Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 - 7UT Diff - Principles PDF
Uploaded by
Name IsOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1 - 7UT Diff - Principles PDF
Uploaded by
Name IsCopyright:
Available Formats
Power Transmission and Distribution
Principles of system protection technology
Transformer Differential Protection
Basic principles : Kirchhoffs knot rule
Basis for Differential-Protection:
I1
I2
I4
I3
I1 + I2 + I3 + I4 = 0 ?
? I=0
Definition:
Currents, which flow into the knot (protected object), are counted positive.
Currents, which flow out of the knot (protected object), are counted negative.
Protection objects:
Line, Transformer, Generator/Motor, Bus bar
Principles Transf. Diff 2
Basic principles: current comparison
IP1
IS1
I1F
Protected
object
IS1
?I
I2F
IP1
IP2
IS2
IS1
IP2
Protected
object
IF
IS2
IS2
?I
IDiff = I1 + I2
external fault or load
internal fault
Assumption: CT- ratio: 1/1
IP1 = I1F
IP2 = I2F
IDiff = IP1 + IP2 = I1F + I2F
? Trip
IDiff = I1 + I2
Assumption: CT- ratio: 1/1
IP1 = IF
IP2 = -IF
IDiff = IP1 + IP2 = IF - IF = 0
? no Trip
Requirements for Differential Protection:
1) Internal faults ( faults between CT-sets ) ? Trip
2) External faults ? no Trip
Principles Transf. Diff 3
Basic principles : restrained current comparison
(1/2)
Example: external fault with linear CT-errors
IP1
Ct 1:
e1= - 5%
Protected
object
IS1=
0.95IP1
Ct 2:
e2 = +5%
IDiff = 0.1IP1
?I
IP2 = -IP1
IF
IS2=
1.05IP2
assumption: CT- ratio: 1/1
IDiff = IS1 + IS2 = (1+e1) IP1 + (1+e2)IP2 = 0.95 IP1 1.05 IP1 = 0.1IP1
-normal operation: IP1 = IN
IDiff = 0.1IP1 = 0.1IN
-external fault: assumption: IP1 = 10IN
IDiff = 0.1IP1 = 1IN
As the setting IDiff> for usual applications
lays below nominal current,
it would cause a wrong trip in case of
external faults with heavy current!
Restrained characteristic necessary!
Principles Transf. Diff 4
Basic principles: restrained current comparison
(2/2)
Example: external fault with linear CT- errors
CT 1:
e1= - 5%
IP1
CT 2:
e2 = + 5%
Protected
object
IRest
IP2 = -IP1
IF
IRest = IS1 + IS2
IRest = 2IP1
IS2=
1.05IP2
IS1=
0.95IP1
IDiff
Setting due to
magnetising or
charging currents
IDiff=
IS1+IS2
IDiff= IS1+ IS2
IDiff = 0.1IP1
Linear error due to
different
CT transformation
Resulting
characteristic
IN
Trip
Block
IDiff>
Under the following assumption
e1 = e2 and I1 = I2
the result for a conventional
Differential Prot. characteristic
should be:
IDiff = IDiff> + e1I1 + e2I2
= IDiff> + 2e1 I1
with IDiff> = setting
10
IRest = IS1 + IS2
Principles Transf. Diff 5
Basic principles: measuring circuit for a 3-phase system
Basic circuit for a 3- phase system:
Generator / Motor / Reactor
L1
L2
L3
Diff.
Rest. current
Conventional
Differential Protection
Principles Transf. Diff 6
Transformer Differential Protection special qualities
Angle shifting N30 due to vector group (0 = N = 11)
for 3-phase transformers.
Different current values of the CT- sets on the high voltage side (HV)
and on the low voltage side (LV)
Zero sequence current in case of external faults will cause
differential current
Transformer-tap changer, magnetising current
Transient currents
Inrush
CT-saturation
Principles Transf. Diff 7
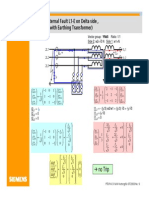
3-phase Transformer: primary values
Load: 100MVA ,vector group: Yd5
side 2: 20kV, 2887A
side 1: 110kV, 525A
3000/1A
2L1
2L2
2L3
I2L1?
