Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Design Criteria for Hunter Soil and Waste Systems
Uploaded by
fayasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Design Criteria for Hunter Soil and Waste Systems
Uploaded by
fayasCopyright:
Available Formats
3.
00
DESIGN CRITERIA
Hunter Soil and Waste Systems
3.01
3.02
3.03
3.04
3.05
3.06
3.07
3.08
3.09
3.10
3.11
3.12
3.13
3.14
3.15
3.16
3.17
Design Criteria
Hunter Plumbers Bits
Depths of water seal in traps
Pipework and sizing
Branch Connections to Stacks
Ventilation of Discharge Stack
Air Admittance Valve
Air Admittance Valve BBA
Specification
Ventilation of Soil & Waste
Stub Stack
Boss Connections
Waste Manifold
WC Connections
Drain Connector Flexible
Waste Adaptor
Access
Gullies
Overflow Discharge
3.00
Design Criteria
3.01 DESIGN CRITERIA
All sanitary pipework and drainage installations must
satisfy Part H1 of the approved documents to the
England, Wales and Northern Ireland Building
Regulations 1991 and 1994 respectively. Also the
Building Standards (Scotland) amendment regulations
1990. These requirements can also be met by
following the relevant recommendations of BS EN
12056:2000 which contains information on
performance rates and discharge levels from sanitary
appliance including, recommendations for design,
testing, installation, and maintenance for all above
ground non-pressure pipework systems.
Regular consultation is essential between plumbing
engineers and architects through every stage of
design. This helps to ensure the positions of sanitary
appliances and ducts permitting efficient pipework
installation at minimum cost.
In addition, a well designed and installed sanitary
waste system will satisfy the following basic criteria:
Be of adequate capacity, with suitable pipe sizes
and gradients, to carry foul water to a suitable
drainage system for disposal.
Allow minimal risk of blockage or leakage and
have the provision for inspection and cleaning.
Stop foul air from entering the building during
normal working conditions (through use of
water seal traps).
Have ventilation to preserve water seal integrity.
Be securely fixed to cope with structure and
environmental conditions and changes.
3.02 HUNTER PLUMBERS BITS TRAPS
To comply with Approved Document H of the Building
Regulations all points of discharge into the drainage
system should be fitted with a water seal trap to
prevent foul air from the system entering the building.
Plus, the waste pipe diameter and gradient must be
selected to maintain a minimum of 25mm water seal in
the trap after an appliance has been used. However,
Hunter manufacture a range of resealing traps and
anti-siphon units that may be used where the integrity
of the water seal cannot be guaranteed. Hunter's traps
can be dismantled for inspection and maintenance,
which should be done on a regular basis to ensure the
trap functions correctly.
3.03 DEPTHS OF WATER SEAL IN TRAPS
BS EN 12056 - 2: 2000 requires that traps that
discharge to a soil stack have a 75mm water seal,
however, 50mm water seal traps can be fitted to
baths; shower trays and basins without plugs fitted
with spray taps. 38mm water seal traps can only be
used on ground floor flat bottomed appliances that
*
discharge to a back inlet gully trap. Traps with outlet
diameters greater than 50mm, should have a minimum
water seal depth of 50mm.
Appliance
Trap outlet size
(mm)
Wash Hand Basin
32
Bidet
32
Bar Well
32
Drinking Fountain
32
Sink
40
*Kitchen
Cleaners Sink
40
*
Waste Disposal (Domestic) 40
Bowl Urinal
40
Sanitary Towel Macerator 40
Dishwasher (Domestic)
40
Washing Machine
40
Bath
40
*
40
*Shower Tray
Waste Disposal (Industrial) 50
Urinal Stall (1-7 persons)
65
Water Closet
75-100
3.00
Design Criteria
3.04 PIPEWORK AND SIZING
SIZES OF BRANCH PIPES
Since June 2001 British Standard, Euro Norm BS EN 12056: 2000 Gravity Drainage Systems Inside Buildings has replaced BS
EN12056-2:2000 as the standard governing the installation of above ground pipework. The United Kingdoms sanitary
pipework system of single stack layouts requiring swept entry on equal branch junctions and our method of designing ranch
waste pipes running full are included in the new standard, listed as System III and in the National Annex of part two. The
national annex will allow the UK to continue to design and install sanitary pipework with only some minor alterations from our
previous standard. Amendments to Par H of the Building Regulations that come into force in April 2002 will bring it in line with
the new British Standards.
Pipes serving a single appliance should have the same diameter as the appliance trap (see table on previous page). However by
increasing the pipe diameter the length of the unventilated waste can be lengthened. Where the larger branch pipe is used the
trap diameter is not increased but 50mm of the smaller pipe is used before increasing the pipe size. To prevent the need for
additional ventilation of the pipework the pipe lengths are restricted as shown in the following DESIGN OF BRANCH
DISCHARGE PIPES chart, the UNVENTILATED BRANCH CONNECTION TO STACK diagram, and the DESIGN CURVE FOR
BASIN WASTE PIPES diagram. Further details can be found in Approved Document H and BS EN 12056-2: 2000.
DISCHARGE UNIT METHOD
A numerical value is assigned to each sanitary appliance to express its load producing property. he unit values of all sanitary
appliances discharging into the discharge stack and internal drainage are calculated to find the pipe diameter by the method
given in the British Standard.
DESIGN OF BRANCH DISCHARGE PIPES
Unventilated branches highlighted in Grey (Bold) , branches requiring ventilation marked in Black
Appliance
No. of
appliances
Trap size mm
and trap type
Branch dia.
Max. length of
branch in m
Max. No. of
bends
Action to be
guarded
against
Trap type
Branch
Gradient in
mm/m
Wash Basin
or Bidet
1
1
1
32P
32P
32P
32
40
32
1.7
3.0
3.0
A
2A
2A
EX SS
EX SS
EX SS
22
18-45
18min
Up
to 4
5
32P
50
4.0
NONE
EX IS SS
TB
TB
R AV
ASU
TB
32P
50
7.0
EX IS SS
18-45
10
32P
50
10.0
A NL
EX IS SS
18-45
40P or S
40
A NL
EX SS
40P
40
3.0
L
3.0
TB
R AV
ASU
TB
AV
ASU
TB
A NL
EX
18-45
1
2-8
8+
1
NL
1
100P or S
100P or S
100P or S
40P or S
40P or S
60P or S
110
110
110
40
50
60
6.0LL
15.0
NL
3 SAP
SAP
3 SAP
A NL
2A
A NL
A NL
A
A NL
EX
EX IS
EX
AAV
T
T
T
18min
9-90
min9
18-90
18-90
18-90
50P or S
50
3 SAP
EX
18-90
Shower, Bath,
Sink
Domestic Washing
Machine or
Dishwasher
WC
Bowl Urinal
Slab Urinal
for Max 7 People
Trough Urinal
NOTES:
A: Only use swept bends or branches
AAV: Air admittance Valve
EX: Excessive deposits
IS: Induced siphonage
LL: Longer branches are allowed in BS EN 12056-2:2000
SAP: As short as practicable to limit excessive deposits
18-45
18-90
ASU: Ant-siphon unit
AV: Anti-vacuum trap
B: Bottle trap
L: Longer branches are allowed which may result in noisier discharge and blockages
NL: No limit
R: Resealing trap
SS: Self-siphonage
T: Tubular trap
3.00
Design Criteria
3.04 PIPEWORK AND SIZING CONT-
UNVENTED BRANCH CONNECTIONS TO STACK
3m max for 40 mm pipe
*4 m max for 50 mm pipe
*3 m max for 40 mm pipe
Slope between 18 to 90 mm/m
Slope (see graph below)
Sink 3m max for 40 mm pipe
*4 m max for 50 mm pipe
Slope between 18 to 90mm/m
1.7 m max for 32 mm pipe
6 m max for single WC
Washbasin
Slope 18 mm/m min
WC
Bath
Note: *Where the larger branch pipe sizes are used the diameter of the trap
is not increased but the tail of the trap should be lengthened by 50 mm
before increasing the diameter.
