Professional Documents
Culture Documents
23 en Caches
Uploaded by
Danladi Shemang KajeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
23 en Caches
Uploaded by
Danladi Shemang KajeCopyright:
Available Formats
How to
Configure Caches for KM
ENTERPRISE PORTAL 5.0/6.0
ASAP How to Paper
Applicable Releases:
May 2003
EP 5.0 SP5 and EP 6.0
HOW TO CONFIGURE CACHES FOR KM
HOW TO CONFIGURE CACHES FOR KM ........................................................................................1
1
BUSINESS SCENARIO ................................................................................................................2
THE RESULT ................................................................................................................................2
THE STEP BY STEP SOLUTION.................................................................................................2
3.1
Summary...................................................................................................................................2
3.2
Prerequisites ............................................................................................................................3
3.3
Activities ...................................................................................................................................3
3.4
Components and Corresponding Caches ............................................................................4
3.4.1
ACL Security Manager .......................................................................................................4
3.4.2
(JDBC) ACL Manager ........................................................................................................4
3.4.3
Application-Defined Properties...........................................................................................6
3.4.4
URL Content Access ..........................................................................................................6
3.4.5
JDBC ID Mapper ................................................................................................................7
3.4.6
CM-Repository....................................................................................................................8
3.4.6.1 CM Cache .......................................................................................................................8
3.4.6.2 Cache for small content ..................................................................................................8
3.4.7
Web Repository ..................................................................................................................9
3.4.8
WebDAV Repository ..........................................................................................................9
3.4.9
Lotus Notes Repository ....................................................................................................10
3.4.10 Object Type Handler Cache .............................................................................................11
3.4.11 Rendering Cache .............................................................................................................12
3.4.12 Control Status Service Cache ..........................................................................................12
3.4.13 XSLT Pipeline Processor Cache ......................................................................................13
3.4.14 TREX Java Client .............................................................................................................14
3.4.14.1 Memory Cache ..........................................................................................................14
3.4.14.2 Administration Cache ................................................................................................14
3.5
Use of the Cache Monitor .....................................................................................................15
3.5.1
Analysis of Displayed Data...............................................................................................15
3.6
4
Recommendations for the cache configuration in a standard scenario. ........................16
COPYRIGHT ...............................................................................................................................17
2003 SAP
HOW TO CONFIGURE CACHES FOR KM
1 Business Scenario
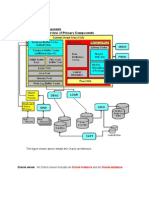
Many caches are used in the Knowledge Management platform to ensure performance in the system.
It is not only important that caches are created; they must also be configured correctly.
2 The Result
After you have configured the caches as described in this how-to guide, you should have an optimally
tuned system as far as caches are concerned.
However, an increase in performance is not dependent only on caches. Other components are also
important. The processor performance and main memory of the Portal server, the available
bandwidth, number of users, and number of documents managed also influence the performance of
the Portal.
3 The Step By Step Solution
3.1
Summary
This document lists the components of the Knowledge Management platform that use caches. As
well as a brief explanation of the respective caches, section 3.6 contains a recommendation for
configuration in a standard scenario.
The configuration of a cache used in Content Management includes parameters such as capacity
and maximum cache size as well as the maximum and average size of a cache entry. You can also
specify how long an entry in the cache can be current (default time to live) and whether it is a
singleton cache. The best values for these attributes depend on several factors:
How many entries are added to the cache during what period of time?
How much memory is needed for the entries in the cache?
For how long do the entries remain current?
How important is the efficiency of the components that use the cache?
How much memory is available on the host?
2003 SAP
HOW TO CONFIGURE CACHES FOR KM
The following parameters denote the memory caches used in KM.
Memory Cache Parameters
Parameter
Description
Restart Lifetime on
Access
Extends the lifetime of cache entries and prevents entries that are still
needed from being deleted from the cache.
A cache normally automatically discards entries that have reached a
certain age. This age can be specified in the configuration of a cache. It
can also be specified by the software that uses the cache when an
entry is set in the cache.
Sometimes, entries ought not be deleted, since they are still being
accessed. This is especially true for caches that contain objects that do
not change often or that that are used by an application that does not
rely on current data.
Singleton
Instantiation type of cache.
If Singleton is activated, the memory is only reserved for the cache
once. All components that use the cache can then use all the objects in
the cache.
If a cache is not a singleton, the memory is reserved separately for
each component that uses the cache. The components can then not
access the objects of other components that are contained in the
cache.
Assumed Entry Size
Space in bytes adopted for a new cache if the system using the cache
specified no other size.
Capacity
Capacity of the cache (that is, maximum number of entries in the
cache).
Default Time-to-Live
Time in seconds after which the cache entry is automatically removed
from the cache. The value 0 means that the entry never becomes
obsolete.
Maximum Cache Size
Maximum total size of all cache entries in bytes. The value 0 means
that there is no limit.
Maximum Entry Size
Maximum size of a cache entry in bytes. The value 0 means that there
is no limit.
The caches listed are memory caches that are stored in the main memory of the Portal server.
3.2
Prerequisites
You need to be assigned the role KM Admin (EP 5.0) or System Administrator (EP 6.0) in order to
configure caches.
3.3
Activities
To create a cache or to change the configuration of an existing cache, choose Content Management
Utilities Caches in the Configuration iView.
