Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cdma
Uploaded by
flatelecom938Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cdma
Uploaded by
flatelecom938Copyright:
Available Formats
AT Ready to Exchange
Data on Access Stream
CHAP
Authentication Succsess
CHAP Challenge Response
PPP and LCP Negotiation
AT Ready to Exchange
Data on Access Stream
Session Established
UATI-Complete
UATI-Assignment
UATI-Request
AN
A9-Setup-A8
A12 Access Accept
A12 Access Request
AA
AN
A
T regreq
Transmitting Packet Data
Establishing PPP Connection
A9-Connect-A8
T A8-setup
Um
RFC
RLC
RLP
RLSD
RPC
SAT
SCCP
SDB
SLTM
SME
SMS
SPI
SSCF
SSCOP
SSD
SSSAR
TCP
TMSI
UDI
UDP
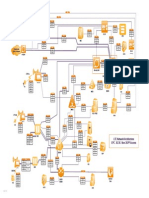
1x EV-DO Session F low
MS
Application Data Delivery Service
ATM Adaptation Layer Type 2
ATM Adaptation Layer Type 5
Base Station Application Part
Base Station Management Application Part
Call Control
Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol
Connection Identifier (used with reference to AAL2)
Connection Management
Dedicated Control Channel
Data Link Connection Identifier
Direct Transfer Application Part
Dual Tone Multi-Frequency
Generic Routing Extension
International Mobile Subscriber Identity
Internet Protocol
Internet Protocol Control Protocol
Integrated Services Digital Network
Intersystem Link Protocol
Location Area Code
Link Control Protocol
Medium Access Control
Mobile Identification Number
Mobile IP
Mobility Management
Message Transfer Part
Message Transfer Part Layer 1
Message Transfer Part Layer 2
Message Transfer Part Layer 3
Pulse Code Modulation
Packet Mode Channel
Point to Point Protocol
Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service
Random Variable
Random Confirmation
Random SSD
Random Variable - Unique Challenge
Radio Configuration, Radio Class
Radio Frequency
PC
A11-Registration Reply
A11-Registration Request
BT
SN
PD
s
bi
BS
Um
MS
3
,A
,A
A8
DM
Physical Layer
Physical Layer
ATM
ATM
BT
AAL5
AAL2
IP
SSSAR
bis
TCP
User Traffic
IOS Application
2,
A5
0
0
0
A2
BS
,A
A1
1x
c
c
A
AT
Um
es
sN
AN
k
or
11
C/
bis
AN
AT
Um
1
3
,A
,
A8
1
5
,A
A9
VC
R
AN
TS
Physical Layer
Link Layer
IP
TCP/UDP
A13/A15 Signaling
A13/A15
,
14
Physical Layer
Physical Layer
Physical Layer
Ax
Link Layer
Link Layer
IP
IP
IP
Link Layer
GRE
TCP/UDP
TCP/UDP
A9 Signaling
A14 A9 User Signaling Protocol Stack A8 User Traffic Protocol Stack
A14 Signaling
,A
10
MS
PC
F
SC
A
1
se
II
Physical Layer
Transport
SCCP/SCMG
TCAP
N,
Physical Layer
Link Layer
IP
,
A8
Ab
is
DM
A2
0
0
0
1x
V
E
-
O
D
-
,A
A9
Physical Layer
Physical Layer
Physical Layer
,A
14
Link Layer
IP
GRE
Link Layer
IP
TCP/UDP
A9 Signaling
AN
ce
N
s
s
PC
w
t
e
k
r
o
Physical Layer
Link Layer
A1
2p
s
ha
Physical Layer
Link Layer
A13 Signaling
TCP/UDP
IP
PPP
A13
SN
A11 Signaling
0
,A
PD
I
A1
eI
A10 User Traffic Protocol Stack A11 Signaling Protocol Stack
Co
re
t
e
N
r
o
w
UDP
d
e
h
HL
AU
GRE
Link Layer
IP
TCP/UDP
A14 Signaling
...
tc
i
w
N,
Ac
t
ui
ISD
TN
PS
IP
irc
EIR
A14 A9 User Signaling Protocol Stack A8 User Traffic Protocol Stack
E
MAP
Physical Layer
Transport
SCCP/SCMG
TCAP
MAP
ISD
...