BRANCH VENTILATION PIPES
Vent pipe connection above
spillover level
Spillover
750 mm max
level
Discharge
pipe
DESIGN CURVE FOR 32 mm
UNVENTED WASH BASIN WASTE PIPES
3.00
Design Criteria
3.05 BRANCH CONNECTIONS TO STACKS
3.06 VENTILATION OF DISCHARGE STACK
SINGLE STACK SYSTEM (SYSTEM III)
Building regulations and code of practice requirements
1.The distance between the lowest branch connection to
the discharge stack and the invert of the bend at the foot
of the stack should not be less than the table below:
LOW RISE
up to 3 storeys
450 mm
MULTI-STOREY
up to 5 storeys
Over 5 storeys
Over 20 storeys
750 mm
Ground floor connections
should discharge direct to
drain or into their own stack.
Ventilation of the discharge stack is required to
prevent water seals in traps from being lost by
pressure which can develop in the system, allowing
foul air to escape.
Separate ventilation of branch pipes will not be
needed if the length and slope of the branch does
not exceed those in the diagram below.
In cases where these figures are exceeded, the
branch pipe should be ventilated by a branch
ventilating pipe or by a Hunter anti-siphon unit.
Ground and first floor
connections should discharge
into their own stack.
2.A branch pipe should not discharge into a stack in
a way which could cause crossflow into any other
branch pipe.
The Hunter waste manifold has been developed precisely to
facilitate multi point connections to the stack,
eradicating the danger of crossflow even within the danger
zones marked by A and B on the soil stack below.
BRANCH CONNECTIONS TO STACKS
3m max for 40 mm pipe
*4 m max for 50 mm pipe
1.7 m max for 32 mm pipe
*3 m max for 40 mm pipe
Slope between 18 to 90 mm/m
Slope (see graph below)
Sink 3m max for 40 mm pipe
*4 m max for 50 mm pipe
Slope between 18 to 90mm/m
6 m max for single WC
Washbasin
Slope 18 mm/m min
WC
Bath
Note: *Where the larger branch pipe sizes are used the diameter of the trap
is not increased but the tail of the trap should be lengthened by 50 mm
before increasing the diameter.
BRANCH VENTILATION PIPES
WC
Lowest
connection
50 mm
parallel
junction
B
450 mm
min
mm
50
Offset
200 mm
Danger
zone
Drain
invert
Minimum
Radius 200mm
Key
A small similar sized connections not exceeding 65 mm and directly opposite
should be offset by 110mm on a 100 mm diameter stack 250 mm on a 150
mm diameter stack.
B Angled connection or 50 mm diameter parallel junction where a waste
branch directly opposite a WC would enter the stack within 200 mm below
the WC connection centreline.
For further information see section 3.11
Vent pipe connection above
spillover level
Spillover
750 mm max
level
Discharge
pipe
DESIGN CURVE FOR 32mm
UNVENTED WASH BASIN
WASTE PIPES
3.00
Design Criteria
3.07 AIR ADMITTANCE VALVE
AIR ADMITTANCE VALVES
Air admittance valves are designed to decrease the
number of suspended floor and roof penetrations required
to accommodate soil and ventilating stacks without
reducing the effectiveness or performance of the system.
They also reduce the quantity of components required to
complete a system.
Figure 1 Relief Valve
Cover
Moving seal
carrier
Star-lok
washer
Spring
retainer
Stainless
steel spring
Seal
Screw cap
Outer body
any soil stack. It should be situated in a non-habitable area
of the building, e.g. the roof space, where it will be easily
accessible and there is reduced risk of freezing. Care must
be taken to prevent contamination of moving parts. In the
event of accidental damage or vandalism once installed, the
cover can be unscrewed and the damaged part (s)
replaced.
The underground drain which serves a group of stacks to
which air admittance valves are fitted may require
additional ventilation. This will minimise the effects of
excessive back pressure if blockage should occur in a drain.
In determining the requirement for additional ventilation to
the underground drainage system the following rules can be
used for general guidance (see figure 9).
I. Up to and including four domestic dwellings up to 3 storeys
high, additional drain ventilation is not necessary.
Inner body
Positive pressure
(closed position)
110mm
soil pipe
Diaphragm
seal
2.Where an underground drain serves more than four such
dwellings which have soil systems fitted with an air admittance
valve, the drain must be vented as follows:
a.In the case of five to ten such dwellings, additional
conventional ventilation must be provided at the head of the
underground drainage system.
Negative pressure
(open position)
The valve contains a diaphragm which under light spring
pressure is normally held closed, containing foul air within
the system. When there is a discharge from an appliance, a
negative air pressure is produced in the system. This
pressure causes the diaphragm in the valve to lift from its
seat, allowing air to be drawn into the system: this intake
and the rapid equalisation of air pressure prevents foul air
escaping and prevents the water seals in traps from being
broken.
b.In the case of eleven to twenty such dwellings, additional
conventional ventilation must be provided at the head and
midpoint of the underground drainage system.
Vent Cowl
Soil stack without Hunter Relief Valve and
Hunter Anti-Siphon Valve
Weathering Slate
ROOF SPACE
ROOF TRUSS
Polystyrene tops can be fitted over the valve cover after
installation, providing insulation for the valve in use.
The valve incorporates a socket for solvent welding to 110mm
PVCu pipe to BS EN1329:2000. It can be fitted to sanitary
pipe work systems of buildings up to 5 storeys high.
Air admittance valves must be installed in a vertical position
above the flood level of the highest appliance connected to
Wash hand basin
32mm pipe
Bath
40mm pipe
3.00
Design Criteria
3.07 AIR ADMITTANCE VALVE CONTSoil stack with Hunter
Relief Valve and Hunter
Anti-Siphon Valve
Vent Cowl not required
Requirement: H1(1)
Foul water drainage
Comment:
The products will:
(1) provide adequate ventilation to
prevent the loss of water seals in
trapped appliances. See sections 6.1, 7.1
to 7.3, 7.8 to 7.10, 8.1 and 8.2 of
this Certificate.
(2) prevent foul air from entering the building.
See section 8.2 of this Certificate.
(3) enable access to the sanitary pipework for
cleaning blockages. See section 7.1 of this
Certificate.
(4) contribute to the ventilation of
underground drains. See sections 7.2 and
7.3 of this Certificate.
Weathering Slate not required
ROOF SPACE
Bends not required
Alternative positions for Hunter
Relief Valve
ROOF TRUSS
110mm Soil pipe not required
Requirement: Regulation 7 Materials and workmanship
The products are acceptable.
Comment:
Hunter Relief Valve
Wash hand basin
Hunter
Anti-Siphon Unit
Bath
2 The Building Standards (Scotland) Regulations 1990 (as amended)
In the opinion of the BBA, Hunter Air Admittance Valve and Hunter
Anti-Siphon Unit, if used in accordance with the provisions of
this Certificate, will satisfy the various Regulations as listed below.
32mm reducer
40mm tee
40mm pipe
3.08 AIR ADMITTANCE BBA SPECIFICATION
Regulation:
10
Fitness of materials
Standards:
B2.1.B2.2
Selection and use of materials, components
and other manufactured products
The products are acceptable.
Comment:
Regulation:
24
Drainage and sanitary facilities
PRODUCT
Standard:
M2.2
Drainage system
THIS CERTIFICATE REPLACES
CERTIFICATE No 83/1066 AND
RELATES TO THE HUNTER AIR
ADMITTANCE VALVE AND HUNTER
ANTI-SIPHON UNIT,
FOR ABOVE-GROUND
DRAINAGE SYSTEMS.
Comment:
The products are for use
within buildings in above
ground drainage
systems designed in
accordance with this
Certificate.
The valve and unit provide a
means of ventilation to the
drainage
system to prevent the loss of
water seals in traps and
consequent
release of foul air into the
building.
The drainage systems and the installation and use of the products
must be in accordance with the conditions set out in the Design Data
and installation parts of this Certificate.
1 The Building Regulations 1991 (as amended) (England
and Wales) 2002 Edition effective April 2002
The Secretary of State has agreed with the British Board of
Agrment the requirements of the Building Regulations to which air
admittance valves can contribute in achieving compliance. In the
opinion of the BBA, Hunter Air Admittance Valve and Hunter AntiSiphon Unit, used in accordance with the provisions of this Certificate,
will contribute to meeting the relevant requirements.
