Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Importing and Exporting Metadata
Uploaded by
Mathias EderOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Importing and Exporting Metadata
Uploaded by
Mathias EderCopyright:
Available Formats
2 Geographic Data Management
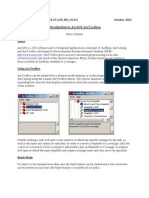
Importing and exporting metadata
If you have metadata that was created outside of ArcCatalog, you can import it if its stored in one of the input formats
supported by the FGDCs metadata parser utility.
You might export metadata to publish it on a data clearinghouse website. Exporting to HTML format creates a le that
represents the selected items metadata exactly as you see it in the Metadata tab. Exporting to XML format creates an
exact copy of the items metadata in a new XML le; this lets you work with metadata for geodatabase items outside
ArcCatalog.
Use the buttons on the Metadata toolbar to import a datasets metadata from (or
export it to) one of several standard formats.
101
Using ArcGIS Desktop
Creating a geodatabase
The process for building a geodatabase is to create the design for the geodatabase, build the structure for the
geodatabase (the schema) in ArcGIS, and then import existing data into the geodatabase, or create new datasets within
it. There are two ways to turn a geodatabase design into a geodatabase structure: create an empty geodatabase and
then use ArcCatalog tools to create the various components (as dened in the design); or copy an existing schema or
geodatabase template and modify it, if necessary.
After the geodatabase is constructed, you can import data (see Collecting, importing, and converting GIS data in
Chapter 3). You may want to start by importing a subset of data to test the design. You can then make changes to the
geodatabase design before loading all your data.
Creating a geodatabase using ArcCatalog tools
To build a geodatabase using tools in ArcCatalog, you rst create the geodatabase, which is initially empty. You then
use the tools provided in ArcCatalog to create or import the feature datasets, feature classes, tables, geometric networks,
topologies, and other items in the geodatabase. These tools are described in separate sections in this chapter. Use these
same tools to modify a geodatabase youve imported from a template.
There are three kinds of geodatabases: le geodatabases, personal geodatabases, and ArcSDE geodatabases. A le
geodatabase stores datasets as a folder of les on your computer. A personal geodatabase stores datasets in a Microsoft
Access le on disk. They both look the same in ArcCatalog (except for the extension.gdb and .mdb, respectively),
although they vary in functionality and performance. A le geodatabase can be up to 1TB in size (versus up to 2GB
for a personal geodatabase) and will perform searches and queries faster than will a personal geodatabase. A personal
geodatabase, however, provides the advanced table operations found in Microsoft Access (some GIS applications may
require these).
You create a le or personal geodatabase within a folder (usually for a workspace youve set up) by right-clicking the
folder.
Right-click a folder, click New, and click either
File Geodatabase or Personal Geodatabase.
A new, empty geodatabase is created in the foldertype over the name to
rename the geodatabase.
102
You might also like
- Microstation WorkflowDocument34 pagesMicrostation WorkflowGeorgeman LópezNo ratings yet
- ArcSDE Geodatabase CreationDocument2 pagesArcSDE Geodatabase CreationMathias EderNo ratings yet
- ArcGis ConceptsDocument60 pagesArcGis Conceptssri_charan100% (1)
- Guide To Creating and Editing Metadata in Arcgis For Publishing To The Msdis GeoportalDocument24 pagesGuide To Creating and Editing Metadata in Arcgis For Publishing To The Msdis Geoportalvela.letaNo ratings yet
- Arcgis For Experienced Gis Users: Theresa Valentine Usda Forest Service Corvallis Forest Science LaboratoryDocument19 pagesArcgis For Experienced Gis Users: Theresa Valentine Usda Forest Service Corvallis Forest Science Laboratoryyasir2010No ratings yet
- Differences Between ArcGIS 9&10Document8 pagesDifferences Between ArcGIS 9&10Aditya KapoorNo ratings yet
- 1.1 HTML Imagemapper Ng2Document10 pages1.1 HTML Imagemapper Ng2sharmalalit15No ratings yet
- Sharing Data: Between CAD and GIS EnvironmentsDocument4 pagesSharing Data: Between CAD and GIS Environmentsrvkumar3619690No ratings yet
