Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PILE ANALYSIS (EN1997
Uploaded by
ikanyu79Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PILE ANALYSIS (EN1997
Uploaded by
ikanyu79Copyright:
Available Formats
Project
Job Ref.
Section
Sheet no./rev.
1
Calc. by
Date
Chk'd by
Date
App'd by
Date
20/3/2015
PILE ANALYSIS (EN1997)
PILE ANALYSIS
In accordance with EN 1997-1:2004 incorporating Corrigendum dated February 2009 and the Singapore national
annex
Tedds calculation version 1.0.00
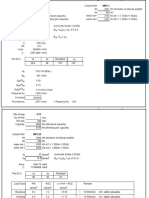
Pile details
Installation method
Driven
Shape
600 mm diameter
Length
L = 4000 mm
Material details
Material
Concrete
Concrete strength class
C25/30
Part. factor, concrete (EN1992-1-1 cl. 2.4.2.4(1))
C = 1.50
Coefficient cc (EN1992-1-1 cl. 3.1.6(1))
cc = 0.85
Characteristic compression cylinder strength
fck = 25 N/mm2
Design comp. strength (EN1992-1-1 cl. 3.1.6(1))
fcd = cc fck / C = 14.2 N/mm2
Mean value of cyl. strength (EN1992-1-1 Table 3.1) fcm = fck + 8 MPa = 33.0 N/mm2
Secant mod. of elasticity (EN1992-1-1 Table 3.1)
Ecm = 22000 MPa (fcm / 10 MPa)0.3 = 31.5 kN/mm2
Modulus of elasticity
E = Ecm = 31.5 kN/mm2
Geometric properties
Pile section depth
h = 600 mm
Bearing area
Abearing = h2 / 4 = 0.283 m2
Pile perimeter
Perimpile = h = 1.885 m
Moment of inertia
I = h4 / 64 = 636173 cm4
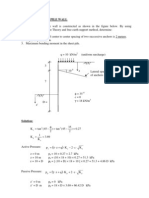
Fd
4000 mm
5000
Ftr,d
qsk1 = 100 kN/m2
qbk1 = 100 kN/m2
Stratum 2
Stratum 3
qski = Characteristic value, shaft resistance, qbki = Characteristic value, base
Project
Job Ref.
Section
Sheet no./rev.
2
Calc. by
Date
Chk'd by
Date
App'd by
Date
20/3/2015
Action details
Characteristic perm. unfav. action, compression
Gc,k,unfav = 100 kN
Characteristic perm. fav. action, compression
Gc,k,fav = 0 kN
Characteristic variable unfav. action, compression
Qc,k = 0 kN
Characteristic perm. unfav. action, tension
Gt,k,unfav = 0 kN
Characteristic perm. fav. action, tension
Gt,k,fav = 0 kN
Characteristic variable unfav. action, tension
Qt,k = 0 kN
Characteristic unfavourable perm. lateral action
Gtr,k,unfav = 0 kN
Characteristic favourable permanent lateral action
Gtr,k,fav = 0 kN
Characteristic variable lateral action
Qtr,k = 3 kN
Geotechnical partial and model factors:
Design approach 1:
Model factor on axial resistance
model = 1.00
Permanent unfavourable, A1 (Table A.3)
G,unfav,A1 = 1.35
Permanent favourable, A1 (1)
G,fav,A1 = 1.00
Variable unfavourable, A1 (Table A.3)
Q,A1 = 1.50
Permanent unfavourable, A2 (Table A.3)
G,unfav,A2 = 1.00
Permanent favourable, A2 (Table A.3)
G,fav,A2 = 1.00
Variable unfavourable, A2 (Table A.3)
Q,A2 = 1.30
Characteristic axial resistance
Characteristic axial base resistance
Rbk = Abearing qbk = 28.3 kN
Characteristic axial shaft resistance per stratum
Stratum 1
Rsk1 = qsk1 Perimpile (L - Dstrata1) =754 kN
Characteristic total axial shaft resistance
Rsk = Rsk1 = 754 kN
Axial compressive resistance
Load combination 1: A1 + M1 + R1
Design compression action
