cannot optimize out malicious
action.
temperature, sound, pressure, etc. and to
2.LITERATURE REVIEW:
industrial and consumer applications,
Literature survey is the most important
such as industrial process monitoring
step in software development process.
and control, machine health monitoring,
Before
and so on.
developing
the
tool
it
cooperatively pass their data through the
network to a main location. The more
modern networks are bi-directional, also
enabling control of sensor activity. The
development of wireless sensor networks
was motivated by military applications
such as battlefield surveillance; today
such networks are used in
is
INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY FOR SKILL DEVELOPMENT
157
many
www.iaetsd.in
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON CURRENT INNOVATIONS IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
The WSN is built of "nodes"
ISBN: 378 - 26 - 138420 - 5
3.IMPLIMENTATION:
from a few to several hundreds or even
thousands, where each node is connected
As
to one (or sometimes several) sensors.
cooperatively build a Chord overlay
Each such sensor network node has
network over the sensor network. Cloned
typically
node
several
parts:
radio
prerequisite,
may
not
all
participate
nodes
in
this
transceiver with an internal antenna or
procedure, but it does not give them any
connection to an external antenna, a
advantage of avoiding detection. The
microcontroller, an electronic circuit for
construction of the overlay network is
interfacing with the sensors and an
independent of node clone detection. As
energy source, usually a battery or an
a result, nodes possess the information
embedded form of energy harvesting. A
of their direct predecessor and successor
sensor node might vary in size from that
in the Chord ring. In addition, each node
of a shoebox down to the size of a grain
caches information of its g consecutive
of dust, although functioning "motes" of
successors in its successors table. Many
genuine microscopic dimensions have
Chord systems utilize this kind of cache
yet to be created. The cost of sensor
mechanism to reduce the communication
nodes is similarly variable, ranging from
cost and enhance systems robustness.
a few to hundreds of dollars, depending
More importantly in our protocol, the
on the complexity of the individual
facility
sensor nodes. Size and cost constraints
contributes to the economical selection
on sensor nodes result in corresponding
of inspectors. One detection round
constraints on resources such as energy,
consists of three stages.
memory,
and
Stage 1: Initialization
The
To activate all nodes starting a new
topology of the WSNs can vary from a
round of node clone detection, the
simple star network to an advanced
initiator uses a broadcast authentication
multi-hop wireless mesh network. The
scheme to release an action message
propagation technique between the hops
including a monotonously increasing
of the network can be routing or
nonce, a random round seed, and an
flooding.
action time. The nonce is intended to
computational
communications
speed
bandwidth.
of
INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY FOR SKILL DEVELOPMENT
158
the
successors
table
www.iaetsd.in
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON CURRENT INNOVATIONS IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
ISBN: 378 - 26 - 138420 - 5
prevent adversaries from launching a
period, during which nodes randomly
DoS attack by repeating broadcasting
pick up a transmission time for every
action messages. The action message is
claiming message.
dened by
Stage 3: Processing claiming messages
A claiming message will be forwarded to
its destination node via several Chord
intermediate nodes. Only those nodes in
Stage 2: Claiming neighbors information
the overlay network layer (i.e., the
Upon receiving an action message, a
source node, Chord intermediate nodes,
node veries if the message nonce is
and the destination node) need to process
greater than last nonce and if the
a message,
message signature is valid. If both pass,
whereas other nodes along the path
the node updates the nonce and stores
simply route the message to temporary
the seed. At the designated action time,
targets. Algorithm 1 for handling a
the node operates as an observer that
message is the kernel of our DHT-based
generates a claiming message for each
detection protocol. If the algorithm
neighbor (examinee) and transmits the
returns NIL, then the message has
message through the overlay network
with
respect
to
the
arrived at its destination. Otherwise, the
claiming
message will be subsequently forwarded
probability .The claiming message by
observer for examinee is
to the next node with the ID that is
constructed
returned by Algorithm 1.
by
Criteria
of
determining
inspectors:
During handling a message in Algorithm
1, the node acts as an inspector if one of
Where
, are locations of
,respectively.
