Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Earth Science/Geology
Uploaded by
arionbothraCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To Earth Science/Geology
Uploaded by
arionbothraCopyright:
Available Formats
2/8/2015
Earth Science
or
Geology
February-2015
n.k.agarwal
ex-Director, GSI
1
2/8/2015
2/8/2015
Geology
In its Most Simple Meaning :
Geology is the Study of Earth
Geology is the History of Earth
How earth was formed ?
How old is earth ?
What is earth made up of ?
Interdisciplinary
Science
Why earth is called a unique planet ?
What are the biotic and a-biotic components of earth ?
What are Natural Resources ?
What is its Environment ?
How to manage Natural Resources ?
2/8/2015
Main Branches of Geology
1.Physical Geology
2.Geomorphology & Environmental Geology
3.Petrology
4.Stratigraphy
5.Paleontology
6.Structural Geology
7.Geochronology
8.Economic Geology Minerals Oil & Gas etc.
9.Seismo-Tectonics
10.Engineering Geology
11.Geochemistry
12.Geophysics etc.
2/8/2015
The Big Bang
~15 billion years ago
ENERGY and MASS TRANSFORMATION
Ma= Million Anum = 10x6
Ga= Giga Anum = 10x9
5
2/8/2015
2/8/2015
The Origin of the Earth
Making of Solar System
~15 billion years ago :
The Earth and the other 8 planets and the
Sun accreted at about the same time from a
vast cloud of dust and gas (nebula).
~5 billion years ago :
The nebula began to gravitationally contract,
began to rotate and flattened. Eventually, the
Sun ignited (fusion) and the newly formed
planets began to differentiate - heavier
elements and chemical components sank to
the center and rocky material formed the
crust. The newly formed planets and moons
released gas forming early atmospheres.
2/8/2015
Making of Solar System
2/8/2015
Solar System
Inner Planets
Asteroids
Outer Planets
2/8/2015
Earth From Outer Space
10
10
2/8/2015
Indian Sub-Continent from Outer Space
11
11
2/8/2015
Uttarakhand from Outer Space
12
12
2/8/2015
University of Petroleum and Energy Studies
13
13
2/8/2015
14
14
2/8/2015
What's the first
thing that you
notice about
our planet
when you see
this image?
Unique Planet - Earth
The Earth is composed
of several integrated
parts (spheres) that
interact with one
another:
Atmosphere
Hydrosphere
Solid earth (lithosphere)
Biosphere
15
15
2/8/2015
Unique Planet - Earth
Atmosphere:
The swirling clouds of the
atmosphere represent the
very thin blanket of air that
covers our planet. It is not
only the air we breathe, but
protects us from harmful
radiation from the sun.
Hydrosphere:
The global ocean is the
most prominent feature of
our (blue) planet. The
oceans cover ~71% of our
planet and represent 97% of
all the water on our planet.
16
16
2/8/2015
The Earth
System
Unique Planet - Earth
Solid Earth:
Represents the majority of
the Earth system. Most of
the Earth lies at inaccessible
depths.
Biosphere:
Includes all life forms on
Earth - concentrated on land,
water and air- Plants and
Animals.
17
17
2/8/2015
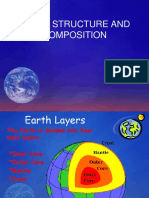
Inside the Earth
Crust thickness varies
From 5-70 km
Crust
6357 km at Poles
3486 km
1216 km
Mantle
0
Liquid
Core
Solid
Core
Density (gm/cm3)
Earth
5.517
Continental Crust
2.80
Oceanic Crust
2.90
Mantle
4.53
Outer Core
9.71
Inner Core
16.0
18
18
2/8/2015
Earth's Internal Structure
The Earth's interior is
characterized by a gradual
increase in temperature,
pressure and density with
depth.
At only 100 km depth, the
temp is ~1300C.
At the Earth's center, the
temperature is >6700C.
The pressure in the crust
increases ~280 bars for
every kilometer depth.
