Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Under What Regulation?: Arthur A. Tracton
Uploaded by
srkadaliOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Under What Regulation?: Arthur A. Tracton
Uploaded by
srkadaliCopyright:
Available Formats
17
Under What
Regulation?
Arthur A. Tracton
Consultant
17.1
17.2
17.3
17.4
17.5
17.6
17.7
17.8
17.9
Introduction ......................................................................17-1
Code of Federal Regulations ............................................17-1
Title 29 (Labor) .................................................................17-1
Protection...........................................................................17-2
Biocides ..............................................................................17-3
Testing ................................................................................17-3
Volatile Organic Substances (VOCs) ...............................17-3
Food and Drug Administration (FDA) ...........................17-3
Which Regulation? ............................................................17-4
17.1 Introduction
Civilization is based on laws and regulations for the common good. Way back, the law was as simple as,
dont kill each other. As time passed and technology grew, the laws and regulations became more
complex to keep up with the technology. Regulations were and are issued by the federal government, the
state government, the county government, and the local government. With everyone enacting regulations,
confusion abounds. There are just too many regulations to compile in a single list. The following looks
at some of the major regulations governing the coatings and inks industries.
17.2 Code of Federal Regulations
The government of the United States of America discusses possible regulations and publishes the discussion in the Federal Register on a daily basis. When it is concluded that a regulation, or change in regulation,
is needed, it will be published in the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR). This CFR is an enormous work
comprising some 50 titles, each subdivided into a number of books.
17.3 Title 29 (Labor)
In Title 29 (Labor) is section XVII (Occupational Safety and Health Administration, Department of
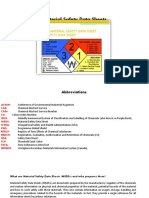
Labor). Under this section is part 1910.1200, Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS). The MSDS started by
proposing safety considerations for asbestos during the process of cutting ships apart. It has progressed
to cover almost all chemicals used in industry and commerce. The MSDS lists the manufacturer responsible for the product, the composition, and safety and health concerns. This form has gone, in practice,
from seven sections to 16 or more. An example listing of the section titles is as follows:
17-1
2007 by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC
17-2
Coatings Technology: Fundamentals, Testing, and Processing Techniques
Section 1: Chemical Product and Company Identification
Section 2: Composition Information or Ingredients
Section 3: Hazards Identification
Section 4: First-Aid Measures
Section 5: Fire Fighting Measures
Section 6: Accidental Release Measures
Section 7: Handling and Storage
Section 8: Exposure Controls and Personal Protection
Section 9: Physical and Chemical Properties
Section 10: Stability and Reactivity
Section 11: Toxicological Information
Section 12: Ecological Information
Section 13: Disposal Considerations
Section 14: Transport Information
Section 15: Regulatory Information
Section 16: Other Information
Note that the MSDS for each product is to be updated every year and distributed to product users.
Under the section on Regulatory Information, all sorts of abbreviations and acronyms can be found.
Some of these are as follows:
WHMIS (Canada): Controlled Substances
WHMIS (Canada): Hazard Classification
Superfund SARA 311-312: Hazard Classification
Superfund SARA313: Disposal
TSCA: U.S. Toxic Substances Control Act
DSL: Canadian Domestic Substances List
CEPA: Canadian Environmental Protection Act
EINECS: European Inventory of Existing Commercial Chemical Substances
AICN: Australian Inventory of Chemical Substances
NICNAS: Australian National Industrial Chemical Notification and Assessment Scheme
MITI: Japanese Handbook of Existing and New Chemical Substances
ECL: Korean Toxic Substances Control Act
CPM: Inventory of Existing Chemical Substances in China
RICRA: Resource Conservation and Recovery Act
State Right to Know: Including Massachusetts, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania
California Proposition 65
CONEG: Coalition of New England Governors
17.4 Protection
We want to protect the environment and materials in transit. Some of these regulations and abbreviations
include the following:
DOT: Department of Transportation
49 CFR (Title is Transportation) 107: Packing for Hazardous Material
49 CFR 172: Shipping
40 CFR (Title is Protection of Environment) 60 and 61: Clean Air Act
40 CFR 261.20 to 261.24: Classification as Hazardous Waste
40 CFR 401: Clean Water Act
2007 by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC
Under What Regulation?