- Building A Geodatabase TutorialDocument32 pagesBuilding A Geodatabase TutorialArda Young100% (1)
- Use ArcGIS Stylesheets to Present MetadataDocument2 pagesUse ArcGIS Stylesheets to Present MetadataMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Tips and Tricks I: Getting the Most Out of ArcGIS DesktopDocument108 pagesTips and Tricks I: Getting the Most Out of ArcGIS Desktoptanja222No ratings yet
- Chap 1 - Introdcution To GIS - Exercise - ArcGISDocument17 pagesChap 1 - Introdcution To GIS - Exercise - ArcGISAnkur GuptaNo ratings yet
- Setup Wireframing ProjectDocument3 pagesSetup Wireframing ProjectLuter MinNo ratings yet
- Working in ArcGIS Mode Working (Manual Bemtley)Document335 pagesWorking in ArcGIS Mode Working (Manual Bemtley)Elizabeth huamantinco veraNo ratings yet
- CIVIL 3D Handout A Practical Guide To Gis in Autocad Civil 3dDocument35 pagesCIVIL 3D Handout A Practical Guide To Gis in Autocad Civil 3ddavinci1234No ratings yet
- SketchUp ArcGIS User GuideDocument7 pagesSketchUp ArcGIS User Guidemx100sanookNo ratings yet
- Arc Marine Tutorial for Beginners in ArcGIS 10Document39 pagesArc Marine Tutorial for Beginners in ArcGIS 10Bang NarkoNo ratings yet
- GIS Project in ARCGISDocument20 pagesGIS Project in ARCGISRegNo ratings yet
- Arc ToolboxDocument10 pagesArc ToolboxQudri SaufiNo ratings yet
- CES322263-L Class Handout CES322263L Rick EllisDocument40 pagesCES322263-L Class Handout CES322263L Rick EllisMohamed HammamiNo ratings yet
- XTools Pro 71Document4 pagesXTools Pro 71Andréa CysneNo ratings yet
- Lab 1: Introduction To Geoinformatics Introduction To Arcgis Time For Completion: One Week - Due September 6Document16 pagesLab 1: Introduction To Geoinformatics Introduction To Arcgis Time For Completion: One Week - Due September 6Pre PdxNo ratings yet
- ASPdotNet DAL Tutorial: Creating a Data Access LayerDocument42 pagesASPdotNet DAL Tutorial: Creating a Data Access Layersan000jayNo ratings yet
- Intro To GisDocument15 pagesIntro To Gismiss mdNo ratings yet
- Making A Geologic Map in ArcGIS 10 PDFDocument39 pagesMaking A Geologic Map in ArcGIS 10 PDFRonald AthallahNo ratings yet
- Finding and Using Spatial DataDocument12 pagesFinding and Using Spatial DataEnoch ArdenNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1: 1. Getting To Know ArcgisDocument19 pagesExercise 1: 1. Getting To Know ArcgisbirukNo ratings yet
- Enerprise Geodatabases and Web MappingDocument29 pagesEnerprise Geodatabases and Web Mappingapi-295783313No ratings yet
- Introduction To Arc Catalog/ArcGISDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Arc Catalog/ArcGISAshok Peddi100% (1)
- MAN2 DesignerDocument16 pagesMAN2 Designerlpm40No ratings yet
- Tableau GeoreferenceDocument25 pagesTableau GeoreferenceemedinillaNo ratings yet
- Digitize geological interpretations on Target for ArcGIS drillhole mapsDocument6 pagesDigitize geological interpretations on Target for ArcGIS drillhole mapsAmy OlsonNo ratings yet
- WSCAD SUITE X Project and Data ImportDocument14 pagesWSCAD SUITE X Project and Data ImportDiep Tran NgocNo ratings yet
- ASP.NET Data Access TutorialDocument70 pagesASP.NET Data Access TutorialnageshNo ratings yet
- What'S New in Esri Arcgis 10 Desktop: Gis Services, Mit Libraries Gishelp@Mit - EduDocument36 pagesWhat'S New in Esri Arcgis 10 Desktop: Gis Services, Mit Libraries Gishelp@Mit - EduLuzianeRibeiroNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document40 pagesUnit 4data1.waangooNo ratings yet
- Laz DB DesktopDocument12 pagesLaz DB DesktopBocage Elmano SadinoNo ratings yet
- Access Import SHPDocument3 pagesAccess Import SHPmlgtsamuelNo ratings yet
- MKPL MicrosoftSQLMetadatatoCatalog 180219 1849 1876Document12 pagesMKPL MicrosoftSQLMetadatatoCatalog 180219 1849 1876Ahsan FarooquiNo ratings yet
- Access Data and Create Reports in ADO.NET and Visual BasicDocument1 pageAccess Data and Create Reports in ADO.NET and Visual BasicNiña Chris BuenNo ratings yet
- Handout 10904 Ellis APractical Guideto GISin Civil 3 DDocument37 pagesHandout 10904 Ellis APractical Guideto GISin Civil 3 DMphatso GondweNo ratings yet
- Integrating Microsoft Access With Autocad VbaDocument19 pagesIntegrating Microsoft Access With Autocad VbaLuiz Paulo Cruz JrNo ratings yet
- VBADocument16 pagesVBAmayur_lanjewarNo ratings yet