Polar Radius
~6357 km
Equatorial Radius ~6378 km
19
19
2/8/2015
Earth's Internal Structure (contd.)
Depth wise the Earth
consists of 3 major
divisions marked by
differences in chemical
composition Crust,
Mantle and Core
Crust:
Outermost rigid
layer - 2 types:
1. oceanic - 3-15 km
thick and is composed
of basalt (igneous).
Young (<180 million
years old).
2. continental - up to
70 km thick comprising
of a wide variety of rock
types Ranges from
young to old (>3.8
billion years old).
20
20
2/8/2015
Earth's Internal Structure (contd.)
Mantle: comprises
~82% of the Earth by
volume (~2900 km).
The mantle is
characterized denser
rocks and is able to flow
(plastically) at very slow
rates.
Core: composed of
iron, nickel and other
minor elements.
The outer core is liquid
capable of flow and
source of the Earth's
magnetic field (~2270km).
The inner core is solid
Fe-Ni (~1216km).
21
21
2/8/2015
EARTH A UNIQUE PLANET
Only Planet known to have Life Supporting
Conditions
ATMOSPHERE
BIOSPHERE
HYDROSPHERE
SOLID EARTH
22
22
2/8/2015
Biotic and A-Biotic Constituents
All Life Forms
Plants
Animals
Terrestrial
Land
Fresh Water
Marine
Rocks and Minerals
Soil
Water
Most of Solid Biotic
Constituents are
Made up of Minerals
and Rocks
Gases
23
23
2/8/2015
What is Mineral ?
It is a Natural Inorganic Solid Substance with a
Definite Range of Chemical Composition,
Atomic Structure and Measurable Properties.
Loose Definition of Mineral
What about Coal, Oil, Water
Coral etc.
?
24
24
2/8/2015
How Many Minerals are known ?
> 3500 are Identified
About 100 are Commonly found
Abundance of elements
in earths crust (% Wt.)
1
Oxygen
46.71
About 30 are important
rock forming minerals.
Silicon
27.69
Aluminum
8.07
Iron
5.05
Rock forming minerals
are composed of the most
abundant elements found
in the earths crust
Calcium
3.65
Sodium
2.75
Potassium
2.58
Magnesium
2.08
Titanium
0.62
10
Hydrogen
0.14
11
Phosphorus
0.13
12
Carbon
0.094
13
Manganese
0.09
14
Sulphur
0.002
15
Barium
0.050
Rest
0.244
Total
100.0
15 elements constitute 99.75 %
of Earths crust
25
25
2/8/2015
Rocks and Minerals Raw Material
Life Revolves around Rocks & Minerals
Needle
Soil
Forest
Tooth paste
Talcum Powder
Utensils
Direct Useable
Minerals & Rocks
Electronics
Appliances
Indirect Useable
Minerals & Rocks
Fertilizers
Agriculture - Soil
Energy Fuels (Coal, Oil & Gas)
Energy Nuclear
Ornaments and Gem Stones
Gold, Silver
Clay
Sand
Gravel, boulder
Lime
Gem Stones
Glass
Copper, Zinc, Lead, Steel
Borax, Sulphur
26
26
2/8/2015
Important Mineral Compositions
S.No. Composition
1
Oxides
Silicates
Carbonates
Phosphates
Sulphides
6
7
8
9
10
Nitrates
Borates
Hydrocarbon Compounds
Mixed
Native
27
27
2/8/2015
Common Rock Forming Minerals (simplified)
S.N.
Name
S.N.
Name
Quartz*
Montmorinillonite*
Orthoclase
Microcline
Albite etc.
10
Chromite
Hematite*
Magnetite*
Pyrolusite*
Psilomelane*
Muscovite, Biotite, Chlorite
11
Garnet
Calcite*
Dolomite*
Magnesite*
12
Epidote
Sillimanite*
Kyanite*
Amphiboles
13
Pyrite*
Chalcopyrite*
Pyrrhotite*
Pyroxenes
14
Peat, Lignite, Coal,
Olivine
15
Apatite*
Kaolin*
16
Gold**, Silver** etc.