Nodes
can
and
the following conditions is satised.
start
transmitting claiming messages at the
same time, but then huge trafc may
cause serious interference and degrade
the network capacity. To relieve this
problem, we may specify a sending
INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY FOR SKILL DEVELOPMENT
159
www.iaetsd.in
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON CURRENT INNOVATIONS IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
ISBN: 378 - 26 - 138420 - 5
performance. By Algorithm 1, roughly
4.ALGORITHMS:
of all claiming messages related to a
same examinees ID will pass through
one
of
the
predecessors
of
the
destination. Thus, those nodes are much
more likely to be able to detect a clone
than randomly selected inspectors. As a
result, this criterion to decide inspectors
can increase the average number of
witnesses at a little extra memory cost.
We will theoretically quantify those
performance measurements later. In
Algorithm 1, to examine a message for
node clone detection, an inspector will
invoke Algorithm 2, which compares the
message
with
previous
inspected
messages that are buffered in the cache
table. Naturally, all records in the cache
table should have different examinee
IDs, as implied in Algorithm 2. If
detecting a clone, which means that
there exist two messages
satisfying
and
and
, the
1) This node is the destination node of
witness
the claiming message.
evidence to notify the whole network.
2) The destination node is one of the g
All integrity nodes verify the evidence
node
successors of the node. In other words,
then
broadcasts
message
the destination node will be reached in
the
and
stop communicating with the cloned
the next Chord hop. While the rst
nodes. To prevent cloned nodes from
criterion is intuitive, the second one is
joining the network in the future, a
subtle and critical for the protocol
INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY FOR SKILL DEVELOPMENT
160
www.iaetsd.in
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON CURRENT INNOVATIONS IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
revocation list of compromised nodes
expense
IDs may be maintained by nodes
probability. The RDE protocol shares the
individually. It is worth noting that
major merit with broadcasting detection:
messages
are
Every node only needs to know and
and,
buffer a neighbor-list containing all
respectively. Therefore, the witness does
neighbors IDs and locations. For both
not need to sign the evidence message. If
detection
a malicious node tries to launch a DoS
constructs a claiming message with
attack by broadcasting a bogus evidence
signed version of its neighbor-list, and
message,
node
then tries to deliver the message to
receiving it can immediately detect the
others which will compare with its own
wicked
the
neighbor-list to detect clone. For a dense
before
network, broadcasting will drive all
and
authenticated
by
the
next
behavior
signatures
observers
integrity
by
of
verifying
and
with
ISBN: 378 - 26 - 138420 - 5
adequate
procedures,
detection
every
node
neighbors of cloned nodes to nd the
forwarding to other nodes.
attack, but in fact one witness that
The DHT-based detection protocol
successfully catches the clone and then
can be applied to general sensor
noties the entire network would sufce
networks, and its security level is
for the detection purpose. To achieve
remarkable, as cloned nodes will be
that in a communicatively efcient way,
caught by one deterministic witness plus
several
probabilistic
we bring several
witnesses.
Chord
overlap
network
protocol. First, a claiming message
incurs
needs to provide maximal h op limit, and
considerable communication cost, which
initially it is sent to a random neighbor.
may not be desired for some sensor
Then,
networks that are extremely sensitive to
(RDE),
and
presents
optimal
subsequent
helps a message go through the network
which
as fast as possible from a locally optimal
tremendously reduces communication
cost
message
line. The line transmission property
challenge, we propose the randomly
exploration
the
transmission will roughly maintain a
energy consumption. To fulll this
directed
and
effectively construct a multicast routing
However, the message transmission over
a
mechanisms
perspective. In addition, we introduce
storage
border
determination
INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY FOR SKILL DEVELOPMENT
161
mechanism to
www.iaetsd.in
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON CURRENT INNOVATIONS IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
ISBN: 378 - 26 - 138420 - 5
signicantly reduce communication cost.
We can do all of those because every
node is aware of its neighbors locations,
which is a basic assumption for all
where is time to live (a.k.a. message
witness-based detection protocols but
maximum hop). Since tt1 will be altered
rarely utilized by other protocols.
by
intermediate
transmission,
nodes
it
should
during
not
be
authenticated. The observer willdeliver
the claiming message r times. In each
time, the node transmits it to a random
neighbor as indicated. Note that can be a
real
number,
and
accordingly
an
observer transmits its claiming message
at least[r] ,up to ,[r] and on average r
times. When an intermediate node
receives a claiming message
4.1 Protocol Description:
it
launches , which is described by
pseudo code in Algorithm 3, to
One round of clone detection is still
process
the
message.