You can determine the exact value for the capacity of a cache by using the cache monitor (see 3.5).
2003 SAP
HOW TO CONFIGURE CACHES FOR KM
3.4
3.4.1
Components and Corresponding Caches
ACL Security Manager
The ACL security manager uses a cache in which the access control lists (ACLs) that are valid for
resources are stored (effective ACLs). Since ACLs are inherited, there may be an entry in this cache
for every resource of the underlying repository. ACLs are small cache entries (a few KB). The
AclSecurityManager is used heavily, so its cache should be large.
ca _rsrc_acl (effective ACL cache)
Parameter
Setting
Description
Restart Lifetime on
Access
Not activated
Singleton
Activated
Multiple ACL security managers can use the cache
together.
Assumed Entry Size
This value is not used if the maximum size of the
cache is set to unlimited (that is, Maximum Cache
Size = 0)
Capacity
This value depends on the number of frequently used resources within
the repository that are assigned to the ACL security manager.
Default Time-to-Live
Half an hour to
several hours
The cache is checked for obsolete entries within
one CM installation, so this value can be high.
Maximum Cache Size
0 (unlimited)
The actual size of the ACLs is not determined.
Maximum Entry Size
0 (unlimited)
You select the ca_rsrc_acl cache in the configuration of repository managers under Content
Management Repository Managers in the ACL Manager Cache parameter.
3.4.2
(JDBC) ACL Manager
The (JDCB) ACL manager uses two caches; one for the ACLS, and one for permissions and object
types. The ACL cache contains entries for every ACL that is used by the system. The cache for
permissions only contains a small number of entries, most of which are static.
ACLs are small cache entries that need little memory (a few KB), as permissions and object types are
very small (< 1 KB). The ACL manager is used heavily, so its cache should be large.
2003 SAP
HOW TO CONFIGURE CACHES FOR KM
ca_cm_rep_acl, ca_cm_srv_acl (ACL cache)
Parameter
Setting
Description
Restart Lifetime on
Access
Not activated
Singleton
Activated
Multiple ACL managers can use the cache
together.
Assumed Entry Size
This value is not used if the maximum size of the
cache is set to unlimited (that is, Maximum Cache
Size = 0)
Capacity
This value depends on the number of frequently used resources with an
ACL within the repository that are assigned to the ACL security
manager.
Default Time-to-Live
Half an hour to
several hours
The cache is checked for obsolete entries within
one CM installation, so this value can be high.
Maximum Cache Size
0 (unlimited)
The actual size of the ACLs is not determined.
Maximum Entry Size
0 (unlimited)
You can select the ca_cm_rep_acl and ca_cm_srv_acl caches in the configuration of the ACL
manager under Content Management Utilities ACL Managers in the ACL Cache parameter.
ca_cm_rep_acl_perm, ca_cm_srv_acl_perm (Permission cache)
Parameter
Setting
Description
Restart Lifetime on
Access
Not activated
Singleton
Activated
Multiple ACL managers can use the cache
together.
Assumed Entry Size
This value is not used if the maximum size of the
cache is set to unlimited (that is, Maximum Cache
Size = 0)
Capacity
100
Default Time-to-Live
Half an hour to
several hours
Maximum Cache Size
0 (unlimited)
Maximum Entry Size
0 (unlimited)
The cache is checked for obsolete entries within
one CM installation, so this value can be high.
You can select the ca_cm_rep_acl_perm and ca_cm_srv_acl_perm caches in the configuration of
the ACL manager under Content Management Utilities ACL Managers in the Permission Cache
parameter.
2003 SAP
HOW TO CONFIGURE CACHES FOR KM
3.4.3
Application-Defined Properties
The application property service uses one cache to store the properties of resources. Depending on
the number and content of the properties, entries can be small or of medium size.
ca_props_1 (Cache for Application-Defined Properties)
Parameter
Setting
Description
Restart Lifetime on
Access
Not activated
Singleton
Activated
Assumed Entry Size
Capacity
This value depends on the number of frequently used resources with
application-defined properties within the repositories that use the
application property service.
Default Time-to-Live
Half an hour to
several hours
The cache is checked for obsolete entries within
one CM installation, so this value can be high.
Maximum Cache Size
0 (unlimited)
The actual size is not determined.
Maximum Entry Size
0 (unlimited)
This value is not used if the maximum size of the
cache is set to unlimited (that is, Maximum Cache
Size = 0)
The ca_props_1 cache is already selected under Content Management Repository Services
Application Properties Repository Service.
3.4.4
URL Content Access
The URL content access utility uses its cache to store the content of external link resources. The
entries can be large.
ca_ca (Cache for URL Content Access)
Parameter
Setting
Description
Restart Lifetime on
Access
Not activated
Singleton
Activated
Assumed Entry Size
Capacity
This value depends on the number of frequently used external link
resources.
Default Time-to-Live
Half an hour to
several hours
The cache is checked for obsolete entries within
one CM installation, so this value can be high.
Maximum Cache Size
0 (unlimited)
The actual size of the content is not determined.
Maximum Entry Size
0 (unlimited)
This value is not used if the maximum size of the
cache is set to unlimited (that is, Maximum Cache
Size = 0)
The ca_ca cache is already selected under Content Management Utilities URL Content Access.