The products can meet the relevant
requirements of this Standard. See sections
6.1, 7.1 to 7.3, 7.8, 7.9, 8.1 and 8.2 of
this Certificate.
3 The Building Regulations (Northern Ireland) 1994 (as amended)
In the opinion of the BBA, Hunter Air Admittance Valve and Hunter
Anti-Siphon Unit, if used in accordance with the provisions of this
Certificate, will satisfy the various Building Regulations as listed below.
Regulation:
B2
Regulation:
Fitness of materials and workmanship
The products are acceptable.
Comment:
N2
Comment:
Drainage Systems
The valves provide adequate ventilation to
prevent the destruction of the water seals in
traps. See sections 6.1, 7.1 to 7.3, 7.8, 7.9,
8.1 and 8.2 of this Certificate.
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATION
4 Description
4.1 Hunters Air Admittance Valve comprises a two-part acrylonitrilebutadiene-styrene (ABS) inner body, seal carrier, spring retainer and
cover, an unplasticized polyvinyl chloride (PVCu) outer body and
screw cap, a neoprene diaphragm seal to BS 2752 :1990, a nitrile
seal washer to BS EN681:1996, a stainless steel spring and a
stainless steel Star-Lok washer (see Figure 1).
4.2 the Hunter Anti-Siphon Unit comprises an ABS seal carrier, cover,
body and screw cap, a nitrile diaphragm and washer to BS
EN681:1996, and a stainless steel Star-Lok washer (see Figure 2).
4.3 The Air Admittance Valve incorporates a socket for solvent welding
to 110mm PVCu soil pipe to BS EN1329:2000
3.00
Design Criteria
4.4 With the use or an appropriate adaptor to BS EN1329:2000 the
Hunter Air Admittance Valve can be connected to other
materials (eg cast iron).
4.5 The Anti-Siphon Units are available in five spigot outlet sizes to
connect to either 32 mm or 40 mm waste systems to BS EN1566/BS
EN1566:2000 or 32 mm, 40 mm and 50 mm metric waste pipe systems.
4.6 The ABS and PVCu parts are manufactured by injection moulding.
4.7 The diaphragm seals, sea washer, stainless steel Star-Lok washers
and springs are bought in.
4.8 Continuous quality control is carried out during manufacture and
assembly of the valves and units, including visual checks, checks on
dimensional accuracy, airtightness and stress relief. At hourly intervals the
ABS components of the Hunter Air Admittance Valve are assembled and
checked for freedom of rotation and flatness. The raw materials and
bought-in components are also subject to quality control checks.
Figure 2 Hunter Anti-Siphon Unit
All dimensions in millimetres
7 Drainage system design
7.1 The following above-ground drainage systems, designed in
accordance with BS EN 12056-2: 2000 and incorporating
Hunter valves and units, have been assessed as satisfactory:
(a) Domestic Buildings (eg bungalows, houses, multi-storey flats, halls
of residence) - satisfactory drainage systems incorporating the valves
and units are shown in Figures 3, 4 and 5.
(b) Non-domestic buildings (eg offices, factories, schools and other
types of public buildings) - satisfactory drainage systems incorporating
the valves and units are shown in Figures 6 and 7.
Note: In each case referred to, different combinations of sanitary
fittings are permissible, provided the siphonage effects occurring
within the systems are not made more onerous. Where individual
appliances are liable to self-siphonage (eg S-trap connections) venting
with an additional Hunter Anti-Siphon Unit may be required.
Figure 3 Typical domestic installation
61
Hunter Air Admittance Valve fitted above
flood level
Seal washer
22
Vent ducts
36
6.4 The valve and unit are for use in association with each other or
separately.
Spigot to
socket fitting
Diaphragm
seal
Sink
P-trap
Hunter
Anti-Siphon Unit
Wash basin
32mm
pipe
Bath
Star-lok
washer
P-trap
Variable spigot size
5 Delivery and site handling
5.1 The manufacturers emblem and the BBA identification mark
incorporating the number of this Certificate are printed on the cover
of each Hunter Air Admittance Valve.
5.2 The valves are individually packed in plastic bags or cardboard
boxes and should remain stored upright and so protected until they
are required for use.
5.3 The manufacturers emblem and the BBA identification mark
incorporating the number of this Certificate are printed on the cover
of each Hunter Anti-Siphon Unit.
5.4 The units are packed in a plastic bag. Each bag carries a label
bearing the BBA identification mark incorporating the number of this
Certificate.
DESIGN DATA
6 General
6.1 When used in accordance with the provisions of this
Certificate in above-ground drainage systems designed in
accordance with BS EN 12056-2: 2000, the valves:
(a) admit air under conditions of reduced pressure in the discharge
pipes and prevent water seals in traps from being drawn
(b) prevent the release of foul air from the drainage system, and
(c) contribute to the ventilation of the main drain to which the
discharge stack incorporating the valve is connected.
6.2 The Hunter Air Admittance Valve is for use on discharge stacks
serving up to five storeys.
6.3 The Hunter Anti-Siphon Unit is for use on branch discharge pipes.
110mm soil and vent pipe
40mm pipe
Notes:
The maximum distance of appliance traps from the discharge
stack must be in accordance with BS EN12056-2:2000,
paragraph 7.2.2 and figures 16, 18, 19 and 20. The separate
ventilation shown on the BS figures may be provided by a Hunter
Anti-Siphon Unit which must be within 750mm of the appliance trap
The size of the branch discharge pipework and the location of
appliances must be designed in accordance with
BS EN 12056-2: 2000
7.2 The Air Admittance Valve must be fitted in a vertical position
above the flood level of the appliance. being served.
7.3 To contribute to the ventilation of the underground drain and to
minimise the effects of excessive back pressures when a drain blockage.
occurs, the branch or main drain serving a stack or stacks fitted with
Hunter valves and units may require venting at point upstream of the
stack connection. For guidance the following should be noted
(see Figure 9):
(a) For up to and including four dwellings, 1, 2, or 3 storeys in height,
additional drain venting is not required. Where a drain serves more
than four such dwellings equipped with the valve or unit, the drain
should be vented according to the following rule, by either a
conventional open-topped ventilation or a discharge stack:
5 to 10 such dwellings - conventional ventilation to be provided at the
head of the system.
11 to 20 such dwellings - conventional ventilation to be provided at the
mid-point and at the head of the system.
(b) For multi-storey domestic dwellings (other than those referred to
above) and non-domestic buildings, conventional drain venting should
be provided if more than one such building, each equipped with the
valves and units, is connected to a common drain which is not itself
vented by means of a ventilation stack or a discharge stack not fitted
with a valve or unit.
3.00
Design Criteria
Figure 4 Typical layout using Hunter Air Admittance Valve and Hunter Anti-Syphon Unit on a 110mm branch line
Hunter Air Admittance Valve
or conventional open stack
Hunter Anti-Siphon Unit
Wash hand basin
32mm pipe
Bath
40mm pipe
Hunter Anti-Siphon Unit
Hunter Anti-Siphon Unit
Wash hand basin
Hunter Air
Admittance Valve
Wash hand basin
32mm pipe
32mm pipe
Bath
Bath
40mm pipe
40mm pipe
110mm pipe
110mm pipe
Notes:
Maximum of two groups of appliances per floor.
A group of appliances consists of one wc, one or two wash basin, one sink and one bath (and/or shower) and a washing machine.
The maximum distance of appliance traps from the discharge stack must be in accordance with BS EN 12056-2: 2000. The separate
ventilation shown on the BS figures may be provided By Hunter Anti-Siphon Unit which must be within 300 mm of the appliance trap.
The size of the branch discharge pipework and the location of appliances must be designed in accordance with BS EN 12056-2: 2000.
3.00
Design Criteria
Figure 5 Domestic discharge system
Hunter Anti-Siphon unit
32mm
pipe
Hunter Air Admittance Valve
Wash hand
basin
Sink
P-trap
Bath
40mm pipe
40mm pipe
maximum 5 floors
maximum 2 groups of
appliances per floor
Hunter Anti-Siphon unit
32mm
pipe
Wash hand
basin
Sink
P-trap
Bath
40mm pipe
40mm pipe
Long radius bend
Notes:
>110mm diameter
Maximum of two groups of appliances per floor.