During
the
activated by the initiator. Subsequently,
processing, node
at the designated action time, each node
compares its own neighbor-list to the
creates its own neighbor-list including
neighbor-list in the message, checking if
the neighbors IDs and locations, which
there is a clone. Similarly, if detecting a
constitutes the sole storage consumption
clone,
of the protocol. Then, it, as an observer
the
claiming message containing its own ID,
and
its
claiming
message
neighb-list.
by
node
the
witness
node
will
broadcast an evidence messageto notify
for all its neighbors, starts to generate a
location,
, as an inspector,
whole
that
The
network
such
the
cloned
nodes are expelled from the sensor
is
network. To deal with routing, node
constructed by
INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY FOR SKILL DEVELOPMENT
162
www.iaetsd.in
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON CURRENT INNOVATIONS IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
ISBN: 378 - 26 - 138420 - 5
decreases the messages by 1 and
can be directly discarded. In our
discards the message if reaches zero;
proposal for border local determination,
another parameter
4.4target range :
This is used along with ideal direction to
determine a target zone. When no
neighbor is found in this zone, the
current node will conclude that the
message has reached a border, and thus
throw it away.
Essentially, Algorithm 4 contains the
following three mechanisms.
4.2Deterministicdirected
transmission:
When node receives a claiming message
from previous node, the ideal direction
can be calculated. In order to achieve the
best effect of line transmission, the next
destination node should be node , which
is closest to the ideal direction.
Fig:Loose source routing performance
4.3Networkborder
compared to optimal, in a network with
determination:
This
takes
diameter slightly above 10. The dashed
into
trend line represents expected path
the
length when nodes store logN local state,
communication cost. In many sensor
and the solid trend line shows actual
network applications, there exist outside
observed performance.
consideration
network
to
shape
reduce
borders of network due to physical
5.CONCLUSION:
constrains. When reaching some border
We defined Vampire attacks, a new class
in the network, the claiming message
of resource consumption attacks that use
INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY FOR SKILL DEVELOPMENT
163
www.iaetsd.in
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON CURRENT INNOVATIONS IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
ISBN: 378 - 26 - 138420 - 5
routing protocols to permanently disable
[5] J. Bellardo and S. Savage, 802.11
ad-hoc wireless sensor networks by
Denial-of-Service
depleting nodes battery power. These
Vulnerabilities and Practical Solutions,
attacks do not depend on particular
Proc. 12th Conf. USENIX Security,
protocols or implementations, but rather
2003.
expose vulnerabilities in a number of
[6] D. Bernstein and P. Schwabe, New
popular protocol classes. We showed a
AES Software Speed Records, Proc.
number
of proof-of-concept
Ninth Intl Conf. Cryptology in India:
against
representative
attacks
examples
of
Attacks:
Real
Progress in Cryptology (INDOCRYPT),
existing routing protocols using a small
2008.
number
[7] D.J. Bernstein, Syn Cookies,
of
weak
adversaries,
and
measured their attack success on a
http://cr.yp.to/syncookies.html, 1996.
randomly-generated topology of 30
[8] I.F. Blaked, G. Seroussi, and N.P.
nodes.
Smart, Elliptic Curves in cryptography,
vol. 265. Cambridge Univ. , 1999.
REFERENCES:
[9] J.W. Bos, D.A. Osvik, and D. Stefan,
Fast
[1] The Network Simulator - ns-2,
Various Platforms, Cryptology ePrint
http://www.isi.edu/nsnam/ns,2012.
Archive,
[2] I. Aad, J.-P. Hubaux, and E.W.
501,
and Privacy in Sensor Networks,
MobiCom, 2004.
Computer, vol. 36, no. 10, pp. 103-105,
[3] G. Acs, L. Buttyan, and I. Vajda,
Oct. 2003.
