Professional Documents
Culture Documents
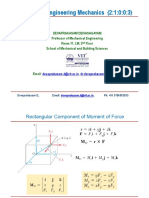
Lecture Engineering MEchanics
Uploaded by
Devaprakasam DeivasagayamCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture Engineering MEchanics
Uploaded by
Devaprakasam DeivasagayamCopyright:
Available Formats
ME 101: Engineering Mechanics
A. Narayana Reddy
Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati,
Guwahati - 781039, India.
Beams and cables
Previous discussion
determining external forces acting on a structure
determining forces which hold together the various members of a
structure
Current discussion
Determining the internal forces (i.e., tension/compression, shear, and
bending) which hold together the various parts of a given member.
Beams and cables
Beams - usually long, straight, prismatic members designed to support
loads applied at various points along the member
Cables - flexible members capable of withstanding only tension,
designed to support concentrated or distributed loads
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
2 / 33
Beams
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
3 / 33
Internal forces in beams
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
4 / 33
Example
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
5 / 33
Example
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
6 / 33
Example
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
7 / 33
Example
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
8 / 33
Example
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
9 / 33
Beams with different type of loads
(c) Distributed load with discontinuity
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
10 / 33
Statically determinate and indeterminate beams
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
11 / 33
Distributed loads
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
12 / 33
General distributed load
The reaction forces can be evaluated by replacing the distrubuted load
with the concentrated load R at centroid.
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
13 / 33
Example-1
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
14 / 33
Example-2
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
15 / 33
Example-3
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
16 / 33
Internal effects
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
17 / 33
Internal effects
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
18 / 33
Internal effects
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
19 / 33
Sign convention
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
20 / 33
Sign convention
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
21 / 33
Shear force and bending moment diagrams
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
22 / 33
Shear force and bending moment diagrams
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
23 / 33
Example-1
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
24 / 33
Example-1
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
25 / 33
Example-1
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
26 / 33
Example-2
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
27 / 33
Example-2
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
28 / 33
Example-2
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
29 / 33
Example-2
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
30 / 33
Example-2
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
31 / 33
Relation between shear force and bending moment
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
32 / 33
Relation between shear force and bending moment
Lecture 5
A Narayana Reddy
Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati
33 / 33
You might also like
- MEE1002 Engineering Mechanics L9Document17 pagesMEE1002 Engineering Mechanics L9Devaprakasam DeivasagayamNo ratings yet
- Fourier Series TutorialDocument80 pagesFourier Series TutorialJose VillegasNo ratings yet
- Intro To NDTDocument34 pagesIntro To NDTkbldamNo ratings yet
- MEE1002 Engineering Mechanics L8Document22 pagesMEE1002 Engineering Mechanics L8Devaprakasam DeivasagayamNo ratings yet
- Fourier Series TutorialDocument80 pagesFourier Series TutorialJose VillegasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Genetic AlgorithmDocument57 pagesIntroduction To Genetic AlgorithmDevaprakasam DeivasagayamNo ratings yet
- Energy SourcesDocument9 pagesEnergy SourcesDevaprakasam DeivasagayamNo ratings yet
- MEE1002 Engineering Mechanics LecturesDocument7 pagesMEE1002 Engineering Mechanics LecturesDevaprakasam DeivasagayamNo ratings yet
- 238798917PC - Indian Lubricants Sector - Sep 2016 20160920081329Document44 pages238798917PC - Indian Lubricants Sector - Sep 2016 20160920081329Devaprakasam DeivasagayamNo ratings yet
- Genetic Algorithms: Muhannad HarrimDocument44 pagesGenetic Algorithms: Muhannad HarrimDebabrata PalNo ratings yet
- Materials Science & Engineering Introductory E-BookDocument13 pagesMaterials Science & Engineering Introductory E-Bookkaushaltrivedi46No ratings yet