17-3
17.5 Biocides
If biocides are used, they are regulated under The Federal Insecticide, Fungicide and Rodenticide Act
(FIFRA). Some exemptions may be found in 40 CFR 152. This may include working through an EPA
(Federal Environmental Protection Agency) approach for biocides used in Paints and Coatings.
17.6 Testing
A lot of testing is performed by governmental and independent laboratories to determine if a hazard
exists, and if so, what is tolerable. The following list contains terms found in several sections of the
MSDS:
OSHA: Occupational Safety and Health Administration
NIOSH: National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
TLV: Threshold Limit Value
TWA: Time Weighted Average
PEL: Permissible Exposure Level
NTP: National Toxicity Program
IARC: International Agency for Research on Cancer
ANSI: American National Standards Institute
ISO: International Standards Organization
ACGIH: American College of Governmental Industrial Hygienists
NFPA: National Fire Protection Association
CPSC: Consumer Products Safety Commission
FHSA: Federal Hazardous Substances Act (administered by CPSC)
17.7 Volatile Organic Substances (VOCs)
Around 1966, Los Angeles, California, enacted a regulation called Rule 66 to try to stop the release of
photogenic materials into the atmosphere which cause smog. This rule dictated what materials are
controlled and at what levels. Xylene could only be at 12 volume percent in a paint. Toluene was at 20
volume percent. Soon afterwards, San Francisco enacted Regulation 3, which is the same thing. Years
later, the concept of photochemically reactive solvents spawned the volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
concept of total release of any solvent into the atmosphere. These rules and regulations have gone through
a number of iterations. Some solvents were banned and then reinstated for use as more testing was
performed. Now we have Hazardous Air Pollutants (HAPs). Some solvents meet this ever-changing
standard, and some do not.
17.8 Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
When a coating or ink is related to food, drugs, or cosmetics, another set of regulations covers the area.
This is Title 21 of the CFR (Food and Drugs). Section I, Food and Drug Administration, Department
of Health and Human Services, covers the materials that may come in direct or indirect contact with
foods and what materials may be used in cosmetics and drugs. For example, colorants (pigments and
dyes) are covered in one area, while resins and binders are covered in another area. Note that neither
the FDA nor the USDA (United States Department of Agriculture, another set of regulations) will
stipulate the compliance of a paint or ink to a regulation. The best you can get is that the ingredients
are listed somewhere.
2007 by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC
17-4
Coatings Technology: Fundamentals, Testing, and Processing Techniques
17.9 Which Regulation?
The above lists are by no means complete. They give an indication of what is happening. Many companies
retain employees just to handle the regulations to make sure they are in compliance. In the long run, the
question is, What are the regulations for your product?
2007 by Taylor & Francis Group, LLC
You might also like
- Homework 2 Unit 1Document5 pagesHomework 2 Unit 1David MayNo ratings yet
- CSEC Social Studies NotesDocument243 pagesCSEC Social Studies NotesAction100% (10)
- Intro To Hazardous Materials Unit 1Document17 pagesIntro To Hazardous Materials Unit 1Anonymous pzXvSP25I100% (1)
- MsdsDocument1 pageMsdsHamdi RafiekNo ratings yet
- Afosh 48-8Document26 pagesAfosh 48-8jesse_sharpNo ratings yet
- LEVIS RSL 2010 EnglishDocument48 pagesLEVIS RSL 2010 EnglishHasan SozeriNo ratings yet
