Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Midterm EE456 11
Uploaded by
Erdinç KayacıkCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Midterm EE456 11
Uploaded by
Erdinç KayacıkCopyright:
Available Formats
Name:
Student Number:
Page 1
EE456: Digital Communications
MIDTERM EXAM, 5:30PM7:30PM, October 26, 2011
(2 hours, open-textbook)
Examiner: Ha H. Nguyen
Note: There are 3 questions. All questions are of equal value (with part marks
indicated) but not necessarily of equal difficulty. Full marks shall only be given
to solutions that are properly explained and justified.
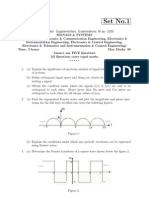
1. The input noise x(t) applied to the filter below is modeled as a wide-sense stationary,
zero-mean white, Gaussian random process with power spectral density N0 /2. Let y(t)
denote the random process at the output of the filter.
A linear filter
H( f )
1
y (t )
x (t )
Figure 1: A filter considered in Question 1.
[3]
(a) Find and sketch the power spectral density of the random process y(t).
[3]
(b) What are the average DC level and the average power of the noise y(t)?
[2]
(c) Find the
Z autocorrelation function of the random process y(t).
Hint:
x2 cos xdx = 2x cos x + (x2 2) sin x.
[2]
1
(d) Now suppose that the output noise is sampled every Ts = 2W
seconds to obtain
the noise samples y(kTs ), k = 0, 1, 2, . . .. Determine whether the noise samples
are statistically independent. Explain your answer.
EE456Digital Communications
Electrical & Computer Engineering
Name:
Student Number:
Page 2
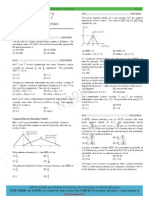
2. Consider the signal space diagram in Figure 2, where the waveforms of the two basis
functions are also shown. The signal set is used for data transmission over an AWGN
channel in which the noise is zero-mean and has two-sided power spectral density of
N0 /2. As usual, s1 (t) is used for the transmission of bit 0 and s2 (t) is for the
transmission of bit 1. Furthermore, the two bits are equally likely and the bit
duration is Tb .
2 (t )
1
Tb
Tb
1
Tb
s2 (t ) 1T
2V Tb
2V Tb
1 (t )
4V Tb
1
Tb
2V Tb
s1 (t ) 0T
Tb
Figure 2: Signal space diagram considered in Question 2.
[2]
(a) Determine and neatly sketch the two signals s1 (t) and s2 (t). Without performing
the integration but by observing Figure 2, can you tell whether s1 (t) and s2 (t)
are orthogonal ? Why?
[2]
(b) Clearly draw the optimum decision boundary and label the two decision regions.
Write the expression for the optimum decision rule in terms of r1 and r2 , the
EE456Digital Communications
Electrical & Computer Engineering
Name:
Student Number:
Page 3
projections of the received signal on 1 (t) and 2 (t). Simplify the decision rule as
much as you can.
[2]
(c) Let N0 = 1012 watts/Hz. What is the lowest voltage level V you can set in order
to transmit at the rate of 1 Mbps (megabits per second) and with a probability
of error P [error] 105 . Hint: Q1 (105 ) 4.25.
[2]
(d) Clearly explain how you can perform axis rotation to obtain new basis functions
1 (t) and 2 (t) so that the optimum receiver can be implemented with only one
matched filter. Draw the block diagram of such an optimum receiver. Determine
and plot the impulse response of the matched filter. Note: You do not need to
determine the exact value of the threshold for the comparison block.
[2]
(e) Your friend argues that, instead of performing axis rotation, she can move signal
s2 (t) in the signal space diagram in such a way that the new signal, called sM
2 (t),
has the same component with s1 (t) along 2 (t). Assuming that the energy of
s2 (t) cannot be changed, clearly identify the location of sM
2 (t). What would you
tell your friend about the performance (over an AWGN channel) of her modified
signal set as compared to the performance of the original signal set? Explain your
answer.
3. (AMI-RZ ) Alternate-Mark-Invert Return-to-Zero is a binary line coding scheme that
has memory. The output signal is determined from the sources bit stream as follows:
If the bit to be transmitted is a 0, then the signal is 0 volts over the bit period of
Tb seconds.