I2L2?
I2L3?
750/1A
I2*L1
?I1L1
I2*L2
?I1L2
I2*L3
?I1L3
1L1
1L2
1L3
kU = U1N/U2N = 110kV/20kV = 5.5
kWinding = w1/w2 = kU/v3
I2*L1 = -I1L1ku /v3 + I1L2ku /v3
I2*L3
I1L1ku/v3
I1L1
530
I2*L2
I1L2ku /v3
I1L3
I1L2
-I1L1ku /v3
I2*L1
Principles Transf. Diff 8
3-phase Transformer : secondary values
I L1sec ?
SN
I
? NCT1sec
3 ?U N I NCTlprim
I1L1sec ?
100MVA 1A
?
? 0.7A
3 ?110kV 750A
I2 L1sec ?
I1L1sec= 0.7A , 0
100MVA 1A
?
? 0.96A
3 ?20kV 3000A
IDiff L1 = I1L1sec+ I2L1sec
= 0.5A
I2L1sec = 0.96A , -150
Principles Transf. Diff 9
Vector group and current value adaptation in case of
conventional Transformer Differential Protection
3000/1A
Load: 100MVA ,vector group: YNd5
side 2: 20kV
side1: 110kV
(1/2)
ILoad=
525A
750/1A
L1
2887A
L2
L3
0.7A
0.96A
Diff.
IR
29
Wdg.
23
Wdg.
Rest. current
Conventional
Differential Prot.
Matching transformer
-Vector group adaptation
-Current value adaptation
-Zero seq. current handling
nominal Load (no fault): 0.70A 23Wdg = 0.555A 29Wdg,
IR = 0.555v3 = 0.96A
Principles Transf. Diff 10
Transformers in star-delta connection: I0-current
Vector group: YNd5 , Ratio: 1/v3
side 2:
side 1:
L1
L2
L3
3I0
IL1(S2) = -IL1(S1) , IL3(S2) = IL1(S1)
IL3(S2)
I L1(S2)
IL1(S1)
1
positive
sequence
I1
No Problem for
Differential Protection
- 530
IL1(S1)= I1 + I2 + I0 = 3I0
IL1(S2) = I1 + I2
IL2(S2) = a2I1 + aI2 = 0
IL3(S2) = aI1 + a2I2
IL2(S1)= a2I1 + aI2 + I0 = 0
IL3(S1)= aI1 + a2I2 + I0 = 0
+ 530
negative
sequence
I2
No Problem for
Differential Protection
I0
Differential Protection
I0 elimination nessesary
+
zero sequence
Principles Transf. Diff 11
Vector group and current value adaptation in case of
conventional Transformer Differential Protection
3000/1A
Load: 100MVA ,vector group: YNd5
side 2: 20kV
side1: 110kV
(2/2)
750/1A
~
~
L1
13655A
L2
L3
3I0
4.55A
5.73A
Diff.
IR
29
Wdg.
IP=
4300A
23
Wdg.
Rest. current
Conventional
Differential Prot.
single pole fault HV -side:
Matching transformer
-Vector group adaptation
-Current value adaptation
-Zero seq. current handling
5.73A 23Wdg = 4.550A 29Wdg , IR = 4.55A
Principles Transf. Diff 12
Vector group and current value adaptation in case of
numerical Transformer Differential Protection
CT 2
3000/1A
2L1
2L2
Load: 100MVA ,vector group: YNd5
side 2: 20kV
side 1: 110kV
I2 L1P ?
?I1 L1P
I2 L2P ?
?I1 L2P
I2 L3P ?
