Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EME1026 - Fluid Mechanics
Uploaded by
Garett MasterOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EME1026 - Fluid Mechanics
Uploaded by
Garett MasterCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
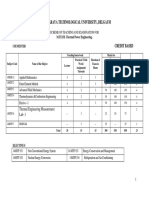
Title of Subject
Fluid Mechanics
2. Subject Code
EME1026
3. Credit Hour
4. Pre-Requisite
EME1016 Applied Statics and EEM1016 Engineering Mathematics I
5. Aim of Subject
To introduce to the students the basics of fluid mechanics.
6. Learning
Outcomes
and Program
Outcomes
of Subject
At the completion of the subject, students should be able to :
Learning Outcomes:
LO1 Solve problems related to the fundamental principles of fluid
mechanics. (cognitive applying, level 3).
LO2 Analyse a control volume by developing fundamental principles
such as the linear momentum equation and energy equation in the
treatment of the control volume. (cognitive - analysing, level 4).
LO3 Compare fundamental Reynolds Number and fluid flow behaviour
observation in pipe flow. (cognitive - analysing, level 4).
LO4 Apply Buckingham -theorem to determine a suitable set of
dimensionless parameters. (cognitive - applying, level 3).
LO5 Solve turbomachinery problems from the staindpoint of fluid
mechanics. (cognitive - understanding, level 2).
Programme Outcomes:
PO1 Acquire and apply knowledge of mathematics, science and
engineering
PO2 Acquire technical competence in specialised areas of
engineering discipline to solve complex engineering problems
7. Assessment
Scheme
8. Details of
Subject
Lab
Experiments
Work in groups
Lab report writing
Oral assessment at the end of
lab
10%
Tutorial /
Assignment
Group/individual assignment
Focus group discussion
To enhance understanding of
basic concepts in lecture
10%
Test /Quiz
Final Exam
Written exam
Written exam
Topics
Mechanics of Non-Flowing Fluids
Fluid properties. Pascals law.
Pressure variation.
Manometry and pressure measurements. Force on
20%
60%
Hours
surfaces,submerged bodies.
9. Teaching and
Learning
Activities
10. Laboratory
11. Reading
Materials
Flow Analysis
Fluid flow. Continuity equation. Bernoulli's equation.
Linear momentum equation. Energy equation.
11
Pipe Flow
Laminar and turbulent flows. Friction factor. Darcy
formula.Moody diagram. Pipe losses. Flow in pipe
networks.
Similarity and Dimensional Analysis
Concepts of similarity between model and prototype.
Use of dimensionless numbers. Buckingham -theorem
and application.
Turbomachinery
Dimensional analysis of rotodynamic machines
performance curves. Use of moment-of-momentum
equation, blade angles. Centrifugal pump, reaction
turbines. Pelton wheel. Draft tubes, cavitations
phenomenon.
This subject will be delivered using the following means:
Lecture Hours = 39 hours
Supervised Tutorial Hours = 6
Laboratory Experiments = 6
Total Contact Hours = 51
1. Force on Submerged Body
2. Internal Pipe Flow
Textbook
Reading
Materials
1. B.R. Munson, A.P. Rothmayer, T.H. Okiishi and W. W.
Huebsch Fundamentals of Fluid Mechanics, 7th Edition,
John Wiley,2013.
1. C.T. Crowe, D.F. Elger, B.C. Williams and J. A.
Roberson, "Engineering Fluid Mechanics", 9th
Edition, John Wiley, 2010.
2. R. Street, G.Z. Watters and J. Vennard, Elementary
Fluid Mechanics, 7th Edition, John Wiley, 1996.
3. V. Streeter, K.W. Bedford and E.B. Wylie, Fluid
Mechanics, 9th Edition, McGraw-Hill, 1998.
4. R.W. Fox, P. J. Pritchard and A.T. McDonald,
"Introduction to Fluid Mechanics", John Wiley, 2010.