2003 SAP
HOW TO CONFIGURE CACHES FOR KM
3.4.5
JDBC ID Mapper
The JDBC ID mapper uses its cache to store mappings between resource URIs and fixed IDs that
remain unchanged even if the resource is renamed. The cache entries are small.
ca_idmapper (JDBC ID Mapper Cache)
Parameter
Setting
Description
Restart Lifetime on
Access
Not activated
Singleton
Activated
Assumed Entry Size
Capacity
This value depends on the number of frequently used resources within
CM.
Default Time-to-Live
Half an hour to
several hours
The cache is checked for obsolete entries within
one CM installation, so this value can be high.
Maximum Cache Size
0 (unlimited)
The actual size of the mappings is not determined.
Maximum Entry Size
0 (unlimited)
This value is not used if the maximum size of the
cache is set to unlimited (that is, Maximum Cache
Size = 0)
The cache is already selected under Content Management Utilities JDBC ID Mapper.
2003 SAP
HOW TO CONFIGURE CACHES FOR KM
3.4.6
CM-Repository
A CM repository uses two other caches in addition to the ACL cache.
3.4.6.1
CM Cache
This cache stores the names of resources, properties, and locks. It does not store content.
ca_cm (CM Cache)
Parameter
Setting
Description
Restart Lifetime on
Access
Not activated
Singleton
Activated
Assumed Entry Size
Capacity
This value depends on the number of frequently used resources within
the repository.
Default Time-to-Live
Half an hour to
several hours
The cache is checked for obsolete entries within
one CM installation, so this value can be high.
Maximum Cache Size
0 (unlimited)
The actual size of the mappings is not determined.
Maximum Entry Size
0 (unlimited)
This value is not used if the maximum size of the
cache is set to unlimited (that is, Maximum Cache
Size = 0)
The cache ca_cm is already selected under Content Management Repository Managers CM Repository.
3.4.6.2
Cache for small content
This cache is used by a CM repository manager for content that is smaller than 32 KB.
ca_cm_content (Cache for small content)
Parameter
Setting
Description
Restart Lifetime on
Access
Not activated
Singleton
Activated
Assumed Entry Size
Capacity
This value depends on the number of frequently used collections within
the repository and the number of resources they contain.
Default Time-to-Live
Half an hour to
several hours
The cache is checked for obsolete entries within
one CM installation, so this value can be high.
Maximum Cache Size
0 (unlimited)
The actual size of the mappings is not determined.
Maximum Entry Size
0 (unlimited)
This value is not used if the maximum size of the
cache is set to unlimited (that is, Maximum Cache
Size = 0)
The cache ca_cm_content is already selected under Content Management Repository Managers
CM Repository.
2003 SAP
HOW TO CONFIGURE CACHES FOR KM
3.4.7
Web Repository
The Web repository cache is used to store the content of resources (Web pages). The entries can be
of medium size or large, but usually they are small (10 KB 20 KB).
Web Repository Cache
Parameter
Setting
Description
Restart Lifetime on
Access
Not activated
Singleton
Activated
Assumed Entry Size
10 KB
Capacity
This value depends on the number of frequently used resources within
the repository.
Default Time-to-Live
1-2 hours
Maximum Cache Size
This value depends on the amount of memory that should be used by
the cache.
Maximum Entry Size
10 KB
Multiple Web repositories can use the cache
together.
You should create a separate cache for each Web repository. You can select it in the configuration of
the Web repository manager under Content Management Repository Managers Web
Repository.
3.4.8
WebDAV Repository
The WebDAV repository cache is used to store resources. The cache entries are small.
WebDAV Repository Cache
Parameter
Setting
Description
Restart Lifetime on
Access
Not activated
Singleton
Activated
Assumed Entry Size
Capacity
This value depends on the number of frequently used resources within
the repository.
Default Time-to-Live
This value depends on the usage of the connected WebDAV server.
Choose a value of minutes if changes are frequently made by other
clients.
Maximum Cache Size
0 (unlimited)
Maximum Entry Size
0 (unlimited)
This value is not used if the maximum size of the
cache is set to unlimited (that is, Maximum Cache
Size = 0)
The actual size of the mappings is not determined.
You should create a separate cache for each WebDAV repository. You can select it in the
configuration of the WebDAV repository manager under Content Management Repository
Managers WebDAV Repository.
2003 SAP
HOW TO CONFIGURE CACHES FOR KM
3.4.9
Lotus Notes Repository
The notes repository cache is used to store databases, views and documents. The cache entries are
small.
For each Lotus Notes repository you need to create separate caches for databases, views, and
documents. You can select the caches in the configuration of the Lotus Notes repository manager
under Content Management Repository Managers Lotus Notes Repository.
ca_domino (Database cache)
Parameter
Setting
Description
Restart Lifetime on
Access
Not activated
Singleton
Activated
Assumed Entry Size
Capacity
This value depends on the number of frequently used resources and
collections within the repository.
Default Time-to-Live
This value depends on the usage of the connected Lotus Domino
server. Choose a value of minutes if changes are frequently made in
existing databases.
Maximum Cache Size
0 (unlimited)
Maximum Entry Size
0 (unlimited)
This value is not used if the maximum size of the
cache is set to unlimited (that is, Maximum Cache
Size = 0)
The actual size of the mappings is not determined.
ca_lotus_view (View cache)
Parameter
Setting
Restart Lifetime on
Access
Not activated
Singleton
Activated
Assumed Entry Size
Capacity
This value depends on the number of frequently used resources and
collections within the repository.