2L3
I2 L1S
I2 L2S
I2 L3S
(1/2)
CT 1
750/1A
1L1
1L2
?I1 L3P
I2 A
Current
Vector
Io
value
group
handling
I2 B
adaptation
adaptation
CT 2
I2 C
I1 A
comparison
?I
I1 B
Io
handling
I1 C
Current
value
adaptation
CT 1
1L3
I1 L1S
I1 L2S
I1 L3S
Numerical Transformer Differential Protection
Principles Transf. Diff 13
Vector group and current value adaptation in case of
numerical Transformer Differential Protection
(2/2)
Parameterisation of transformer and CT- data
in a 7UT6 Differential Protection Device
Principles Transf. Diff 14
Tripping characteristic of Transformer Differential Protection
CT-errors , Tap changer , Magnetising current
I Diff
InO
3.0
2.5
Trip
slope 2
Total error
2.0
Block
45
1.5
CT- error
1.0
slope 1
Tap changer error
0.5
IDiff>
0
Transf. magnetising current
0
1.0
Characteristic:
2.0
3.0
4.0
5.0
IDiff = f (IRest)
IRest = |I1| + |I2|
6.0
7.0
8.0
9.0
I Rest InO
InO = nominal current of the protected object
Principles Transf. Diff 15
Transient currents (with Harmonics)
- Inrush of Transformers
2)
even
2. Harm.
Inrush
(1 of
iDiff = i1
i1
Y Y
t=0
i1
i2 = 0
t
even
2. Harm.
Inrush
iDiff = i1
i1
t=0
i1
I2 = 0
t
Connecting -T2 in parallel with -T1
(Sympathetic Inrush T1)
-T1
i1
t=0
Inrush -T2
-T2
i1
-T1: iDiff = i1
I2 = 0
t=0
Principles Transf. Diff 16
Inrush, cross block, over excitation [V/Hz]
(2 of 2)
filter window
1 cycle
iRUSH
= iDiff
Cross-block = No (phase separate blocking)
Inrush current
in one phase
1P
I2har
IDiff
2P
IDiff, L1 > trip blocking
L2-block
IDiff, L2 > trip blocking
L3-block
IDiff, L3 > trip blocking
3P t
Cross-block = Yes (blocking of all phases)
block
Setting
value
15 %
L1-block
L1-block
L2-block
OR
=1
IDiff > trip blocking
for an adjustable time
L3-block
no block
0
recognise inrush condition by evaluating the ratio 2nd harmonic I2har to basic wave IDiff.
Time limit for cross-block. Reliable reaction to the inrush condition with cross-block.
Trip of a short circuit after the set time delay.
recognise over excitation [V/Hz] by evaluating the ratio 3rd or 5th harmonic to basic wave
Principles Transf. Diff 17
Demonstration of Inrush with evolving fault
Internal
fault
IDiff>>
Inrush
IDiff>
3 cycles
Cross Blocking
Principles Transf. Diff 18
Transient currents (with harmonics)
- Over excitation and CT- saturation
(1/2)
iDiff = i1 + i2
Over excitation (U/f)
UTr > UN
uneven
5. Harm.
i2
i1
External fault with
CT-saturation at the
Low voltage side
HV
even
and
uneven
LV
i1
i2
Internal fault with
CT-saturation at the
High voltage side
HV
i1
iDiff = i1 + i2
iDiff = i1
even
and
uneven
LV
I2 0
Principles Transf. Diff 19
Transient currents (with harmonics)
- Over excitation and CT- saturation
(2/2)
Principle of Add-on stabilisation for external faults
Tripping characteristic 7UT6
I Diff
InO
IDiff>>
7
6
Trip
45
Block
5
D
C
4
3
Add-on
Stabilisation
2
1
Begin of saturation
IDiff>
0 0
A
10
12
14
16
I Rest
InO
Principles Transf. Diff 20
Demonstration of add-on stabilisation
Block
45
Trip
AddStabilisation
Principles Transf. Diff 21
Differential elements IDiff> and IDiff>>
Instantaneous
values
measured value
pre-processing
( vector gr. ,Cts )
i1L
iRest = i1 + i2
side 1
i2L
iDiff = i1 + i2
side 2
rectified mean value:
IRest = iRest
fundamental wave:
IDiff = rms(iDiff)50Hz
Tripping characteristic,
saturation detection
IDiff
IDiff>
IRest
&
Trip
IDiff>
=1
Trip
IDiff>>
Motor start
DC off set
analysing of harmonics:
-block by 2. & 3. or 5.har
-cross block
iRest IRest
IDiff
IDiff
IDiff>>
I / InO
I / InO
iDiff
ms
iDiff
kIDiff>>
ms
IDiff> restrained (biased) differential function, ?IDiff> = f(IRest)
- Ct-saturation detector (add on stabilization) for external faults.