A group of appliances consists of one wc, one wash basin, one sink and one Both (and/or shower).
The maximum distance of appliance traps from the discharge stack must be in accordance with BS EN 12056-2: 2000. The separate
ventilation shown on the BS figures may be provided by a Hunter Anti-Siphon Unit which must be within 300 mm of the appliance trap.
The size of branch discharge pipework and the location of appliances must be designed in accordance with BS EN 12056-2: 2000.
Figure 6 Commercial and public discharge system
40mm ASU
Up to 5 wash basins
Hunter Air Admittance Valve
Up to 5 WC connections
P-traps
50mm minimum
Typical P-trap installation
S-traps or P-traps
can be used
Maximum 5 floors
Up to 5 wash basins
Up to 5 WC connections
S-traps or P-traps
can be used
ASU
ASU
ASU
Typical S-trap installation
50mm minimum
110mm pipe
Notes:
160mm pipe
Valves to be fitted vertically.
If the valve is fitted inside a duct then the duct will require ventilation.
Branch discharge pipes to ranges of appliances must be designed in accordance with BS EN 12056-2: 2000. Where required,
branch pipe ventilation may be provided by the Hunter Anti-Siphon Unit.
3.00
Design Criteria
Figure 7 Permitted number of appliances in non-domestic buildings (eg offices, factories, schools and other types of
public buildings)
Hunter Air Admittance Valve
Hunter Anti-Siphon Unit
on each storey
2(1)
5(1)
5(3)
2(1)
5(1)
5(3)
2(1)
5(1)
5(3)
2(1)
5(1)
5(3)
2(1)
5(1)
Hunter Air
Admittance Valve
110mm dia pipe
110mm dia pipe
(i) 1 to 4 storeys
110mm dia pipe
(ii) 1 to 5 storeys
(iii) 1 to 5 storeys
Maximum 2 or 5 groups of appliances per floor (1 or 3 groups in congested circumstances)
Notes:
A group of appliances consists of one wc and one wash basin.
Congested circumstances are where the frequency of use of each appliance is approximately five minutes
Normal use in non-domestic buildings corresponds to frequencies of use of approximately ten minutes.
Hydraulic performance tests carried out in accordance with BS EN 12056-2: 2000, indicate that the installations shown
above are acceptable.
Figure 8 Typical installation of the Anti-Siphon Valve
Sanitary appliance
Hunter Anti-Siphon Unit
Solvent weld
Tee
Vacuum releases diaphragm - pressure neutralised
Plug of water flowing
full bore
Water level retained due to
Hunter Anti-Siphon Unit
921 2 tee
Constant
76mm seal
Negative pressure area
300mm max
distance centre
line of unit to
crown of trap
Bottle/tubular trap
3.00
Design Criteria
Figure 9 Examples of drain ventilation provisions
Notes:
Access arrangements shown are indicative only and may he varied to suit particular system layouts
The underground drain must be designed in accordance with BS EN 752: 1996
if the Branch drain is fitted with an intercepting trap before the connection to the main drain/sewer then a conventional open topped
ventilation discharge stack must be provided at the nearest point upstream of the intercepting trap
7.4 In installations other than as shown in Figure 9 stacks should not be
fitted with the valves when the connecting drain(s) are subject to periodic
surcharging or are fitted with intercepting traps. An open-topped
discharge stack or ventilating stack should be used in such cases.
7.5 The valve should be installed within the building, preferably in a nonhabitable space, such as a duct or roof, where there is no risk of freezing,
and where it is easily accessible but not subject to interference by
vandals.
7.6 If the valve is to be installed in, or in close proximity to, a habitable
space where noise of operation may cause a nuisance then consideration
must be given to the use of a suitable form of sound insulation.
7.7 To prevent self-siphonage, a connection to the Hunter Anti-Siphon Unit
is required within 300 mm of the trap (see Figure 8).
7.8 To prevent induced siphonage in a row of wash basins, a
Hunter Anti-Siphon Unit should be fitted near the end of the branch
remote from the discharge stack (see Figure 6).
7.9 The Anti-Siphon Unit must be fitted in a vertical position above the
pipe being ventilated.
7.10 Air admittance valves should not be used when the soil stack
provides the only ventilation to septic tanks or cesspools.
8 Effect on water seals
8.1 The valves will admit sufficient quantities of air into the stack
when they are subjected to a reduced pressure and thereby
prevent loss of the water seals in appliance traps.
8.2 Under conditions of increased pressure in the drainage system, each
valve will remain closed, thereby preventing the release of foul air into the
building.
8.3 A pressure increase sufficient to raise the level of the water seal or to
cause foul air to bubble up through the seal is an indication that a drain
blockage has occurred or that the system is being overloaded or otherwise
misused.
9 Durability
Hunter valves and anti-siphon units are - manufactured from
materials conventionally used in drainage systems. Repeated
opening and closing will not adversely affect the sealing or
operation of the valve. When used in the context of this Certificate the
product will not be subject to significant deterioration and will have a life
equivalent to that of the drainage system in which it is installed.
3.00
Design Criteria
INSTALLATION
10 Procedure
10.01 Installation must be carried out in accordance with the
manufacturers instructions for the products.
BS EN1329:2000/BS EN727:1996, EN 1055: 1996 Specification for
unplasticized PVC soil and ventilating pipes, fittings and accessories
Specification for P.P Waste Systems and Soil and Waste Discharge within
the building structure Chlorinated Poly (vinyl chloride (PVC-c)
BS EN1451:2000 and BS EN1566:2000, BS EN1566
10.2 The Hunter Air Admittance Valve must be fitted to the top of the
discharge stack above the over-spill level of the highest appliance. The
110mm diameter spigot tail valve may be push fitted into ring seal sockets
after applying Hunters lubricant to the spigot tail, or solvent welded into
PVCu sockets. The 110mm socket outlet is for solvent welding to PVCu
pipe.
BS EN 12056: 2000 Gravity drainage systems inside buildings
10.3 The Hunter Anti-Siphon Units (code Nos W150 and W151) may be
solvent welded into 32mm or 40mm ABS, PVC-c or PVCu waste fittings to
BS 5256, BS EN1566:2000, or BS EN 1329:2000, using solvent cement.
BS 6209 1982.
14 Conditions
The cementing procedure should follow the instructions on the Hunter
solvent cement label. The 32mm, 40mm and 50mm metric waste pipe
sizes may be jointed to polypropylene on thermoplastic systems, using the
methods described here.
BS 6209 : 1982 Specification for solvent cement for non-pressure
thermoplastics pipe systems
BS EN 752: 1998 Drain and sewer systems outside buildings
14.1 This Certificate:
(a) relates only to the product that is described, installed, used and
maintained or set out in this Certificate;
(b) is granted only to the company, firm or person identified on the front
cover no other company, firm or person may hold or claim any entitlement
to this Certificate;
10.4 Care must be taken in making solvent welded joints to prevent
contamination of the moving parts.
(c) has to be read, considered and used as a whole document - it may be
misleading and will be incomplete to be selective;
11 Maintenance
(d) is copyright of the BBA.
11.1 The Hunter Air Admittance Valve does not normally require
maintenance. However, in the event of accidental damage or vandalism
the cover can be unscrewed and the damaged component parts or the
complete assembly replaced.
14.2 References in this Certificate to any Act of Parliament, Regulation
made thereunder, Directive or Regulation of the European Union, Statutory
Instrument, Code of Practice, British Standard, manufacturers instructions or
similar publication shall be construed or references to such publication in the
form in which it was current at the date of this Certificate.
11.2 The Hunter Anti-Siphon Unit does not normally require maintenance.
However, in the event of misuse, accidental damage or vandalism the
cover can be removed and the diaphragm seal cleaned, or the complete
assembly replaced if necessary.
Technical Investigations
14.3 This Certificate will remain valid for an unlimited period provided that
the product and the manufacture and/or fabricating process(es) thereof:
(a) are maintained at or above the levels which have been assessed and
found to be satisfactory by the BBA;
The following is a summary of the technical investigations carried out on
the Hunter Air Admittance Valve and Hunter Anti-Siphon Unit.