Fc,d,C1 = G,unfav,A1 Gc,k,unfav - G,fav,A1 Gc,k,fav + Q,A1 Qc,k = 135 kN
Partial resistance factor, bearing (Table A.NA.6)
b,R1 = 1.00
Partial resistance factor, shaft (Table A.NA.6)
s,R1 = 1.00
Design compressive resistance
Rc,d,C1 = (Rbk / b,R1 + Rsk / s,R1) / model = 782.3 kN
Fc,d,C1 / R c,d,C1 = 0.173
PASS - Design compressive resistance exceeds design load
Load combination 2: A2 + M1 + R4
Design compression action
Fc,d,C2 = G,unfav,A2 Gc,k,unfav - G,fav,A2 Gc,k,fav + Q,A2 Qc,k = 100 kN
Partial resistance factor, bearing (Table A.NA.6)
b,R4 = 1.70
Partial resistance factor, shaft (Table A.NA.6)
s,R4 = 1.50
Design compressive resistance
Rc,d,C2 = (Rbk / b,R4 + Rsk / s,R4) / model = 519.3 kN
Fc,d,C2 / R c,d,C2 = 0.193
PASS - Design compressive resistance exceeds design load
Lateral analysis properties
Pile head fixity
Free
Eccentricity of applied action
eactual = 0 mm
Lateral action duration
Short-term
Project
Job Ref.
Section
Sheet no./rev.
3
Calc. by
Date
Chk'd by
Date
App'd by
Date
20/3/2015
Lateral stratum details
n
pozSi =
Overburden pressure,
' t
i 1
Stratum
Characteristic
stratai
Characteristic friction
Characteristic unit
Characteristic
cohesion,
angle,
weight of soil,
overburden pressure,
ci,k (kN/m2)
i,k (degrees)
i,k (kN/m3)
pozSi,k (kN/m2)
10
9.8
49
10
9.8
98
10
9.8
137.2
Load combination 1: A1 + M1 + R1
Partial factors:
Angle of shearing resistance (Table A.4)
',M1 = 1.00
Effective cohesion (Table A.4)
c',M1 = 1.00
Undrained shear strength (Table A.4)
cu,M1 = 1.00
Weight density (Table A.4)
,M1 = 1.00
Lateral resistance factor
tr,R1 = 1.00
Stratum
Design cohesion,
Design friction angle,
Design unit weight of
Design overburden
ci,d (kN/m2)
i,d (degrees)
soil,
pressure, pozSi,d
i,d (kN/m3)
(kN/m2)
10
9.8
49
10
9.8
98
10
9.8
137.2
Resisting soil is divided into 10 segments to determine lateral resistance
From iteration, assume depth of point of rotation
X = 3212 mm
Distance from lateral action to ground
e = eactual = 0 mm
Sum of moments about point of load application near zero
Mtr = MtrS1 + MtrS2 + MtrS3 + MtrS4 + MtrS5 + MtrS6 + MtrS7 + MtrS8 + MtrS9t
+ MtrS9b + MtrS10 = -0 kNm
Sum of moments about point of rotation
MX = MXS1 + MXS2 + MXS3 + MXS4 + MXS5 + MXS6 + MXS7 + MXS8 + MXS9t
+ MXS9b + MXS10 = 51.2 kNm
Calculated soil lateral resist. (Tomlinson Eqn 7.52) Rtr,calc = MX / (e + X) = 15.9 kN
Ftr,d,C1 = G,unfav,A1 Gtr,k,unfav - G,fav,A1 Gtr,k,fav + Q,A1 Qtr,k = 4.5 kN
Design lateral action
Rtr,d,C1 = Rtr,calc / tr,R1 = 15.9 kN
Design lateral resistance
Ftr,d,C1 / R tr,d,C1 = 0.282
PASS - Design lateral resistance exceeds lateral load
Load combination 2: A2 + M2 + R4
Partial factors:
Angle of shearing resistance (Table A.4)
',M2 = 1.25
Effective cohesion (Table A.4)
c',M2 = 1.25
Undrained shear strength (Table A.4)
cu,M2 = 1.40
Weight density (Table A.4)
,M2 = 1.00
tr,R4 = 1.00
Lateral resistance factor
Stratum
Design cohesion,
ci,d
(kN/m2)
Design friction angle,
Design unit weight of
Design overburden
i,d (degrees)
soil,
pressure, pozSi,d
Project
Job Ref.
