Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Plant Reproduction Questions
Uploaded by
Irwan PriyantoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Plant Reproduction Questions
Uploaded by
Irwan PriyantoCopyright:
Available Formats
Self-assessment questions
8.01
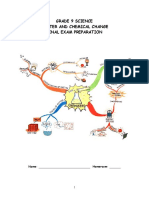
8 Reproduction in flowering plants
1 Which is the most accurate statement?
The principal role of a flower in the life
cycle of a plant is:
(a) attracting insects
(b) producing seeds
(c) producing pollen
(d) producing nectar
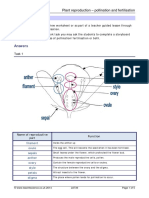
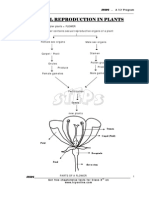
2 Name the parts A-J shown on this drawing
of a half-flower of a Stitchwort.
3 What is (a) the male gamete, and (b) the
female gamete in a flowering plant?
E
F
A
H
B
I
C
4 Complete the following paragraph selecting words from the list below. Pollination is the
transfer of . from the .. to the . in a flower. In cross-pollination, the . from a
flower on one .is transferred to the .of another . of the same species.
anthers, ovule, stigma, plant, flower, pollen, ovary, petal, style, receptacle, stamens
5 Complete the following sentences:
In a flowering plant fertilisation occurs when the ..of the . fuses with the .of
the . After fertilisation , the . becomes the . and the . becomes the . .
6 Which of the following statements is correct? In flowering plants:
(a) pollination can take place without fertilisation
(b) fertilisation can take place without pollination
(c) pollination and fertilisation are the same
(d) pollination and fertilisation must occur at the same time
7 Some species of plant are strongly adapted to pollination by certain insects. Which of the
following characteristics would you regard as adaptations to pollination by bees:
(a) white or coloured petals
(f) small green petals
(b) light, smooth pollen grains
(g) production of nectar
(c) spiky or sticky pollen grains
(h) production of pollen
(d) anthers and stigma inside the flower
(i) production of scent?
(e) anthers and stigma protruding from the flower
pollen grain
8 A bee visits several flowers in succession on
a single willow herb plant. In doing so, the
bee transfers pollen from the younger flowers,
near the top of the inflorescence (group of
flowers) to the older flowers near
the base of the inflorescence. Is this an
example of self-pollination or cross-pollination?
9 Complete the drawing to show what has to
happen before fertilisation can occur
stigma
ovule
micropyle
ovary
Self-assessment questions
8.02
Reproduction in flowering plants (continued)
10 The drawings show seeds or fruits of different plants.
(a) From the appearance of the structures, make a guess at how each one is dispersed giving
reasons for your answers.
(b) What are the advantages to a plant of an effective method of seed dispersal?
A
B
C
D
11 The root of the pea seedling is marked with equally spaced lines
as shown here. Draw what you would expect to see in two days' time if the
root
(a) grew only from the tip
(c) grew only at the top
(b) grew uniformly along its length (d) did not grow.
12 (a) What conditions do most seeds need in order to begin germination?
(b) What other condition do the seedlings need to continue growth to mature
plants?
13 How would you design, in principle, an experiment to test the hypothesis that a certain
variety of lettuce seed needed daylight in order to germinate?
D
14 Figure 1 represents a pea seed split open to
show its structure. Name the parts A-C
and state the function of each.
Figure 2 represents a pea seedling-5 days
after germination. Name the parts D-H.
15 The early stages of germination take place
in the soil where there is little or no light for
photosynthesis. How does the seedling obtain
materials for its growth
and energy during
Self-assessment
questions
needs during this time?
F
G
Figure 1
8.03
Figure 2
Reproduction in flowering plants (continued)
16 You are asked to set up an experiment to investigate the effect of temperature on the rate of
germination. You place ten soaked peas in each of three flower pots containing moist sand. One
pot is placed in a refrigerator at 4C, one is placed in a cupboard at room temperature
(about18C) and the third is placed in an incubator at 25C. You leave them for a week, checking
each day that the sand is kept moist.
(a) How would you judge the results?
(b) Why was the pot, at room temperature, kept in a cupboard rather than on the
laboratory bench?
17 Starch is one of the most common storage product in seeds. What happens to the starch
before it can be used by the germinating seed?
18 The diagram represent an experiment to
test the hypothesis that seeds need oxygen
in order to germinate.