You might also like
- MAE 333 SyllabusDocument4 pagesMAE 333 SyllabusastrobarbyNo ratings yet
- Optimal Control: An Introduction to the Theory and Its ApplicationsFrom EverandOptimal Control: An Introduction to the Theory and Its ApplicationsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- 100 Pushups PocketMod (Black and White)Document1 page100 Pushups PocketMod (Black and White)wiredpsycheNo ratings yet
- Displace 3D Presentation Open Day 09.06Document28 pagesDisplace 3D Presentation Open Day 09.06Ghadames in Our HeartNo ratings yet
- CHE 323-Syllabus (2016-2017)Document4 pagesCHE 323-Syllabus (2016-2017)ming_zhu10No ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Fluid Flow Operation B.E. Semester: IIIDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University: Fluid Flow Operation B.E. Semester: IIIMohammad ImranNo ratings yet
- ME200-Fluid Mechanics and MachineryDocument3 pagesME200-Fluid Mechanics and Machinerynandan144No ratings yet
- 3B2Document2 pages3B2imanadibiNo ratings yet
- Ucsi University B.Eng (Hons) in Chemical Engineering Course OutlineDocument2 pagesUcsi University B.Eng (Hons) in Chemical Engineering Course OutlinetkjingNo ratings yet
- CHE131 Fluid Mechanics Course OverviewDocument18 pagesCHE131 Fluid Mechanics Course OverviewChristianNo ratings yet
- Engineering Fluid Mechanics Information and IntroductionDocument17 pagesEngineering Fluid Mechanics Information and Introductionmavimu_20No ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument3 pagesFluid MechanicsRudransh KatiyarNo ratings yet
- Course Description MT338Document4 pagesCourse Description MT338UsamaNo ratings yet
- FLUID MECHANICS I COURSE OVERVIEWDocument14 pagesFLUID MECHANICS I COURSE OVERVIEWOyedotun TundeNo ratings yet
- M.tech Syllabus PDFDocument51 pagesM.tech Syllabus PDFAnonymous MR8PLYNo ratings yet
- Aero4syll PDFDocument28 pagesAero4syll PDFLokeshNo ratings yet
- M.E. (Mechanical - Heat Power Engineering) SyllabusDocument37 pagesM.E. (Mechanical - Heat Power Engineering) SyllabusKapil KotangaleNo ratings yet
- Course Folder (Fluid Mechanics - II)Document3 pagesCourse Folder (Fluid Mechanics - II)fawad naeemNo ratings yet
- Mech Sylabus 19Document1 pageMech Sylabus 19Nishikant KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Mechanical (Automobile) EngineeringDocument96 pagesMechanical (Automobile) Engineeringshiyas sNo ratings yet
- MENG1003 Course Descriptor (1) - 54645703Document7 pagesMENG1003 Course Descriptor (1) - 54645703Gregory CameraNo ratings yet
- 1.course Plan-text-ME 3111Document4 pages1.course Plan-text-ME 3111mama dullaNo ratings yet
- ME207 Thermal Engineering CourseDocument2 pagesME207 Thermal Engineering Coursenandan144No ratings yet
- Fluent and CFX TascflowDocument2 pagesFluent and CFX TascflowSimon AmboiseNo ratings yet
- Course Plan KNJ1053-Sem2!10!11Document2 pagesCourse Plan KNJ1053-Sem2!10!11Ash MochiNo ratings yet
- KKKP2034 Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer Course StructureDocument12 pagesKKKP2034 Thermodynamics and Heat Transfer Course StructureZulfadli SyamimNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus (Mechanical Engineering Program) : T.D. Eastop& A. McconkeyDocument6 pagesCourse Syllabus (Mechanical Engineering Program) : T.D. Eastop& A. McconkeyGordon ChaiNo ratings yet
- Computational Fluid Dynamics IDocument3 pagesComputational Fluid Dynamics Iapi-296698256No ratings yet
- Course Learning Outcome 1Document3 pagesCourse Learning Outcome 1engineer63No ratings yet