Section
Sheet no./rev.
4
Calc. by
Date
Chk'd by
Date
App'd by
Date
20/3/2015
i,d (kN/m3)
(kN/m2)
49
9.8
9.8
98
9.8
137.2
Resisting soil is divided into 10 segments to determine lateral resistance
From iteration, assume depth of point of rotation
X = 3212 mm
Distance from lateral action to ground
e = eactual = 0 mm
Sum of moments about point of load application near zero
Mtr = MtrS1 + MtrS2 + MtrS3 + MtrS4 + MtrS5 + MtrS6 + MtrS7 + MtrS8 + MtrS9t
+ MtrS9b + MtrS10 = 0 kNm
Sum of moments about point of rotation
MX = MXS1 + MXS2 + MXS3 + MXS4 + MXS5 + MXS6 + MXS7 + MXS8 + MXS9t
+ MXS9b + MXS10 = 38.9 kNm
Calculated soil lateral resist. (Tomlinson Eqn 7.52) Rtr,calc = MX / (e + X) = 12.1 kN
Design lateral action
Design lateral resistance
Ftr,d,C2 = G,unfav,A2 Gtr,k,unfav - G,fav,A2 Gtr,k,fav + Q,A2 Qtr,k = 3.9 kN
Rtr,d,C2 = Rtr,calc / tr,R4 = 12.1 kN
Ftr,d,C2 / R tr,d,C2 = 0.322
PASS - Design lateral resistance exceeds lateral load
Lateral deflection analysis (Characteristic values)
Resisting soil is divided into 10 segments to determine lateral resistance
From iteration, assume depth of point of rotation
X = 3212 mm
Distance from lateral action to ground
e = eactual = 0 mm
Sum of moments about point of load application near zero
Mtr = MtrS1 + MtrS2 + MtrS3 + MtrS4 + MtrS5 + MtrS6 + MtrS7 + MtrS8 + MtrS9t
+ MtrS9b + MtrS10 = -0 kNm
Sum of moments about point of rotation
MX = MXS1 + MXS2 + MXS3 + MXS4 + MXS5 + MXS6 + MXS7 + MXS8 + MXS9t
+ MXS9b + MXS10 = 51.2 kNm
Calculated soil lateral resist. (Tomlinson Eqn 7.52) Rtr,calc = MX / (e + X) = 15.9 kN
Lateral deflection
Characteristic lateral action
Virtual point of fixity, from iteration
Ftr,k = Gtr,k,unfav - Gtr,k,fav + Qtr,k = 3 kN
Vzf = Rtr,calc - PLatS1 - PLatS2 - PLatS3 - PLatS4 - PLatS5 - R PLatS6 = 0 kN
zf = (5 + R) L / 10 = 2086 mm
Actual lateral deflection at top of pile
Lat = (Ftr,k (e + zf)3) / (3 E I) = 0.05 mm
Allowable lateral deflection
LatAllow = 25 mm
Lat / LatAllow = 0.002
PASS - Allowable lateral deflection exceeds actual lateral deflection
You might also like
- Pile CapacityDocument41 pagesPile CapacityChee Soon Lee100% (1)
- Box Culvert Calculation As Per BD3101Document21 pagesBox Culvert Calculation As Per BD3101Pilippenge Asanka Iraj LaknathaNo ratings yet
- Bored Pile - Estimated Pile Length & Capacity: RB6191-DASHDocument6 pagesBored Pile - Estimated Pile Length & Capacity: RB6191-DASHHoihogo HoiNo ratings yet
- GeoTechnical Design of PileDocument2 pagesGeoTechnical Design of PileSabbir Siddique100% (1)
- Retaining Wall Euro CodeDocument7 pagesRetaining Wall Euro CodeKelvin Lau100% (1)
- Basement Wall Rev1Document9 pagesBasement Wall Rev1Tee Bun Pin0% (1)
- Kda - Factory Ii (Gen - Trias, Cavite) Design of MicropilesDocument4 pagesKda - Factory Ii (Gen - Trias, Cavite) Design of MicropilesRoda Cadiz100% (4)
- Design of Ground Anchors For ClaysDocument1 pageDesign of Ground Anchors For ClaysMUHAMMAD ALINo ratings yet
- Sheet Pile CapacityDocument1 pageSheet Pile CapacityHamza NadeemNo ratings yet
- Design of Bored Pile at Abut A & BDocument10 pagesDesign of Bored Pile at Abut A & BLenielle AmatosaNo ratings yet