If the bit to be transmitted is a 1, then the signal is either +V volts or V volts
over the first half of Tb and it is zero over the second half of Tb . Over the first
half of Tb , the signal is +V volts if V was used previously to represent bit 1 and
it is V volts if +V was previously used to represent bit 1. Hence the name and
mnemonic for the modulation.
[3]
(a) Draw the AMI-RZ waveform for the information sequence {11010010}. Assume
that the amplitude level before the transmission of the above sequence is V
volts. Comment on the synchronization property of AMI-RZ scheme.
[5]
(b) Identify and clearly plot the three signals used in AMI-RZ scheme. Show a signal
space representation of these three waveforms and associate bits 0 and 1 with the
corresponding signals. Then clearly draw the minimum-distance boundary and
the block diagram of the corresponding bit-by-bit minimum-distance receiver. If
you have a matched filter in your block diagram, clearly show the impulse response
of the filter.
[2]
(c) Assume that the AMI-RZ modulation is used over an AWGN channel with twosided PSD of N0 /2 (watts/Hz). Determine the conditional bit error probability
P [error|0T ]. Remark: The error expression should be in the form of a Q-function,
whose argument depends on V , Tb and N0 .
EE456Digital Communications
Electrical & Computer Engineering
Name:
s1 (t )
s2 ( t )
A
Student Number:
t
POTENTIALLY
FACTS:
0 USEFUL
T 2
T 2
Page 4
Fourier transform:
Z
j2f t
x(t) =
X(f )e
FT
df X(f ) =
x(t)ej2f t dt
(1)
t = Tb
r 0 0D
r (t )
Minimum-distance
h (t )decision
= s1 (Tb rule
t ) for equally likely bits:
r < 0 1D
1D
(r1 s11 )2 + (r2
(r1 s21 )2 + (r2 s22 )2 .
2 (st12) )2 R
1
0
(2)
2 (t ) 2
1T s 2 (t )
0
1
s2 (t )
d2
1
2
r(t )
( s21 , s22 )
0
( r1 , r2 )
s1 (t )
1 (t ) 1
( s11 , s12 )
s1 (t ) 0T
d1
1 (t )
0 2
Rotation of axes:
2 (t )
s2 ( t )
1 (t )
2 (t )
s1 (t )
1 (t )
1 (t)
2 (t)
cos sin
sin cos
1 (t)
2 (t)
(3)
1
f m (m),
volts
1
EE456Digital Communications
Electrical & Computer Engineering
m, (volts)
You might also like
- Bioethanol From CornDocument13 pagesBioethanol From Cornpricett100% (1)
- Design of a PAM Telemetry Multiplexing SystemDocument6 pagesDesign of a PAM Telemetry Multiplexing SystemRana FaisalNo ratings yet
- Thermit Australia Product Catalogue 2012Document20 pagesThermit Australia Product Catalogue 2012Rey Luis TehNo ratings yet
- Inspection Checklist For Lifting Tools & TacklesDocument2 pagesInspection Checklist For Lifting Tools & Tacklesnil thaeu100% (1)
- Duobinary IntroDocument14 pagesDuobinary IntroAmar ShresthaNo ratings yet
- EE419 Digital Communication Systems QuestionsDocument7 pagesEE419 Digital Communication Systems QuestionsSalai JeyaseelanNo ratings yet
- n (t) × cos (2πf t + φ) Low-pass filterDocument3 pagesn (t) × cos (2πf t + φ) Low-pass filterkhawasikarNo ratings yet
- To The Approximation of Ideal Ambiguity Surface: I. Gladkova and D. ChebanovDocument4 pagesTo The Approximation of Ideal Ambiguity Surface: I. Gladkova and D. ChebanovSuri Sali SuriNo ratings yet
- RR210402 Signals - SystemsDocument8 pagesRR210402 Signals - SystemsThanikonda Reddy SreedharNo ratings yet
- Exam of Digital Communications 26/06/2013Document2 pagesExam of Digital Communications 26/06/2013pnkc80No ratings yet
