Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry Section 6.5 PowerPoint Notes
Uploaded by
anon-5794470 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
138 views5 pages_______________________________ theory says that valence electrons surround an atom causes them to be oriented as far away from each other as possible. Electron pairs want to get as far apart from each other to minimize the effects of likecharges caused by likecharges. BeF2 (beryllium fluoride) is an example of a molecule with a ___________________ shape.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document_______________________________ theory says that valence electrons surround an atom causes them to be oriented as far away from each other as possible. Electron pairs want to get as far apart from each other to minimize the effects of likecharges caused by likecharges. BeF2 (beryllium fluoride) is an example of a molecule with a ___________________ shape.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
138 views5 pagesChemistry Section 6.5 PowerPoint Notes
Uploaded by
anon-579447_______________________________ theory says that valence electrons surround an atom causes them to be oriented as far away from each other as possible. Electron pairs want to get as far apart from each other to minimize the effects of likecharges caused by likecharges. BeF2 (beryllium fluoride) is an example of a molecule with a ___________________ shape.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
Chemistry
Section 6.5
PowerPoint Notes
Fill in the blanks and take any applicable notes as participate in the power point
presentation.
Slide 2:
VSEPR stands for “______________________________________________________”.
VSEPR says that ________________________________ between the pairs of valence
electrons (shared and unshared pairs) surrounding an atom causes them to be oriented as
far________________________________as possible.
This theory accounts for different ________________________________
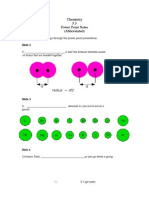
Slide 3: Molecular Shapes:
It is easy to see that _______________________________ molecules will have a
_______________________________ shape (two _______________________________
make a line)
_______________________________ helps us understand more complex molecules.
_______________________________want to get as far apart from each other to
minimize the effects of _______________________________ forces caused by like-
charges.
Slide 4: Some Basic Shapes:
Let’s say A represents a “________________________” atom.
Let’s say B represents atoms ________________________ to the central atom.
AB2, AB3, and AB4 would have the following shapes: ________________________,
________________________, and ________________________, respectively.
Linear means ________________________________________________
Trigonal means ________________________ sides and planar means in the shape of a
________________________
Tetrahedral means ________________________ equal sides.
BeF2 (Beryllium fluoride) is an example of a molecule with a
________________________shape. The angle between bonds is __________________
degrees.
Chem 6.5 ppt NOTES 1
BF3 (boron trifluoride) is a an example of molecule with a ___________________ shape.
There is an angle of ________________________ degrees between bonds.
Methane (CH4) has a ________________________ shape. The angle between bonds is
________________________ degrees.
Electron pairs want to ________________________________________________.
Identity the following molecular shapes:
________________________ ________________________ ______________________
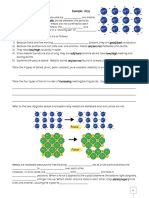
Slide 5: VSEPR also considers unshared pairs
If A is a central atom, B are atoms bonded to the central atom, and E represents
________________________, then. . Ammonia (NH3), AB3E and water (H2O), AB2E2
have ________________________ and________________________shapes,
respectively.
________________________ has a pyramidal shape. The
unshared pair are on ________________________ of the
molecule.
Water has a ________________________ shape because the
Shared and ________________________ pairs of electrons
Want to get as far apart from each other as possible.
Chem 6.5 ppt NOTES 2
Slide 7: Hybridization
Another thing that controls molecular shape is ________________________.
Hybridization is the creation of ________________________ of equal energy by
rearranging ________________________ from orbitals of nearly the same energy.
________________________ is a great example of hybridization.
Draw the orbital notation for carbon:
Draw the orbital notation for hybridized carbon:
When carbon hybridizes an electron from the ________________________ moves Into
the empty ________________________ orbital. This creates
________________________ orbitals of equal energy. There are _________________
sites for bonding. That is why carbon forms four bonds.
Slide 8: More Hybridization
Carbon forms an ________________________: one s orbital and three p orbitals of
equal energy.
________________________ hybrids can also be formed. ________________________
are orbitals of equal energy produced by the combination of two or more orbitals on the
same atom.
Slide 9: Hybrid Orbitals
This shows the formation of sp hybrids.