Default Time-to-Live
This value depends on the usage of the connected Lotus Domino
server. Choose a value of minutes if changes are frequently made in
existing views.
Maximum Cache Size
0 (unlimited)
Maximum Entry Size
0 (unlimited)
2003 SAP
Description
This value is not used if the maximum size of the
cache is set to unlimited (that is, Maximum Cache
Size = 0)
The actual size of the mappings is not determined.
10
HOW TO CONFIGURE CACHES FOR KM
ca_lotus_document (Document cache)
Parameter
Setting
Description
Restart Lifetime on
Access
Not activated
Singleton
Activated
Assumed Entry Size
Capacity
This value depends on the number of frequently used resources and
collections within the repository.
Default Time-to-Live
This value depends on the usage of the connected Lotus Domino
server. Choose a value of minutes if changes are frequently made in
existing documents.
Maximum Cache Size
0 (unlimited)
Maximum Entry Size
0 (unlimited)
This value is not used if the maximum size of the
cache is set to unlimited (that is, Maximum Cache
Size = 0)
The actual size of the mappings is not determined.
3.4.10 Object Type Handler Cache
This cache is used by the object type handler service. It stores URIs of resources for which object
type definition files exist, and have already been found.
oth (Object Type Handler Cache)
Parameter
Setting
Description
Restart Lifetime on
Access
Activated
Prevents entries that are still needed from being
deleted from the cache.
Singleton
Activated
Assumed Entry Size
Capacity
This value depends on the number of frequently-used resource URIs
within CM as a whole.
Default Time-to-Live
Half an hour
(1800 seconds)
The cache is checked for obsolete entries within
one CM installation, so this value can be high.
Maximum Cache Size
0 (unlimited)
The actual size of the mappings is not determined.
Maximum Entry Size
0 (unlimited)
This value is not used if the maximum size of the
cache is set to unlimited (that is, Maximum Cache
Size = 0)
The cache oth is already selected under Content Management Global Services Object Type
Handler Service.
2003 SAP
11
HOW TO CONFIGURE CACHES FOR KM
3.4.11 Rendering Cache
This cache is used by the KM user interface. It stores various interface-related objects and settings
temporarily.
rendering (Rendering Cache)
Parameter
Setting
Description
Restart Lifetime on
Access
Activated
Prevents entries that are still needed from being
deleted from the cache.
Singleton
Activated
Assumed Entry Size
Capacity
5000
Default Time-to-Live
Half an hour
(1800 seconds)
The cache is checked for obsolete entries within
one CM installation, so this value can be high.
Maximum Cache Size
0 (unlimited)
The actual size of the mappings is not determined.
Maximum Entry Size
0 (unlimited)
This value is not used if the maximum size of the
cache is set to unlimited (that is, Maximum Cache
Size = 0)
The cache rendering is already selected under Content Management User Interface
Debugging Settings.
3.4.12 Control Status Service Cache
The control status service allows rendering components (for example, controls) to persist structured
data using HTTP request cycles and to access this data. The data is stored temporarily in the
corresponding cache.
css (Status Cache)
Parameter
Setting
Description
Restart Lifetime on
Access
Activated
Prevents entries that are still needed from being
deleted from the cache.
Singleton
Activated
Assumed Entry Size
This value is not used if the maximum size of the
cache is set to unlimited (that is, Maximum Cache
Size = 0)
Capacity
5000
Increase this value if you receive error messages
(for example, Cache Expired) when working with
iViews based on the flexible user interface.
Default Time-to-Live
Half an hour
(1800 seconds)
The cache is checked for obsolete entries within
one CM installation, so this value can be high.
Maximum Cache Size
0 (unlimited)
The actual size of the mappings is not determined.
Maximum Entry Size
0 (unlimited)
The cache css is already configured and used internally by the system.
2003 SAP
12
HOW TO CONFIGURE CACHES FOR KM
3.4.13 XSLT Pipeline Processor Cache
This cache stores data structures of the XSLT pipeline processor temporarily. These data structures
are used for XML transformations.
ca_pipeline (XSLT Pipeline Processor Cache)
Parameter
Setting
Restart Lifetime on
Access
Not activated
Singleton
Activated
Assumed Entry Size
Capacity
50
Default Time-to-Live
Maximum Cache Size
0 (unlimited)
Maximum Entry Size
0 (unlimited)
The cache ca_pipeline is already selected under Content Management Global Services
Pipeline Add-Ons XSLT Pipeline Processor.
2003 SAP
13
HOW TO CONFIGURE CACHES FOR KM
3.4.14 TREX Java Client
The TREX Java Client uses the following caches:
Memory cache
Administration cache
For an overview of TREX caches, see Configuration TREX Caches. The necessary caches are
already selected. The persistent caches trexfile and trexfilesec are currently not used.
3.4.14.1 Memory Cache
This cache is used to store search requests and responses.
trexmemory (Memory Cache)
Parameter
Setting
Description
Restart Lifetime on
Access
Not activated
Singleton
Activated
Assumed Entry Size
Capacity
This value depends on the number of different search requests.
Default Time-to-Live
A few minutes
Maximum Cache Size
0 (unlimited)
Maximum Entry Size
0 (unlimited)
This value is not used if the maximum size of the
cache is set to unlimited (that is, Maximum Cache
Size = 0)
The actual size of the mappings is not determined.