- Summary KH2134 Fluid MechanicsDocument4 pagesSummary KH2134 Fluid MechanicsAzman SamerNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Course OverviewDocument29 pagesFluid Mechanics Course OverviewNicholas ChiaNo ratings yet
- Che1005 - Momentum-Transfer - Eth - 1.1 - 47 - Che1005 - 55 AcpDocument2 pagesChe1005 - Momentum-Transfer - Eth - 1.1 - 47 - Che1005 - 55 Acpblub blueNo ratings yet
- Fakulti Kejuruteraan Universiti Malaysia Sarawak SESI 2-2008/2009 Course PlanDocument3 pagesFakulti Kejuruteraan Universiti Malaysia Sarawak SESI 2-2008/2009 Course PlanOng George SammyNo ratings yet
- M.Tech (Full Time) - Chemical Engineering Curriculum & Syllabus 2013 - 2014Document40 pagesM.Tech (Full Time) - Chemical Engineering Curriculum & Syllabus 2013 - 2014hmasif456No ratings yet
- Mass and Energy BalanceDocument2 pagesMass and Energy BalanceDevakan BalaganeshNo ratings yet
- 1-Lecture One - Overview and General Information - 17 Oct 2022Document12 pages1-Lecture One - Overview and General Information - 17 Oct 2022Kingsley CassityNo ratings yet
- CFD SyllabusDocument3 pagesCFD SyllabusSelvamuthu KumaranNo ratings yet
- Applied Thermo DynamicsDocument3 pagesApplied Thermo DynamicsAshley_RulzzzzzzzNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcomes and Course Objectives: Module 1: Fundamental EquationsDocument2 pagesLearning Outcomes and Course Objectives: Module 1: Fundamental Equations1AdityaPathania1No ratings yet
- Mia 502eDocument2 pagesMia 502ekanuni41No ratings yet
- CIV 2213 Fluid Mechanics II CourseDocument3 pagesCIV 2213 Fluid Mechanics II Coursemunroe wilsonNo ratings yet
- ME2201 FluidMechaincs Batch22Document3 pagesME2201 FluidMechaincs Batch22Mallinath OgiralaNo ratings yet
- Maeg3030 CHP 1Document19 pagesMaeg3030 CHP 1Ben ChanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Control EngineeringDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Control EngineeringGAYTRI SACHDEVANo ratings yet
- Che416 Course Compact 2016 2017Document5 pagesChe416 Course Compact 2016 2017DanielNo ratings yet
- MECHANICAL (AUTOMOBILE) ENGINEERING - 2019-Scheme-S3-Syllabus - Ktustudents - inDocument44 pagesMECHANICAL (AUTOMOBILE) ENGINEERING - 2019-Scheme-S3-Syllabus - Ktustudents - injishnu unniNo ratings yet
- EE3010 Electrical Devices and Machines - OBTLDocument6 pagesEE3010 Electrical Devices and Machines - OBTLAaron TanNo ratings yet
- Computer Methods in Chemical EngineeringDocument247 pagesComputer Methods in Chemical Engineeringkris010100% (1)
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Document3 pagesGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Nisarg ShahNo ratings yet
- Syllabus MEE1004 FM PDFDocument3 pagesSyllabus MEE1004 FM PDFSidhant JaiswalNo ratings yet
- ME 203 Mechanics of FluidsDocument3 pagesME 203 Mechanics of FluidsSherwinNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer I: Concepts of Diffusion, Distillation & Membrane SeparationDocument13 pagesMass Transfer I: Concepts of Diffusion, Distillation & Membrane SeparationAditya GuptaNo ratings yet
- 3340 Fall16 SyllabusDocument3 pages3340 Fall16 SyllabusJoseNo ratings yet
- Preface To The First EditionDocument2 pagesPreface To The First EditionTưMãNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics SyllabusDocument4 pagesFluid Mechanics Syllabusjohn@gmail.com0% (1)
- Course Outline ELEC 1002 Electrical Principles IDocument4 pagesCourse Outline ELEC 1002 Electrical Principles IFiveCent NickelNo ratings yet
- Understanding Fluid Flow and Momentum TransferDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Fluid Flow and Momentum TransferAbhishek KarpeNo ratings yet
- BENG Mechanical AccrediationDocument1 pageBENG Mechanical AccrediationGarett MasterNo ratings yet