(a) What is the liquid in A and what does it do?
(b) What is the liquid in B and what does it do?
(c) Which of the two flasks represents the control
and what is its purpose?
(d) What results would you expect
(i) if oxygen is necessary for germination
(ii) if oxygen is not necessary for germination?
B
wet cotton
wool
cress
seeds
no oxygen
19 What differences would you expect to see between pea seedlings grown for 10 days in total
darkness and pea seedlings grown in the light for the same period of time?
26
You might also like
- Characteristics of Living Things-PracticeDocument5 pagesCharacteristics of Living Things-Practicesmbdy tbhhhNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Science Exam Prep GuideDocument15 pagesGrade 9 Science Exam Prep GuideBekki VanderlendeNo ratings yet
- Adaptation in Plants Worksheet PDFDocument7 pagesAdaptation in Plants Worksheet PDFSamit Kumar Saha100% (2)
- Plant Structures Quiz - Answer KeyDocument2 pagesPlant Structures Quiz - Answer Keyapi-254428474No ratings yet
- Topic 1 Test - Cells & Organisms 2019.pdf AnsDocument9 pagesTopic 1 Test - Cells & Organisms 2019.pdf AnsHal OgleNo ratings yet
- Formative assessment on plant reproductionDocument2 pagesFormative assessment on plant reproductionelsa khairunnisa100% (3)
- Variation and SelectionDocument46 pagesVariation and SelectionLili MagossNo ratings yet
- Plant Flower and Seed WorksheetDocument5 pagesPlant Flower and Seed WorksheetHannah Rosenfeld100% (1)
- Extensions of Mendelian InheritanceDocument6 pagesExtensions of Mendelian Inheritance13ucciNo ratings yet
- PlantsDocument5 pagesPlantsShapee ManzanitasNo ratings yet
- Microorganisms Test Multiple ChoiceDocument5 pagesMicroorganisms Test Multiple ChoiceBalan MuthuNo ratings yet
- 12 Reproduction Biology Notes IGCSE PDFDocument51 pages12 Reproduction Biology Notes IGCSE PDFUmair Khan Marwat100% (1)
- Plant Reproduction QuestionsDocument3 pagesPlant Reproduction QuestionsBenjamin YapNo ratings yet
- MC Science - Revision WS - Stage 5 - C03Document9 pagesMC Science - Revision WS - Stage 5 - C03Camille HugoNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument12 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsSubrata SarkarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Periodic TableDocument0 pagesIntroduction To The Periodic TableAdnan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- 3rd Summative in Science 4-2nd QDocument2 pages3rd Summative in Science 4-2nd QERMIDA SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Investigating Living Things Chapter 1Document5 pagesInvestigating Living Things Chapter 1Saya MenangNo ratings yet
- 2022 17 Reactivity Series Checkpoint - Sec - 1 ChemistryDocument11 pages2022 17 Reactivity Series Checkpoint - Sec - 1 ChemistrySourabhiNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheets: The Plant KingdomDocument8 pagesSummary Sheets: The Plant KingdomEngy AlasutyNo ratings yet
- Biology Practical NotebookDocument38 pagesBiology Practical Notebookabdulmalik saniNo ratings yet
- 4.8 Sexual Reproductive System of Flowering PlantsDocument16 pages4.8 Sexual Reproductive System of Flowering PlantsYu HasNo ratings yet
- Science Form 5 Chapter 3 Preservation Conservation StudentDocument8 pagesScience Form 5 Chapter 3 Preservation Conservation StudentAngie Kong Su MeiNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument1 pageReproduction in PlantsravilullaNo ratings yet
- Paper 3 Essentials GuidelineDocument19 pagesPaper 3 Essentials GuidelineAtharva DangreNo ratings yet
- Paper 4 (A) (I) IGCSE Biology (Time - 30 Mins)Document12 pagesPaper 4 (A) (I) IGCSE Biology (Time - 30 Mins)Hisham AlEnaiziNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in AnimalsDocument6 pagesSexual Reproduction in AnimalsRahul Ecka100% (1)
- (TS) Junior Botany Ipe Pre Final Examination (Batch-Ii) 16-04-2022Document2 pages(TS) Junior Botany Ipe Pre Final Examination (Batch-Ii) 16-04-2022xxxxxxNo ratings yet