3.4.14.2 Administration Cache
This cache is used to store TREX commands that are initiated by the TREX administrator control.
trexadmin (Administration Cache)
Parameter
Setting
Restart Lifetime on
Access
Not activated
Singleton
Activated
Assumed Entry Size
Capacity
This value depends on the number of different search requests.
Default Time-to-Live
A few minutes
Maximum Cache Size
0 (unlimited)
Maximum Entry Size
0 (unlimited)
2003 SAP
Description
This value is not used if the maximum size of an
entry is set to unlimited (that is, Maximum Cache
Size = 0)
The actual size of the mappings is not determined.
14
HOW TO CONFIGURE CACHES FOR KM
3.5
Use of the Cache Monitor
You can find the cache monitor in the KM Admin workset. You can use the cache monitor to check
the current status of caches. You can use the displayed data for analyses.
Entries in the Cache Monitor
Entry
Description
ID
Cache identifier
Size
Current size of the cache in bytes. The size of the entries is not known for all caches.
This is because not every program specifies a size explicitly when an entry is created.
However, in the case of a Web repository manager, the size is specified and displayed.
Capacity
Capacity of the cache that was specified when the cache was configured.
Maximum
Maximum number of entries that can be stored in the cache at one time.
Current
Current number of entries in the cache.
Gets
Total number of all successful accesses to the entries in the cache.
Hits
Number of successful accesses to entries in the cache. A successful access means that
the entry searched for by the system was found in the cache.
Ratio
Ratio of Hits to Gets. Specified as a percentage. The higher the value, the more
effective the cache.
Added
Number of objects added to the cache since the start of the measurement period.
Removed
Number of objects removed from the cache since the start of the measurement period.
Such objects have been overwritten by new objects or have become invalid due to
exceeding the Entry Default Time to Live value.
Note that the memory caches are reset when the Portal is restarted. Therefore, a restart
sets the data displayed in the cache monitor to zero.
3.5.1
Analysis of Displayed Data
Depending on the scenario and the caches used, there are different ways of analyzing the data
displayed in the cache monitor.
The following example shows how you can optimize the capacity of a cache.
If the displayed peak value for a measurement over a long period of time is smaller than
the capacity of the cache, you can reduce the capacity of the cache under Content
Management Utilities Caches.
However, if the peak value and the current number of entries reached the capacity limit,
you should increase the value of the cache.
2003 SAP
15
HOW TO CONFIGURE CACHES FOR KM
3.6
Recommendations for the cache configuration in a standard scenario.
The following table contains recommendations for the cache configuration of a 'normal' KM
implementation. If certain repositories are accessed particularly often (for example, a Web
repository), adapt the listed values appropriately. The cache monitor is helpful for this.
Cache
Technical name
Restart
Lifetime
on
Access
Singleton
Assumed
Entry
Size
Capacity
Default
timeto-live
Max
Cache
Size
Max
Entry
Size
effective ACL
Cache
ca _rsrc_acl
Activated
10000
1800
ACL Cache
ca_cm_rep_acl
ca_cm_srv_acl
Activated
10000
1800
Permission Cache
ca_cm_rep_acl_perm
ca_cm_srv_acl_perm
Activated
100
1800
Caches for
ApplicationDefined Properties
ca_props_1
Activated
10000
1800
Cache for URL
Content for
Access
ca_ca
Activated
1000
1800
JDBC ID Mapper
Cache
ca_idmapper
Activated
10000
1800
CM Cache
ca_cm
5000
1800
CM Cache for
Small Content
ca_cm_content
Activated
10000
1800
Web Repository
Cache
Not defined by default.
Activated
10000
10000
7200
10000000
10000
WebDAV
Repository Cache
Not defined by default.
Activated
1000
1800
Lotus Notes
Repository Cache
Not defined by default.
Activated
100
1800
Lotus Notes View
Cache
Not defined by default.
Activated
1000
1800
Lotus Notes
Document Cache
Not defined by default.
Activated
10000
1800
Object Type
Handler Cache
oth
Activated
Activated
5000
1800
Rendering Cache
rendering
Activated
Activated
5000
1800
Control Status
Service Cache
css
Activated
Activated
5000
1800
XSLT Pipeline
Processor Cache
ca_pipeline
Activated
50
TREX
Administration
Cache
trexadmin
Activated
100
300
TREX Memory
Cache
trexmemory
Activated
100
300
2003 SAP
16
HOW TO CONFIGURE CACHES FOR KM
4 Copyright
No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or for any purpose
without the express permission of SAP AG. The information contained herein may be
changed without prior notice.
Some software products marketed by SAP AG and its distributors contain proprietary
software components of other software vendors.
Microsoft, WINDOWS, NT, EXCEL, Word, PowerPoint and SQL Server are
registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
IBM, DB2, DB2 Universal Database, OS/2, Parallel Sysplex, MVS/ESA, AIX, S/390,
AS/400, OS/390, OS/400, iSeries, pSeries, xSeries, zSeries, z/OS, AFP, Intelligent
Miner, WebSphere, Netfinity, Tivoli, Informix and Informix Dynamic ServerTM are
trademarks of IBM Corporation in USA and/or other countries.
ORACLE is a registered trademark of ORACLE Corporation.
UNIX, X/Open, OSF/1, and Motif are registered trademarks of the Open Group.