Provably Secure On-Demand Source
[11] J.-H. Chang and L. Tassiulas,
Routing in Mobile Ad Hoc Networks,
Maximum
IEEE Trans. Mobile Computing, vol. 5,
Lifetime
Routing
in
Wireless Sensor Networks, IEEE/ACM
no. 11, pp. 1533-1546, Nov. 2006.
Aura,
2009/
[10] H. Chan and A. Perrig, Security
in Ad Hoc Networks, Proc. ACM
T.
Report
http://eprint.iacr.org, 2009.
Knightly, Denial of Service Resilience
[4]
Implementations of AES on
Trans. Networking, vol. 12, no. 4, pp.
Dos-Resistant
609-619, Aug. 2004.
Authentication with Client Puzzles,
Proc. Intl Workshop Security Protocols,
2001.
INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY FOR SKILL DEVELOPMENT
164
www.iaetsd.in
INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON CURRENT INNOVATIONS IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
ISBN: 378 - 26 - 138420 - 5
[12] T.H. Clausen and P. Jacquet,
Optimized
Link
State
Routing
Protocol(OLSR), IETF RFC 3626, 2003.
[13] J. Deng, R. Han, and S. Mishra,
Defending against Path-Based DoS
Attacks in Wireless Sensor Networks,
Proc. ACM Workshop Security of Ad
Hoc and Sensor Networks, 2005.
[14] J. Deng, R. Han, and S. Mishra,
INSENS: Intrusion-Tolerant Routing
for
Wireless
Sensor
Networks,
Computer Comm., vol. 29, 1. 2, pp. 216230, 2006.
[15] S. Doshi, S. Bhandare, and T.X.
Brown, An On-Demand Minimum
Energy Routing Protocol for a Wireless
Ad Hoc Network, ACM SIGMOBILE
Mobile Computing and Comm. Rev.,
vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 50-66, 2002.
[16] J.R. Douceur, The Sybil Attack,
Proc.
Intl
Workshop
Peer-to-Peer
Systems, 2002.
[17] H. Eberle, A. Wander, N. Gura, C.S.
Sheueling,
and
V.
Gupta,
Architectural Extensions for Elliptic
Curve Cryptography over GF(2m) on 8bit Microprocessors, Proc. IEEE Intl
Conf Application- Specific Systems,
Architecture Processors (ASAP), 2005.
INTERNATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY FOR SKILL DEVELOPMENT
165
www.iaetsd.in
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Sediment Classification Using Side Scan SONARDocument5 pagesSediment Classification Using Side Scan SONARiaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Review On Performance Improvement of Induction Motor by DTC TechniqueDocument8 pagesA Review On Performance Improvement of Induction Motor by DTC TechniqueiaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Optimum Sizing and Composition of Agricultural Residue As Biomass Fuel For A Downdraft Gasifier For Efficient Production of Producergas On A Comercial ScaleDocument11 pagesOptimum Sizing and Composition of Agricultural Residue As Biomass Fuel For A Downdraft Gasifier For Efficient Production of Producergas On A Comercial ScaleiaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- IOT Based Waste Management System For Smart CityDocument7 pagesIOT Based Waste Management System For Smart Cityiaetsdiaetsd100% (2)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Essence of Soft Skills Proficiency To Foster Mercantile SectorDocument4 pagesEssence of Soft Skills Proficiency To Foster Mercantile SectoriaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Using Word Net For Document Clustering: A Detailed ReviewDocument5 pagesUsing Word Net For Document Clustering: A Detailed ReviewiaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Novel and Green Route For Synthesis of Pyrazoline Derivatives in An Aqueous Media by Using Ionic Liquid at Reflux ConditionDocument4 pagesA Novel and Green Route For Synthesis of Pyrazoline Derivatives in An Aqueous Media by Using Ionic Liquid at Reflux ConditioniaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Duplicated Region in Digital Image Detection Approaches EvaluationDocument7 pagesDuplicated Region in Digital Image Detection Approaches EvaluationiaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Working Women - A Broader PerspectiveDocument6 pagesWorking Women - A Broader PerspectiveiaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- Slow Intelligence System Based Software TestingDocument6 pagesSlow