- Tugas Basis Data SpasialDocument35 pagesTugas Basis Data SpasialfaizalprbwNo ratings yet
- Tutorial: Introducing Autocad Map 3D 2012: Lesson 1: Get Ready To Use The TutorialsDocument32 pagesTutorial: Introducing Autocad Map 3D 2012: Lesson 1: Get Ready To Use The TutorialsprofsovaNo ratings yet
- Setting Up An Arc Hydro Based GeoprocessingDocument51 pagesSetting Up An Arc Hydro Based GeoprocessingAlicia GordonNo ratings yet
- WebMap Using Leaflet-For BeginnersDocument21 pagesWebMap Using Leaflet-For BeginnersRit marvibNo ratings yet
- Creating GeodatabaseDocument36 pagesCreating Geodatabasedino_becicNo ratings yet
- Lab1GIS G1.2Document7 pagesLab1GIS G1.2Muhammad Hizbullah BaharomNo ratings yet
- Hypack 2015 ChangesDocument35 pagesHypack 2015 ChangesNatalyChirinosHerreraNo ratings yet
- Exercise Creating A File GeodatabaseDocument5 pagesExercise Creating A File GeodatabaseMarco MagalhãesNo ratings yet
- Gis RD 02-15Document2 pagesGis RD 02-15salhi01No ratings yet
- Instructiuni ToolPac 13 (Engleza)Document26 pagesInstructiuni ToolPac 13 (Engleza)jijimanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Working With Data From External SourcesDocument21 pagesLesson 7 Working With Data From External Sourcesjjrelucio3748100% (1)
- Opening Map Files in ArcGISDocument15 pagesOpening Map Files in ArcGISashry09No ratings yet
- Integrating Survey and GIS DataDocument17 pagesIntegrating Survey and GIS DataW1CHM4NNo ratings yet
- The Following Was Presented at DMT'10 (May 16-19, 2010)Document26 pagesThe Following Was Presented at DMT'10 (May 16-19, 2010)Fixed7777No ratings yet
- Using Building Height. The Attribute Values Are Used As Relative Heights in The View. You Can Also Combine PerspectiveDocument2 pagesUsing Building Height. The Attribute Values Are Used As Relative Heights in The View. You Can Also Combine PerspectiveMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Assembler GuideDocument2 pagesAssembler GuideMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Abap Manual 2Document2 pagesAbap Manual 2Mathias EderNo ratings yet
- Description: Opengis Simple Features Implementation Specification For SQL 1.1Document2 pagesDescription: Opengis Simple Features Implementation Specification For SQL 1.1Mathias EderNo ratings yet
- PostGIS 1.5.1 Manual - Examples of ST_AddMeasure and long transaction supportDocument2 pagesPostGIS 1.5.1 Manual - Examples of ST_AddMeasure and long transaction supportMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Examples: ST - Centroid ST - Point - Inside - CircleDocument2 pagesExamples: ST - Centroid ST - Point - Inside - CircleMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Centos Intro PDFDocument2 pagesCentos Intro PDFMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Unix ManualDocument2 pagesUnix ManualMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Examples: Opengis Simple Features Implementation Specification For SQL 1.1Document2 pagesExamples: Opengis Simple Features Implementation Specification For SQL 1.1Mathias EderNo ratings yet
- Centos ManualDocument2 pagesCentos ManualMathias EderNo ratings yet
- See Also: ST - Asewkt ST - Extent3D ST - Setsrid ST - SridDocument2 pagesSee Also: ST - Asewkt ST - Extent3D ST - Setsrid ST - SridMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Lisp GuideDocument330 pagesLisp GuideMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Fortran IntroDocument2 pagesFortran IntroMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Guide MysqlDocument2 pagesGuide MysqlMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Lisp IntroDocument2 pagesLisp IntroMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Examples: Postgis 1.5.1 ManualDocument2 pagesExamples: Postgis 1.5.1 ManualMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Cobol PrimerDocument2 pagesCobol PrimerMathias EderNo ratings yet
- PostGIS Geometry, Box, and 3D Functions GuideDocument2 pagesPostGIS Geometry, Box, and 3D Functions GuideMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Cobol Doku PDFDocument2 pagesCobol Doku PDFMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Perl PrimerDocument2 pagesPerl PrimerMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Cobol IntroDocument2 pagesCobol IntroMathias EderNo ratings yet
