Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0910
Uploaded by
Ng SoohsienCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
0910
Uploaded by
Ng SoohsienCopyright:
Available Formats
--=-- ~
_..l~~\
~~A;;_ ~~~
UNIVERSITI KEBANGSAAN MALAYSIA
PEPERIKSAAN AKHIR
SEMESTER II SESI AKADEMIK 2009/2010
IJAZAH SARJANAMUDA
DENGAN KEPUJIAN
APRIL 2010
MASA:
1 JAM 30 MINIT
KOD KURSUS
STKM2122
TAJUK KURSUS
AMALI KIMIA MAKANAN
ARAHAN
1.
Kertas ini mempunyai
C.
2.
Jawab soalan Bahagian A dalam borang OMR dengan
menggunakan pensil 2B.
3.
Jawab soalan Bahagian B dan C dalam bukujawapan
diedarkan.
4.
Jumlah markah keseluruhan
5.
Kertas soalan tidak dibenarkan dibawa keluar daripada
Dewan Peperiksaan.
3 Bahagian iaitu bahagian A, B dan
yang
kertas ini ialah 100 markah.
No. Pendaftaran :
(dengan perkataan)
Kertas soalan ini mengandungi 9 muka surat bercetak, tidak termasuk muka surat ini.
STKM2l22
PART A (30 marks)
Instruction: Answer All questions in the OMR form used 2B pencil.
1.
The titration that uses sodium thiosulphate solution
solution as an indicator is called
titration.
A
B
C
D
E
2.
acid-base
complexometric
iodometric
redox
None of the above.
The disappearance of blue colour in the titration (Question 1) used to indicate
the end point is due to
_
A
B
C
D
E
3.
as titrant and starch
entrapment ofI2 in the starch a-helix
hydrolysis of starch into reducing sugar
oxidation of to 12
reduction of 12 to
release of 12 from the starch a-helix
Why is it necessary to shake the flask vigorously during the titration (Question
I)?
A
B
C
D
E
4.
is immiscible in water.
more in cyclohexane
To release 12 from cyclohexane.
Thiosulphate is not soluble in cyclohexane
All the above answers.
Why is it necessary to determine the iodine value (IV) of fats/oils?
A
B
C
D
E
5.
Cyclohexane
b is partitioned
To determine stability
To ensure freshness
To determine the degree of un saturation
To determine the extent of oxidation
All the above answers.
In iodine value (IV) test, the purpose of adding saturated KI solution into the
Wijs reagent-oil mixture after 1 hour is to
_
A
B
C
D
E
break down the oil - 12 linkage
oxidize
ion to 12
reduce excess ICI to 12
release excess 12 from oil
All the above answers.
STKM2122
6.
You are given 2 oil samples X and Y treated with an alcoholic solution of
CUS04 and are asked to determine their iodine value (IV). Results from the
test showed that X oil has a lower IV than Y. What conclusion can you make
from the observation?
A
B
C
D
E
7.
In the determination of peroxide value (PV), the 12 released from KI is titrated
with a standardized Na2S203 solution using starch solution as an indicator.
The release of 12 is caused by
_
A
B
C
D
E
8.
r to h
r to h
It
forms complex with double bonds
binds free radicals
reacts with peroxides
reduces peroxides
resonances with free radicals
In the determination
function of I2?
A
B
C
D
E
10.
formation of free radicals by peroxides
loss of double bonds due to oxidation
the peroxides present in the sample reduce
the peroxides present in the sample oxidize
None of the above.
How does BHT prevent oxidation of fats/oils?
A
B
C
D
E
9.
X is more saturated than Y
Y is more saturated than X
X has a lower content of unsaturated fatty acids
X has a higher content of unsaturated fatty acids
Double bonds in X have been cleft due to oxidation
of reducing
sugar by Somogyi
method,
what is the
To react with the carbonyl group of reducing sugar
To oxidize reducing sugar to sugar acids
To reoxidize Cu + to Cu +2
To turn the colour of starch solution to blue
All the above answers.
In the test mentioned in Question 9, the mixture of sample and Somogyi
reagent was incubated in a boiling water bath for 15 minutes in order to
allow
_
A
B
C
D
E
oxidation of Cu + to Cu +2
oxidation of to 12
reduction of Cu +2to CU20 by the reducing sugar present
release of 12from starch a-helix
All the above answers.