RADCOM home page: www.radcom.com
TS
w
et
Physical Layer
Physical Layer
PC
Link Layer
Link Layer
Physical Layer
Physical Layer
A3 User Traffic Protocol Stack A3 and A7 Signaling Protocol Stack
PPP
IP
Link Layer
Link Layer
IP
IP
A11 Signaling Protocol Stack A10 User Traffic Protocol Stack
UDP
GRE
TCP/UDP
IP
GRE
PC
Physical Layer
ISLP
DSO
MTP 1
MTP 3
SCCP
IOS Application
MTP 2
DSO
64 Kbps UDI
Data Octet Stream
or
A1 Signaling Protocol Stack
A5 User Traffic Protocol Stack
DSO
56/64 Kbps PCM
A2 User Traffic Protocol Stack
MS
GM
TN
PS
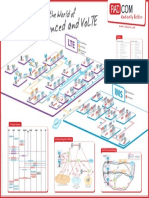
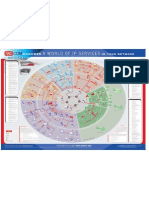
World of CDMA2000
A11 Signaling
A9 Signaling
A9 User Signaling Protocol Stack A8 User Traffic Protocol Stack
Remote Feature Control
Release Complete (SCCP)
Radio Link Protocol
Release (SCCP)
Reverse Power Control
Supervisory Audio Tone
Signaling Connection Control Part
Short Data Burst
Signaling Link Test Message
Signaling Message Encryption
Short Message Service
Security Parameter Index
Service Specific Convergence Function
Service Specific Connection Oriented Protocol
Shared Secret Data
Service Specific Segmentation and Reassembly Sublayer
Transmission Control Protocol
Temporary Mobile Station Identity
Unrestricted Digital Information
User Datagram Protocol
Protocol information and updates: www.protocols.com
AT
ADDS
AAL2
AAL5
BSAP
BSMAP
CC
CHAP
CID
CM
DCCH
DLCI
DTAP
DTMF
GRE
IMSI
IP
IPCP
ISDN
ISLP
LAC
LCP
MAC
MIN
MIP
MM
MTP
MTP1
MTP2
MTP3
PCM
PMC
PPP
RADIUS
RAND
RANDC
RANDSSD
RANDU
RC
RF
CDMA2000 Protocols
Monitors your CDMA2000 network
Physical Layer
Link Layer
IP
UPP
RADIUS
A12 User Protocols Stack
AN
P1
AA
Ho
AA me
A
Physical Layer
Link Layer
IP
UDF
RADIUS or DIAMETR
k
c
a
HA
-H
S
t
e
d
e
h
P1
Co
re
Authentication Center
Authentication, Authorization and Accounting Server
Access Network
Access Terminal
Base Station
Base Station Controller
Base Transceiver System
Foreign Agent
Home Agent
Home Location Register
Interworking Function
Mobile Station
Mobile Switching Center
Packet Control Function
Packet Data Serving Node
Public Land Mobile Network
Public Switched Telephone Network
Visitor Location Register
w
t
e
k
r
o
Pi
The E interface carries user signaling information between
the MSC/VLR and GMSC.
The Pi interface connects the FA and the HA to the external
Packet Data Network such as Internet, Intranet and Extranet.
The P1 interface carries signaling information related to
terminal authentication for data session initiation, between
the Session Control (SC)/Mobility Management (MM)
functions in the Home AAA and Visited AAA (Authentication,
Athorization and Accounting entities for CDMA2000 1x)
and the HA and FA respectively.
The P-H interface carries Mobile IP/user application data
between the Home Agent (HA) and the Foreign Agent (FA).
The A11 interface carries signaling information between
the PCF and the PDSN.
The A10 interface carries user traffic between the PCF
and the PDSN.
The A9 interface carries signaling information between
the BS and the PCF.
The A8 interface causer traffic between
the BS and the PCF.
The A7 interface carries signaling information between
a source BS and a target BS.
The A5 interface carries a full duplex stream of bytes
between the MSC and the SDU function of the BSC.
The A3 interface carries coded user information
(voice/data) and signaling information between the
source BS SDU function and the channel element
component (BTS) of the target BS. This is a logical
description of the endpoints of the A3 interface. The
A3 interface is composed of two parts: signaling and
user traffic. The signaling information is carried across
a separate logical channel from the user traffic channel,
and controls the allocation and use of channels for
transporting user traffic.
OC3 digital transmission interfaces supporting
transmission rates of 155.52 Mbps.
T3 digital transmission interfaces supporting transmission
rates of 43.232 Mbps.
E1 digital transmission interfaces consisting of 30*64
Kbps user channels can also be used for traffic or signaling.