- Emran Ismail 2017Document10 pagesEmran Ismail 2017Garett MasterNo ratings yet
- Tutorials Set 1Document1 pageTutorials Set 1Garett MasterNo ratings yet
- Assignment GroupsDocument2 pagesAssignment GroupsGarett MasterNo ratings yet
- Total Midterm and TestDocument4 pagesTotal Midterm and TestGarett MasterNo ratings yet
- Prepare Yourself For The Final Exam (French Exercise)Document10 pagesPrepare Yourself For The Final Exam (French Exercise)epy90No ratings yet
- Re Marking ProcedureDocument2 pagesRe Marking ProcedureGarett MasterNo ratings yet
- French Coursework MarksDocument8 pagesFrench Coursework MarksGarett MasterNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Marks - WordDocument3 pagesMid Term Marks - WordGarett MasterNo ratings yet
- LAPLACE TRANSFORMS TABLEDocument2 pagesLAPLACE TRANSFORMS TABLEGarett MasterNo ratings yet
- Student Turnitin InstructionsDocument1 pageStudent Turnitin InstructionsGarett MasterNo ratings yet
- Teaching Plan ECP1016 Tri-1 2016-17Document3 pagesTeaching Plan ECP1016 Tri-1 2016-17Garett MasterNo ratings yet
- Rest 120 Seconds Between Each Set (Longer If Required) : Week - 2Document8 pagesRest 120 Seconds Between Each Set (Longer If Required) : Week - 2Ramón Nogueras PérezNo ratings yet
- Crushing Performances of Winding Square Kenaf Fiber Reinforced CompositesDocument5 pagesCrushing Performances of Winding Square Kenaf Fiber Reinforced CompositesGarett MasterNo ratings yet
- Sales ReceiptDocument1 pageSales ReceiptGarett MasterNo ratings yet
- Latest Student Teaching PlanDocument3 pagesLatest Student Teaching PlanGarett MasterNo ratings yet
- Mark Display - TestDocument7 pagesMark Display - TestGarett MasterNo ratings yet
- Midterm ResultsDocument4 pagesMidterm ResultsGarett MasterNo ratings yet
- FYP Presentation Time-Slot (By Students' Name) : Student Project Title Supervisor Moderator Date Time-Slot VenueDocument5 pagesFYP Presentation Time-Slot (By Students' Name) : Student Project Title Supervisor Moderator Date Time-Slot VenueGarett MasterNo ratings yet
- Subject OfferDocument24 pagesSubject OfferGarett MasterNo ratings yet
- FYP Presentation Time-Slot (By Students' Name) : Student Project Title Supervisor Moderator Date Time-Slot VenueDocument5 pagesFYP Presentation Time-Slot (By Students' Name) : Student Project Title Supervisor Moderator Date Time-Slot VenueGarett MasterNo ratings yet
- CV ExampleDocument8 pagesCV ExampleGarett MasterNo ratings yet
- Trimester 2 PlannerDocument6 pagesTrimester 2 PlannerGarett MasterNo ratings yet
- 2015 T3 ITP TimelinesDocument1 page2015 T3 ITP TimelinesGarett MasterNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 QDocument1 pageTutorial 1 QGarett MasterNo ratings yet
- Trimester 1 2016 PlannerDocument5 pagesTrimester 1 2016 PlannerGarett MasterNo ratings yet
- 3555 - EHM3066 Tutorial 1Document4 pages3555 - EHM3066 Tutorial 1Garett MasterNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 QDocument1 pageTutorial 5 QGarett MasterNo ratings yet
- Numerical Simulations of Interrupted and Conventional Microchannel Heat SinksDocument12 pagesNumerical Simulations of Interrupted and Conventional Microchannel Heat SinksAnkit LonareNo ratings yet
- Proportional Hydraulic Drive DesignDocument22 pagesProportional Hydraulic Drive DesignThafer MajeedNo ratings yet
- ANALYSIS OF WAY BESAI RIVER FLOODING WITH MATHEMATICAL MODELINGDocument16 pagesANALYSIS OF WAY BESAI RIVER FLOODING WITH MATHEMATICAL MODELINGsugendengalNo ratings yet
- Artificial-Lift RapportDocument32 pagesArtificial-Lift RapportFakher JemliNo ratings yet