STKM2122
11.
After adding 2N H2S04 into the cooled solution in Question 10, the colour of
the mixture turned to blue. This was caused by the
_
A
B
C
D
E
12.
solubilize myoglobin
precipitate globin (protein) at its isoelectric point
to precipitate impurities
stabilize myoglobin
All the above answers.
To
To
To
To
To
fix the colour of myoglobin.
stabilize myoglobin
oxidize myoglobin to the brown metmyoglobin
reduce all metmyoglobin to bright red oxymyoglobin
bind proteins that might interfere with the reaction
Why is it important to determine the content of myoglobin in muscle?
A
B
C
D
E
16.
In the determination of myoglobin, why do KCN crystals added just before the
reading of the solution at A 540nm?
A
B
C
D
E
15.
To determine the content of residual b
To oxidize Cu + to Cu +2
To oxidize reducing sugar to sugar acids
to 12
To oxidize
All the above answers.
During preparation of sample for the determination of myoglobin in meat, the
pH of the supernatant is adjusted to pH 7.2 in order to
_
A
B
C
D
E
14.
In the above test (Question 9), what is the purpose of thiosulfate titration?
A
B
C
D
E
13.
oxidation of Cu + to Cu +2
oxidation of to 12
reduction of Cu+2 to CU20 by the reducing sugar present
release of 12from starch a-helix
All the above answers.
To predict the level of microbial contamination
To determine the amount of nitrate added
To determine the amount of nitrite added
To determine the freshness of meat
All the above answers.
What is the purpose of adding diethyl ether : ethanol (1: 1) solution during
determination of FFA content in coconut milk?
A
To extract FFA from coconut milk
B
C
D
E
To
To
To
All
coagulate protein in coconut milk
facilitate the determination of end point
stop any enzymatic reaction
the above answers.
3
STKM2122
17.
In the hydrolytic rancidity experiment of coconut milk, the CUS04 sample has
a lower FFA content than control because
_
A
B
C
D
E
18.
Why was the result in Question 16 expressed as % lauric acid?
A
B
C
D
E
19.
20.
Lauric acid is a stable fatty acid
Lauric acid is soluble in water
Lauric acid is the dominant fatty acid in coconut oil.
Other fatty acids are fat soluble
All the above answers.
The control sample in the hydrolytic rancidity experiment,
has separated into two layers. This is because
_
the coconut milk
A
B
C
FF A is reduced to alcohol which cause the protein to denature
FF A released denatures the protein
the microbial contamination causes fermentation
D
E
the microbes present break down the protein
All the above answers.
Food dishes cooked with coconut milk kept at room temperature may turn bad
or "basi" after some time because
A
B
C
D
E
21.
Cu +2 forms insoluble Cu-soap with FF A
Cu +2 inhibits the activity of lipase
Cu +2 inhibits the proliferation of microbes
Cu +2 oxidizes FF A to aldehyde
None of the above.
FFA is reduced to alcohol which cause the protein to denature
FFA released denatures the protein
the microbial contamination causes fermentation
the microbes present break down the protein
All the above answers.
In the determination
to protein in
to
A
B
C
D
E
of soluble protein by Bradford method, the binding of dye
solution causes the dye to change colour from
acidic, bluish, reddish
acidic, reddish, bluish
alkaline, bluish, reddish
alkaline, reddish, bluish
None of the above.
STKM2122
22.
The shift in
A
B
C
D
E
23.
shift.
red, bathochromic
red, hypsochromic
blue, bathochromic
blue, hypsochromic
None of the above.
the
the
the
the
All
protein is more soluble in salt solution
extraction of protein is better in salt solution
salt stabilizes the protein
salt dissolves the protein
the above answers.
sucrose is a non-reducing sugar
sucrose does not react with glycine
the reaction requires reducing sugar
there is no hemiacetal group in sucrose
All the above answers.
The fructose-glycine and glucose-glycine
solution at pH 8.0. This shows that
A
B
C
D
E
26.
or
In the non-enzymatic browning experiment, there is no or very little colour
was formed after heating sucrose-glycine
mixture at both pH 5.0 and 8.0.