- Rectangular 2nd Pile Arrangement for Badak Field, East KalimantanDocument7 pagesRectangular 2nd Pile Arrangement for Badak Field, East KalimantanbonnicoNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Lateral Capacity by Evan and Duncan AnalysisDocument12 pagesEstimation of Lateral Capacity by Evan and Duncan AnalysisPriodeep ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Soil Modulus of ElasticityDocument31 pagesSoil Modulus of ElasticityChainun TaidamrongNo ratings yet
- Lateral Loads On PilesDocument5 pagesLateral Loads On Pilesandyhr100% (1)
- Pad Footing Analysis and Design (Bs8110-1:1997)Document6 pagesPad Footing Analysis and Design (Bs8110-1:1997)ikanyu79No ratings yet
- Compression Test Pile (Debond 12m)Document3 pagesCompression Test Pile (Debond 12m)Anonymous S7Cq7ZDgPNo ratings yet
- Design of Slab (Two Way)Document9 pagesDesign of Slab (Two Way)shivshankar kushwahaNo ratings yet
- Ground Anchor DesignDocument4 pagesGround Anchor DesignVardhanNo ratings yet
- Bearing Capacity of Shallow Foundation Latest (Edit For Report-Wisnu)Document101 pagesBearing Capacity of Shallow Foundation Latest (Edit For Report-Wisnu)Agus SumarsonoNo ratings yet
- Circular Column Design - MPA-ECDocument1 pageCircular Column Design - MPA-ECmayphyoNo ratings yet
- Pile SpringDocument6 pagesPile Springkaleswara_tellakula100% (2)
- Calculations by Yg Plot 55 & 56 01.02.23Document63 pagesCalculations by Yg Plot 55 & 56 01.02.23Shanil BussooaNo ratings yet
- Brinch Hansen Lateral CapacityDocument18 pagesBrinch Hansen Lateral CapacityDhimas Surya NegaraNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Pile Bearing CapacityDocument3 pagesCalculation of Pile Bearing Capacityhayder1974No ratings yet
- PILE Analysis - Design 1.4Document99 pagesPILE Analysis - Design 1.4HanafiahHamzahNo ratings yet
- Design - BorepileDocument10 pagesDesign - BorepileSumedha MayadunnaNo ratings yet
- Boredpile CapacityDocument14 pagesBoredpile CapacityMar Martillano100% (1)
- Anchorage Length CalculationDocument5 pagesAnchorage Length Calculationstavros_stergNo ratings yet
- Pile DesignDocument17 pagesPile DesignTuan Syed100% (4)
- Pile Capacity SettlementDocument10 pagesPile Capacity SettlementDhimas Surya NegaraNo ratings yet
- Strut Waler Connection Design TemplateDocument1 pageStrut Waler Connection Design TemplateArjun Raja100% (1)
- Anchored Sheet Pile WallDocument10 pagesAnchored Sheet Pile Wall12151973No ratings yet
- Pile Design Tables To EC7Document4 pagesPile Design Tables To EC7Zaky MessengerNo ratings yet
- Pile Foundation Concrete Column DesignDocument27 pagesPile Foundation Concrete Column DesignSaid FauzieNo ratings yet
- Pile Cap ACI - EC2-20161217Document27 pagesPile Cap ACI - EC2-20161217mongkol_1001100% (1)
- Cantilever Sheet Pile Wall SolutionDocument20 pagesCantilever Sheet Pile Wall SolutionAlfredo A LopezNo ratings yet
- Spreadsheets To BS 8110etc: Advisory Group Grid Line 1 RC 24-Feb-2019 101 CHG - R68Document11 pagesSpreadsheets To BS 8110etc: Advisory Group Grid Line 1 RC 24-Feb-2019 101 CHG - R68Gertjan DuniceriNo ratings yet