- Learn English in 30 Days PDFDocument21 pagesLearn English in 30 Days PDFmanojj6556% (43)
- MSDSDocument32 pagesMSDSDeepak ThapliyalNo ratings yet
- Ch3 Green Engineering Textbook 508Document7 pagesCh3 Green Engineering Textbook 508Arslan AzharNo ratings yet
- Format of CSDS Form Chemical)Document44 pagesFormat of CSDS Form Chemical)zaleiha100% (1)
- Find MSDS onlineDocument4 pagesFind MSDS onlineHoài ThươngNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)Document27 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheets (MSDS)ahmet yasin karlıkNo ratings yet
- Chemical Process Safety and Industrial Hygiene RegulationsDocument63 pagesChemical Process Safety and Industrial Hygiene RegulationsRaushan KumarNo ratings yet
- How To Use This Pocket GuideDocument12 pagesHow To Use This Pocket GuideYusuf Al AzizNo ratings yet
- 16-Heading MSDS (International Format)Document15 pages16-Heading MSDS (International Format)Tim ZhangNo ratings yet
- Pesticide Law: A Summary of The Statutes: Updated January 3, 2007Document16 pagesPesticide Law: A Summary of The Statutes: Updated January 3, 2007AgricultureCaseLawNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Part 2:: Occupational Regulations and ResourcesDocument25 pagesUnit 1 - Part 2:: Occupational Regulations and ResourcesAndré SantosNo ratings yet
- EPA Guide to Testing Antimicrobial ProductsDocument20 pagesEPA Guide to Testing Antimicrobial ProductsAdriana HusniNo ratings yet
- Agriculture Law: RL32884Document19 pagesAgriculture Law: RL32884AgricultureCaseLawNo ratings yet
- 5.2HCS-Safety Data Sheet (SDS)Document35 pages5.2HCS-Safety Data Sheet (SDS)Christian MeanaNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data SheetDocument15 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheethomam Salim Khalaf100% (1)
- By David R. Shonnard: Chapter 3. Environmental Law and Regulations: From End-of-Pipe To Pollution PreventionDocument7 pagesBy David R. Shonnard: Chapter 3. Environmental Law and Regulations: From End-of-Pipe To Pollution PreventionAsmara KanthiNo ratings yet
- ANSI Standardized MSDS Format SectionsDocument3 pagesANSI Standardized MSDS Format SectionsRASHMINo ratings yet
- Agriculture Law: RL32948Document30 pagesAgriculture Law: RL32948AgricultureCaseLawNo ratings yet
- ReachDocument22 pagesReachromedic36No ratings yet
- Understanding Safety Data Sheets Fact SheetDocument9 pagesUnderstanding Safety Data Sheets Fact SheetMuthukumar SankaranNo ratings yet
- Health-Based Exposure Limits: How Do The EMA's Q&As Compare With New and Forthcoming ASTM Standards?Document17 pagesHealth-Based Exposure Limits: How Do The EMA's Q&As Compare With New and Forthcoming ASTM Standards?Ikram TAOUAMNo ratings yet
- Hazard Communication and Chemical Safety: By: Francis Ivan BarcelonaDocument11 pagesHazard Communication and Chemical Safety: By: Francis Ivan BarcelonaAko C. IvanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Safety: Message BoxDocument82 pagesChemical Safety: Message BoxGobindaSahuNo ratings yet
- (CLASS Reg. 2013) - Icop - Pub - 128Document374 pages(CLASS Reg. 2013) - Icop - Pub - 128Woan YingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document7 pagesChapter 2Hasan Abdel-FattahNo ratings yet
- Osha 3514Document7 pagesOsha 3514Styx CraigNo ratings yet
- WHMIS TrainingDocument31 pagesWHMIS TrainingJ_MacCoonNo ratings yet
- OCSPP 810.2200 - Disinfectants For Use On Environmental SurfacesDocument19 pagesOCSPP 810.2200 - Disinfectants For Use On Environmental Surfacesstubble27No ratings yet
- Reach Prop 0604Document23 pagesReach Prop 0604Karl TaokNo ratings yet