As the operator requires, and as applicable to the network.
As a BS/MSC agreed option, dedicated DSO signaling
link(s) may be used instead of the T1/E1 interface.
T1 digital transmission system interfaces. Each 1.544 Mbps
interface provides 24*56 or 24*64 Kbps channels, which
can be used for traffic or signaling as operator requires.
The A8 to A15 interfaces are based on the use of the Internet
Protocol, which can operate across various physical layer media
(generally, Ethernet Fast LAN or GbE).
The A1, A2, A3, A5 and A7 interfaces are based on the use of:
Physical Layer Interfaces
Pi
P1
P-H
A11
A10
A9
A8
A7
A5
A3
The A2 interface carries 64/56 Kbps PCM information
of 64 Kbps Unrestricted Digital Information (UDI, for
ISDN) between the Switch component of the MSC and
the Selection/Distribution Unit (SDU) function of the BS.
The C interface carries user signaling information between
the MSC/VLR and HLR.
A2
The A1 interface carries signaling information between
the Call Control (CC) and Mobility Management (MM)
functions of the MSC and the Call Control component
of the BS (BSC).
A1
Interface Description - CDMA2000 - 1x
US office: RADCOM Equipment Inc., 6 Forest Avenue, Paramus NJ 07652, USA
Tel: (201) 518-0033, Fax: (201) 556-9030, 1-800-RADCOM-4, e-mail: info@radcomusa.com
Israel office: RADCOM Ltd., 24 Raoul Wallenberg Street, Tel-Aviv 69719, Israel
Tel: +972-3-6455055, Fax:+972-3-6474681, e-mail: info@radcom.com
AC
AAA
AN
AT
BS
BSC
BTS
FA
HA
HLR
IWF
MS
MSC
PCF
PDSN
PLMN
PSTN
VLR
FA
PDN
Internet
Intranet
Extranet
User Application Data
(IP/TCP, HTTP, etc.)
The Ax interface carries user traffic between the SC/MM
function in the PCF and the AN.
The A15 interface carries signaling information between
ANs when inter-AN paging is used.
The A14 interface carries signaling information between
the SC/MM function in the PCF and the AN.
CDMA2000 Entities
tc
i
w
Vis
AA ited
A
Physical Layer
Link Layer
IP
UDF
RADIUS or DIAMETR
Pi
Physical Layer
MAC
IP
UDP
MIP
Ax
A15
A14
The A13 interface carries signaling information between
the SC/MM function in the source AN and the SC/MM
function in the target AN (Phase I) or in phase II
between the SC/MM function in the source PCF and
the SC/MM function in the target PCF.
The A11 interface carries signaling information between
the PCF and the PDSN.
A11
A13
The A10 interface carries user traffic between the PCF
and the PDSN.
A10
The A12 interface carries signaling information related
to terminal authentication between the SC/MM function
in the AN and the AN AAA (Phase I) or in Phase II
between the PCF and the AN AAA (Authentication,
Authorization, and Accounting entity for 1x-EV-DO).
The A9 interface carries signaling information between
the AN and the PCF.
A9
A12
The A8 interface carries user traffic between the Access
Network (AN) and the Packet Control Function (PCF).
A8
Interface Description - CDMA2000 - 1x-EV-DO
Product brand names may be trademarks of their respective owners and are mentioned for reference only. Information subject to change without notice. RADCOM makes no warranty of any kind, expressed or implied, including, but not limited to, the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. RADCOM is not liable for errors contained herein.