- 3.3.1 Retaining WallDocument31 pages3.3.1 Retaining WallNeil SonNo ratings yet
- Pile Group:: Piling Works For Bukit Batok N4C18 To C21 468A Pile Ecentricity Calculation G22Document2 pagesPile Group:: Piling Works For Bukit Batok N4C18 To C21 468A Pile Ecentricity Calculation G22lattmdy100% (3)
- Lateral Pile Capacity - BromsDocument2 pagesLateral Pile Capacity - Bromscalky117100% (1)
- Kentledge Design SpreadsheetDocument16 pagesKentledge Design Spreadsheethabibur Rahman Khan100% (1)
- Mathcad - Concrete FootingDocument5 pagesMathcad - Concrete FootingtestvietnamNo ratings yet
- Design of Toe Wall PDFDocument15 pagesDesign of Toe Wall PDFaselabambarandageNo ratings yet
- Meyerhof Method - Pile CapacityDocument2 pagesMeyerhof Method - Pile CapacityTee Bun Pin77% (26)
- Wall Geometry SEO Optimized TitleDocument8 pagesWall Geometry SEO Optimized TitleDadi YashwantNo ratings yet
- Pile Design CalculationDocument7 pagesPile Design Calculationhabibur Rahman KhanNo ratings yet
- EC2 Beam DesignDocument4 pagesEC2 Beam Designikanyu79No ratings yet
- Load Combination EurocodeDocument23 pagesLoad Combination EurocodelucianduNo ratings yet
- 2.5. Settlement 2.5. 1 Consolidation SettlementDocument10 pages2.5. Settlement 2.5. 1 Consolidation SettlementTaufik GunawanNo ratings yet
- Pile DesignDocument3 pagesPile Designalinawaz91100% (9)
- Pile Analysis (EN1997)Document2 pagesPile Analysis (EN1997)rshyamsNo ratings yet
- Pad Foundation Example TeddsDocument7 pagesPad Foundation Example TeddsWei Hong TehNo ratings yet
- RC Beam Design To EC2Document3 pagesRC Beam Design To EC2suman_civilNo ratings yet
- Abutment Worked ExampleDocument9 pagesAbutment Worked ExampleKenaia Adeleye100% (2)
- Timber Examples - TeddsDocument19 pagesTimber Examples - TeddsTom KwoNo ratings yet
- BeamDocument10 pagesBeamdoggNo ratings yet
- Substation Design ExampleDocument14 pagesSubstation Design ExampleLeonichevNo ratings yet
- Concrete Industrial Ground Floor Slab (TR34)Document3 pagesConcrete Industrial Ground Floor Slab (TR34)David Thomson100% (5)
- RC box culvert design calculationsDocument15 pagesRC box culvert design calculationsYoshua Yang62% (21)
- RISA-3D Report DataDocument4 pagesRISA-3D Report DatagertkroonNo ratings yet
- Hollow Section Connection Using BoltDocument4 pagesHollow Section Connection Using Boltikanyu79No ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Designers Handbook 10th Edition Reynolds Steedman 2 Part PrintDocument7 pagesReinforced Concrete Designers Handbook 10th Edition Reynolds Steedman 2 Part Printikanyu79No ratings yet
- Railing DesignDocument3 pagesRailing Designikanyu79No ratings yet
- Connection Design: UB To UB ConnectionDocument4 pagesConnection Design: UB To UB Connectionikanyu79No ratings yet
- Column Base DesignDocument2 pagesColumn Base Designikanyu79No ratings yet
- Timber Racking DesignDocument6 pagesTimber Racking Designikanyu79No ratings yet
- Beam AnalysisDocument2 pagesBeam Analysisikanyu79No ratings yet
