Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology
Uploaded by
Rosemond FabienOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology
Uploaded by
Rosemond FabienCopyright:
Available Formats
8/25/15
CAMPBELL
BIOLOGY
TENTH
EDITION
Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson
Concept 1.1: The study of life reveals common
themes
Biology is a subject of enormous scope
There are five unifying themes
Organization
Information
Evolution, the
Themes of Biology,
and Scientific Inquiry
Energy and matter
Interactions
Evolution
Lecture Presentation by
Nicole Tunbridge and
Kathleen Fitzpatrick
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Figure 1.3
Theme: New Properties Emerge at Successive
Levels of Biological Organization
7 Tissues
1 The Biosphere
Life can be studied at different levels, from
molecules to the entire living planet
6 Organs
and Organ
Systems
2
Ecosystems
This enormous range can be divided into different
levels of biological organization
10
Molecules
3
Communities
8
Cells
5
Organisms
9 Organelles
4 Populations
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Emergent Properties
Emergent properties result from the arrangement
and interaction of parts within a system
Emergent properties characterize nonbiological
entities as well
For example, a functioning bicycle emerges only
when all of the necessary parts connect in the
correct way
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Reductionism is the reduction of complex systems
to simpler components that are more manageable
to study
For example, studying the molecular structure of
DNA helps us to understand the chemical basis of
inheritance
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
8/25/15
The Cell: An Organisms Basic Unit of Structure
and Function
To explore emergent properties, biologists
complement reductionism with systems biology,
analysis of the interactions among the parts of a
biological system
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
The cell is the lowest level of organization that can
perform all activities required for life
Every cell is enclosed by a membrane that
regulates passage of materials between the cell
and its environment
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Figure 1.4
Prokaryotic cell
Eukaryotic cell
A eukaryotic cell has membrane-enclosed
organelles, the largest of which is usually the
nucleus
Membrane
DNA
(no nucleus)
Membrane
Cytoplasm
By comparison, a prokaryotic cell is simpler and
usually smaller, and does not contain a nucleus or
other membrane-enclosed organelles
Nucleus
(membraneenclosed)
Membraneenclosed organelles
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Theme: Lifes Processes Involve the Expression
and Transmission of Genetic Information
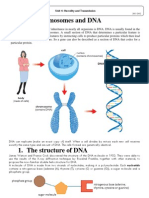
DNA, the Genetic Material
Within cells, structures called chromosomes
contain genetic material in the form of DNA
(deoxyribonucleic acid)
DNA (throughout
nucleus)
1 m
Each chromosome has one long DNA molecule
with hundreds or thousands of genes
Genes encode information for building the
molecules synthesized within the cell
Genes are the units of inheritance
DNA controls the development and maintenance
of organisms
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
8/25/15
Figure 1.6
Figure 1.6a
Nuclei containing DNA
Sperm cell
Egg cell
Fertilized egg
with DNA from
both parents
Embryos cells
with copies of
inherited DNA
Offspring with
traits inherited
from both parents
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Each DNA molecule is made up of two long chains
arranged in a double helix
Each chain is made up of four kinds of chemical
building blocks called nucleotides and nicknamed
A, G, C, and T
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Genes control protein production indirectly
DNA is transcribed into RNA, which is then
translated into a protein
Gene expression is the process of converting
information from gene to cellular product
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Figure 1.8
Genomics: Large-Scale Analysis of DNA
Sequences
(b) How do lens cells make crystallin proteins?
Crystallin gene
(a) Lens cells are
tightly packed
with transparent
proteins called
crystallin.
Lens
cell
DNA
G A
G G
G C
The human genome and those of many other
organisms have been sequenced
TRANSCRIPTION
mRNA
An organisms genome is its entire set of genetic
instructions
G G
U G
G C
Genomics is the study of sets of genes within and
between species
TRANSLATION
Chain of amino
acids
PROTEIN FOLDING
Proteomics is the study of whole sets of proteins
encoded by the genome (known as proteomes)
Protein
Crystallin protein
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
8/25/15
Theme: Life Requires the Transfer and
Transformation of Energy and Matter
The genomics approach depends on
The input of energy from the sun and the
transformation of energy from one form to another
make life possible
High-throughput technology, which yields
enormous amounts of data
Bioinformatics, which is the use of computational
tools to process a large volume of data
When organisms use energy to perform work,
some energy is lost to the surroundings as heat
Interdisciplinary research teams
As a result, energy flows through an ecosystem,
usually entering as light and exiting as heat
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Figure 1.9
ENERGY FLOW
Chemicals
pass to
organisms
that eat the
plants.