Citrix, the Citrix logo, ICA, Program Neighborhood, MetaFrame, WinFrame,
VideoFrame, MultiWin and other Citrix product names referenced herein are trademarks
of Citrix Systems, Inc.HTML, DHTML, XML, XHTML are trademarks or registered trademarks
of W3C, World Wide Web Consortium, Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
JAVA is a registered trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc.
JAVASCRIPT is a registered trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc., used under license for
technology invented and implemented by Netscape.
MarketSet and Enterprise Buyer are jointly owned trademarks of SAP AG and Commerce
One.
SAP, SAP Logo, R/2, R/3, mySAP, mySAP.com and other SAP products and services
mentioned herein as well as their respective logos are trademarks or registered trademarks
of SAP AG in Germany and in several other countries all over the world. All other product and
service names mentioned are trademarks of their respective companies.
2003 SAP
17
You might also like
- SAS Programming Guidelines Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandSAS Programming Guidelines Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNo ratings yet
- Optimizing Session Caches in PowercenterDocument10 pagesOptimizing Session Caches in Powercenterjustfun_sweetNo ratings yet
- MICROSOFT AZURE ADMINISTRATOR EXAM PREP(AZ-104) Part-3: AZ 104 EXAM STUDY GUIDEFrom EverandMICROSOFT AZURE ADMINISTRATOR EXAM PREP(AZ-104) Part-3: AZ 104 EXAM STUDY GUIDENo ratings yet
- KafkaDocument3 pagesKafkagogula sivannarayanaNo ratings yet
- OBIEE Caching Best PracticesDocument3 pagesOBIEE Caching Best PracticesRaghurami Reddy K100% (1)
- TL DR With Careful Tuning of Your Webcenter Sites Caching Strategy, You Can Dramatically Increase TheDocument16 pagesTL DR With Careful Tuning of Your Webcenter Sites Caching Strategy, You Can Dramatically Increase Theradha_1990No ratings yet
- Oracle Database 10G - Automatic Sga Memory ManagementDocument14 pagesOracle Database 10G - Automatic Sga Memory Managementapi-3848967No ratings yet
- JAVA PROGRAMMING FOR BEGINNERS: Master Java Fundamentals and Build Your Own Applications (2023 Crash Course)From EverandJAVA PROGRAMMING FOR BEGINNERS: Master Java Fundamentals and Build Your Own Applications (2023 Crash Course)No ratings yet
- Performance TuningDocument38 pagesPerformance TuningAnweshKota100% (1)
- 4602 - r11x - Bestpractices - AutosysDocument13 pages4602 - r11x - Bestpractices - AutosysRavi DNo ratings yet
- Automatic Shared Memory Management in Oracle 10g: ZahidDocument10 pagesAutomatic Shared Memory Management in Oracle 10g: ZahidNst TnagarNo ratings yet
- Heap Memory ManagementDocument9 pagesHeap Memory ManagementAbdul SattarNo ratings yet
- F5 Ram CacheDocument9 pagesF5 Ram CacheRichardLaraNo ratings yet
- Web Intelligence XI 3.0 Parameter GuideDocument10 pagesWeb Intelligence XI 3.0 Parameter GuideJaime Andrés Triviño Sánchez0% (1)
- HibernateDocument161 pagesHibernateNagendra VenkatNo ratings yet
- Awr Report AnalysisDocument13 pagesAwr Report Analysissrinivas1224No ratings yet
- 01 - Initialization ParametersDocument11 pages01 - Initialization ParameterstolukesNo ratings yet
- Oracle Asm Emc TF-SRDF 02-06-0Document22 pagesOracle Asm Emc TF-SRDF 02-06-0Saeed MeethalNo ratings yet
- TuningDocument53 pagesTuningbalajismithNo ratings yet
- Cartridge Management IBM Protectier PDFDocument4 pagesCartridge Management IBM Protectier PDFmajumder_subhrajitNo ratings yet
- The Peformance Adjuster: IseriesDocument18 pagesThe Peformance Adjuster: IseriesJoseph MarreirosNo ratings yet
- ASM Interview QuestionDocument14 pagesASM Interview QuestiondayascNo ratings yet
- Practices: Steve's Caching TipsDocument8 pagesPractices: Steve's Caching Tipssanc199000No ratings yet
- Best Practices Document: Eventlog AnalyzerDocument9 pagesBest Practices Document: Eventlog AnalyzerHeo nonNo ratings yet
- IBM DS8000 Storage Allocation Overview Including Thin ProvisioningDocument39 pagesIBM DS8000 Storage Allocation Overview Including Thin ProvisioningRam GuggulNo ratings yet
- Esb New FeaturesDocument16 pagesEsb New Featurespuli_prasanna21No ratings yet
- Oracle ArchitectureDocument102 pagesOracle ArchitecturemanavalanmichaleNo ratings yet
- ASO Common Questions and AnswersDocument10 pagesASO Common Questions and AnswersAmit SharmaNo ratings yet
- MMM MM M M MMMM M MMMMMMMMMMMMMMM M MM MMMMMMMMM MMMMMMMMMMMDocument10 pagesMMM MM M M MMMM M MMMMMMMMMMMMMMM M MM MMMMMMMMM MMMMMMMMMMMLokesh ChinniNo ratings yet
- Day 18Document14 pagesDay 18Rohith WilliamNo ratings yet
- 1404 Booz PDFDocument7 pages1404 Booz PDFkumarNo ratings yet
- Beaker Documentation: Release 1.6.2Document40 pagesBeaker Documentation: Release 1.6.2Euclides JuniorNo ratings yet