- Year 7 Chapter 5 WorksheetDocument3 pagesYear 7 Chapter 5 WorksheetNicholas LeongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Review PacketDocument17 pagesChapter 11 Review PacketLalisampt.20% (1)
- Unit 9A Inheritance and Selection: Name: .Document17 pagesUnit 9A Inheritance and Selection: Name: .박찬우No ratings yet
- Answers: Plant Reproduction - Pollination and Fertilisation Teaching NotesDocument5 pagesAnswers: Plant Reproduction - Pollination and Fertilisation Teaching NotesKhoo Ying WeiNo ratings yet
- Biology CH 7 Practice TestDocument6 pagesBiology CH 7 Practice Testvaleria100% (1)
- Transport in PlantsDocument6 pagesTransport in PlantsFred H HalderNo ratings yet
- Life Process WorksheetDocument2 pagesLife Process WorksheetShamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Grouping and Identifying Organisms NotesDocument12 pagesChapter 4 - Grouping and Identifying Organisms Notesjavanjude67No ratings yet
- Reflection.: - Complete The Questions BelowDocument4 pagesReflection.: - Complete The Questions BelowDuyBùiNo ratings yet
- PlantReproduction MultipleChoiceDocument2 pagesPlantReproduction MultipleChoicealemu yadessaNo ratings yet
- Pollination, Fertilisation and GerminationDocument25 pagesPollination, Fertilisation and GerminationAsad RazaNo ratings yet
- Classification NOTESDocument8 pagesClassification NOTESShahadMahmoud100% (1)
- Biology Revision - Structures in the Thorax and Respiration ProcessesDocument2 pagesBiology Revision - Structures in the Thorax and Respiration ProcessesskeltenboiNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument3 pagesSexual Reproduction in PlantsRahul Ecka67% (3)
- Section A Answer All QuestionsDocument21 pagesSection A Answer All QuestionsSJKC SUNGAI DURIANNo ratings yet
- 0610 Topic QuestionsDocument302 pages0610 Topic QuestionsFor GamingNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Science Worksheet - Cell - Structure and FunctionsDocument3 pagesClass 8 Science Worksheet - Cell - Structure and FunctionsSandyaNo ratings yet
- Section 3.1 Solids, Liquids, and Gases: Reading StrategyDocument2 pagesSection 3.1 Solids, Liquids, and Gases: Reading StrategyensentisNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 2 Form 4Document16 pagesScience Chapter 2 Form 4Muhammad Akmal Kamaluddin75% (4)
- Flashcards - Topic 10 Diseases and Immunity - CIE Biology IGCSEDocument37 pagesFlashcards - Topic 10 Diseases and Immunity - CIE Biology IGCSEJane Lea100% (1)
- Reproduction in Organisms: Asexual Reproduction and Life SpanDocument11 pagesReproduction in Organisms: Asexual Reproduction and Life SpanRiya MondalNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Maths Paper 3 Model AnswersDocument22 pagesIGCSE Maths Paper 3 Model AnswersDON-thegreat100% (7)
- Cambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/43Document20 pagesCambridge IGCSE: BIOLOGY 0610/43Rino DoctNo ratings yet
- Short QuizDocument2 pagesShort QuizAnonymous MGMgUWNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology 17 Reproduction in PlantsDocument45 pagesO Level Biology 17 Reproduction in PlantsHamzu GamingNo ratings yet
- CBSE EVS Notes on Roots and FlowersDocument4 pagesCBSE EVS Notes on Roots and FlowersK LohithNo ratings yet
- Ch4 States of Matter & ChangesDocument3 pagesCh4 States of Matter & ChangesSiti Norhayati100% (2)
- Saraswati Vidya Niketan Human and Social Biology Name: Form: Instructions: Answer All Questions. Time: 30 MinsDocument2 pagesSaraswati Vidya Niketan Human and Social Biology Name: Form: Instructions: Answer All Questions. Time: 30 Minsnehru09No ratings yet
- 8 Science Worksheet ch2 1Document3 pages8 Science Worksheet ch2 1KSP Classes GondiaNo ratings yet
- April Holiday assignment (24)Document3 pagesApril Holiday assignment (24)Kevin KiplangatNo ratings yet