- Wind Load Reaction Force Due To Wind Action From Stack Acting On The Fan DeckDocument3 pagesWind Load Reaction Force Due To Wind Action From Stack Acting On The Fan Deckikanyu79No ratings yet
- Wind Pressure on LouversDocument2 pagesWind Pressure on Louversikanyu79No ratings yet
- Splice Joint Design To EurocodeDocument3 pagesSplice Joint Design To Eurocodeikanyu79No ratings yet
- TG1-Side 20170829Document4 pagesTG1-Side 20170829ikanyu79No ratings yet
- One Way Spanning Slab Design CalculationDocument4 pagesOne Way Spanning Slab Design Calculationikanyu79No ratings yet
- Punching Shear ExampleDocument3 pagesPunching Shear Exampleikanyu7950% (2)
- Glulam - Service Class 1Document3 pagesGlulam - Service Class 1ikanyu79No ratings yet
- STR & GEO bearing capacity BH1Document2 pagesSTR & GEO bearing capacity BH1ikanyu79No ratings yet
- Equal Angle Design: Distance of Centre of GravityDocument4 pagesEqual Angle Design: Distance of Centre of Gravityikanyu79No ratings yet
- RC Beam Design Calculation SheetDocument3 pagesRC Beam Design Calculation Sheetikanyu79100% (1)
- Bolted Cover Plate Splice Connection B1Document4 pagesBolted Cover Plate Splice Connection B1ikanyu79No ratings yet
- Singapore Standards Singapore StandardsDocument2 pagesSingapore Standards Singapore Standardsikanyu79No ratings yet
- EC2 Continuous Beam DesignDocument14 pagesEC2 Continuous Beam Designikanyu79No ratings yet
- Pad Footing Analysis and Design (Bs8110-1:1997)Document6 pagesPad Footing Analysis and Design (Bs8110-1:1997)ikanyu79No ratings yet
- Restrained Beams HandoutDocument2 pagesRestrained Beams Handoutikanyu79No ratings yet
- EC2 Beam DesignDocument4 pagesEC2 Beam Designikanyu79No ratings yet
- Single-Span Beam Analysis: Input Data: Beam DataDocument1 pageSingle-Span Beam Analysis: Input Data: Beam Dataikanyu79No ratings yet
- Cold Form Strut DesignDocument5 pagesCold Form Strut Designikanyu79No ratings yet
- Aluminium DesignDocument9 pagesAluminium Designikanyu79No ratings yet
- Colded Form Design BS5950Document5 pagesColded Form Design BS5950ikanyu79No ratings yet
- CV6311 Shear Strength Lect2 2012Document53 pagesCV6311 Shear Strength Lect2 2012ikanyu79No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 (EC4 Version)Document67 pagesLecture 4 (EC4 Version)ikanyu79100% (1)
- Heat Tech PresentationDocument49 pagesHeat Tech Presentationquality.sarthakautoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 - PVT Behaviour of FluidsDocument8 pagesChapter 03 - PVT Behaviour of FluidsAlok kumarNo ratings yet
- Akulon K222-D: Property DataDocument2 pagesAkulon K222-D: Property DataDiegoTierradentroNo ratings yet
- Density Functional Theory Investigations of Bismuth VanadateDocument7 pagesDensity Functional Theory Investigations of Bismuth VanadateNurSalahuddinNo ratings yet
- Facile Method of Prpeare Lotus-Leaf Like SHyrophobic PVC FilmDocument6 pagesFacile Method of Prpeare Lotus-Leaf Like SHyrophobic PVC FilmNiroshanNo ratings yet