- ME202 Engineering Mechanics L1Document9 pagesME202 Engineering Mechanics L1Devaprakasam DeivasagayamNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machines Textbook Scanned PDFDocument287 pagesFluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machines Textbook Scanned PDFPullavartisrikanthChowdaryNo ratings yet
- PrimarysecDocument22 pagesPrimarysecilhammkaNo ratings yet
- The Fourier Transform and Its ApplicationsDocument428 pagesThe Fourier Transform and Its Applicationsmachinelearner100% (3)
- ME202 Engineering Mechanics L3Document20 pagesME202 Engineering Mechanics L3Devaprakasam DeivasagayamNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 PDFDocument9 pagesLecture 2 PDFDevaprakasam DeivasagayamNo ratings yet
- ME 101: Engineering Mechanics: A. Narayana ReddyDocument13 pagesME 101: Engineering Mechanics: A. Narayana ReddyDevaprakasam DeivasagayamNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Engineering MechanicsDocument18 pagesLecture On Engineering MechanicsDevaprakasam DeivasagayamNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics LectureDocument36 pagesEngineering Mechanics LectureDevaprakasam DeivasagayamNo ratings yet
- ME202 Engineering Mechanics L2Document17 pagesME202 Engineering Mechanics L2Devaprakasam DeivasagayamNo ratings yet
- STM Electronics: AG Moeller - University of Essen M. Matena 25th May 2004Document12 pagesSTM Electronics: AG Moeller - University of Essen M. Matena 25th May 2004Devaprakasam DeivasagayamNo ratings yet
- PartOne Final SAXSDocument62 pagesPartOne Final SAXSDevaprakasam DeivasagayamNo ratings yet
- Raman ScatteringDocument65 pagesRaman ScatteringPragna ReddyNo ratings yet
- Light Microscopy HandoutDocument24 pagesLight Microscopy HandoutDevaprakasam DeivasagayamNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Wave-Particle Duality FundamentalsDocument7 pagesWave-Particle Duality FundamentalsRahmatullahNo ratings yet
- Orifice Meter ReportDocument19 pagesOrifice Meter ReportDilli Babu PNo ratings yet
- Combined stresses and beam designDocument15 pagesCombined stresses and beam designEngr Zin Myo MinNo ratings yet
- IEO Sample Paper For Class 4thDocument4 pagesIEO Sample Paper For Class 4thDavid Farmer33% (3)
- MeldesDocument28 pagesMeldesPallav KumarNo ratings yet
- Air Ingress CalculationsDocument5 pagesAir Ingress CalculationsMallinatha PNNo ratings yet
- Applied Mathematical Modelling: Mahesh Prakash, Paul W. ClearyDocument15 pagesApplied Mathematical Modelling: Mahesh Prakash, Paul W. ClearyDeepak Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Wind Loads UK - Portal Frame WEDocument31 pagesWind Loads UK - Portal Frame WEjohnsmith198083% (6)
- Holzer's Method and Geared SystemsDocument15 pagesHolzer's Method and Geared SystemsWen Ming Lau100% (2)
- 1-D Kinematics - Lesson 1 - Motion DescriptionDocument31 pages1-D Kinematics - Lesson 1 - Motion DescriptionErica Joy EstrellaNo ratings yet
- LAWS OF MOTIONDocument22 pagesLAWS OF MOTIONArijit MondalNo ratings yet
- D7300 PDFDocument6 pagesD7300 PDFJesús Luis Arce GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Mushtaq Ahmed MSc Physics Sound Intensity LevelDocument18 pagesMushtaq Ahmed MSc Physics Sound Intensity LevelMushtaq AhmedNo ratings yet
- 35-07 - Spur Gears-1Document28 pages35-07 - Spur Gears-1Frances PasanaNo ratings yet
- Stress Analysis TechniquesDocument13 pagesStress Analysis Techniquesaap1No ratings yet
- Crane GirderDocument45 pagesCrane GirderbolarinwadeNo ratings yet
- Buckling Analysis of Composite Plates with CutoutsDocument11 pagesBuckling Analysis of Composite Plates with Cutoutsசெல்வ குமார்No ratings yet
- PR - en 13445-3Document159 pagesPR - en 13445-3David CubillosNo ratings yet
- Design of Raft Foundations On Winkler Springs: F. R. LopesDocument28 pagesDesign of Raft Foundations On Winkler Springs: F. R. LopesCarlo RabaiottiNo ratings yet
- Classwork / Assignment: EquilibriumDocument3 pagesClasswork / Assignment: EquilibriumSelwah Hj AkipNo ratings yet
- Fatigue Assessment of Ship StructuresDocument25 pagesFatigue Assessment of Ship StructuresAlex TheodoulNo ratings yet
- OpenFoam Solvers ListDocument4 pagesOpenFoam Solvers ListAbhishek VermaNo ratings yet
- Aces Review Center: Ree Online Review Refresher Math 9 by Engr. Jimmy L. Ocampo 0920 - 644 - 6246Document3 pagesAces Review Center: Ree Online Review Refresher Math 9 by Engr. Jimmy L. Ocampo 0920 - 644 - 6246Jr TrinidadNo ratings yet
- A Study of Static & Dynamic Modulus of Elasticity of Concrete PDFDocument16 pagesA Study of Static & Dynamic Modulus of Elasticity of Concrete PDFben indrawanNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Lecture Notes PDFDocument24 pagesDiffusion Lecture Notes PDFSuraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Laminar Flow between Fixed Parallel PlatesDocument11 pagesLaminar Flow between Fixed Parallel PlatesLeillane BeatrizNo ratings yet
- Diseno Sismico ASCE 7-02-05Document2 pagesDiseno Sismico ASCE 7-02-05Juan Carlos VillalbaNo ratings yet
- 22MSP10028 - ANAND SAGAR - Lorentz Transformation & MatrixDocument11 pages22MSP10028 - ANAND SAGAR - Lorentz Transformation & MatrixAnandNo ratings yet
- Poisson TermodinamicaDocument97 pagesPoisson TermodinamicaJoshua WrightNo ratings yet
- EE207 Assignment 1Document7 pagesEE207 Assignment 1Anuranan DasNo ratings yet