Light
energy
Chemical
energy
Heat
Theme: From Ecosystems to Molecules,
Interactions Are Important in Biological
Systems
Interactions between the components of the
system ensure smooth integration of all the parts
This holds true equally well for components of an
ecosystem and the molecules in a cell
Plants take
up chemicals
from the soil
and air.
Chemicals
Decomposers
return
chemicals
to the soil.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Figure 1.10
Ecosystems: An Organisms Interactions with
Other Organisms and the Physical Environment
At the ecosystem level, each organism interacts
continuously with other organisms
Sunlight
Leaves absorb light
energy from the sun.
CO2 Leaves take in
carbon dioxide
from the air and
release oxygen.
O2
These interactions may be beneficial or harmful to
one or both of the organisms
Organisms also interact continuously with the
physical factors in their environment, and the
environment is affected by the organisms living
there
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Leaves fall to the
ground and are
decomposed by
organisms that
return minerals
to the soil.
Water and
minerals in
the soil are
taken up
by the tree
through its
roots.
Animals eat leaves
and fruit from the tree,
returning nutrients
and minerals to the
soil in their waste
products.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
8/25/15
Figure 1.11
Molecules: Interactions Within Organisms
STIMULUS: High
blood glucose level
Interactions between componentsorgans,
tissues, cells, and moleculesthat make up living
organisms are crucial to their smooth operation
Negative feedback
Insulin-producing
cell in pancreas
Cells are able to coordinate various chemical
pathways through a mechanism called feedback
Insulin
Circulation
throughout
body via
blood
Liver and
muscle cells
RESPONSE: Glucose
uptake by liver and
muscle cells
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Animation: Negative Feedback
In feedback regulation the output, or product of a
process, regulates that very process
The most common form of regulation in living
organisms is negative feedback, in which the
response reduces the initial stimulus
Feedback is a regulatory motif common to life at
all levels
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Figure 1.16
Evolution, the Core Theme of Biology
Evolution is the one idea that makes logical sense
of everything we know about living organisms
The scientific explanation for both the unity and
diversity of organisms is the concept that living
organisms are modified descendants of common
ancestors
Many kinds of evidence support the occurrence of
evolution
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
8/25/15
Video: Albatross Courtship Ritual
Charles Darwin published On the Origin of
Species by Means of Natural Selection in 1859
Darwin made two main points
Species showed evidence of descent with
modification from common ancestors
Natural selection is the mechanism behind
descent with modification
Darwins theory explained the duality of unity and
diversity
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Darwin observed that
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Darwin inferred that
Individuals in a population vary in their traits, many
of which are heritable
Individuals that are best suited to their environment
are more likely to survive and reproduce
More offspring are produced than survive, and
competition is inevitable
Over time, more individuals in a population will have
the advantageous traits
Species generally suit their environment
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Evolution occurs as the unequal reproductive
success of individuals
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Figure 1.18-1
In other words, the environment selects for the
propagation of beneficial traits
Darwin called this process natural selection
1 Population
with varied
inherited
traits
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
8/25/15
Figure 1.18-2
1 Population
with varied
inherited
traits
Figure 1.18-3
2 Elimination
1 Population
of individuals
with certain
traits
with varied
inherited
traits
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
2 Elimination
of individuals
with certain
traits
3 Reproduction
of survivors
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Figure 1.18-4
A Case Study in Scientific Inquiry: Investigating
Coat Coloration in Mouse Populations
Color patterns of animals vary widely in nature,
sometimes even between members of the same
species
1 Population
with varied
inherited
traits
2 Elimination
of individuals
with certain
traits
3 Reproduction
of survivors
4 Increasing
frequency
of traits that
enhance
survival
Two populations of mice belonging to the same
species (Peromyscus polionotus) but with different