RA PCDMA2000 Revision B
You might also like
- Introduction To SIPDocument19 pagesIntroduction To SIPandago9993No ratings yet
- Ericsson UCIP Library for XML-RPC CallsDocument3 pagesEricsson UCIP Library for XML-RPC Callsyannis_benNo ratings yet
- iCON (IPX-3200) IPSTAR Satellite Terminal Release 1.1 PDFDocument18 pagesiCON (IPX-3200) IPSTAR Satellite Terminal Release 1.1 PDFMelkiNo ratings yet
- Genband Q21 SBC: High Performance, High Density Session Border ControllerDocument4 pagesGenband Q21 SBC: High Performance, High Density Session Border Controllerkaz7878No ratings yet
- Technical Report on Virtualized RAN ArchitectureDocument16 pagesTechnical Report on Virtualized RAN Architectureflatelecom938No ratings yet
- CCIE LabDocument144 pagesCCIE LabCông SơnNo ratings yet
- Zenith User Manual Mk2 SensorDocument56 pagesZenith User Manual Mk2 SensorArmel Gildas100% (4)
- 98-366 MVA Slides Lesson 8Document28 pages98-366 MVA Slides Lesson 8cvigaNo ratings yet
- Nexus Telecom Networks PosterDocument1 pageNexus Telecom Networks PosterFeras ElbakriNo ratings yet
- Mobile WiMAX: A Systems Approach to Understanding IEEE 802.16m Radio Access TechnologyFrom EverandMobile WiMAX: A Systems Approach to Understanding IEEE 802.16m Radio Access TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Mobile Computing Deployment and Management: Real World Skills for CompTIA Mobility+ Certification and BeyondFrom EverandMobile Computing Deployment and Management: Real World Skills for CompTIA Mobility+ Certification and BeyondNo ratings yet
- Lte Poster2013 Web PDFDocument1 pageLte Poster2013 Web PDFLuis José Rivas LoretoNo ratings yet
- GSM GPRS 021903Document16 pagesGSM GPRS 021903RUTUJA GOGULWARNo ratings yet
- Audio Encryption Optimization: Harsh Bijlani Dikshant Gupta Mayank LovanshiDocument5 pagesAudio Encryption Optimization: Harsh Bijlani Dikshant Gupta Mayank LovanshiAman Kumar TrivediNo ratings yet
- Hdmi™ (High-Defi Nition Multimedia Interface) : Connectors and Pin AssignmentDocument2 pagesHdmi™ (High-Defi Nition Multimedia Interface) : Connectors and Pin AssignmentmattgirvNo ratings yet
- LTE EPC Interfaces ProtocolStackDocument1 pageLTE EPC Interfaces ProtocolStackMigueljfgNo ratings yet
- TJ 1400 OLT BrochureDocument2 pagesTJ 1400 OLT BrochureShine JosephNo ratings yet
- GSM Based SMS Driven Automatic Display Tool KitDocument120 pagesGSM Based SMS Driven Automatic Display Tool KitAman BaranwalNo ratings yet
- DR Poster v2Document1 pageDR Poster v2eagleniNo ratings yet
- LTE Case Study on LTE Network ArchitectureDocument16 pagesLTE Case Study on LTE Network ArchitectureVenkatraman SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Apsfl Brochure Web PurposeDocument16 pagesApsfl Brochure Web PurposeBharath CNWNo ratings yet
- HCIE Interview Questions by SherazDocument42 pagesHCIE Interview Questions by SherazAdnan KhanNo ratings yet
- ATCA and MicroATCA GuideDocument60 pagesATCA and MicroATCA Guidedenkins2020100% (1)
- Radcom LTE Poster 2011Document1 pageRadcom LTE Poster 2011Sergiy RipskyyNo ratings yet
- IR.34-V9.1 - Guidelines For IPX Provider Networks (Previously Inter-Service Provider IP Backbone Guidelines)Document50 pagesIR.34-V9.1 - Guidelines For IPX Provider Networks (Previously Inter-Service Provider IP Backbone Guidelines)a_big_friendNo ratings yet
- 2G, 3G, 4G Mobile CommunicationDocument50 pages2G, 3G, 4G Mobile CommunicationSujoy ShivdeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 14: Qos in Ip Networks: Intserv and Diffserv: Slide Supporting MaterialDocument52 pagesLesson 14: Qos in Ip Networks: Intserv and Diffserv: Slide Supporting MaterialSallam SallakhoNo ratings yet
- CV - Experienced NGN and Voip EngineerDocument3 pagesCV - Experienced NGN and Voip EngineeramirNo ratings yet
- World of Protocols 1999-2000Document1 pageWorld of Protocols 1999-2000rzanazziNo ratings yet