- PostGIS 1.5.1 Manual Appendix A Release NotesDocument2 pagesPostGIS 1.5.1 Manual Appendix A Release NotesMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Cobol GuideDocument2 pagesCobol GuideMathias EderNo ratings yet
- PostGIS 1.5.1 Manual Functions ReferenceDocument2 pagesPostGIS 1.5.1 Manual Functions ReferenceMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Cobol ManualDocument2 pagesCobol ManualMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Office PrimerDocument2 pagesOffice PrimerMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Prolog PrimerDocument2 pagesProlog PrimerMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Windows ManualDocument2 pagesWindows ManualMathias EderNo ratings yet
- Mba Thesis-Enhanced Banking Services For Uplifitng The Standard of Living of Rural People in Kanchipuram DistrictDocument26 pagesMba Thesis-Enhanced Banking Services For Uplifitng The Standard of Living of Rural People in Kanchipuram DistrictSarath KumarNo ratings yet
- ERA2010 Conference ListDocument136 pagesERA2010 Conference Listasif1253No ratings yet
- Big Data HadoopDocument34 pagesBig Data Hadoopkuldeep singhNo ratings yet
- Corporate Environmental Responsibility in Ethiopia: A Case Study of The Akaki River BasinDocument11 pagesCorporate Environmental Responsibility in Ethiopia: A Case Study of The Akaki River BasinBemnet LeykunNo ratings yet
- Storage Area Network Module-1Document77 pagesStorage Area Network Module-1student MITM CSENo ratings yet
- Arabic Characters Do Not Display Correctly in PDF Format Using Arabic Transparent Font or Simplified Arabic FontDocument2 pagesArabic Characters Do Not Display Correctly in PDF Format Using Arabic Transparent Font or Simplified Arabic FontSHAHID FAROOQNo ratings yet
- ARM Memory Management UnitDocument44 pagesARM Memory Management UnitSuhas Rohit PaiNo ratings yet
- Data Science Interview QnAs by CloudyMLDocument21 pagesData Science Interview QnAs by CloudyMLmacoyigNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Report WritingDocument85 pagesFundamentals of Report WritingStephen Sumipo BastatasNo ratings yet
- Report On PaggingDocument16 pagesReport On Paggingnurin khatoonNo ratings yet
- ER diagram for IT training groupDocument2 pagesER diagram for IT training grouphemarubini96No ratings yet
- Ethics of ResearchDocument10 pagesEthics of ResearchAiman Ameer PiaNo ratings yet
- Group Asssignment CHAP11Document5 pagesGroup Asssignment CHAP11Lê Trọng Nhân67% (3)
- Data Dictionary For Inventory SchemaDocument6 pagesData Dictionary For Inventory SchemaUsama Bin Alam0% (1)
- 02 - XML - FundamentalsDocument26 pages02 - XML - FundamentalsHop HuynhNo ratings yet
- B+ Trees IndexingDocument23 pagesB+ Trees IndexingKishor PeddiNo ratings yet
- DDL and DML Commands in Oracle DatabaseDocument80 pagesDDL and DML Commands in Oracle DatabaseSagar PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Memory and Data StructuresDocument25 pagesDynamic Memory and Data Structuresabraham_sse1594No ratings yet
- 2marks and 3marks-12.06.2020Document15 pages2marks and 3marks-12.06.2020thanigesan100% (1)
- Building A Data-Driven OrganizationDocument14 pagesBuilding A Data-Driven Organizationandini eldanantyNo ratings yet
- CellWireless___Spectrum_Monitoring___Installation_Manual_rev11Document30 pagesCellWireless___Spectrum_Monitoring___Installation_Manual_rev11larissa.inglesNo ratings yet
- Symcli PDFDocument22 pagesSymcli PDFShawn PrafulNo ratings yet
- Oracle 8i For Linux - Data SheetDocument10 pagesOracle 8i For Linux - Data Sheetsuneetha.alluriNo ratings yet
- AIS Chapter 2 - ERPDocument58 pagesAIS Chapter 2 - ERPnatalie clyde matesNo ratings yet
- Literature Review of User Needs: Descriptive Metadata For Web ArchivingDocument52 pagesLiterature Review of User Needs: Descriptive Metadata For Web ArchivingSofia D'AlessandroNo ratings yet
- Oracle CBO and Siebel Business Applications (ID 478028.1)Document9 pagesOracle CBO and Siebel Business Applications (ID 478028.1)munesh76No ratings yet
- COS3721 TL 202 2 2018 B PDFDocument10 pagesCOS3721 TL 202 2 2018 B PDFThanyani SirumulaNo ratings yet
- OBIA 12c Implementation PlanningDocument5 pagesOBIA 12c Implementation PlanningGCNo ratings yet
- Deposit Analysis of NABIL Bank LTD.: A Case Study OnDocument49 pagesDeposit Analysis of NABIL Bank LTD.: A Case Study OnRabi Shrestha80% (25)
- Week 4Document8 pagesWeek 4JAMES DARYLNo ratings yet