Chem 6.5 ppt NOTES 3
An sp2 hybrid forms when an s orbital hybridizes with 2 p orbitals.
Slide 10: Intermolecular Forces
________________________ forces are forces of attraction between molecules. They are
generally ________________________ than ionic, covalent or metallic bonds. The
higher the boiling point of a substance the ________________________ the forces
between particles in the substance. ________________________ have the greatest forces
of attraction, followed by ________________________ bonds, polar covalent bonds, and
finally ________________________ covalent bonds.
Slide 11: Types of Intermolecular Forces.
List three major types of intermolecular forces:
a) ________________________________________________
b) ________________________________________________
c) ________________________________________________
Slide 12: Dipole-Dipole Forces
These are forces that form between ________________________ (dipoles)
Polarity of a molecule depends on the type of ________________________ and the
________________________ of the molecule. Hydrogen chloride (HCl), water (H20),
and ammonia (NH3) are all ________________________
Chem 6.5 ppt NOTES 4
Slide 13: Hydrogen Bonds
Hydrogen Bond is a type of ________________________force.
________________________is the intermolecular force in which a _________________
atom that is bonded to a highly electronegative atom is ________________________ to
an ________________________ pair of electrons of an electronegative atom in a nearby
molecule.
Slide 14: London Dispersion Forces
The ________________________ of intermolecular forces produced by unequal
distribution of ________________________ in atoms or molecules as they move about.
causes ________________________ in adjacent atoms. Electrons move around and may
so ________________________ build a ________________________ Only force of
attraction between ________________________and ________________________.The
more electrons in the atom or molecule (larger the ________________________or
molecular mass) the ________________________the attraction.
Slide 15:
Chem 6.5 ppt NOTES 5
You might also like
- Chemistry Chapter 6 6.2 Notes.Document7 pagesChemistry Chapter 6 6.2 Notes.anon-579447No ratings yet
- 08 - Intermolecular ForcesDocument4 pages08 - Intermolecular Forcesleafyfun100No ratings yet
- Biochemistry Homework EditDocument18 pagesBiochemistry Homework Editterris jamesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Physical Science Notes RevDocument4 pagesChapter 6 Physical Science Notes Revapi-30718309No ratings yet
- Classifying Matter and Energy StatesDocument7 pagesClassifying Matter and Energy StatesJam Uly GastyNo ratings yet
- Intro To Covalent BondingDocument5 pagesIntro To Covalent BondingDustin MoenchNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Classifying Matter NotesDocument5 pages3.1 Classifying Matter NotesJam Uly GastyNo ratings yet
- Slide 2: Chemistry 5.3 Power Point Notes (Abbreviated)Document7 pagesSlide 2: Chemistry 5.3 Power Point Notes (Abbreviated)anon-579447No ratings yet
- Chemistry Chapter 6 6.3 Power Point NotesDocument4 pagesChemistry Chapter 6 6.3 Power Point Notesanon-579447No ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionDocument4 pagesChemical ReactionABDULRAHMAN ABDRABBONo ratings yet
- 3.1 Classifying Matter NotesDocument6 pages3.1 Classifying Matter NotesKeshaun BowserNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument2 pagesMetallic BondingJohanna LipioNo ratings yet
- Ionic Covalent Bonding Web QuestDocument5 pagesIonic Covalent Bonding Web QuestFiona IsbellNo ratings yet
- Spring 2009 Final Exam Review: Modified True/FalseDocument14 pagesSpring 2009 Final Exam Review: Modified True/FalsejkeelenNo ratings yet
- PKT Bonding2 Student NotesDocument40 pagesPKT Bonding2 Student NotesrajaijahNo ratings yet