- Compre Solution 2022Document3 pagesCompre Solution 2022Aman GuptaNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Exam19-20 PartBDocument4 pagesComprehensive Exam19-20 PartBAman GuptaNo ratings yet
- 2communication SystemDocument68 pages2communication SystemkhyatichavdaNo ratings yet
- FinalsolDocument5 pagesFinalsolof30002000No ratings yet
- Numerical Transmission Systems: 1 Part I (10 Points) : Carrier Frequency ModulationDocument3 pagesNumerical Transmission Systems: 1 Part I (10 Points) : Carrier Frequency Modulationkid4888No ratings yet
- CLab ProcedureDocument6 pagesCLab ProcedureChuah Chian YeongNo ratings yet
- Complexbaseband Representation of Bandpass SignalsDocument18 pagesComplexbaseband Representation of Bandpass SignalsPraneeth Karthikeya IndanaNo ratings yet
- 3 Year: Digital CommunicationsDocument3 pages3 Year: Digital Communications'Adil Mohd RaisNo ratings yet
- Analog and Digital Communications: 2. Amplitude ModulationDocument17 pagesAnalog and Digital Communications: 2. Amplitude ModulationIbra NazlaNo ratings yet
- Assignment-3Document5 pagesAssignment-3Alok KumarNo ratings yet
- EE 179 Digital and Analog Communication Systems Homework SolutionsDocument6 pagesEE 179 Digital and Analog Communication Systems Homework SolutionsAnthony KwoNo ratings yet
- Data Transmission ExercisesDocument23 pagesData Transmission ExercisesSubash PandeyNo ratings yet
- , Vs Zsis =, And - Vt Zt It Vt - T Zt T Ν Ν = Ν Τ ΤDocument13 pages, Vs Zsis =, And - Vt Zt It Vt - T Zt T Ν Ν = Ν Τ ΤAsad MohammadNo ratings yet
- 4-PSK Balanced STTC With Two Transmit AntennasDocument5 pages4-PSK Balanced STTC With Two Transmit AntennasQuang Dat NguyenNo ratings yet
- FEE 422 Practice Questions SolutionsDocument13 pagesFEE 422 Practice Questions SolutionsJoshua MNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication 601 - TutorialDocument12 pagesDigital Communication 601 - TutorialHemanth Vinay Kumar0% (1)
- EE436 HW1 Spring2014Document2 pagesEE436 HW1 Spring2014techaddicttNo ratings yet
- Complexbaseband Representation of Bandpass SignalsDocument18 pagesComplexbaseband Representation of Bandpass SignalsKedir HassenNo ratings yet
- HW 5Document2 pagesHW 5milad_7410No ratings yet
- Communication Solved ProblemsDocument145 pagesCommunication Solved ProblemsAngel Linton50% (4)
- UWBin Fading ChannelsDocument10 pagesUWBin Fading Channelsneek4uNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication Systems Worksheet: N at T, 0 T TDocument5 pagesDigital Communication Systems Worksheet: N at T, 0 T TAbrham GojjamNo ratings yet
- Gate Ec - 1991:, Vs Zsis =, And - Vt Zt It Vt - T Zt T Ν Ν = Ν Τ ΤDocument13 pagesGate Ec - 1991:, Vs Zsis =, And - Vt Zt It Vt - T Zt T Ν Ν = Ν Τ ΤSanthi SriNo ratings yet
- LTI Systems Power Spectra Gaussian Noise (39Document4 pagesLTI Systems Power Spectra Gaussian Noise (39Arin KudlacekNo ratings yet
- 21modulation v110Document70 pages21modulation v110Abdullah Ashraf ElkordyNo ratings yet
- Solved Problems: EE160: Analog and Digital CommunicationsDocument145 pagesSolved Problems: EE160: Analog and Digital CommunicationsJoseSimoes100% (1)
- Lec30 - 210108063 - SAYAK BHATTACHARYADocument5 pagesLec30 - 210108063 - SAYAK BHATTACHARYAvasu sainNo ratings yet