28
* - Also forms mineral deposits ; ** - Occurs in small quantities in some rocks.
28
2/8/2015
Soils
Weathering and Erosion of Rocks
Generates Soils
Alluvium
Lateritic
Transported
Residual
Indo Gangetic Brahmaputra Plains
Terraces along valleys
Coastal Plains
Laterite, Bauxite, Clays etc.
Sand Rock, Silica Sand
29
29
2/8/2015
Natural Resources
Mineral Resources
Rocks & Minerals
Soil
Water Resources
Water Bodies
Ground Water
Plant & Animal Resources
Forest & Wild Life etc.
Renewable & Non-Renewable Resources
Finite Resources
30
30
2/8/2015
Environment
Total biotic & a-biotic components surrounding us
Mutual relation and interrelation
Sustainability
Man is Unique pest, parasite and predator
31
31
2/8/2015
Natural Resource Management
Quality of Life
Resilience
Over Exploitation
Conservation
New Resources & Replacement
Global Climate Change
Environment Protection
Sustainable Development
32
32
2/8/2015
Our Main Concern
To Understand Use of Geology in Oil &
Gas Exploration
or
To Understand What is Oil & Gas Exploration
All Oil & Gas Exploration and Exploitation
revolves around Geology
Understanding of Geology tells us where to
search for Oil & Gas and How to Exploit it
33
33
2/8/2015
What is Applied Geology
?
In most simple meaning : It is the
application of the knowledge of Geology
for the benefit of mankind Improving the
Quality of Life
34
34
2/8/2015
Summary :
This chapter helps you in understanding :
1)
What is Geology & Applied Geology?
2)
How Mineral Resources including Oil & Gas
related to the knowledge of Geology?
3)
Relation between Knowledge of Geology and
Sustainable Development
35
35
2/8/2015
36
36
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- UCE Spare Parts Price ListDocument4 pagesUCE Spare Parts Price ListarionbothraNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Eligible Models Under The Delhi Ev PolicyDocument11 pagesEligible Models Under The Delhi Ev Policyabhinay anandNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Vendor ItemsDocument2 pagesVendor ItemsarionbothraNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- ArihantDocument2 pagesArihantarionbothraNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- List of Dealers of Evs: Last Updated October 19, 2020Document7 pagesList of Dealers of Evs: Last Updated October 19, 2020arionbothraNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- 407 New Classic 350 PDFDocument2 pages407 New Classic 350 PDFarionbothraNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Parts List for Motorcycle Components with PricesDocument143 pagesParts List for Motorcycle Components with Pricesarionbothra100% (1)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Ganesh MandirDocument1 pageGanesh MandirarionbothraNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Burgreviewof Prosperityby Colin MayerDocument11 pagesBurgreviewof Prosperityby Colin MayerarionbothraNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- Chapter 4 (Continues) : Pipe NetworkDocument49 pagesChapter 4 (Continues) : Pipe NetworkarionbothraNo ratings yet
- Lect 2.2 Extr Intr EarthDocument54 pagesLect 2.2 Extr Intr EartharionbothraNo ratings yet
- Adsorption DehydratrionDocument27 pagesAdsorption DehydratrionarionbothraNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Lect 2.1 Origin Earth UPES Feb 4 2k15Document39 pagesLect 2.1 Origin Earth UPES Feb 4 2k15arionbothraNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Lect 2.1 Origin Earth UPES Feb 4 2k15Document39 pagesLect 2.1 Origin Earth UPES Feb 4 2k15arionbothraNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Astm F139Document5 pagesAstm F139diegomez84No ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Evacuated Tube SystemDocument2 pagesEvacuated Tube SystemAaron James RuedasNo ratings yet