- GPRSDocument14 pagesGPRSRuhisha AnandNo ratings yet
- T1 and E1 PCM systems explainedDocument10 pagesT1 and E1 PCM systems explainedPrafull BNo ratings yet
- PDH SDH Presentation 1Document67 pagesPDH SDH Presentation 1Mhamad DannawiNo ratings yet
- DS Neptune NPT-1100Document2 pagesDS Neptune NPT-1100Deepak Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Livre AoIP PDFDocument135 pagesLivre AoIP PDFfdbttTKLCNo ratings yet
- Ds Nemo Outdoor LTE Altair TerminalsDocument3 pagesDs Nemo Outdoor LTE Altair TerminalsjuanahumadaNo ratings yet
- Analyzing SS7/Sigtran Attacks Using Wireshark, Tshark & SnortDocument68 pagesAnalyzing SS7/Sigtran Attacks Using Wireshark, Tshark & SnortLuca GarufiNo ratings yet
- IP-SM-GW Transport - How SMS is Sent over IP in VoLTE NetworksDocument12 pagesIP-SM-GW Transport - How SMS is Sent over IP in VoLTE Networksabhijit010379No ratings yet
- 10 ErrorDocument51 pages10 Errorベラ ジェークNo ratings yet
- 01-Chapter 1 H.248Document22 pages01-Chapter 1 H.248aranibarm67% (3)
- Anritsu PDFDocument35 pagesAnritsu PDFPriya SNo ratings yet
- Packet Switched-Core: Provided By: Soroush GhamariDocument23 pagesPacket Switched-Core: Provided By: Soroush GhamariElham AnarakiNo ratings yet
- IMS General BC en Theoretical Basic Inetface and Protocol Introduction of SIP Protocol 1 PPT 201010 44Document44 pagesIMS General BC en Theoretical Basic Inetface and Protocol Introduction of SIP Protocol 1 PPT 201010 44BSSNo ratings yet
- Sprient AttrenoDocument9 pagesSprient AttrenoYogesh DurairajaNo ratings yet
- Advantages of TETRADocument11 pagesAdvantages of TETRAtetraprimigNo ratings yet
- Evolved EPC For LTE by Cisco 1Document70 pagesEvolved EPC For LTE by Cisco 1Virender SinghNo ratings yet
- Comparison LTE WiMax CiscoDocument7 pagesComparison LTE WiMax Ciscozbalouch15No ratings yet
- CMTS ArchitectureDocument10 pagesCMTS ArchitectureAshish KNo ratings yet
- Diameter Interfaces SupportDocument5 pagesDiameter Interfaces Supportariful_islam_20067643100% (1)
- PGW Troubleshooting 01Document530 pagesPGW Troubleshooting 01sl4dyNo ratings yet
- IoT Networking Part 2Document24 pagesIoT Networking Part 2Dr. Hitesh MohapatraNo ratings yet
- 4g The End of Intelligent NetworkDocument12 pages4g The End of Intelligent Networkarteepu4No ratings yet
- TK150 Rel 45 - SG - v1.0.Document136 pagesTK150 Rel 45 - SG - v1.0.Fred_SPbNo ratings yet
- Ota000004 SDH Principle Issue 2.30Document48 pagesOta000004 SDH Principle Issue 2.30Allan MwennyNo ratings yet
- 01 GSM IntroductionDocument42 pages01 GSM IntroductionBrian ScarellaNo ratings yet
- 4G Asr5000Document42 pages4G Asr5000Sri VagiralaNo ratings yet
- All The Information Involved in The File Belongs To ZTE. Any Kind of Releasing Without Permission Is ProhibitedDocument51 pagesAll The Information Involved in The File Belongs To ZTE. Any Kind of Releasing Without Permission Is ProhibitedMaroof RazaNo ratings yet
- 3800x3600x GuideDocument119 pages3800x3600x GuidescorcdNo ratings yet
- ECI Apollo - 9603 - DatasheetDocument2 pagesECI Apollo - 9603 - DatasheetashishNo ratings yet
- NTT Docomo Vol20 e en TotalDocument68 pagesNTT Docomo Vol20 e en TotalscribdenerNo ratings yet
- 5G Voice Aspects 27jan2020Document46 pages5G Voice Aspects 27jan2020flatelecom938No ratings yet
- PAPER - Performance Analysis of Uplink Cellular IoT Using Different Deployments of Data Aggregators PDFDocument6 pagesPAPER - Performance Analysis of Uplink Cellular IoT Using Different Deployments of Data Aggregators PDFflatelecom938No ratings yet
- White Paper Du-Huawei For 5G Core Network Evolution v12Document34 pagesWhite Paper Du-Huawei For 5G Core Network Evolution v12flatelecom938100% (1)
- VoipDocument1 pageVoipAdeel ShamsiNo ratings yet
- NTT Docomo Vol20 e en TotalDocument68 pagesNTT Docomo Vol20 e en TotalscribdenerNo ratings yet