IDiff>> fast unrestrained high current differential function, its setting therefore should be higher then
the maximum possible through flowing current! Example Transformer: IDiff >> > (1/uk)InO
This function will be not blocked by harmonics due to an inrush or Ct-saturation!
The IDiff >> stage evaluates the fundamental wave of the currents as well as the instantaneous values.
- Fundamental wave processing:
fast tripping at the set threshold.
- Instantaneous value processing: ensures fast tripping even in case the fundamental wave
of the current is strongly reduced by Ct-saturation. Because of the possible DC offset after fault
inception, the instantaneous value stage operates only above twice the set threshold.
Principles Transf. Diff 22
Measuring Pre-processing, Example for CT Matching
(1/2)
SN = 100 MVA
UN2 = 20 kV
IP2 = 2750A
(load current)
UN1 = 110 kV
3000/1A
750/1A
Side 2
Side 1
InO1 = 525A
InO2 = 2887A
IS2 = -0.916A
IP1 = 500A
(load current)
7UT6
7UM62
IS1 = 0.66A
measured
secondary currents
IDiff = ?
IRest = ?
Principles Transf. Diff 23
Measuring Pre-processing, Example for CT Matching
(2/2)
SN
3 ?U N
1. Calculation of the transformer nominal current
I nO ?
2. Correction factor
kW ?
3. Correction nominal current
I* = kW IS
4. Calculation of the differential and
restraint current
IDiff = |I 1* + I2*| IRest = |I1*| + |I2*|
I NCT
InO
Calculation example:
SN = 100MVA
UN1 =
IN1CT =
110kV
750A
UN2 =
IN2CT =
20kV
3000A
Correction factors:
kW1 =
1.428
kW2 =
1.039
IDiff =
0A
Load conditions:
Ip1 =
500A
Ip2 =
2750A
IRest =
1.9A
Secondary
currents:
Is1 =
0.666A
Is2 =
-0.916A
IDiff =
0InO
I1* =
0.95A
I2* =
-0.95A
IRest =
1.9InO
Matched currents:
Principles Transf. Diff 24
Applications for Transformer Differential Protection
three winding
transformer
1 or 3 phases
two winding
transformer
1 or 3 phases
1 CB method
on
one side
7UT613
7UT633
7UT612
7UM62
7UT613
7UT633
Unit Protection
1 CB method
on two sides
Y
7UT635
7UT635
G
3~
Principles Transf. Diff 25
You might also like
- 8 Test Features and DiagnosticDocument40 pages8 Test Features and DiagnosticName IsNo ratings yet
- 21 7UT6 Family enDocument13 pages21 7UT6 Family enName IsNo ratings yet
- 4 - 7UT6 Low Imp REFDocument26 pages4 - 7UT6 Low Imp REFName IsNo ratings yet
- 03 Diff PrinciplesDocument21 pages03 Diff PrinciplesName Is100% (2)
- 1 IEC61850 - Scope and Parts of The Standard PDFDocument56 pages1 IEC61850 - Scope and Parts of The Standard PDFName Is50% (2)
- 4 Practice Fkey Simple Test of Goose CommunicationDocument60 pages4 Practice Fkey Simple Test of Goose CommunicationName IsNo ratings yet
- 06 - Overcurrent and Impedance ProtectionDocument16 pages06 - Overcurrent and Impedance ProtectionName IsNo ratings yet
- 02a - Basis Stator Ground Fault Protection PDFDocument19 pages02a - Basis Stator Ground Fault Protection PDFName IsNo ratings yet
- 02b - SGF100 - Procent - Protection PDFDocument22 pages02b - SGF100 - Procent - Protection PDFName IsNo ratings yet
- 7 Configuration of Ruggedcom Switches PDFDocument38 pages7 Configuration of Ruggedcom Switches PDFName Is67% (3)