(b) continue to be checked by the BBA or its agefits; and
12 Tests
14.4 In granting this Certificate, the BBA makes no representation as to:
Tests were carried out to determine:
(a) the presence of absence of any patent or similar rights subsisting in the
product or any other product;
effect of pressure cycling, performance in use an a stack when tested in
accordance with BS EN1055:1996, airtightness under normal operating
conditions, airtightness when tested to pressures of 40mm and 200mm
water gauge, airtightness at low positive pressure, reduced pressure
required to open the valve, watertightness under positive pressure, effect
on the seal depth of a bottle trap when fitted near an anti-siphon unit with
the discharge pipe running full, prevention of loss of trap seals due to
induced and self-siphonage, Vicat softening point to BS EN727:1994,
tensile strength, Shore hardness of diaphragm seals, dimension,
practicability of installation, load test on the spring, corrosion resistance of
materials, effects of impact drop test and correct functioning and effect of
repeated operation.
13 Other investigations
13.1 The manufacturing process was examined, including the methods
adopted for quality control, and details were obtained of the quality and
composition of materials used.
13.2 An examination was made of data on induced siphonage.
13.3 A user survey was carried out to evaluate the performance in use.
13.4 No failures of the product have been reported to the BBA.
13.5 An examination was made on airflow capacity.
Bibliography
BS EN681 Part 1 or 2:1996 Specification for elastomeric seals for joints in
pipework and pipelines
BS 2752 : 1990(1997) Specification for chloroprene rubber compounds
BS 2782 Methods of testing plastics
Part 1 Thermal properties
Determination of Vicat softening temperature of thermoplastics
(c) are reviewed by the BBA or and when it considers appropriate.
(b) the right of the Certificate holder to market, supply, install or maintain the
product; and
(c) the nature of individual installations of the product, including methods
and workmanship.
14.5 Any recommendations relating to the use or installation of this product
which are contained or referred to in this Certificate are the minimum
standards required to be met when the product is used. They do not purport
in any way to restate the requirements of the Health & Safety at Work Act
1974, or of any other statutory, common law or other duty which may exist
at the date of this Certificate or in the future; nor is conformity with such
recommendations to be taken as satisfying the requirements of the 1974 Act
or of any present or future statutory, common law or other duty of care. In
granting this Certificate, the BBA does not accept responsibility to any
person or body for any loss or damage, including personal injury, arising as
a direct or indirect result of the installation and use of this product.
In the opinion of the British Board of Agrment, Hunter Air Admittance Valve
and Hunter Anti-Siphon Unit are fit for their intended use provided they are
installed, used and maintained as set out in this Certificate. Certificate No
86/1737 is accordingly awarded to Hunter Plastics Ltd.
On behalf of the British Board of Agrment
Date of Second issue: 24th November 1998
DIRECTOR
Original Certificate issued to Hunter Building Products Ltd on 15th
September 1986. This amended version includes change of Certificate
holders name, addition of spigot connector to range, reference to revised
Building Regulations and associated text, revised British Standards and
Conditions of Certification, and addition of Bibliography.
3.00
Design Criteria
3.09 VENTILATION OF SOIL & WASTE SYSTEM
TRADITIONAL VENTILATION
Ventilation of a soil and waste system is necessary to
prevent water seals in traps being broken due to
negative pressure or pressure fluctuations within the
system. Broken seals permit foul air and smells to
escape from the system, contaminating the air in and
around the building. There are two ways of
ventilating a soil stack, either externally to the
atmosphere, or with an Air Admittance Valve sited in
a non-inhabited space within a building.
Venting cage or cover
allowing free air flow
900 mm
min
Less than 3 m
Discharge stack
Ventilating stack
Branch ventilating pipe
Door, window,
or other
opening into a
building
The termination of an externally vented system must
comply with the dimensional requirements illustrated
in the diagram on the right.
3.10 TYPICAL STUB STACK IN COMPLIANCE WITH BUILDING REGULATIONS
Pan Connector to suit WC outlet
1. If WC, to BS5503 and depending on layout,
Hunter S224, S221, S254, S251, or S267
WC connectors can be used.
2. If old type WC, to BS1213 the Hunter S231
and S248 WC connector and gasket should
be used.
Stub Stacks
A group of appliances may
be connected above ground
into a ventilated discharge
stack or into a drain via
an unventilated stub stack.
A stub stack consists of
a short length of 110mmdiameter pipe capped
off with an access fitting
(S667). Where one or more
stub stacks are connected
directly to an underground
drainage system, ventilation
must be provided via a vent
stack or soil and vent pipe at
the head of the drain. The
distance from the finished
floor level to the drain invert
must not exceed 1.3 metres.
While the highest connection
should be within 2 metres to
comply with Approved
Document H of the Building
Regulations 2002 Edition.
DS663 (871/2Rest Bend)
Note: The loading on a stub stack should not
exceed 5L/s.
Please note that there is a
variation
between
the
requirements of the Building
Regulations and Part 2 of BS
EN 1205.
3.00
Design Criteria
3.11 BOSS CONNECTIONS
VERSATILE AND SIMPLE TO INSTALL
To make life easy for the installer Hunters 82mm, 110mm and 160mm boss fittings are supplied with
either open or unopened bosses that are the same size. In addition, boss adaptors offer the simplest
waste to soil connections, whether using push-fit or solvent weld pipework. Unopened bosses may be
accessed using standard 48mm hole cutter.
HUNTERS EASY TO USE BOSS CONNECTIONS
32mm
40mm
50mm
CREATES PUSH-FIT CONNECTION PUSH-FIT PIPEWORK TO BSEN1451
W58
W59
S751
CREATES PUSH-FIT CONNECTION SOLVENT WELD PIPEWORK TO BS5255
W59
W58
CREATES SOLVENT WELD CONNECTION SOLVENT WELD PIPEWORK TO BS5255
W104
W106
S750
ANGLED OPTIONS FOR SOLVENT WELD PIPEWORK
S753
2.5
90
W104 + W111
W106 + W112
W725
3.00
Design Criteria
3.12 WASTE MANIFOLD
PREVENTION OF CROSS FLOW
In any soil and vent pipe the discharge from one branch pipe must not
be able to flow across and enter an opposing branch pipe connection.
A PVCu branch between 82mm and 160mm diameter has a restricted
area of 200mm as shown in diagram (a) whilst a small diameter branch
pipe up to 63mm has a restricted area dependent on the discharge
stack diameter. See table adjacent.
Branch diameter
82mm to 160mm
Section
Centre line of
opposed branch
not to be above
this point
PVC stack dia.
82
110
160
Height of restricted area
90
110
250
Small branch
diameter
63mm max.
Centre line of
opposed branch
not to be below
this point
200mm
RESTRICTED AREA FOR OPPOSING
SMALL DIA. BRANCH PIPES
Unopposed
connection
permissible in
this area
(See table above)
200mm
Section
Section
Plan
Plan
Plan
(a) Restricted connection area on stack
(b) Examples of permitted connections
(c) Opposing waste pipes
HUNTERS WASTE MANIFOLD IS DESIGNED TO PREVENT CROSS FLOW
Plumbing in the bathroom
or WC is made easier by
using the Hunter S200
Waste pipes may be
connected to the S200
above floor level using
any one of the four inlets
to suit site conditions.
The four waste inlets,
will permit connections
of extra pipework at a
later date.
The S200 will accept
waste pipes to BS EN1451
and BS EN1566:2000,
The S200 fits neatly against a wall or into a corner of the
room. The dimensions allow standard pipe or socket bracket to
be used to support pipework.
Should the need arise to gain access for rodding purposes, it
may be done via one of the inlets.
3.00
Design Criteria
HOW TO INSTALL A WC, BASIN AND BATH USING THE S200 WASTE MANIFOLD
Anti-Siphon Unit
Basin
For maximum distance see table below
Centre line of WC Pan outlet
to conform to BS5503
horizontal outlet (190mm)
Bath
NB. If the distance of the bath exceeds
3000mm 50mm Waste pipe must be used to
conform with building regulations H1 1991.
Connecting 110mm to the S200 is made in the normal
manner by use of the Hunter ring seal jointing
technique, i.e. lubricating pipe or branch spigot prior to
insertion.
To open the closed bosses on the S200;
Cut open the required connection ports using a fine
tooth saw.