- CMC Safety Data Sheets Powerpoint Updated March 2019Document31 pagesCMC Safety Data Sheets Powerpoint Updated March 2019John WalkerNo ratings yet
- HG20660 2000 EnglishDocument43 pagesHG20660 2000 EnglishMingxia TuNo ratings yet
- FDA Guidelines For End-Product LAL Testing ValidationDocument13 pagesFDA Guidelines For End-Product LAL Testing Validationrajeev_s_nairNo ratings yet
- Negative Brief Nelson-Yeager Chemical TestingDocument6 pagesNegative Brief Nelson-Yeager Chemical TestingcalebprofittNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Section 1 - Chemical Product and Company IdentificationDocument5 pagesMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Section 1 - Chemical Product and Company IdentificationrinthusNo ratings yet
- Translation of Korean Standard for Classification and Labeling of Chemical Substance and Material Safety Data SheetDocument100 pagesTranslation of Korean Standard for Classification and Labeling of Chemical Substance and Material Safety Data SheetGokul pNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Air Pollutants: Assessment, Liabilities and Regulatory ComplianceFrom EverandHazardous Air Pollutants: Assessment, Liabilities and Regulatory ComplianceNo ratings yet
- House Bill Section by SectionDocument6 pagesHouse Bill Section by SectionEnvironmental Working GroupNo ratings yet
- MSDS Tape Safety DataDocument5 pagesMSDS Tape Safety Dataalex6inNo ratings yet
- Hazard Communication Standard - Safety Data Sheets - OSHA 3514 - Occupational Safety and Health AdministrationDocument11 pagesHazard Communication Standard - Safety Data Sheets - OSHA 3514 - Occupational Safety and Health Administrationr afriantoNo ratings yet
- Methylene Chloride SDSDocument18 pagesMethylene Chloride SDSUmme Fariha Tasnim TanimaNo ratings yet
- AspeDocument8 pagesAspe185412No ratings yet
- 116 Draft TricloDocument311 pages116 Draft TricloJerzy NawrockiNo ratings yet
- Sds Hazchem Info SheetDocument4 pagesSds Hazchem Info Sheetmaiman.mzakiNo ratings yet
- Esa Workplan UpdateDocument51 pagesEsa Workplan UpdateMichael JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Control of Substances Hazardous To HealthDocument38 pagesControl of Substances Hazardous To HealtharjmandquestNo ratings yet
- Product Properties Test Guidelines: OPPTS 830.6303 Physical StateDocument3 pagesProduct Properties Test Guidelines: OPPTS 830.6303 Physical Statedouglas jahir solorzano palaciosNo ratings yet
- Ib 1Document146 pagesIb 1kanishkaNo ratings yet
- ATSDR - Landfill Gas Primer - Chapter 1 - IntroductionDocument2 pagesATSDR - Landfill Gas Primer - Chapter 1 - IntroductionCezar FerreiraNo ratings yet
- PhthalsubDocument106 pagesPhthalsubliang102009No ratings yet
- OSHA Brief Safety Data SheetsDocument7 pagesOSHA Brief Safety Data SheetsDigitalGeeksNo ratings yet
- RMOA for Terephtalic Acid risk assessmentDocument22 pagesRMOA for Terephtalic Acid risk assessmentmarcmaxNo ratings yet
- Rescuing the Strong Precautionary Principle from CriticsDocument54 pagesRescuing the Strong Precautionary Principle from CriticsCo pNo ratings yet
- United States Court of Appeals, Third CircuitDocument9 pagesUnited States Court of Appeals, Third CircuitScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- HAZCOM and GHS - Chemical HazardsDocument42 pagesHAZCOM and GHS - Chemical HazardsAwalludin Pandu NegaraNo ratings yet
- Lecture #2 Chemical Engineering Plant Design: Prof - Dr.A.K SALARIYADocument49 pagesLecture #2 Chemical Engineering Plant Design: Prof - Dr.A.K SALARIYAAdil AslamNo ratings yet
- International Code of Conduct on Pesticide Management: Guidance on Pesticide Legislation - Second EditionFrom EverandInternational Code of Conduct on Pesticide Management: Guidance on Pesticide Legislation - Second EditionNo ratings yet