- IEC en 1013 61850Document2 pagesIEC en 1013 61850Name IsNo ratings yet
- 2 - 7UT6 Vectorgroup - en PDFDocument11 pages2 - 7UT6 Vectorgroup - en PDFName IsNo ratings yet
- 2 HW SW Ethernet IEC61850 PDFDocument72 pages2 HW SW Ethernet IEC61850 PDFName IsNo ratings yet
- Hindalco 150 MW Block Diagram Model (Sheet 1)Document1 pageHindalco 150 MW Block Diagram Model (Sheet 1)Name IsNo ratings yet
- 04 Rotor Ground Fault ProtectionDocument26 pages04 Rotor Ground Fault ProtectionName IsNo ratings yet
- Substation Automation - Networks and Automation26-28 PDFDocument3 pagesSubstation Automation - Networks and Automation26-28 PDFName IsNo ratings yet
- Aditya DAVR QP PDFDocument16 pagesAditya DAVR QP PDFName IsNo ratings yet
- 5c - 7UT613 V4.6 - Setting Powersystem Data 2 PDFDocument1 page5c - 7UT613 V4.6 - Setting Powersystem Data 2 PDFName IsNo ratings yet
- 3 IEC61850-Engineering in DIGSI PDFDocument12 pages3 IEC61850-Engineering in DIGSI PDFName IsNo ratings yet
- 5 Practice - Reverse Interlocking PDFDocument18 pages5 Practice - Reverse Interlocking PDFName IsNo ratings yet
- 4a - 7UT6 Vectorgr - F.earthingtransf - en PDFDocument5 pages4a - 7UT6 Vectorgr - F.earthingtransf - en PDFName IsNo ratings yet
- Hindalco 150 MW Block Diagram Model Sheet2 PDFDocument1 pageHindalco 150 MW Block Diagram Model Sheet2 PDFName IsNo ratings yet
- 17-Generator and Generator Transf ProtDocument35 pages17-Generator and Generator Transf ProtSristick100% (7)
- Transfer FN SEE PDFDocument1 pageTransfer FN SEE PDFName IsNo ratings yet
- Aditya DAVR TP PDFDocument10 pagesAditya DAVR TP PDFName IsNo ratings yet
- SIPROTEC 7SJ80x - Multifunction MV RelayDocument34 pagesSIPROTEC 7SJ80x - Multifunction MV RelayAnonymous m65TTcfOTNo ratings yet
- Page 100 PDFDocument1 pagePage 100 PDFName IsNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- VNL-Essar Field Trial: Nairobi-KenyaDocument13 pagesVNL-Essar Field Trial: Nairobi-Kenyapoppy tooNo ratings yet
- Role of MicrofinanceDocument1 pageRole of MicrofinanceuttamsudhirNo ratings yet
- Regenerative Braking System: An Efficient Way to Conserve EnergyDocument31 pagesRegenerative Braking System: An Efficient Way to Conserve EnergyPRAVIN KUMAR NNo ratings yet
- Cardboard Dream HouseDocument1 pageCardboard Dream Houseapi-630719553No ratings yet
- TBEM CII Exim Bank Award ComparisonDocument38 pagesTBEM CII Exim Bank Award ComparisonSamNo ratings yet
- MGN 363Document14 pagesMGN 363Nitin PatidarNo ratings yet
- SC WD 1 WashHandsFlyerFormatted JacobHahn Report 1Document3 pagesSC WD 1 WashHandsFlyerFormatted JacobHahn Report 1jackson leeNo ratings yet
- CH 9 - Spontaneity, Entropy, and Free EnergyDocument65 pagesCH 9 - Spontaneity, Entropy, and Free EnergyCharbel RahmeNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Powers of The State (Police Power) Ynot v. IAC Facts: Ermita Malate v. City of Manila 20 SCRA 849 (1967)Document18 pagesFundamental Powers of The State (Police Power) Ynot v. IAC Facts: Ermita Malate v. City of Manila 20 SCRA 849 (1967)Ella QuiNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Planning and Corroporate Strategies: Meaning and Definition of StrategyDocument19 pagesHuman Resource Planning and Corroporate Strategies: Meaning and Definition of StrategyRashmi KhublaniNo ratings yet