- Biology (Form 4) Chapter 4 Chemical Composition of The CellDocument2 pagesBiology (Form 4) Chapter 4 Chemical Composition of The CellSiti MadihahNo ratings yet
- Crash Course Chemistry 22 Atomic Hook-Ups BlankDocument1 pageCrash Course Chemistry 22 Atomic Hook-Ups BlankShantelle SorbitoNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Unit 2 Guided NotesDocument9 pagesPhysical Science Unit 2 Guided NotesflyingmsNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equations: A Shorthand for Describing ReactionsDocument6 pagesChemical Equations: A Shorthand for Describing ReactionsMelva GuerraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Matter and Atomic StructureDocument4 pagesChapter 3 Matter and Atomic StructureMari LarryNo ratings yet
- snc1d Chemistry Unit ReviewDocument6 pagessnc1d Chemistry Unit Reviewapi-54435418No ratings yet
- Physical Science SHS 4.3 Worksheet 2Document3 pagesPhysical Science SHS 4.3 Worksheet 2Maricris Jane PeranteNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Study Guide-AnswersDocument2 pagesChemistry Study Guide-Answersstrathman_3No ratings yet
- CH1 Classification of Matter Study Guide 1Document2 pagesCH1 Classification of Matter Study Guide 1PCNo ratings yet
- Electrons in Atoms: Light and Quantized EnergyDocument9 pagesElectrons in Atoms: Light and Quantized EnergyRicki HanNo ratings yet
- 12sc Day177 GuidedNotes Ch28Document8 pages12sc Day177 GuidedNotes Ch28Dwayne Ashley DavidNo ratings yet
- P S M E: University of BoholDocument3 pagesP S M E: University of BoholXenita VeraNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonding Lewis Structure WebquestDocument16 pagesCovalent Bonding Lewis Structure WebquestDean JezerNo ratings yet
- 03b ENSC 488W Kinematics 2024 AnnotatedDocument10 pages03b ENSC 488W Kinematics 2024 Annotatedaarea3No ratings yet
- Junior Lyceum Annual Exams 2009 Form 1 Integrated ScienceDocument9 pagesJunior Lyceum Annual Exams 2009 Form 1 Integrated ScienceTheviyan RajNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Unit 3 Guided NotesDocument11 pagesPhysical Science Unit 3 Guided NotesflyingmsNo ratings yet
- S9 - End-Of-Unit 2 TestDocument2 pagesS9 - End-Of-Unit 2 TestMoganoni MogaNo ratings yet
- Ionic Bonding and Hydrates Webercise: VideoDocument3 pagesIonic Bonding and Hydrates Webercise: Videoapi-439932199No ratings yet
- Nicky - Phases of Matter Webquest WorksheetDocument5 pagesNicky - Phases of Matter Webquest Worksheetapi-443024841100% (1)
- IIT Foundation - XI Chemistry MCQ #4 on Chemical BondingDocument5 pagesIIT Foundation - XI Chemistry MCQ #4 on Chemical BondingDatta SurwaseNo ratings yet
- Ntctaoc Toonmi Stceboj Rceof NeriitaDocument16 pagesNtctaoc Toonmi Stceboj Rceof NeriitaMary Luz Dolente EderNo ratings yet
- Classifying Matter and Chemical ChangesDocument31 pagesClassifying Matter and Chemical ChangesBhuwneesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Movement of Substance Across The Plasma MembraneDocument13 pagesChapter 3: Movement of Substance Across The Plasma MembraneEma FatimahNo ratings yet
- PSCH 0814 KeyDocument2 pagesPSCH 0814 KeyJan Ira RenolayanNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Ionic Compounds and Metals Student Editable PDFDocument8 pagesStudy Guide Ionic Compounds and Metals Student Editable PDFNicolyNo ratings yet
- Kerja Cuti Sains 5paDocument4 pagesKerja Cuti Sains 5pazoulezNo ratings yet
- 15 Atomic Structure Practice WorksheetDocument2 pages15 Atomic Structure Practice WorksheetJeffrey DavisNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Vs Meiosis WorksheetDocument2 pagesMitosis Vs Meiosis WorksheetFabian Andres Paez Velandia100% (1)
- Physical Science SHS 4.2 Worksheet 2Document3 pagesPhysical Science SHS 4.2 Worksheet 2Maricris Jane PeranteNo ratings yet
- Physics 10th Class Key ConceptsDocument43 pagesPhysics 10th Class Key ConceptsMirza Tahir BaigNo ratings yet