- ECE 461: Digital Communication Lecture 8b: Pulse Shaping and SamplingDocument9 pagesECE 461: Digital Communication Lecture 8b: Pulse Shaping and SamplingShounak DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing NotesDocument18 pagesDigital Signal Processing NotesDanial ZamanNo ratings yet
- Total GMAT Math ExcerptDocument18 pagesTotal GMAT Math ExcerptvinothNo ratings yet
- Channel Noise ZiemerTranterDocument6 pagesChannel Noise ZiemerTranterSoumitra BhowmickNo ratings yet
- Experiment 6: Pulse Code Modulation: T x T t + 2x (t) cos 4πf t + 2x (t) cos 6πf t + - . .) x (t) T t)Document6 pagesExperiment 6: Pulse Code Modulation: T x T t + 2x (t) cos 4πf t + 2x (t) cos 6πf t + - . .) x (t) T t)Pruthvi TrinathNo ratings yet
- EE320A Tutorial Solutions Power Efficiency AM Modulation RLC Circuit Spectrum AnalysisDocument10 pagesEE320A Tutorial Solutions Power Efficiency AM Modulation RLC Circuit Spectrum AnalysisManish MathuriyaNo ratings yet
- L5 - Fourier Series (Proposed Exercises)Document3 pagesL5 - Fourier Series (Proposed Exercises)Rodrigo Andres Calderon NaranjoNo ratings yet
- TE311: Introduction to Analogue Telecommunications - Linear Continuous Wave Modulation-IDocument29 pagesTE311: Introduction to Analogue Telecommunications - Linear Continuous Wave Modulation-IIbra NazlaNo ratings yet
- 通訊系統(二)第六單元Document53 pages通訊系統(二)第六單元郭彥甫No ratings yet
- EE 5140: Digital Modulation and Coding: 1 ProblemDocument2 pagesEE 5140: Digital Modulation and Coding: 1 ProblemVignesh Kumar S ee20m002No ratings yet
- PAM Modulation TechniquesDocument18 pagesPAM Modulation TechniquesGabrielNo ratings yet
- Lecture 09Document7 pagesLecture 09Dr. Rami HalloushNo ratings yet
- DSSS DetectionDocument4 pagesDSSS DetectionissameNo ratings yet
- Demodulation and beamforming in ultrasound imagingDocument8 pagesDemodulation and beamforming in ultrasound imagingManjunath RamachandraNo ratings yet
- Presented at The American Mathematical Society Short Course On Computer Communications, Denver, CO, January 3-4, 1983Document10 pagesPresented at The American Mathematical Society Short Course On Computer Communications, Denver, CO, January 3-4, 1983duncanndegwaNo ratings yet
- ENSC327 Digital Bandpass ModulationDocument28 pagesENSC327 Digital Bandpass ModulationSaurabh PandeyNo ratings yet
- Communication SystemsDocument29 pagesCommunication SystemsDivyashree CkNo ratings yet
- Fitz BandpassDocument41 pagesFitz BandpassJoshua D JohnNo ratings yet
- KFUPM EE370 Final Exam Signals and SystemsDocument6 pagesKFUPM EE370 Final Exam Signals and Systemsthinkberry22No ratings yet
- Full4 PDFDocument20 pagesFull4 PDFthumatimadhusudhanNo ratings yet
- Digital Modulation 1Document153 pagesDigital Modulation 1William Lopez JaramilloNo ratings yet
- Introduction - Analog CommunicationDocument71 pagesIntroduction - Analog CommunicationVinod MogadalaNo ratings yet
- Wave Form GeometryDocument24 pagesWave Form GeometryMK KhnNo ratings yet
- Complexbaseband Representation of Bandpass SignalsDocument18 pagesComplexbaseband Representation of Bandpass SignalsSrinivas KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsNo ratings yet
- CRI PumpsDocument13 pagesCRI Pumpscrigroups0% (1)
- 2SC1344, 2SC1345: Silicon NPN EpitaxialDocument9 pages2SC1344, 2SC1345: Silicon NPN EpitaxialrolandseNo ratings yet
- Manual JX PDFDocument263 pagesManual JX PDFArvind KumarNo ratings yet