- Philips Solar+LED Marketing StrategyDocument15 pagesPhilips Solar+LED Marketing StrategyrejinairNo ratings yet
- Bleed Fan SelectionDocument4 pagesBleed Fan Selectionomar abdullahNo ratings yet
- BLDG TECH Juson Assignment Lecture 1Document23 pagesBLDG TECH Juson Assignment Lecture 1Ma. Janelle GoNo ratings yet
- Chobani: The Falling First Mover: Jianan LiaoDocument5 pagesChobani: The Falling First Mover: Jianan Liaowofop34547No ratings yet
- Application Sheet: Series CW SeriesDocument2 pagesApplication Sheet: Series CW SerieskamalNo ratings yet
- Breadth First Search (BFS) Depth First Search (DFS) A-Star Search (A ) Minimax Algorithm Alpha-Beta PruningDocument31 pagesBreadth First Search (BFS) Depth First Search (DFS) A-Star Search (A ) Minimax Algorithm Alpha-Beta Pruninglevecem778No ratings yet
- Return On Marketing InvestmentDocument16 pagesReturn On Marketing Investmentraj_thanviNo ratings yet
- J S S 1 Maths 1st Term E-Note 2017Document39 pagesJ S S 1 Maths 1st Term E-Note 2017preciousNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Agriculture 5038/12 October/November 2020Document30 pagesCambridge O Level: Agriculture 5038/12 October/November 2020Sraboni ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Bildiri Sunum - 02Document12 pagesBildiri Sunum - 02Orhan Veli KazancıNo ratings yet
- Komatsu PC01-1 (JPN) 14001-Up Shop ManualDocument217 pagesKomatsu PC01-1 (JPN) 14001-Up Shop Manualhaimay118100% (2)
- Praveen Verma Auto CAD IntershipDocument15 pagesPraveen Verma Auto CAD IntershipPraveen vermaNo ratings yet
- Sciencedirect Sciencedirect SciencedirectDocument7 pagesSciencedirect Sciencedirect SciencedirectMohamed Amine NZNo ratings yet
- Preparing For 2024: Election Technology and The Battle Against DisinformationDocument13 pagesPreparing For 2024: Election Technology and The Battle Against DisinformationVerified VotingNo ratings yet
- Examen 03 Aula - F PostgradoDocument5 pagesExamen 03 Aula - F PostgradodiegoNo ratings yet
- Build A Tunnel: What You NeedDocument2 pagesBuild A Tunnel: What You NeedManila Business ShopsNo ratings yet
- Corporations Defined and FormedDocument16 pagesCorporations Defined and FormedSheryn Mae AlinNo ratings yet
- Appetizers Fire-Grilled Gourmet Burgers: Red Robin'S Finest Burgers Red'S Tavern MenuDocument2 pagesAppetizers Fire-Grilled Gourmet Burgers: Red Robin'S Finest Burgers Red'S Tavern MenufruitfuckNo ratings yet
- Gen-6000-0mh0/0mhe Gen-6000-0mk0 Gen-6000-0ms0/0mse Gen-7500-0mh0/0mhe Gen-8000-0mk0/0mke Gen-8000-0ms0/0mseDocument26 pagesGen-6000-0mh0/0mhe Gen-6000-0mk0 Gen-6000-0ms0/0mse Gen-7500-0mh0/0mhe Gen-8000-0mk0/0mke Gen-8000-0ms0/0mseAhmed Khodja KarimNo ratings yet
- Simplex-4004 Installation Operating Manual Rev C PDFDocument36 pagesSimplex-4004 Installation Operating Manual Rev C PDFElias Rangel100% (1)