Intelligence System Based Software TestingiaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- A Survey On Detection and Computing The Amount of Plant Diseases Using Image ProcessingDocument10 pagesA Survey On Detection and Computing The Amount of Plant Diseases Using Image ProcessingiaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- Comparison Study of Related Data Sharing Security Issues in Cloud ComputingDocument5 pagesComparison Study of Related Data Sharing Security Issues in Cloud ComputingiaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Cassandra DB - A Cloud Deployment ToolDocument4 pagesCassandra DB - A Cloud Deployment TooliaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Structural Change in Composition of India's Export: EraDocument8 pagesStructural Change in Composition of India's Export: EraiaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Cavitation Analysis On Propeller Turbine Through CFDDocument13 pagesCavitation Analysis On Propeller Turbine Through CFDiaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Survey - Data Security and Privacy Big DataDocument6 pagesA Survey - Data Security and Privacy Big DataiaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- An Evaluation of Socio-Legal and Economic Consequences of Benami Act, 2016Document8 pagesAn Evaluation of Socio-Legal and Economic Consequences of Benami Act, 2016iaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- A Novel Design Methodology of 1-Bit Hybrid Full Adder Using SVL TechniqueDocument6 pagesA Novel Design Methodology of 1-Bit Hybrid Full Adder Using SVL TechniqueiaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- Design of Transformer Peripharals by Computer Aided Design Drafting (Cadd)Document8 pagesDesign of Transformer Peripharals by Computer Aided Design Drafting (Cadd)iaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Partition As Revealed in Bapsi Sidhwa's Ice Candy ManDocument9 pagesThe Impact of Partition As Revealed in Bapsi Sidhwa's Ice Candy ManiaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- ON LINE FAULTS IN FIFO BUFFERS OF NOC ROUTERS - Http://iaetsdjaras - Org/gallery/2-D130-23 PDFDocument7 pagesON LINE FAULTS IN FIFO BUFFERS OF NOC ROUTERS - Http://iaetsdjaras - Org/gallery/2-D130-23 PDFiaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Sensing Performance of PEO: KClO4 Polymer Electrolyte As Gas SensorDocument5 pagesSensing Performance of PEO: KClO4 Polymer Electrolyte As Gas SensoriaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- Influence of Strontium As A Dopant in Hydroxyapatite For Potential Biomedical ApplicationsDocument6 pagesInfluence of Strontium As A Dopant in Hydroxyapatite For Potential Biomedical ApplicationsiaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- In Vitro Propagation of Anisochilus Carnosus (LF.) Wallich - A Medicinal PlantDocument3 pagesIn Vitro Propagation of Anisochilus Carnosus (LF.) Wallich - A Medicinal PlantiaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- ON LINE FAULTS IN FIFO BUFFERS OF NOC ROUTERS - Http://iaetsdjaras - Org/gallery/2-D130-23 PDFDocument7 pagesON LINE FAULTS IN FIFO BUFFERS OF NOC ROUTERS - Http://iaetsdjaras - Org/gallery/2-D130-23 PDFiaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Online Signature Verification Using Hybrid Wavelet Transform (HWT) - 1 and 2 With HMM ClassifierDocument10 pagesComparative Analysis of Online Signature Verification Using Hybrid Wavelet Transform (HWT) - 1 and 2 With HMM ClassifieriaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- Humidity Sensor: A ReviewDocument5 pagesHumidity Sensor: A ReviewiaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- ON LINE FAULTS IN FIFO BUFFERS OF NOC ROUTERS - Http://iaetsdjaras - Org/gallery/2-D130-23 PDFDocument7 pagesON LINE FAULTS IN FIFO BUFFERS OF NOC ROUTERS - Http://iaetsdjaras - Org/gallery/2-D130-23 PDFiaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Mathematical Model For Marangoni Convection MHD Flow of Carbon Nanotubes Through A Porous MediumDocument7 pagesMathematical Model For Marangoni Convection MHD Flow of Carbon Nanotubes Through A Porous MediumiaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- Action of Photo Activated Cow Urine With The Different Combination of Neem and Aloe Vera Extracts Against Pathogenic MicroorganismsDocument4 pagesAction of Photo Activated Cow Urine With The Different Combination of Neem and Aloe Vera Extracts Against Pathogenic MicroorganismsiaetsdiaetsdNo ratings yet