For 50mm connections, solvent weld the W725
adaptor bends directly into the socket.
For 32mm connections use the W58 rubber boss
adaptor and either the P019 polypropylene spigot
tail bends to (BS EN 1451: 2000) or W111
MUPVC spigot tail bends to (BS EN 1566). The
W104 glued adaptor can only be used with
MUPVC spigot tail bends
For 40mm connections use the W59 Rubber boss
adaptor and either the P029 polypropylene spigot
tail bends to (BS EN 1451: 2000) or the W119
MUPVC spigot tail bends (BS EN 1566). The
W106 adaptor can only be used with MUPVC
spigot tail bends
WC
BATH
70mm
60mm
50mm
40mm
240mm
320mm
545mm
770mm
1700mm
1790mm
2340mm
2870mm
30mm
20mm
10mm
F/L
1000mm
1200mm
1365mm
1620mm
3270mm
3760mm
4800mm
5300mm
3.00
Design Criteria
WASTE MANIFOLD EXAMPLES FOR USE
S200
W151 W151
W718
Basins
W714
W718
Basins
W714
50mm
S214 or S246
S200
DS663
DS211
To Drain
PLAN
S200
PLAN
PO10/W78
Basin
32mm
32mm
PO20/W79
PO21/W81
40mm
Bath
Basin
40mm
Bath
3.00
Design Criteria
WASTE MANIFOLD EXAMPLES FOR USE
Basin
PLAN
ELEVATION A - A
32mm
110mm SVP
S254
110mm
40mm
40mm
40mm
S200
40mm
FFL
Bath
Kitchen
A
Basin
PLAN
ELEVATION B - B
32mm
External
110mm SVP
110mm
FFL
40mm
B
B
Bath
3.00
Design Criteria
3.13 WC CONNECTIONS
PRODUCT CODE S224
STRAIGHT PAN CONNECTOR
ALL PURPOSE TAIL
For use with BS5503 H/O pans.
May be used with PVCu, cast iron or
clayware pipes.
Ideal for refurbishment work.
Ideal for connecting to concealed pipework.
Smooth wipe clean finish.
Z=
Min
Max
150mm
250mm
Where dimension X exceeds 160mm use S224
in conjunction with S226 extension piece.
Measure between the pipe end and the pan spigot,
dimension X. Add on 90mm to allow for insertion
depths.
Remove the finned seal and mark a cut line
on the connector.
Cut the connector spigot squarely using a fine
toothed saw. Remove any burr.
Replace finned seal onto connector. Lubricate
finned seal using silicone lubricant.
Push connector into pipe ensuring it is fully home.
Lubricate pan spigot and install into connector.
3.00
Design Criteria
3.13 WC CONNECTIONS CONT-
WC FLOAT SYSTEM USING THE S253 VARIABLE WC CONNECTOR
SOIL STACK
S334
Branch
S312 + S253
*S750 may be solvent welded into
a side boss to allow for a 50mm
traditional ventilation pipe
(if required)
S312 + S253
WC
S312 + S253
WC
Minimum gradient on horizontal
float should be 1/2 or 9 mm/m
S312 + S253
WC
S312 + S253
WC
Note:
If solvent jointing is preferred use S292 instead of
S312 and S297 instead of S334
WC
S253 variable
WC connector
S312
branch
Back to wall closet
S253 variable
WC connector
S312 branch
Section
S246
Rodding eye
Close coupled closet
3.00
Design Criteria
3.13 WC CONNECTIONS CONT-
PRODUCT CODE S253 WC FLOAT SYSTEM USING THE S253 VARIABLE WC CONNECTOR CONT-
SOIL STACK
345
+/10mm
800mm
800mm
800mm
800mm
Float laid to fall of 1/2
(9mm drop/1 metre run)
WC connector to suit BS5503
horizontal outlet pan
WC
S217/220
90mm
WC Position
H (mm)
190mm
Up to +/-2 movement
on joint between branch
and WC connector
125 134 143 152 161
Approx angle of 18
WC connector
16
F.F.L.
*For pan centres less or greater than 800mm contact the technical department at Hunter Plastics Limited
13
11
3.00
Design Criteria
3.14 DRAIN CONNECTOR FLEXIBLE WASTE ADAPTOR
PRODUCT CODE DS25
The DS25 will accept two waste pipes of either 32mm or 40mm diameter. It is made from flexible EPDM
and manufactured with one inlet open and one closed. The closed inlet can be opened with a sharp knife.
The DS25 can be fitted into a socket by replacing the ring seal with it, or inside the bore of 110mm pipe,
see the illustration below.
Waste
pipe
DS25
110mm
socket
Ground floor
installations only
110mm
pipe
3.00
Design Criteria
3.15 ACCESS
ACCESS
Access to stacks are to be fitted above the over-spill level of the appliances to ensure ease of access as and when
it is required. All discharge pipework must be easily accessible and traceable access covers and cleaning eyes
should also be positioned to allow cleaning and maintenance equipment to be easily inserted into the pipework
and to permit cleaning and clearing of all parts of the system. Sanitary pipework systems should be capable of
being tested to ensure that the required performance is attained. Whilst adequate access should be provided to
enable these tests to be carried out.
3.16 GULLIES
GULLIES
Ground floor appliances that produce waste water only may discharge into a gully. Waste pipes from such
appliances should terminate above the gullys water seal and below the gully grid.The design of Hunters back
inlet gullies allow several appliances to discharge to the same gully.
3.17 OVERFLOW DISCHARGE
Hunters Overflow System
The 22mm polypropylene and unplasticized polyvinyl chloride (PVCu) pipe is available in white in three metre
Iengths. The range of high temperature MuPVC overflow fittings are designed so that they can be either push fit
onto the polypropylene pipe or solvent welded onto the unplasticized polyvinyl chloride (PVCu) pipe. Hunters
22mm pipe can be connected to other manufacturers pipe by using the universal adaptor O220.
Overflow Pipes
To warn occupiers of problems with the stopvalve before the water level reaches the spillover level of the cold water
storage cisterns, they must be fitted with a warning pipe. The pipe must be adequately supported to have a
consistent fall to a conspicuous position, preferably outside the building. To evacuate the incoming water before
the stopvalve becomes submerged the pipe should be positioned to create a Type B air gap and be a larger
diameter than the incoming water supply, at least 22mm outside diameter. See diagram.
Bore of Supply Pipe
Type B Air Gap
Not exceeding l4mm
20mm
Exceeding l4mm but not
exceeding 21mm
25mm
Exceeding 21mm but not
exceeding 41mm
70mm
Exceeding 41 mm
twice bore of supply pipe
A warning pipe must not be fitted with a flap on the outlet to prevent
icy wind from blowing along the pipe and freezing the stopvalve in
the closed position. Instead, it should be fitted with a bend or tee.
When fitted in unheated roof spaces warning and overflow pipes
must be insulated. They should also be included in the maintenance
schedule to ensure that they comply with all of the above.
Supply
pipe inlet
Stop valve
Type B
Gap
Overflow
3.00
Design Criteria
3.17 OVERFLOW DISCHARGE CONT-
Conspicuous Discharge
The use of internal bathrooms means that it is not always possible to discharge overflowing water outside the
building. Therefore, Hunter Plastics Ltd manufactures a combined bath/cistern waste and overflow (W040CF) so
that the water conspicuously overflows into the bath.
Combined Warning Pipe
Two or more warning pipes may discharge to a combined warning pipe providing that the overflowing cistern is
easily detected and that the overflow from one cistern cannot discharge into another. This is achieved by providing
a 25mm air gap between the cisterns warning pipe and the combined overflow pipe. The combined warning
pipe should discharge externally but in exceptional circumstances the termination point may have no visible outlet.
See diagram.