- Daily Science Test for 7th GradeDocument2 pagesDaily Science Test for 7th GradeFitria Istikomah Dewi100% (1)
- 7 Atomic, Nuclear and Particle Physics: 7.3 The Structure of MatterDocument8 pages7 Atomic, Nuclear and Particle Physics: 7.3 The Structure of MatterTrúc HồNo ratings yet
- 3.1.3.7 Forces Between Molecules-UnblockedDocument3 pages3.1.3.7 Forces Between Molecules-UnblockedsuccesshustlerclubNo ratings yet
- unit 4 test ngss chemistryDocument4 pagesunit 4 test ngss chemistryapi-664258676No ratings yet
- The Structure of the Atom DocumentDocument7 pagesThe Structure of the Atom DocumentAbdullah AlthaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Structure and Function of The CellDocument14 pagesChapter 3: Structure and Function of The CellAveen ShabanNo ratings yet
- Notes and Questions: Aqa GcseDocument28 pagesNotes and Questions: Aqa Gcseapi-422428700No ratings yet
- Worksheet: Molecular Geometry and Name - Intermolecular ForcesDocument2 pagesWorksheet: Molecular Geometry and Name - Intermolecular Forcesapi-369690183No ratings yet
- Matter Webquest - KeyDocument5 pagesMatter Webquest - KeyAden LarsonNo ratings yet
- SG Life's Chemical BasisDocument3 pagesSG Life's Chemical BasisrkvNo ratings yet
- Evolution Review WorksheetDocument5 pagesEvolution Review WorksheetRobert KarovicNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 Chemistry/Physics/BiologyDocument7 pagesQuiz 1 Chemistry/Physics/Biologyeric sivaneshNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: Essential Chemistry Self-Teaching GuideFrom EverandChemical Bonding: Essential Chemistry Self-Teaching GuideNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledanon-579447No ratings yet
- Assistive Technology Assessment Plan (ATAP) : DemographicsDocument5 pagesAssistive Technology Assessment Plan (ATAP) : Demographicsanon-579447No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledanon-579447No ratings yet
- 'Oal 6/#!"5,!29 3lope 9our: %xampleDocument3 pages'Oal 6/#!"5,!29 3lope 9our: %xampleanon-579447No ratings yet
- $raw "Est: %stimateDocument3 pages$raw "Est: %stimateanon-579447No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledanon-579447No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledanon-579447No ratings yet
- 7 RiteDocument3 pages7 Riteanon-579447No ratings yet
- 3olve: 'RaphDocument4 pages3olve: 'Raphanon-579447No ratings yet
- 5SE 3trategies: %xampleDocument3 pages5SE 3trategies: %xampleanon-579447No ratings yet
- 5SE AND:, Esson #OpyrightDocument5 pages5SE AND:, Esson #Opyrightanon-579447No ratings yet
- 'Raph: 'Oal Standard 6/#!"5,!29 0arent 9ourDocument4 pages'Raph: 'Oal Standard 6/#!"5,!29 0arent 9ouranon-579447No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledanon-579447No ratings yet
- The Civil WarDocument2 pagesThe Civil Waranon-579447No ratings yet
- 'Raph 4WO: #HeckingDocument3 pages'Raph 4WO: #Heckinganon-579447No ratings yet
- Soccer Rules - IntroductionDocument6 pagesSoccer Rules - Introductionanon-579447No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledanon-579447No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Worksheet Section 1 & 2 Section 1Document2 pagesChapter 6 Worksheet Section 1 & 2 Section 1anon-579447No ratings yet
- Questions?: Graduated Driver LicensingDocument2 pagesQuestions?: Graduated Driver Licensinganon-579447No ratings yet
- Lesson 18Document1 pageLesson 18anon-579447No ratings yet
- Aerobics SyllabusDocument3 pagesAerobics Syllabusanon-579447No ratings yet
- Time Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: P.E. P.EDocument1 pageTime Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday: P.E. P.Eanon-579447No ratings yet
- Lesson 18Document1 pageLesson 18anon-579447No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledanon-579447No ratings yet
- Curriculum For Aerobics Units To Be CoveredDocument1 pageCurriculum For Aerobics Units To Be Coveredanon-579447No ratings yet