- Steam Trap - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesSteam Trap - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAnbu Ayyappan100% (1)
- Path LineDocument4 pagesPath LineAien Nurul AinNo ratings yet
- Water Flow Experiments: Single and Double Bottle SystemsDocument13 pagesWater Flow Experiments: Single and Double Bottle SystemsJiggy Lawrence BathanNo ratings yet
- What Are Navier-Stokes Equations - QuoraDocument7 pagesWhat Are Navier-Stokes Equations - QuoraHyan GontijoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 Sayas Ej2Document5 pagesExercise 1 Sayas Ej2bryan50% (2)
- Ejector vs Eductor - What's the DifferenceDocument2 pagesEjector vs Eductor - What's the DifferencePierre NorrisNo ratings yet
- Experimental Results For Eppler 387 AirfoilDocument238 pagesExperimental Results For Eppler 387 Airfoilweelad35No ratings yet
- Tugas 2 Hidrodinamika 1 Dosen Bapak Sujantoko ST, MTDocument17 pagesTugas 2 Hidrodinamika 1 Dosen Bapak Sujantoko ST, MTAriefNo ratings yet
- BernaulliDocument6 pagesBernaulliCamille SemillaNo ratings yet
- Pump Size: 1-1/2 X 2 X 9L Model: B1-1/2Z - L: Type CCMD FM CPLG FM Belt Sae Hydraulic Ac EngineDocument2 pagesPump Size: 1-1/2 X 2 X 9L Model: B1-1/2Z - L: Type CCMD FM CPLG FM Belt Sae Hydraulic Ac EngineWilmer CaceresNo ratings yet
- Pump Maintenance EssentialsDocument29 pagesPump Maintenance EssentialsnaushadmnnitNo ratings yet
- Rheologica Acta Volume 7 Issue 3 1968 (Doi 10.1007 - bf01985784) Teoman Ariman - Ahmet S. Cakmak - Some Basic Viscous Flows in Micropolar Fluids PDFDocument7 pagesRheologica Acta Volume 7 Issue 3 1968 (Doi 10.1007 - bf01985784) Teoman Ariman - Ahmet S. Cakmak - Some Basic Viscous Flows in Micropolar Fluids PDFSrinivas JangiliNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Solved ProblemsDocument2 pages1.4 Solved ProblemsMohammad Hussain Raza ShaikNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Boundary Layers and Turbulence I: Wind Loading and Structural Response Lecture 6 Dr. J.D. HolmesDocument27 pagesAtmospheric Boundary Layers and Turbulence I: Wind Loading and Structural Response Lecture 6 Dr. J.D. HolmesSNADANo ratings yet
- HydraulicjumpDocument20 pagesHydraulicjumpJahno UdondeNo ratings yet
- AFT Fathom Model Analysis of 15W40 Oil PipelineDocument9 pagesAFT Fathom Model Analysis of 15W40 Oil Pipelineruben estebanNo ratings yet
- Discharge Relations For Hydraulic Structures and Head Losses From Different ComponentsDocument160 pagesDischarge Relations For Hydraulic Structures and Head Losses From Different ComponentsEdgar Chuquipiondo VargasNo ratings yet
- Withdrawal and Drainage of Generalized Second Grade Fluid On Vertical Cylinder With Slip ConditionsDocument14 pagesWithdrawal and Drainage of Generalized Second Grade Fluid On Vertical Cylinder With Slip ConditionsMuhammad FarooqNo ratings yet
- Viscosity Ratio of SlurriesDocument13 pagesViscosity Ratio of SlurriesTamaNo ratings yet
- Problemas ResueltosDocument13 pagesProblemas ResueltosLiz Navarro MonteroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document15 pagesChapter 3abdu yimerNo ratings yet
- Orifice and Jet Flow (HB 019)Document12 pagesOrifice and Jet Flow (HB 019)Usman AliNo ratings yet
- Appendix D.4 Intake Design ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesAppendix D.4 Intake Design Considerationsnikom kraitadNo ratings yet
- The Thin Film Approximation in Hydrodynamic, Including Elastohydrodynamic, LubricationDocument43 pagesThe Thin Film Approximation in Hydrodynamic, Including Elastohydrodynamic, Lubricationحسين مهديNo ratings yet
- 100 Vip Topic For BWDBDocument8 pages100 Vip Topic For BWDBMd. Maruf HasanNo ratings yet