This indicates that
A
B
C
D
E
25.
max (Question 21) is called
In this experiment (Question 21), the salt solution is used to extract the protein
because
A
B
C
D
E
24.
mixtures produce deeply co loured
_
amino-sugar reaction has taken place
fructose and glucose are reducing sugars
the browning reaction run faster at high pH
the hemiacetal groups are present
An the above answers.
The reaction in Question 24 is also known as
A
B
C
D
E
Amadori arrangement
Heyns arrangement
Maillard reaction
Strecker degradation
All the above answers.
STKM2122
27.
28.
29.
Apart from producing brown colour, the
responsible for the production of aroma compounds.
A
B
C
Amadori arrangement
Heyns arrangement
Maillard reaction
D
E
Strecker degradation
All the above answers.
Besides peroxidase, this/these
adequacy of blanching.
A
Catalase
B
C
D
E
Lipase
Lipoxygenase
Polyphenol oxidase
All the above answers.
26) is also
can also be used to indicate
the
At lower blanching temperature, the absorbance reading may be erroneously
high due to the formation of air bubble caused by the activity of this enzyme.
A
B
C
D
E
30.
enzyme/s
(Question
Catalase
Lipase
Lipoxygenase
Polyphenol oxidase
None of the above.
The purpose of removing the residual enzyme activities in processed foods
is/are to
_
A
B
C
D
E
prolong the shelf life
avoid the formation of off-flavour
stop discolouration
retain texture
All the above answers.
STKM2122
SECTION B: (40 marks)
Instruction: Answer ALL questions in the answer book provided.
1.
You are going to study the effect of storage conditions on the extent of
hydrolytic rancidity in coconut milk sample A and B. Both samples were
stored for 3 days at different temperatures:
sample A was at room
temperature and sample B was in a refigerator. After 3 days, 10 mL samples
were put into a conical flask containing 25 mL of ethanol-diethyl ether (1: 1)
solution. Then the sample-solvent mixture was titrated with standardized 0.1N
alcoholic KOH solution. The amount of alkali required to change the colour of
phenolphthalein indicator to purple was recorded and found to be 12 mL for
sample A and 5 mL for sample B. The equivalent weight oflauric acid is 200.
a.
Calculate the amount ofFFA as % lauric acid in the sample A and B.
(10 marks)
b.
What is the function of ethanol-diethyl
ether (1: I) solution?
(5 marks)
c.
Why was sample A higher in free fatty acid content
(5 marks)
2.
You are asked to determine the residual activity of peroxidase (POD) in
cabbage after blanching.
In the experiment, 10.0g of sliced cabbage were
soaked in boiling water bath for 30 seconds.
The residual activity of
peroxidase was then determined from 0.1 mL of the water extract in a lcm
cuvette with the total volume of 3.0 mL using 1% guaiacol-OSYo H202 as
substrate. The change in absorbance per minute (L1 A) was monitored at 490nm
and found to be 0.5A/min.
a.
What are the objectives of blanching?
(5 marks)
b.
Given the molar absorbancy of tetraguaicol
is 2.66 x 104 M'lcm,l,
calculate the residual activity (U/mL) of POD.
(10 marks)
c.
Why was POD chosen to check the adequacy
experiment?
of blanching
in this
(5 marks)
Matrix Mo:
STKM2122
SECTION C (30 marks)
Instruction:
provided.
1.
Answer All questions EXCEPT question
Answer question 2(a) in the question sheet.
2(a) in the answer book
Soluble protein content determination by means of the Bradford method
involves the use of a dye. Name the dye and explain the principle behind the
Bradford method determination.
Name a protein commonly used for
preparation of standard solution for protein content determination.
(8 marks)
2.
In one of your laboratory exercises, you will determine reducing sugar content
by using Somogyi Reagent. You are given a sample of spaghetti sauce, of
which you place 2.0181g into a 50-mL beaker before diluting to volume with
distilled water into a 200-mL volumetric flask. After filtration of this sample,
you pipette 5 mL filtrate into a 100-mL volumetric flask and dilute it to
volume with distilled water. You then transfer 5 mL aliquot into a test tube.
This experiment is performed in triplicates.