22mm overflow pipe
25mm air gap
W711
50mm socket
used to form Tundish
W717
32 x 50mm reducer
W84
Tee
W116
32mm bend
You might also like
- Sizing of Sewer DrainsDocument46 pagesSizing of Sewer DrainsvictorNo ratings yet
- Storm Drainage Components GuideDocument2 pagesStorm Drainage Components GuideNiong DavidNo ratings yet
- Plumbing Engg - Services Design Guide 1Document274 pagesPlumbing Engg - Services Design Guide 1Mirza Abbas100% (4)
- Drainagesystemslecturei 091022013358 Phpapp02Document62 pagesDrainagesystemslecturei 091022013358 Phpapp02Abdul Raoof100% (1)
- Tutorial - Cold Water SupplyDocument7 pagesTutorial - Cold Water SupplyyugerajdNo ratings yet
- ISO 9001 Water Supply SystemsDocument88 pagesISO 9001 Water Supply SystemssardarmkhanNo ratings yet
- Max. Height ??: Installation RequirementsDocument1 pageMax. Height ??: Installation RequirementsAlign EngineeringNo ratings yet
- High-Rise Design - Hot Water Recirculations and General Pumping PracticesDocument156 pagesHigh-Rise Design - Hot Water Recirculations and General Pumping PracticesAnonymous PCsoNCt0mFNo ratings yet
- Sprinkler Sloped - Ceilings - 2010 PDFDocument7 pagesSprinkler Sloped - Ceilings - 2010 PDFnrodinis7No ratings yet
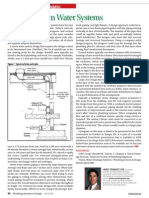
- ASPE PSD - Building Storm Water SystemsDocument1 pageASPE PSD - Building Storm Water SystemsNiong DavidNo ratings yet
- ASPE PSD - Fire Pump InstallationDocument4 pagesASPE PSD - Fire Pump InstallationNiong DavidNo ratings yet
- Chap - 7-Ventilation and Smoke Purging SystemDocument21 pagesChap - 7-Ventilation and Smoke Purging SystemAbubacker Siddique SulthanNo ratings yet
- RainwaterDocument6 pagesRainwaterKarthy GanesanNo ratings yet
- WHA Water Hammer ArrestorsDocument5 pagesWHA Water Hammer ArrestorsvitgahiNo ratings yet
- Plumbing CalculationsDocument14 pagesPlumbing CalculationsKarthy Ganesan100% (6)
- DESCRIPTIONS Garbage ChuteDocument12 pagesDESCRIPTIONS Garbage ChuteYasser Fathy AlyNo ratings yet
- BS Standard - Drainage Fixture Units & Flow Rate Calculation PDFDocument2 pagesBS Standard - Drainage Fixture Units & Flow Rate Calculation PDFlijo john100% (2)
- PSD Ceu 198april13Document16 pagesPSD Ceu 198april13Niong DavidNo ratings yet
- Oil Interceptor CombinedDocument19 pagesOil Interceptor CombinedNiong DavidNo ratings yet
- Building Regs Part H DrainageDocument43 pagesBuilding Regs Part H DrainageJohn LiebermanNo ratings yet
- Swimming Pool Heater SizingDocument1 pageSwimming Pool Heater SizingAmeer AbbasNo ratings yet
- Pool Recirculation Systems and ComponentsDocument58 pagesPool Recirculation Systems and ComponentsMehdi NasriNo ratings yet
- Fixture Units Sizing ChartDocument4 pagesFixture Units Sizing ChartAfrooz Momeni100% (1)
- Code BS en 12056 2-2000-Pipe SizingDocument16 pagesCode BS en 12056 2-2000-Pipe SizingsenghouNo ratings yet
- HighRiseWaterSupplyDocument4 pagesHighRiseWaterSupplySonia Dogra0% (1)
- Sump Pump SizingDocument4 pagesSump Pump Sizingyavorn3348100% (1)
- Hot Water Storage Systems GuideDocument11 pagesHot Water Storage Systems GuideNadeesha BandaraNo ratings yet
- IPC - Chapter 11 Storm DrainageDocument14 pagesIPC - Chapter 11 Storm DrainageyoesofNo ratings yet
- HVAC Beta Linear Slot Diffusers CatalogDocument14 pagesHVAC Beta Linear Slot Diffusers CatalogwissamnafoukhNo ratings yet
- Eaching High-Rise Plumbing DesignDocument19 pagesEaching High-Rise Plumbing Designm_salah20202000No ratings yet
- Villa drainage system calculationsDocument16 pagesVilla drainage system calculationsfady saidNo ratings yet
- Plumbing SpecsDocument15 pagesPlumbing SpecssakeedfaheedNo ratings yet
- Guide To SDRDocument36 pagesGuide To SDRssarang100% (1)
- Ventilation Design Guide for Electrical RoomsDocument8 pagesVentilation Design Guide for Electrical RoomsphilipyongNo ratings yet
- Sizing of InterceptorDocument11 pagesSizing of InterceptorLorence GabayanNo ratings yet
- High-Rise Water Systems DesignDocument7 pagesHigh-Rise Water Systems Designhtosar20% (1)
- ASPE-Domestic Water Heating Design Manual 2013 PDFDocument2 pagesASPE-Domestic Water Heating Design Manual 2013 PDFMohamedHany100% (1)
- Fcu SizingDocument12 pagesFcu SizingLloydNo ratings yet
- CITY HVAC Design Guide AppendicesDocument41 pagesCITY HVAC Design Guide AppendicesSimon Law100% (1)
- Regulation DD-9.0: Drainage: 9.1 Domestic Drainage 9.2 Water Supply 9.3 Rainwater Drainage 9.4 A/C DrainDocument10 pagesRegulation DD-9.0: Drainage: 9.1 Domestic Drainage 9.2 Water Supply 9.3 Rainwater Drainage 9.4 A/C DrainSarathNo ratings yet
- Hot Water Supply (Apprentice) M2 U10Document39 pagesHot Water Supply (Apprentice) M2 U10Sam Wing HongNo ratings yet
- Supply Air Grille SizingDocument12 pagesSupply Air Grille Sizingdynamitedragon100% (1)
- Cold Water StorageDocument5 pagesCold Water Storagemechmohsin4745No ratings yet
- Water Supply and Drainage in BuildingDocument21 pagesWater Supply and Drainage in BuildingAnu KpNo ratings yet
- Save up to 80% on HVAC Energy Costs with Heat Recovery UnitsDocument35 pagesSave up to 80% on HVAC Energy Costs with Heat Recovery UnitsGabetsos KaraflidisNo ratings yet
- Water Heater SizingDocument258 pagesWater Heater SizingJay SuguitanNo ratings yet
- Water Booster Pump Flow CalculationDocument1 pageWater Booster Pump Flow CalculationfebousNo ratings yet
- Hot and Cold Water Supply AMGDDocument26 pagesHot and Cold Water Supply AMGDJasleenNo ratings yet
- Bs 6700 2006 Water Supply Services FormulatedDocument2 pagesBs 6700 2006 Water Supply Services FormulatedLinn Kyaw Zaw100% (1)
- Designing efficient centralized hot water systemsDocument36 pagesDesigning efficient centralized hot water systemsAbhik BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Zurn Roof Drain CatalogDocument22 pagesZurn Roof Drain CatalogperezismaelNo ratings yet
- ASPE Data Book - A Plumbing Engineers Guide To System Design and Specifications, Vol. 2 - Plumbing Systems 2000 EditionDocument377 pagesASPE Data Book - A Plumbing Engineers Guide To System Design and Specifications, Vol. 2 - Plumbing Systems 2000 EditionSusan LamNo ratings yet
- Sanitary PipeworkDocument10 pagesSanitary Pipeworkbocap811No ratings yet
- Building Laws Building UtilitiesDocument32 pagesBuilding Laws Building UtilitiesjbonvierNo ratings yet
- General Materials and Workmanship: Section 1 2 Section 2 7 Section 3 13Document14 pagesGeneral Materials and Workmanship: Section 1 2 Section 2 7 Section 3 13Muhammad EhtshamNo ratings yet
- Phil Arch Review BDocument32 pagesPhil Arch Review BAr. Ryan OrtigasNo ratings yet
- Building Laws Building Utilities - Unrecognizable TextDocument32 pagesBuilding Laws Building Utilities - Unrecognizable TextAe R ONNo ratings yet
- CE335Document243 pagesCE335Junavelle CavanNo ratings yet
- Building Laws Building Utilities - Unrecognizable TextDocument32 pagesBuilding Laws Building Utilities - Unrecognizable TextAlecsisRoeEstañolFrascoNo ratings yet