- Stanley Industries Quality ManualDocument18 pagesStanley Industries Quality ManualsrkadaliNo ratings yet
- Employee MotivationDocument72 pagesEmployee MotivationsrkadaliNo ratings yet
- Color Measurement For The Coatings Industry: Harold Van AkenDocument2 pagesColor Measurement For The Coatings Industry: Harold Van AkensrkadaliNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Bulletin 2015Document59 pagesJEE Main Bulletin 2015pace_saNo ratings yet
- Top 10 Reasons Not To Base Service Life Predictions Upon Accelerated Lab Light Stability TestsDocument6 pagesTop 10 Reasons Not To Base Service Life Predictions Upon Accelerated Lab Light Stability TestssrkadaliNo ratings yet
- Avitation PDFDocument13 pagesAvitation PDFsrkadaliNo ratings yet
- Sunlight, Ultraviolet, and Accelerated Weathering: Patrick Brennan Carol FedorDocument10 pagesSunlight, Ultraviolet, and Accelerated Weathering: Patrick Brennan Carol FedorsrkadaliNo ratings yet
- Fade Resistance of Lithographic Inks - A New Path Forward: Real World Exposures in Florida and Arizona Compared To Accelerated Xenon Arc ExposuresDocument11 pagesFade Resistance of Lithographic Inks - A New Path Forward: Real World Exposures in Florida and Arizona Compared To Accelerated Xenon Arc ExposuressrkadaliNo ratings yet
- Cure Monitoring: Microdielectric Techniques: 13.1 The Dielectric ResponseDocument5 pagesCure Monitoring: Microdielectric Techniques: 13.1 The Dielectric ResponsesrkadaliNo ratings yet
- The Use of X-Ray Fluorescence For Coat Weight DeterminationsDocument5 pagesThe Use of X-Ray Fluorescence For Coat Weight DeterminationssrkadaliNo ratings yet
- Coating Calculations: Arthur A. TractonDocument6 pagesCoating Calculations: Arthur A. TractonsrkadaliNo ratings yet
- Thermal Analysis For Coatings Characterizations: William S. GilmanDocument4 pagesThermal Analysis For Coatings Characterizations: William S. GilmansrkadaliNo ratings yet
- Global Automotive Declarable Substance List (GADSL) - Guidance DocumentDocument9 pagesGlobal Automotive Declarable Substance List (GADSL) - Guidance DocumentsrkadaliNo ratings yet
- Category Wise Obc ListDocument2 pagesCategory Wise Obc ListmahfuzurNo ratings yet
- Guidance For Annex V Exemptions From The Obligation To RegisterDocument55 pagesGuidance For Annex V Exemptions From The Obligation To RegistersrkadaliNo ratings yet
- Directive 2000/53/ec of The European Parliament and of The CouncilDocument9 pagesDirective 2000/53/ec of The European Parliament and of The CouncilVladimir MilasinovicNo ratings yet
- ACEA JAMA KAMA CLEPA Position Paper On RaP in The Context of The REACH Regulation 20140331-FinalDocument6 pagesACEA JAMA KAMA CLEPA Position Paper On RaP in The Context of The REACH Regulation 20140331-FinalsrkadaliNo ratings yet
- EU GuidelineDocument2 pagesEU GuidelinesrkadaliNo ratings yet
- Global Automotive Declarable Substance List (GADSL)Document42 pagesGlobal Automotive Declarable Substance List (GADSL)srkadaliNo ratings yet
- 2013 IMDS Flyer - 060313 PDFDocument1 page2013 IMDS Flyer - 060313 PDFJetesh DevgunNo ratings yet
- The Mole Concept and AtomsDocument86 pagesThe Mole Concept and AtomssrkadaliNo ratings yet
- Maths FundamentalsDocument80 pagesMaths FundamentalssrkadaliNo ratings yet
- 3 Blackbody RadiationDocument41 pages3 Blackbody RadiationsrkadaliNo ratings yet
- CNC Lab NotesDocument49 pagesCNC Lab NotessrkadaliNo ratings yet
- PFMEA Benefits: PreventingDocument3 pagesPFMEA Benefits: PreventingsrkadaliNo ratings yet
- 1st Inter Exams Timetable Ipem2014revisedtimetable - LetterDocument2 pages1st Inter Exams Timetable Ipem2014revisedtimetable - LettersrkadaliNo ratings yet
- Tamil AlphabetDocument84 pagesTamil Alphabetsrkadali100% (1)