color patterns are found in different environments
The beach mouse lives on white sand dunes with
sparse vegetation; the inland mouse lives on
darker soil
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
Concept 1.4: Science benefits from a
cooperative approach and diverse viewpoints
Science, Technology, and Society
Most scientists work in teams, which often include
graduate and undergraduate students
The goal of science is to understand natural
phenomena
Good communication is important in order to share
results through seminars, publications, and
websites
The goal of technology is to apply scientific
knowledge for some specific purpose
Science and technology are interdependent
Biology is marked by discoveries, while
technology is marked by inventions
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
8/25/15
The combination of science and technology has
dramatic effects on society
For example, the discovery of DNA by James
Watson and Francis Crick allowed for advances in
DNA technology such as testing for hereditary
diseases
Ethical issues can arise from new technology, but
have as much to do with politics, economics, and
cultural values as with science and technology
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
You might also like
- Biology Biology: Meiosis and Sexual Life CyclesDocument13 pagesBiology Biology: Meiosis and Sexual Life CyclesRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- Data Structures, Algorithms, & Applications: Instructor: Babak Alipour Slides and Book: Sartaj SahniDocument33 pagesData Structures, Algorithms, & Applications: Instructor: Babak Alipour Slides and Book: Sartaj SahniRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- Lecture 20 - Mendel Genetics PDFDocument15 pagesLecture 20 - Mendel Genetics PDFRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- Lecture 22 - Molecular Basis of Genetics PDFDocument15 pagesLecture 22 - Molecular Basis of Genetics PDFRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- Biology: A Tour of The CellDocument11 pagesBiology: A Tour of The CellRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- Data Representation Methods in Arrays and Linked ListsDocument20 pagesData Representation Methods in Arrays and Linked ListsRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction PDFDocument8 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction PDFRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- Lec24 43 PDFDocument605 pagesLec24 43 PDFRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- Biology Biology: The Chromosomal Basis of InheritanceDocument11 pagesBiology Biology: The Chromosomal Basis of InheritanceRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- Lec3 BDocument24 pagesLec3 BRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- Biology Biology: Membrane Structure and FunctionDocument11 pagesBiology Biology: Membrane Structure and FunctionRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- Lec13-B - 23-b (10 Files Merged) PDFDocument325 pagesLec13-B - 23-b (10 Files Merged) PDFRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- Standard Mathematical Tables 21st EditionDocument634 pagesStandard Mathematical Tables 21st EditionRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- Lec2 BDocument24 pagesLec2 BRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- Lec2-B - 12-b (11 Files Merged) PDFDocument288 pagesLec2-B - 12-b (11 Files Merged) PDFRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- Lab0 U16 Construction PDFDocument2 pagesLab0 U16 Construction PDFRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- Updates on TAs, office hours, and DRC quizzesDocument23 pagesUpdates on TAs, office hours, and DRC quizzesRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- Lab0 ReconfigDocument2 pagesLab0 ReconfigRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Wireless Communications SyllabusDocument19 pagesIntroduction to Wireless Communications SyllabusRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- Computational Photography FundamentalsDocument6 pagesComputational Photography FundamentalsRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- Syl U16 PDFDocument8 pagesSyl U16 PDFRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- Transformada de Fourier PDFDocument5 pagesTransformada de Fourier PDFLndIngenieriaNo ratings yet