- Warranty Information Emea and CisDocument84 pagesWarranty Information Emea and CisHenriques BrunoNo ratings yet
- Request Letter To EDC Used PE PipesDocument1 pageRequest Letter To EDC Used PE PipesBLGU Lake DanaoNo ratings yet
- Book Two - 2da. EdiciónDocument216 pagesBook Two - 2da. EdiciónJhoselainys PachecoNo ratings yet
- 2014 March CaravanDocument48 pages2014 March CaravanbahiashrineNo ratings yet
- SABIC Ethanolamines RDS Global enDocument10 pagesSABIC Ethanolamines RDS Global enmohamedmaher4ever2No ratings yet
- Namal College Admissions FAQsDocument3 pagesNamal College Admissions FAQsSauban AhmedNo ratings yet
- JRC Wind Energy Status Report 2016 EditionDocument62 pagesJRC Wind Energy Status Report 2016 EditionByambaa BattulgaNo ratings yet
- Macdonald v. National City Bank of New YorkDocument6 pagesMacdonald v. National City Bank of New YorkSecret SecretNo ratings yet
- 16 BPI V FernandezDocument1 page16 BPI V FernandezAngelica Joyce BelenNo ratings yet
- GSM Multi-Mode Feature DescriptionDocument39 pagesGSM Multi-Mode Feature DescriptionDiyas KazhiyevNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- HetNet Solution Helps Telcos Improve User Experience & RevenueDocument60 pagesHetNet Solution Helps Telcos Improve User Experience & RevenuefarrukhmohammedNo ratings yet
- PNW 0605Document12 pagesPNW 0605sunf496No ratings yet
- UNIT: 01 Housekeeping SupervisionDocument91 pagesUNIT: 01 Housekeeping SupervisionRamkumar RamkumarNo ratings yet
- WPB Pitch DeckDocument20 pagesWPB Pitch Deckapi-102659575No ratings yet
- BC Specialty Foods DirectoryDocument249 pagesBC Specialty Foods Directoryjcl_da_costa6894No ratings yet
- Admission Checklist (Pre-) Master September 2021Document7 pagesAdmission Checklist (Pre-) Master September 2021Máté HirschNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Charges General Banking 2022Document18 pagesSchedule of Charges General Banking 2022Shohag MahmudNo ratings yet
- Amos Code SystemDocument17 pagesAmos Code SystemViktor KarlashevychNo ratings yet
- San Jose Police Department - Joe Gomez IncriminationDocument2 pagesSan Jose Police Department - Joe Gomez Incriminationchase manuelNo ratings yet
- LNGC Q-Flex Al Rekayyat - Imo 9397339 - Machinery Operating ManualDocument581 pagesLNGC Q-Flex Al Rekayyat - Imo 9397339 - Machinery Operating Manualseawolf50No ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Edge Quality: Mild SteelDocument14 pagesTroubleshooting Edge Quality: Mild SteelAnonymous U6yVe8YYCNo ratings yet
- 2023 Prospectus 2Document69 pages2023 Prospectus 2miclau1123No ratings yet
- Afar Partnerships Ms. Ellery D. de Leon: True or FalseDocument6 pagesAfar Partnerships Ms. Ellery D. de Leon: True or FalsePat DrezaNo ratings yet
- What Role Can IS Play in The Pharmaceutical Industry?Document4 pagesWhat Role Can IS Play in The Pharmaceutical Industry?Đức NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Capran+980 CM en PDFDocument1 pageCapran+980 CM en PDFtino taufiqul hafizhNo ratings yet
- BCM Risk Management and Compliance Training in JakartaDocument2 pagesBCM Risk Management and Compliance Training in Jakartaindra gNo ratings yet
- SHIPPING TERMSDocument1 pageSHIPPING TERMSGung Mayura100% (1)
- CCTV8 PDFDocument2 pagesCCTV8 PDFFelix John NuevaNo ratings yet
- PDF Reply Position Paper For ComplainantDocument4 pagesPDF Reply Position Paper For ComplainantSheron Biase100% (1)
- Embedded Systems: Martin Schoeberl Mschoebe@mail - Tuwien.ac - atDocument27 pagesEmbedded Systems: Martin Schoeberl Mschoebe@mail - Tuwien.ac - atDhirenKumarGoleyNo ratings yet