- DIN EN 10213 - 2008 - Fundidos em AçoDocument29 pagesDIN EN 10213 - 2008 - Fundidos em AçoLeonardo MartinsNo ratings yet
- Python Question Paper Mumbai UnivercityDocument5 pagesPython Question Paper Mumbai UnivercityRahul PawarNo ratings yet
- Genetic AlgorithmDocument46 pagesGenetic AlgorithmJerryNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ReactorsDocument45 pagesNuclear ReactorsAtul100% (3)
- Sunscreen FabricDocument36 pagesSunscreen Fabricfakhrurr44No ratings yet
- Kinematics Horizontal KinematicsDocument5 pagesKinematics Horizontal KinematicsBaiJPNo ratings yet
- Life Pixel - Nikon D5500 DIY Digital Infrared Conversion TutorialDocument6 pagesLife Pixel - Nikon D5500 DIY Digital Infrared Conversion TutorialCNo ratings yet
- Operating Procedure ERLDCDocument154 pagesOperating Procedure ERLDCbramhanand vermaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 XXXDocument8 pagesChapter 1 XXXChristelle Mary Sabile SabanalNo ratings yet
- Specification Substation AutomationDocument258 pagesSpecification Substation Automationmspd2003100% (1)
- TUGAS BAHASA INGGRIS Cahaya Karisma Wilani Faturrachman Rengga Wisnu Resza Bunga Nisa POLITEKNIK NEGERI JAKARTA JURUSAN KONSTRUKSI BANGUNAN SIPILDocument4 pagesTUGAS BAHASA INGGRIS Cahaya Karisma Wilani Faturrachman Rengga Wisnu Resza Bunga Nisa POLITEKNIK NEGERI JAKARTA JURUSAN KONSTRUKSI BANGUNAN SIPILFaturrachman Nanu Rengga WisnuNo ratings yet
- Mousavi, Aliha, Imani - 2020 - On The Use of Edge Cracked Short Bend Beam Specimen For PMMA Fracture Toughness Testing Under Mixed-ModeDocument1 pageMousavi, Aliha, Imani - 2020 - On The Use of Edge Cracked Short Bend Beam Specimen For PMMA Fracture Toughness Testing Under Mixed-ModeMorteza AtaeiNo ratings yet
- R12 Period-End Procedures For Oracle Financials E-Business Suite Document 961285Document3 pagesR12 Period-End Procedures For Oracle Financials E-Business Suite Document 961285Ravi BirhmanNo ratings yet
- NOx Control of Kiln and Preheater Complete AnalysisDocument129 pagesNOx Control of Kiln and Preheater Complete AnalysisAnonymous sfY8T3q0100% (2)
- Wacker Silres Ren - 60 - Silicone Resin Solution For Medium Solids or High Solids Heat ResistancDocument3 pagesWacker Silres Ren - 60 - Silicone Resin Solution For Medium Solids or High Solids Heat ResistancJameel AhsanNo ratings yet
- John Deere X145 Lawn Tractor Service Repair Technical Manual (TM113319)Document16 pagesJohn Deere X145 Lawn Tractor Service Repair Technical Manual (TM113319)zhuangfuqian31No ratings yet
- Sika PDS E SikaRep SDocument3 pagesSika PDS E SikaRep Slwin_oo2435No ratings yet
- HYDRO VesselsDocument5 pagesHYDRO VesselsMarvinPatricioNarca0% (1)
- 9mm!ূຌዡገ๕ۉ࿋ഗ Rotary Potentiometers With Metal Shaft Series: WH9011A-1-18TDocument26 pages9mm!ূຌዡገ๕ۉ࿋ഗ Rotary Potentiometers With Metal Shaft Series: WH9011A-1-18TpeterfunNo ratings yet
- Acopos User's ManualDocument171 pagesAcopos User's ManualKonstantin Gavrilov100% (1)
- MS Electrical Cable InstallationDocument11 pagesMS Electrical Cable InstallationAhmed Rashed ANo ratings yet
- Active Front EndDocument5 pagesActive Front EndDaleel LillaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Solution All Year First Part Ioe NotesDocument31 pagesEngineering Drawing Solution All Year First Part Ioe Notesई. सन्तोष शर्माNo ratings yet