- FORM 3 - Plant Reproduction QuestionsDocument3 pagesFORM 3 - Plant Reproduction QuestionsDAILY IMPARTATION TVNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction QuestionsDocument3 pagesPlant Reproduction Questionsjustinchu1505No ratings yet
- ICSE Class 9 Chapter 5 - Pollination & Fertilizations Back ExceriseDocument6 pagesICSE Class 9 Chapter 5 - Pollination & Fertilizations Back ExceriseArpan KaurNo ratings yet
- Pollen Grain Structure and FunctionDocument6 pagesPollen Grain Structure and Functionsachin sakuNo ratings yet
- Ko ko nut song - Learn about coconut fruit and its many usesDocument1 pageKo ko nut song - Learn about coconut fruit and its many usesLibraria Tic TacNo ratings yet
- Turcz 2011 15-100Document87 pagesTurcz 2011 15-100love gisNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of A Young Dicot RootDocument3 pagesAnatomy of A Young Dicot RootVanessa Leuterio0% (2)
- Plant Reproduction: Click To EnterDocument44 pagesPlant Reproduction: Click To EnterNur NadiahNo ratings yet
- 2001 - Moreno Et Al - Notes On The Genus TulostomaDocument10 pages2001 - Moreno Et Al - Notes On The Genus TulostomaBianca SilvaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Title:: Grade 12 - Day 11Document14 pagesLesson Title:: Grade 12 - Day 11Feedback Or BawiNo ratings yet
- New Zealand Polyporaceae: 6.-The Genus ColtriciaDocument14 pagesNew Zealand Polyporaceae: 6.-The Genus ColtriciacooperjNo ratings yet
- DICRANACEAE Schimper: Robert R. Ireland JRDocument15 pagesDICRANACEAE Schimper: Robert R. Ireland JRCristopher Jimenez OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Plants and Their Functions - Multiple ChoiceDocument3 pagesPlants and Their Functions - Multiple ChoiceMary Mae AlabadoNo ratings yet
- GPB 366 Practical ManualDocument70 pagesGPB 366 Practical ManualSanjay RautNo ratings yet
- PteridophytesDocument5 pagesPteridophytesAsif SultanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document9 pagesChapter 6Roddick BongNo ratings yet
- 307 48 ET V1 S1 - File1 PDFDocument22 pages307 48 ET V1 S1 - File1 PDFaaaatniNo ratings yet
- Leaves Review QuestionsDocument4 pagesLeaves Review QuestionsPhoebe Joy DionisioNo ratings yet
- Karakteristik Morfologi Daun Sirih Merah Piper Crocatum RuitzDocument3 pagesKarakteristik Morfologi Daun Sirih Merah Piper Crocatum RuitzYatyIbrahimNo ratings yet
- BIO 11 Lect - Botany Part 2 AssignmentDocument2 pagesBIO 11 Lect - Botany Part 2 AssignmentLara GreyjoyNo ratings yet
- 6) Types of Vegetative PropagationDocument8 pages6) Types of Vegetative PropagationTioma Kartika LimbongNo ratings yet
- Botany Arjun Shyonak PalanduDocument6 pagesBotany Arjun Shyonak PalanduPrajkta AbnaveNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science for Upper Primary IDocument67 pagesIntegrated Science for Upper Primary IGabriel MashoodNo ratings yet
- Study of Floral Characteristics Through Flower DissectionDocument3 pagesStudy of Floral Characteristics Through Flower DissectionArnabNo ratings yet
- 3 EquisetumDocument13 pages3 EquisetumCDB 1st Semester 2077No ratings yet
- Internal Structure of A LeafDocument38 pagesInternal Structure of A Leafnozel77100% (1)
- Botlab - Flowers, Fruits, Fruits & Seed DispersalDocument6 pagesBotlab - Flowers, Fruits, Fruits & Seed DispersalBerle Joy VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Leon 1919 Sid A Britton IDocument324 pagesLeon 1919 Sid A Britton IgeorgesidneybarachoNo ratings yet
- AGRI 31 Exercise 1B. Worksheet PDFDocument7 pagesAGRI 31 Exercise 1B. Worksheet PDFlexfred55No ratings yet
- Worksheet 9.1: Chapter 9: Plant Science - Fifteen Summary FactsDocument2 pagesWorksheet 9.1: Chapter 9: Plant Science - Fifteen Summary FactsRabia RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Leaf Model GuideDocument8 pagesLeaf Model GuideLina MaflaNo ratings yet
- My Fun Science Corner - Plant System How Do Plants Store Food Article 2Document2 pagesMy Fun Science Corner - Plant System How Do Plants Store Food Article 2api-243322195No ratings yet