- Report STR Overall FinalDesign ScanDocument25 pagesReport STR Overall FinalDesign ScanfayasNo ratings yet
- C01002J 003 AD SI S 1000 SHT 1to3 Rev ADocument3 pagesC01002J 003 AD SI S 1000 SHT 1to3 Rev AfayasNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase Asynchronous MotorsDocument46 pagesThree-Phase Asynchronous Motorswartsil100% (4)
- Insulation TestDocument8 pagesInsulation Test8612045483082No ratings yet
- 3 FlowmeterDocument146 pages3 FlowmeterfayasNo ratings yet
- 06 - Screw Fastening 2011 - Smallest File SizeDocument7 pages06 - Screw Fastening 2011 - Smallest File SizefayasNo ratings yet
- 01 Measuring Systems 2011 Smallest File SizeDocument13 pages01 Measuring Systems 2011 Smallest File SizefayasNo ratings yet
- Grundfos CR ManualDocument21 pagesGrundfos CR Manualfayas100% (1)
- 08 - Anchor Systems 2011 - Smallest File SizeDocument38 pages08 - Anchor Systems 2011 - Smallest File SizefayasNo ratings yet
- 02 - Drilling and Demolition 2011 - Smallest File SizeDocument21 pages02 - Drilling and Demolition 2011 - Smallest File SizefayasNo ratings yet
- ABB Duty Selector SwithDocument68 pagesABB Duty Selector SwithfayasNo ratings yet
- Pressure Transmitter For Al WarqaDocument68 pagesPressure Transmitter For Al WarqafayasNo ratings yet
- RTA Power RequirementDocument3 pagesRTA Power RequirementfayasNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Systems ExplainedDocument30 pagesPower Electronics Systems ExplainedRudra MishraNo ratings yet
- Safe Scaffolding GuideDocument46 pagesSafe Scaffolding Guidedox4use100% (1)
- MIT2 500s09 Lec01Document61 pagesMIT2 500s09 Lec01Pedro PucheNo ratings yet
- Double Slide Rail Shoring - DataDocument1 pageDouble Slide Rail Shoring - DatafayasNo ratings yet
- Modbus Over Serial LineDocument44 pagesModbus Over Serial Linearindammanna123No ratings yet
- 2.500 Desalination and Water Purification: Mit OpencoursewareDocument27 pages2.500 Desalination and Water Purification: Mit OpencoursewarefayasNo ratings yet
- Dewa FactDocument3 pagesDewa FactfayasNo ratings yet
- Concept of DesignDocument10 pagesConcept of DesignfayasNo ratings yet
- Vent DesignDocument11 pagesVent DesignfayasNo ratings yet
- MIT2 500s09 Lec08Document31 pagesMIT2 500s09 Lec08fayasNo ratings yet
- 2014.11.23 - Electrical Specifications Combined - Tender SubmissionDocument426 pages2014.11.23 - Electrical Specifications Combined - Tender Submissionfayas100% (1)
- Thumb RuleDocument1 pageThumb RulefayasNo ratings yet
- ArchitectureDocument645 pagesArchitecturefayas100% (2)
- Essential HVAC Calculations Spreadsheet for Load Estimation, Psychrometrics, Duct DesignDocument52 pagesEssential HVAC Calculations Spreadsheet for Load Estimation, Psychrometrics, Duct DesignSyed ShahbazNo ratings yet
- BS EN 805 (X)Document29 pagesBS EN 805 (X)Stevie Xin Yang100% (1)
- Zuari Cement, YerraguntlaDocument26 pagesZuari Cement, YerraguntlaKvnaveen KvnNo ratings yet
- BenjaminJ 2007reduxDocument379 pagesBenjaminJ 2007reduxhommie pearNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Forms and Concerns in Minnesota WatersDocument22 pagesNitrogen Forms and Concerns in Minnesota WatersCarlos de la TorreNo ratings yet
- Archives Libraries MuseumsDocument2 pagesArchives Libraries Museumsamir shokrNo ratings yet
- Petroleum Microbiology Lecture 1 Acid Mine Drainage (AMD)Document19 pagesPetroleum Microbiology Lecture 1 Acid Mine Drainage (AMD)BarnabasNo ratings yet
- Appendix BDocument13 pagesAppendix BMKNo ratings yet
- Irha Newsletter (Gvi Article)Document4 pagesIrha Newsletter (Gvi Article)Global Vision International FijiNo ratings yet
- CgwaDocument2 pagesCgwaMohammedNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Groundwater Resources in Alluvial Aquifer Based On MODFLOW Program, Case Study: Evan Plain (Iran)Document7 pagesEvaluation of Groundwater Resources in Alluvial Aquifer Based On MODFLOW Program, Case Study: Evan Plain (Iran)Albi HilalNo ratings yet
- Sample ExamDocument4 pagesSample ExamsmaghNo ratings yet
- Cominox SterilClave 18-24 - User and Maintenance ManualDocument68 pagesCominox SterilClave 18-24 - User and Maintenance ManualJose Tavares100% (2)
- Introducing Green Bond in BangladeshDocument19 pagesIntroducing Green Bond in BangladeshAshiq Rayhan0% (1)
- WinS handwashing monitoring toolsDocument13 pagesWinS handwashing monitoring toolsHarold MercadoNo ratings yet
- Cyquest 3223 (Hoja Tecnica) PDFDocument2 pagesCyquest 3223 (Hoja Tecnica) PDFThannee BenitezNo ratings yet
- Theoretical and Practical Models For Drilling Waste Volume Calculation With Field Case StudiesDocument11 pagesTheoretical and Practical Models For Drilling Waste Volume Calculation With Field Case StudiesFerry Triyana AnirunNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Alternation in Fresh Water Fishe Labeo Rohita Exposed To The Sodium Fluoride (NAF) .Document5 pagesBiochemical Alternation in Fresh Water Fishe Labeo Rohita Exposed To The Sodium Fluoride (NAF) .International Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- Instructions For Installation and Operation High Pressure Compressed Air Refrigeration Dryer Drypoint RS 25-1010 HP50Document77 pagesInstructions For Installation and Operation High Pressure Compressed Air Refrigeration Dryer Drypoint RS 25-1010 HP50Katia BarretoNo ratings yet
- Essay On ConductionDocument4 pagesEssay On Conductionnzila43No ratings yet
- References: Pinsao Pilot Project Baguio City MapDocument3 pagesReferences: Pinsao Pilot Project Baguio City MapRaquel Paleyan CalawenNo ratings yet
- Cut Flower Production in OrchidsDocument7 pagesCut Flower Production in OrchidsPrit Ranjan Jha100% (3)
- Is 14458 Part 9Document17 pagesIs 14458 Part 9Jina MandalNo ratings yet
- Legend Heritage Walk Project Material and FinishesDocument3 pagesLegend Heritage Walk Project Material and Finishesk.o.m channel (kmeng)No ratings yet
- CBRN WSL1Document47 pagesCBRN WSL1Trelos1337No ratings yet
- (Bennett, Dawson) Maintenance ManagementDocument53 pages(Bennett, Dawson) Maintenance Managementwesam tawfik salamaNo ratings yet
- Black Gold For Blue Gold? Sudan's Oil, Ethiopia's Water and Regional IntegrationDocument24 pagesBlack Gold For Blue Gold? Sudan's Oil, Ethiopia's Water and Regional IntegrationMark EbrahimNo ratings yet
- Modelling Downstream Change River Flood PowerDocument3 pagesModelling Downstream Change River Flood PowerDestriayu VasistaNo ratings yet
- Rain Water HarvesitingDocument10 pagesRain Water HarvesitingSyed Roshan AliNo ratings yet
- Green Accounting 1Document41 pagesGreen Accounting 1Rahul AroraNo ratings yet
- Use of Mattsson's Solution of PH 7.2 To Evaluate The Stress-Corrosion Cracking Susceptibility of Copper-Zinc AlloysDocument3 pagesUse of Mattsson's Solution of PH 7.2 To Evaluate The Stress-Corrosion Cracking Susceptibility of Copper-Zinc AlloysGrato Jr SingcoNo ratings yet
- Homework 5Document3 pagesHomework 5Engr Ghulam MustafaNo ratings yet