- STBCDocument4 pagesSTBCsravan.appsdbaNo ratings yet
- Build Your Own Oracle Rac 10G Release 2 Cluster On Linux and Firewire (Continued)Document20 pagesBuild Your Own Oracle Rac 10G Release 2 Cluster On Linux and Firewire (Continued)Balvinder Singh RawatNo ratings yet
- Oracle Instance ArchitectureDocument28 pagesOracle Instance ArchitecturemonsonNo ratings yet
- Best Practices Guide For VMware VSphere - V5.xDocument20 pagesBest Practices Guide For VMware VSphere - V5.xachilles7No ratings yet
- In Oracle MilieuDocument6 pagesIn Oracle MilieuzahirhussianNo ratings yet
- Applies To:: How To Perform GSA Repository Tuning (Doc ID 1037289.1)Document3 pagesApplies To:: How To Perform GSA Repository Tuning (Doc ID 1037289.1)ScorpionNo ratings yet
- NetApp Pam CardDocument7 pagesNetApp Pam CardSrikanth MuthyalaNo ratings yet
- Asigra - Rman Interface - DescriptionDocument28 pagesAsigra - Rman Interface - DescriptionCarol Howell DahlinNo ratings yet
- Assignment4-Rennie RamlochanDocument7 pagesAssignment4-Rennie RamlochanRennie RamlochanNo ratings yet
- OpenText Brava! For Content Suite 16.6 - Brava! For CS Troubleshooting Guide English (CLBRVWOTCS160600-GGD-EN-01)Document26 pagesOpenText Brava! For Content Suite 16.6 - Brava! For CS Troubleshooting Guide English (CLBRVWOTCS160600-GGD-EN-01)Dan MedinschiNo ratings yet
- Essbase Application Performance TuningDocument4 pagesEssbase Application Performance TuningksrsarmaNo ratings yet
- Memory Architecture in SQL ServerDocument8 pagesMemory Architecture in SQL Servervenkatesh thulaNo ratings yet
- PDSE TipsDocument8 pagesPDSE TipskartbeNo ratings yet
- Oracle Database Oracle Instance + Data Files: AsktomDocument5 pagesOracle Database Oracle Instance + Data Files: Asktomvaloo_phoolNo ratings yet
- Flashpool DesignDocument25 pagesFlashpool DesignAS KumarNo ratings yet
- Adiva Consulting: Home About Adiva ServicesDocument19 pagesAdiva Consulting: Home About Adiva ServicesAbinash Kumar RoutNo ratings yet
- What Is Query Cache in MySQLDocument4 pagesWhat Is Query Cache in MySQLYarlagaddavamcy YarlagaddaNo ratings yet
- Documentation Otrsclonedb: The Otrs Clonedb Package. Version 6.0.10 EditionDocument13 pagesDocumentation Otrsclonedb: The Otrs Clonedb Package. Version 6.0.10 EditiondarwinNo ratings yet
- Implementation of Caching in C#Document7 pagesImplementation of Caching in C#Haseem AjazNo ratings yet
- Linux 64 Bit Huge Pages Document 361468Document5 pagesLinux 64 Bit Huge Pages Document 361468shastry17No ratings yet
- Understanding and Tuning Buffer Cache and DBWRDocument8 pagesUnderstanding and Tuning Buffer Cache and DBWRMelissa MillerNo ratings yet
- HPE Nimble Storage ArchitectureDocument18 pagesHPE Nimble Storage Architecturefabian AndruskoNo ratings yet
- OraasfsaDocument199 pagesOraasfsabanala.kalyanNo ratings yet
- Squid Performance TuningDocument57 pagesSquid Performance TuningbillyducNo ratings yet
- CAM Demo Guide 0.2Document18 pagesCAM Demo Guide 0.2muhammad Noman AlamNo ratings yet
- How To Customize The Logon User Interface of SAP Enterprise PortalDocument7 pagesHow To Customize The Logon User Interface of SAP Enterprise PortalDanladi Shemang KajeNo ratings yet
- Average Salary For Sap Careers: SAP Consultant SAP Project Manager SAP Analyst SAP DeveloperDocument1 pageAverage Salary For Sap Careers: SAP Consultant SAP Project Manager SAP Analyst SAP DeveloperDanladi Shemang KajeNo ratings yet
- BRTools To Backup SAP On ORACLEDocument12 pagesBRTools To Backup SAP On ORACLEOthman Hendy Suseno100% (1)
- How To Configure Caches For KMDocument18 pagesHow To Configure Caches For KMDanladi Shemang KajeNo ratings yet
- 01 Sizing EP 60 Init2Document9 pages01 Sizing EP 60 Init2Danladi Shemang KajeNo ratings yet
- How To Customize The Logon User Interface of SAP Enterprise PortalDocument7 pagesHow To Customize The Logon User Interface of SAP Enterprise PortalDanladi Shemang KajeNo ratings yet
- SAP QuizDocument1 pageSAP QuizDanladi Shemang KajeNo ratings yet
- How To Use A Business PackageDocument18 pagesHow To Use A Business PackageDanladi Shemang KajeNo ratings yet
- 01 Sizing EP 60 Init2Document9 pages01 Sizing EP 60 Init2Danladi Shemang KajeNo ratings yet
- SAPINTQUEPRINDocument31 pagesSAPINTQUEPRINDanladi Shemang KajeNo ratings yet
- IRM - Press.business - Processes.operational - Solutions.for - SAP.implementation - Dec.2005.ebook DDUDocument351 pagesIRM - Press.business - Processes.operational - Solutions.for - SAP.implementation - Dec.2005.ebook DDUAnna Rhodora QuitalegNo ratings yet
- Database Interview QuestionsDocument21 pagesDatabase Interview QuestionsDanladi Shemang KajeNo ratings yet