Using a stock solution of 0.1 mg dextrose/mL, you prepare a series of standard
solutions as indicated in Table 1. Reducing sugar content is determined by
pipetting 5 mL sample into a test tube (done in triplicates, with test tubes
labeled as Tl, T2 and T3, respectively) and adding 5 mL Somogyi Reagent
into each test tube. All test tubes are covered with aluminium foil and heated
in a boiling water bath for 15 min. After heating, the test tubes are cooled
under running tap water for 5 min and 2 mL 2N H2S04 is added to each tube.
The reducing sugar content in each tube is determined by titration with 0.005N
Na2S203.
Table 1 : Preparation of standard glucose stock solution
30.5
29.8
25.5
30.8
27.2
of
dextrose
0245315Concentration
5Somogyi
4032(mL)
51reagent
30.1
26.8
32.5
Distilled
Na2S203
solution
water
(mL)
(mL) 28.9
Tube Glucose/Sample
(llg/mL)
Matrix Mo:
STKM2122
In order to determine the reducing sugar content in the sample, you construct a
standard curve by plotting the difference between thiosulphate volume
required to titrate the blank and that required to titrate the known dextrose
concentrations vs. concentration of glucose (flg/mL).
a)
Fill in the blanks in Table 1.
b)
With the aid of the standard curve, determine the reducing
concentration of the sample. Show all calculations.
sugar
Formula:
Reducing sugar concentration (g dextrose/1 00 g) =
R x DF x TV x 100
x 1
SV
Wt (g)
106
where,
R: Sugar content from standard curve (flg/mL)
TV : Total sample volume (mL)
SV : Volume of sample used in determinations step (mL)
Wt : Sample weight
DF : Dilution factor
(22 marks)
"SELAMAT MAJU JAY A"
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Knorr FinalDocument25 pagesKnorr Finalimbree100% (3)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Ageism PowerpointDocument11 pagesAgeism Powerpointapi-254132646No ratings yet
- Marketing Strategy and Competitive Positioning PDFDocument647 pagesMarketing Strategy and Competitive Positioning PDFEricKHLeawNo ratings yet
- Coca Cola Primary Activities: 1. Inbound Logistics Include Functions Like Receiving, Warehousing, and Managing InventoryDocument5 pagesCoca Cola Primary Activities: 1. Inbound Logistics Include Functions Like Receiving, Warehousing, and Managing InventoryJaene L.No ratings yet
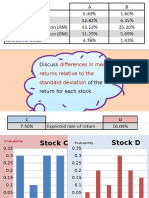
- Discuss Differences in Mean Returns Relative To The Standard Deviation of The Return For Each Stock. DiscussDocument2 pagesDiscuss Differences in Mean Returns Relative To The Standard Deviation of The Return For Each Stock. DiscussNg SoohsienNo ratings yet
- Total Liquid A 473053 Q1 3766Document2 pagesTotal Liquid A 473053 Q1 3766Ng SoohsienNo ratings yet
- 311213Document171 pages311213Ng SoohsienNo ratings yet
- CPO Transportation Issues Costing Palm Oil Company ProfitsDocument6 pagesCPO Transportation Issues Costing Palm Oil Company ProfitsSherry Yong PkTianNo ratings yet
- Credit Risks and Bank Share Valuation in Selected Four Asia Pacific CountriesDocument11 pagesCredit Risks and Bank Share Valuation in Selected Four Asia Pacific CountriesNg SoohsienNo ratings yet
- 300914Document21 pages300914Ng SoohsienNo ratings yet
- MAS Annual Report 2012 Highlights Financial TurnaroundDocument184 pagesMAS Annual Report 2012 Highlights Financial TurnaroundRaj SukkumarNo ratings yet
- 300614Document21 pages300614Ng SoohsienNo ratings yet
- CPO Transportation Issues Costing Palm Oil Company ProfitsDocument6 pagesCPO Transportation Issues Costing Palm Oil Company ProfitsSherry Yong PkTianNo ratings yet
- The Foreign Exchange MarketDocument42 pagesThe Foreign Exchange MarketAtul JainNo ratings yet