- Customer Name: M/S ROOT INDUSTRIES Sizes (MM) : 1.20 X 103 X CF Product / Specification: CRCA STRIPSDocument1 pageCustomer Name: M/S ROOT INDUSTRIES Sizes (MM) : 1.20 X 103 X CF Product / Specification: CRCA STRIPSsrkadaliNo ratings yet
- Creating BioGas With Methane From The Food Waste Produced by The Talisay City Science High School StudentsDocument15 pagesCreating BioGas With Methane From The Food Waste Produced by The Talisay City Science High School StudentsRin Kiyoshi Hazumi-FranciscoNo ratings yet
- 6 VGP Routine Visual Inspection LogDocument1 page6 VGP Routine Visual Inspection Logyaroha777No ratings yet
- Research Laguna Municipal Solid Waste ProgramsDocument15 pagesResearch Laguna Municipal Solid Waste ProgramsSkambalahardarNo ratings yet
- 3i PaperDocument11 pages3i PaperCris Fredrich AndalizaNo ratings yet
- Klargester Septic - Tanks Brochure - UK - Nov2016Document6 pagesKlargester Septic - Tanks Brochure - UK - Nov2016Jim TsikasNo ratings yet
- MTBE Underground Tank DocumentDocument82 pagesMTBE Underground Tank DocumentChris SmithNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Bicycle Usage in India: An Environmental PerspectiveDocument11 pagesAnalysis of Bicycle Usage in India: An Environmental PerspectiveDesktop PCNo ratings yet
- Lynas EIA Assessment Report NTN April 13 Ok BaguihDocument30 pagesLynas EIA Assessment Report NTN April 13 Ok BaguihSyahmi Jaafar100% (1)
- Eia Report PDFDocument23 pagesEia Report PDFAzlyn SyafikahNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document41 pagesUnit 1suck xxxNo ratings yet
- India's Leading Cement Manufacturer ACC Company ProfileDocument2 pagesIndia's Leading Cement Manufacturer ACC Company Profilekaaviya6No ratings yet
- Project Waste NewDocument27 pagesProject Waste Newcristina de marananNo ratings yet
- Response, Cleanup, and Reporting Procedure: SpillsDocument5 pagesResponse, Cleanup, and Reporting Procedure: SpillsakilshaikhNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Waste: Special StuffDocument24 pagesHazardous Waste: Special StuffmohamedtsalehNo ratings yet
- Meta PhenoxybenzaldehydeDocument7 pagesMeta PhenoxybenzaldehydeKartik DhingraNo ratings yet
- Electric Cars and EnviroDocument5 pagesElectric Cars and EnviroC VNo ratings yet
- En07 LOPROX 1305 290909Document2 pagesEn07 LOPROX 1305 290909siddharthchoksiNo ratings yet
- WK 13 M.ed Yr 8 Making Good DecisionsDocument15 pagesWK 13 M.ed Yr 8 Making Good DecisionsMariyaNo ratings yet
- CH and N O Emissions From Waste Water Handling: CknowledgementsDocument14 pagesCH and N O Emissions From Waste Water Handling: CknowledgementsTaha OpedNo ratings yet
- People, Development & EnvironmentDocument14 pagesPeople, Development & EnvironmentSAFA's CreationNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Modelling Links PDFDocument5 pagesAtmospheric Modelling Links PDFArcangelo Di TanoNo ratings yet
- Eia of Wet Coffee - AdaneDocument40 pagesEia of Wet Coffee - AdaneHabtamu Wondyifraw100% (5)
- The Polluter Pays Principle:: A Proper Guide For Environmental PolicyDocument4 pagesThe Polluter Pays Principle:: A Proper Guide For Environmental PolicyHilmaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Indian Transport SystemDocument4 pagesAnalysis of Indian Transport SystemEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- E - Waste Management LPUDocument20 pagesE - Waste Management LPUUsman 1475% (16)
- Marine PollutionDocument27 pagesMarine Pollutionrinda78100% (1)
- Soal Bahasa Inggris Kelas 10 BelajaringgrisDocument9 pagesSoal Bahasa Inggris Kelas 10 BelajaringgrisEmma Novita Sari67% (3)
- M5 Post Task NSTPII Ocdol BSMT2A PDFDocument6 pagesM5 Post Task NSTPII Ocdol BSMT2A PDFPRECIOUS LOVE LAGRIMASNo ratings yet