- Research On Testing Method of Resin Sand High Temperature Compressive StrengthDocument7 pagesResearch On Testing Method of Resin Sand High Temperature Compressive StrengthTalha Nibras AliNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of Glass: Elastic Modulus and Microhardness Strength and Toughness (Chapter 18)Document130 pagesMechanical Properties of Glass: Elastic Modulus and Microhardness Strength and Toughness (Chapter 18)Santiago MolinaNo ratings yet
- Answers Sheet (II) - MergedDocument44 pagesAnswers Sheet (II) - Mergedmarwankh305No ratings yet
- High Temp Furnace Bottom Loading Ceramics MetalsDocument4 pagesHigh Temp Furnace Bottom Loading Ceramics MetalsDekanat FizfakNo ratings yet
- Intro Hardness PDFDocument2 pagesIntro Hardness PDFCali Tamagnini100% (1)
- Structural Concrete - 2013 - Di Prisco - Fibre Reinforced Concrete in Fib Model Code 2010 Principles Models and TestDocument20 pagesStructural Concrete - 2013 - Di Prisco - Fibre Reinforced Concrete in Fib Model Code 2010 Principles Models and TestLeonardoNo ratings yet
- Ae6020 01Document68 pagesAe6020 01Rami KchaouNo ratings yet
- Thesis FormatDocument18 pagesThesis Formatআবির হাসানNo ratings yet
- Broadband Metamaterials in ElectromagneticsDocument399 pagesBroadband Metamaterials in ElectromagneticsFarhad AzadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Fatigue Failure TheoriesDocument32 pagesChapter 3 Fatigue Failure Theoriesmailsk123No ratings yet
- CH 14 Slides 10th EdDocument102 pagesCH 14 Slides 10th EdNutchanon UdchachonNo ratings yet
- Science10Q2 TestBankDocument8 pagesScience10Q2 TestBankCrisante MaruquinNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Parts-6253Document3 pagesUnderstanding The Parts-6253Kumar S pNo ratings yet
- 4.16. Contact FrictionDocument4 pages4.16. Contact FrictionConan EdogawaNo ratings yet
- adhesive used in storage battery systemDocument24 pagesadhesive used in storage battery systemjasonguo901No ratings yet
- Anticorrosive Rubber Lining 2017Document6 pagesAnticorrosive Rubber Lining 2017Ebrahim MohamadikhahNo ratings yet
- 364 - CE8402 Strength of Materials II (SOM 2) - Question BankDocument19 pages364 - CE8402 Strength of Materials II (SOM 2) - Question BankPRASANTHNo ratings yet
- Working Stresses and Failure TheoriesDocument108 pagesWorking Stresses and Failure TheoriesVIFerrata100% (1)
- Novel Integration of Perovskite Solar Cell and Supercapacitor Based On Carbon Electrode For Hybridizing Energy Conversion and StorageDocument8 pagesNovel Integration of Perovskite Solar Cell and Supercapacitor Based On Carbon Electrode For Hybridizing Energy Conversion and StorageAngel Manuel Gómez CoronelNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Characterization of Dental Materials and Its Application in Orthodontics - A ReviewDocument7 pagesMicroscopic Characterization of Dental Materials and Its Application in Orthodontics - A ReviewInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- 2023 2024 Sanwa enDocument27 pages2023 2024 Sanwa enleo14pochNo ratings yet
- Burial of Pipes in OLGADocument2 pagesBurial of Pipes in OLGAVictor YuzhaninNo ratings yet
- GP 1301 Technical Data SheetDocument1 pageGP 1301 Technical Data SheetAPEX SONNo ratings yet
- BS Iso 20975-2-2018Document22 pagesBS Iso 20975-2-2018Shehrije BejtaNo ratings yet