- How To Install Solution ManagerDocument1 pageHow To Install Solution ManagerDanladi Shemang KajeNo ratings yet
- Skulls & Anatomy: Copyright Free Vintage Illustrations for Artists & DesignersFrom EverandSkulls & Anatomy: Copyright Free Vintage Illustrations for Artists & DesignersNo ratings yet
- Excel Essentials: A Step-by-Step Guide with Pictures for Absolute Beginners to Master the Basics and Start Using Excel with ConfidenceFrom EverandExcel Essentials: A Step-by-Step Guide with Pictures for Absolute Beginners to Master the Basics and Start Using Excel with ConfidenceNo ratings yet
- How to Create Cpn Numbers the Right way: A Step by Step Guide to Creating cpn Numbers LegallyFrom EverandHow to Create Cpn Numbers the Right way: A Step by Step Guide to Creating cpn Numbers LegallyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (27)
- NFT per Creators: La guida pratica per creare, investire e vendere token non fungibili ed arte digitale nella blockchain: Guide sul metaverso e l'arte digitale con le criptovaluteFrom EverandNFT per Creators: La guida pratica per creare, investire e vendere token non fungibili ed arte digitale nella blockchain: Guide sul metaverso e l'arte digitale con le criptovaluteRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (15)
- Blender 3D for Jobseekers: Learn professional 3D creation skills using Blender 3D (English Edition)From EverandBlender 3D for Jobseekers: Learn professional 3D creation skills using Blender 3D (English Edition)No ratings yet
- Linux For Beginners: The Comprehensive Guide To Learning Linux Operating System And Mastering Linux Command Line Like A ProFrom EverandLinux For Beginners: The Comprehensive Guide To Learning Linux Operating System And Mastering Linux Command Line Like A ProNo ratings yet
- The Designer’s Guide to Figma: Master Prototyping, Collaboration, Handoff, and WorkflowFrom EverandThe Designer’s Guide to Figma: Master Prototyping, Collaboration, Handoff, and WorkflowNo ratings yet
- SketchUp Success for Woodworkers: Four Simple Rules to Create 3D Drawings Quickly and AccuratelyFrom EverandSketchUp Success for Woodworkers: Four Simple Rules to Create 3D Drawings Quickly and AccuratelyRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Architectural Design with SketchUp: 3D Modeling, Extensions, BIM, Rendering, Making, and ScriptingFrom EverandArchitectural Design with SketchUp: 3D Modeling, Extensions, BIM, Rendering, Making, and ScriptingNo ratings yet
- Memes for Music Producers: Top 100 Funny Memes for Musicians With Hilarious Jokes, Epic Fails & Crazy Comedy (Best Music Production Memes, EDM Memes, DJ Memes & FL Studio Memes 2021)From EverandMemes for Music Producers: Top 100 Funny Memes for Musicians With Hilarious Jokes, Epic Fails & Crazy Comedy (Best Music Production Memes, EDM Memes, DJ Memes & FL Studio Memes 2021)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Learn Power BI: A beginner's guide to developing interactive business intelligence solutions using Microsoft Power BIFrom EverandLearn Power BI: A beginner's guide to developing interactive business intelligence solutions using Microsoft Power BIRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mastering YouTube Automation: The Ultimate Guide to Creating a Successful Faceless ChannelFrom EverandMastering YouTube Automation: The Ultimate Guide to Creating a Successful Faceless ChannelNo ratings yet
- Minecraft Cheats : 70 Top Essential Minecraft Cheats Guide Exposed!From EverandMinecraft Cheats : 70 Top Essential Minecraft Cheats Guide Exposed!Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (7)
- Windows 11 for Beginners: The Complete Step-by-Step User Guide to Learn and Take Full Use of Windows 11 (A Windows 11 Manual with Useful Tips & Tricks)From EverandWindows 11 for Beginners: The Complete Step-by-Step User Guide to Learn and Take Full Use of Windows 11 (A Windows 11 Manual with Useful Tips & Tricks)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Hacks for TikTok: 150 Tips and Tricks for Editing and Posting Videos, Getting Likes, Keeping Your Fans Happy, and Making MoneyFrom EverandHacks for TikTok: 150 Tips and Tricks for Editing and Posting Videos, Getting Likes, Keeping Your Fans Happy, and Making MoneyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Tableau Your Data!: Fast and Easy Visual Analysis with Tableau SoftwareFrom EverandTableau Your Data!: Fast and Easy Visual Analysis with Tableau SoftwareRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- YouTube Takeover - How You Can Grow Your YouTube Channel Into A Regular IncomeFrom EverandYouTube Takeover - How You Can Grow Your YouTube Channel Into A Regular IncomeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)