- Eel 3923 C Spring 2018 SylDocument10 pagesEel 3923 C Spring 2018 SylRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- CDA3101 L01 Introduction MSSDocument20 pagesCDA3101 L01 Introduction MSSRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- ABE 2062/6949 Biology For Engineers (Fall, 2015)Document3 pagesABE 2062/6949 Biology For Engineers (Fall, 2015)Rosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- Eel 3923 C Spring 2018 SylDocument10 pagesEel 3923 C Spring 2018 SylRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- EEE 4373 and EEL 5934 Radio Frequency Electronics Syllabus Fall 2017Document11 pagesEEE 4373 and EEL 5934 Radio Frequency Electronics Syllabus Fall 2017Rosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- Lab #3: Advanced Assembly Programming & Adding SRAMDocument2 pagesLab #3: Advanced Assembly Programming & Adding SRAMRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- EEL 4657 Linear Control SystemsDocument7 pagesEEL 4657 Linear Control SystemsRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- RF Class Notes 2 MOS Basic AnalysisDocument10 pagesRF Class Notes 2 MOS Basic AnalysisRosemond FabienNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- M.SC Biochem Semester Pattern With Scheme Final NAGPUR UNIVERSITYDocument27 pagesM.SC Biochem Semester Pattern With Scheme Final NAGPUR UNIVERSITYupendramolmedNo ratings yet
- TranslationDocument1 pageTranslationGianne AbcedeNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument23 pagesNucleic AcidAbdur DapitillaNo ratings yet
- Transcription Translation Practice WorksheetDocument2 pagesTranscription Translation Practice Worksheetapi-2619420100% (1)
- DNA Structure & ReplicationDocument19 pagesDNA Structure & ReplicationShigrid Ann DocilNo ratings yet
- IBDP BioDocument59 pagesIBDP BioVishnu Sharma100% (1)
- Ariq Ruchiat - Protein Synthesis SimulationDocument2 pagesAriq Ruchiat - Protein Synthesis SimulationARIQ RUCHIATNo ratings yet
- FullDocument2,821 pagesFullSemuel RiakNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology of The Gene: Chapter ObjectivesDocument17 pagesMolecular Biology of The Gene: Chapter Objectivesirene9tan9ailianNo ratings yet
- American Society of Hematology Self-Assessment Program (Adam Cuker, Jessica K. Altman, Aaron T. Gerds Etc.)Document772 pagesAmerican Society of Hematology Self-Assessment Program (Adam Cuker, Jessica K. Altman, Aaron T. Gerds Etc.)Luciano LaranjeiraNo ratings yet
- BIO1400 Test April 2020-3Document17 pagesBIO1400 Test April 2020-3Mohammed NawwabNo ratings yet
- Protein Structure and Function Review QuestionsDocument24 pagesProtein Structure and Function Review QuestionsSudipan RoyNo ratings yet
- Genetics Questions - MCQDocument4 pagesGenetics Questions - MCQManisanthosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Post Translational ModificationsDocument14 pagesPost Translational ModificationschainmaheNo ratings yet
- Chương 1 - GenomicDocument32 pagesChương 1 - GenomicNguyễn Hữu Bảo MinhNo ratings yet
- Biology Problem Set on Nucleic AcidsDocument28 pagesBiology Problem Set on Nucleic AcidsSundaravadivel Prabhav (Njc)No ratings yet
- From Gene To Protein: How Genes WorkDocument58 pagesFrom Gene To Protein: How Genes WorkGabe GallagherNo ratings yet
- Developing mRNA-vaccine TechnologiesDocument12 pagesDeveloping mRNA-vaccine TechnologiesMIZPAH VILLALOBOSNo ratings yet
- Topic 4Document7 pagesTopic 4Antonio López JiménezNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis - Activity Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesProtein Synthesis - Activity Sheet PDFjaneyzhouNo ratings yet
- IBDP Biology Revision Guide (SL) - Knowledge and ApplicationDocument43 pagesIBDP Biology Revision Guide (SL) - Knowledge and Application[5L14] Cheung Samara Nathania100% (1)
- Glycogen Storage Diseases, GAGs, and Mucopolysaccharide DisordersDocument151 pagesGlycogen Storage Diseases, GAGs, and Mucopolysaccharide Disordersfadi100% (1)
- Transcription and TranslationDocument35 pagesTranscription and TranslationMing mingNo ratings yet
- The Cellular Level of Organization PDFDocument7 pagesThe Cellular Level of Organization PDFGol D. AceNo ratings yet
- Full Download Essentials of Physical Anthropology 10th Edition Jurmain Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Essentials of Physical Anthropology 10th Edition Jurmain Solutions Manualudalbornhockeyspl2100% (25)
- Biological Chemistry (Concept To Remember)Document8 pagesBiological Chemistry (Concept To Remember)Kecilyn AmbrocioNo ratings yet
- Activities To Develop Pre-TaskDocument6 pagesActivities To Develop Pre-Taskeduardo arenasNo ratings yet
- Exercise and Problems Types of Nucleic Acids (Section 22.1)Document7 pagesExercise and Problems Types of Nucleic Acids (Section 22.1)Azyrah Lyren Seguban UlpindoNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Structure and FunctionDocument37 pagesNucleic Acid Structure and FunctionLiz VillarNo ratings yet
- Bioinformatics Primer (An Introductory Handbook For Bioinformatics Practitioners)Document258 pagesBioinformatics Primer (An Introductory Handbook For Bioinformatics Practitioners)Sambit NayakNo ratings yet