- The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology: TropoelastinDocument4 pagesThe International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology: TropoelastinNg SoohsienNo ratings yet
- Syariah PLCs - List 2003-2005 - To - IS - 1Document62 pagesSyariah PLCs - List 2003-2005 - To - IS - 1Ng SoohsienNo ratings yet
- Concept and Principles of ToxicologyDocument73 pagesConcept and Principles of ToxicologyNg SoohsienNo ratings yet
- 0910Document10 pages0910Ng SoohsienNo ratings yet
- New ResultDocument21 pagesNew ResultNg SoohsienNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic DrugsDocument29 pagesCholinergic DrugsKiranNo ratings yet
- Greenhouse Effect: Greenhouse Gases and Their Impact On Global WarmingDocument9 pagesGreenhouse Effect: Greenhouse Gases and Their Impact On Global WarmingrabiulNo ratings yet
- Assignment of PsychologyDocument28 pagesAssignment of PsychologyMuhammad Hamza AshfaqNo ratings yet
- As en 540-2002 Clinical Investigation of Medical Devices For Human SubjectsDocument8 pagesAs en 540-2002 Clinical Investigation of Medical Devices For Human SubjectsSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- Surgical Item - Price ListDocument2 pagesSurgical Item - Price ListRamnish MishraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 NotesDocument10 pagesChapter 3 Notesmjamie12345No ratings yet
- Galapagos Penguins: Shelter, Niche and NeedsDocument8 pagesGalapagos Penguins: Shelter, Niche and Needsjim munkNo ratings yet
- Dimensions-Mm (Inch) : Valve Regulated Lead Acid Battery (VRLA)Document2 pagesDimensions-Mm (Inch) : Valve Regulated Lead Acid Battery (VRLA)orunmila123No ratings yet
- Environmental Pollution and DegradationDocument2 pagesEnvironmental Pollution and DegradationCharLene MaRieNo ratings yet
- Port Works Design Manual Part 2 PDFDocument124 pagesPort Works Design Manual Part 2 PDFhessian123No ratings yet
- A Text Book On Nursing Management AccordDocument790 pagesA Text Book On Nursing Management AccordMohammed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Companies Directory Alternative Fuels and Smart Transportation June 20Document82 pagesCompanies Directory Alternative Fuels and Smart Transportation June 20Mbamali Chukwunenye100% (1)
- Rorschach y SuicidioDocument17 pagesRorschach y SuicidioLaura SierraNo ratings yet
- Breading Guide To All FoodDocument1 pageBreading Guide To All FoodInno EspinaNo ratings yet
- Q A With Jaquelyn BurrerDocument3 pagesQ A With Jaquelyn Burrerapi-480718823No ratings yet
- Atlas Copco Generators: 15-360 kVA 15-300 KWDocument10 pagesAtlas Copco Generators: 15-360 kVA 15-300 KWAyoub SolhiNo ratings yet
- Interest RatesDocument207 pagesInterest RatesBenjamin RogersNo ratings yet
- SPR MAN 4 14 ET Operating ManualDocument24 pagesSPR MAN 4 14 ET Operating ManualJason WeeksNo ratings yet
- Certificate of Employment Document TitleDocument1 pageCertificate of Employment Document TitleAyni ReyesNo ratings yet
- Physical Therpay Protocols For Conditions of Neck RegionDocument74 pagesPhysical Therpay Protocols For Conditions of Neck Regionjrpsaavedra4599No ratings yet
- Fall ProtectionDocument5 pagesFall ProtectionAamir AliNo ratings yet
- SureFlo RDocument2 pagesSureFlo RKen NgNo ratings yet
- Barangay Ordinance Vaw 2018Document7 pagesBarangay Ordinance Vaw 2018barangay artacho1964 bautista100% (3)
- Yoga Nidra MethodDocument13 pagesYoga Nidra MethodPrahlad Basnet100% (2)
- Neet Structural Organisation in Animals Important QuestionsDocument18 pagesNeet Structural Organisation in Animals Important QuestionsARKA NEET BIOLOGYNo ratings yet
- Penyakit Palpebra Dan AdneksaDocument39 pagesPenyakit Palpebra Dan AdneksaayucicuNo ratings yet
- Annotated Bibliography Graphic OrganizerDocument4 pagesAnnotated Bibliography Graphic Organizerapi-348035481No ratings yet