- Metal DetectorDocument7 pagesMetal DetectorAlexNo ratings yet
- EXPERIMENT A2: Determination of The Formula of A HydrateDocument5 pagesEXPERIMENT A2: Determination of The Formula of A HydrateTessi SeokoloNo ratings yet
- 6 7 Group RabuDocument102 pages6 7 Group Rabuvita yantiNo ratings yet
- 13 - Chapter 3Document32 pages13 - Chapter 3Wahab Al-QaisiNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Fundamental Building Block: The CellDocument12 pagesThe Fundamental Building Block: The CellTanish JenaNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- What Are Sensors?Document5 pagesWhat Are Sensors?Osama Abdulrahman AlnemerNo ratings yet
- Drilling Engineering Fluid PropertiesDocument29 pagesDrilling Engineering Fluid PropertiesDeepak RanaNo ratings yet
- X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy TechniqueDocument74 pagesX-ray Absorption Spectroscopy TechniqueAnonymous hz3n3HK1RNNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Chapter Wise QuestionsDocument6 pagesChapter Wise QuestionsDr. B. Sree Giri Prasad100% (2)
- Lecture 2 - Cellulose Structure PDFDocument55 pagesLecture 2 - Cellulose Structure PDFpipers10No ratings yet
- Operating Manual: Eagleburgmann Mechanical Seal (M.S.)Document22 pagesOperating Manual: Eagleburgmann Mechanical Seal (M.S.)kiranNo ratings yet
- Emerging Pollutants in The EnvironmentDocument10 pagesEmerging Pollutants in The EnvironmentVita Maryam H.No ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- GUNK Liquid Wrench Rust Inhibitor LC9 - 6 SDSDocument14 pagesGUNK Liquid Wrench Rust Inhibitor LC9 - 6 SDSYoutube For EducationNo ratings yet
- Stainless Steel 1.4404 316lDocument3 pagesStainless Steel 1.4404 316lDilipSinghNo ratings yet
- Using psychrometric charts to analyze HVAC systemsDocument18 pagesUsing psychrometric charts to analyze HVAC systemsRockydel MontesNo ratings yet
- Elsanhouty Pharma Hold Time Study NotesDocument6 pagesElsanhouty Pharma Hold Time Study NotesHuỳnh Ngọc SángNo ratings yet
- Uniz Resin Spec PDFDocument11 pagesUniz Resin Spec PDFYerayNo ratings yet
- LIST OF TSD FACILITIESDocument18 pagesLIST OF TSD FACILITIESAmelia SantosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 MassMicroDocument25 pagesLecture 2 MassMicroPelin KınıkNo ratings yet
- Astm b680-1980Document2 pagesAstm b680-1980Yavuz Solmaz100% (1)
- He's Got The Whole World in His Hands: African-American Spiritual 120 120Document1 pageHe's Got The Whole World in His Hands: African-American Spiritual 120 120kcpsNo ratings yet
- Ardrox 8901w Aerosol Msds v1 5Document6 pagesArdrox 8901w Aerosol Msds v1 5arunkumarNo ratings yet
- Pipes, Tubes, Fittings, FlangesDocument121 pagesPipes, Tubes, Fittings, FlangesCarl Jones100% (2)
- E53-07 (Reapproved 2013) PDFDocument4 pagesE53-07 (Reapproved 2013) PDFearth metallurgical services pvt.ltd.No ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Structure of The EarthDocument21 pagesStructure of The EarthKaren DarilaNo ratings yet
- Toksikologi PDFDocument134 pagesToksikologi PDFPurwani Ni NyomanNo ratings yet
- OH&S Workplace Assessment ChecklistDocument9 pagesOH&S Workplace Assessment ChecklistAldrin ZlmdNo ratings yet
- Construction and Building Materials: Baojian Zhan, Chi Sun Poon, Qiong Liu, Shicong Kou, Caijun ShiDocument5 pagesConstruction and Building Materials: Baojian Zhan, Chi Sun Poon, Qiong Liu, Shicong Kou, Caijun ShiSara_ParkerNo ratings yet