- Lesson 18Document1 pageLesson 18anon-579447No ratings yet
- Agreement QuizDocument2 pagesAgreement Quizanon-579447100% (1)
- Lacrosse Study Guide: About The GameDocument2 pagesLacrosse Study Guide: About The Gameanon-579447No ratings yet
- Lesson 18Document1 pageLesson 18anon-579447No ratings yet
- 14-20 Year Old DriversDocument11 pages14-20 Year Old Driversanon-579447No ratings yet
- Polarity of MoleculesDocument35 pagesPolarity of Moleculesmarizel salcedoNo ratings yet
- First Year Cmestry McqsDocument45 pagesFirst Year Cmestry McqskamilbismaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Redox, and OxidationDocument54 pagesChapter 3: Redox, and OxidationSeanNo ratings yet
- What Is Electronegativity - DateDocument25 pagesWhat Is Electronegativity - DateRuben CastellanosNo ratings yet
- Free Study Materials for Competitive ExamsDocument46 pagesFree Study Materials for Competitive ExamsSuman ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Answered ProblemsDocument38 pagesAnswered ProblemsNida Bagoyboy NatichoNo ratings yet
- Half-Yearly Chemistry Exam Question PaperDocument9 pagesHalf-Yearly Chemistry Exam Question Paperkumar shivamNo ratings yet
- Building Mental Models: Teaching Carbon and Its Components To Class XDocument13 pagesBuilding Mental Models: Teaching Carbon and Its Components To Class Xloly62006No ratings yet
- Week 1 General Chemistry 2Document32 pagesWeek 1 General Chemistry 2Kate MontuyaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Solid State Chemistry: Key Concepts and ApplicationsDocument30 pagesIntroduction to Solid State Chemistry: Key Concepts and ApplicationsAdar DeslolNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Human Anatomy and Physiology 9th Edition Marieb Test Bank PDFDocument10 pagesDwnload Full Human Anatomy and Physiology 9th Edition Marieb Test Bank PDFpeiwenhlmel100% (7)
- Yr 11 Chemistry Exam NotesDocument13 pagesYr 11 Chemistry Exam NotesadfknaljhNo ratings yet
- CMG 100 New SyllabusDocument3 pagesCMG 100 New SyllabusSakib NehalNo ratings yet
- S1-P4b Solid and LiquidDocument78 pagesS1-P4b Solid and LiquidClifford ChenNo ratings yet
- SHS Physical Science Q1 SLM - 3Document25 pagesSHS Physical Science Q1 SLM - 3Adalee ColleenNo ratings yet
- Ap Unit2 Worksheet AnswersDocument7 pagesAp Unit2 Worksheet Answersburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Pretest in Grade 9 ScienceDocument3 pagesPretest in Grade 9 ScienceEj Rafael58% (12)
- Classification of Elements-NotesDocument8 pagesClassification of Elements-NotesSuprathik VineeshNo ratings yet
- 11th ChemistryDocument18 pages11th ChemistryGaurav SarohaNo ratings yet
- UC Davis Chemistry 2A Textbook - LibreBooksDocument447 pagesUC Davis Chemistry 2A Textbook - LibreBooksYourMotherNo ratings yet
- FUNDAMENTALS OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRYDocument38 pagesFUNDAMENTALS OF ORGANIC CHEMISTRYkasun HerathNo ratings yet
- Bellwork-Ionic & Metallic Venn DiagramDocument32 pagesBellwork-Ionic & Metallic Venn Diagramarissa noorNo ratings yet
- Advanced - Periodic Table - DPP 1 To 5Document9 pagesAdvanced - Periodic Table - DPP 1 To 5OJAS DwivediNo ratings yet
- Physical Science 1 1Document58 pagesPhysical Science 1 1Anonymous N0FZEkrSaeNo ratings yet
- P-Block ElementsDocument56 pagesP-Block Elementssc21fs301017No ratings yet
- Properties and Structures of Carbon AllotropesDocument6 pagesProperties and Structures of Carbon Allotropesanonymous1No ratings yet
- Chemistry IGCSE NotesDocument64 pagesChemistry IGCSE NotesMahmoud Ashraf50% (2)
- Chapter 01Document41 pagesChapter 01AC BañaresNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chem Answers WBDocument26 pagesIGCSE Chem Answers WBkrushi patelNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Interatomic BondingDocument32 pagesAtomic Structure and Interatomic BondingMark LoraNo ratings yet