- PAPER - LTE IoT Link Budget and Coverage PDFDocument6 pagesPAPER - LTE IoT Link Budget and Coverage PDFflatelecom938No ratings yet
- Ultima Mentor - Engineers Daily Operation - Automatic Analysis and Optimization PDFDocument34 pagesUltima Mentor - Engineers Daily Operation - Automatic Analysis and Optimization PDFquykiem02100% (1)
- TEMS Investigation (GSM) Ver 001Document0 pagesTEMS Investigation (GSM) Ver 001saeedtarkianNo ratings yet
- Re RadiatorsDocument9 pagesRe Radiatorsflatelecom938No ratings yet
- Adjusting Repeater Path GainDocument3 pagesAdjusting Repeater Path Gainbeni.nass8593No ratings yet
- Aws Band PlanDocument2 pagesAws Band Planmau_mmx5738No ratings yet
- Interference Avoidance With Dynamic Inter-CellDocument6 pagesInterference Avoidance With Dynamic Inter-Cellflatelecom938No ratings yet
- Ts 136300v080900pDocument163 pagesTs 136300v080900pSatender VermaNo ratings yet
- LTE Link Budget (Ejemplo)Document37 pagesLTE Link Budget (Ejemplo)fernetzeroNo ratings yet
- 2009 3GA LTE SON White Paper 12-15-09 FinalDocument26 pages2009 3GA LTE SON White Paper 12-15-09 FinalKalpesh JesalpuraNo ratings yet
- Huawei 5G A Technology Vision 2013Document16 pagesHuawei 5G A Technology Vision 2013giorginoNo ratings yet
- Exporting Logfiles in TEMSDocument18 pagesExporting Logfiles in TEMSflatelecom938No ratings yet
- TelecomHall Hunter DefinitionDocument11 pagesTelecomHall Hunter Definitionflatelecom938No ratings yet
- BSC6900+GSM+Hardware+Description (V900R012C01 03)Document267 pagesBSC6900+GSM+Hardware+Description (V900R012C01 03)Robert Canteli JudolieevNo ratings yet
- Drive Test Parameters: GSM & CdmaDocument15 pagesDrive Test Parameters: GSM & Cdmamoon_4747508No ratings yet
- GSA UMTS900 Information Paper 130214Document8 pagesGSA UMTS900 Information Paper 130214flatelecom938No ratings yet
- Spectrum Used in Commercially Launched LTE Networks 170214Document1 pageSpectrum Used in Commercially Launched LTE Networks 170214flatelecom938No ratings yet
- GSA LTE World Map 100 Countries Launched 050214Document1 pageGSA LTE World Map 100 Countries Launched 050214flatelecom938No ratings yet
- Dino Flore 3GPP RAN Release 12 and Beyond November 2013Document21 pagesDino Flore 3GPP RAN Release 12 and Beyond November 2013Enio LaguardiaNo ratings yet
- F Plan ThesisDocument79 pagesF Plan Thesisflatelecom938No ratings yet
- Adjusting Repeater Path GainDocument3 pagesAdjusting Repeater Path Gainbeni.nass8593No ratings yet
- CDMA GSM Co-Existence GuidelinesDocument13 pagesCDMA GSM Co-Existence Guidelinesflatelecom938No ratings yet
- UG Syllabus (B.a.) (3rd and 4th Sem)Document197 pagesUG Syllabus (B.a.) (3rd and 4th Sem)Tina BhutaniNo ratings yet
- AN-TDMOIP-2E12D V3 Sep2006 PDFDocument27 pagesAN-TDMOIP-2E12D V3 Sep2006 PDFwakyzaiNo ratings yet
- (User Manual) USR DR302 User ManualDocument70 pages(User Manual) USR DR302 User ManualٍJordan SportNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document4 pagesLab 1Suranga LakmalNo ratings yet
- CS6551 CN NotesDocument216 pagesCS6551 CN NotesPapithaNo ratings yet
- Forensic Method Analysis Involving VoIP CrimeDocument3 pagesForensic Method Analysis Involving VoIP CrimeAi AdhiNo ratings yet
- Fortigate CommandDocument17 pagesFortigate Commandmanoj22490100% (1)
- UT Dallas Syllabus For cs4390.001.07s Taught by Jorge Cobb (Jcobb)Document5 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For cs4390.001.07s Taught by Jorge Cobb (Jcobb)UT Dallas Provost's Technology Group100% (1)
- Communications and Networking - John CowleyDocument264 pagesCommunications and Networking - John CowleyEdson GimenezNo ratings yet
- 548 16sccca8-16scccs6-16sccit6 2020051603545429Document16 pages548 16sccca8-16scccs6-16sccit6 2020051603545429kolle arunkumarNo ratings yet
- CCN IntroductionDocument102 pagesCCN Introductionprakashkumar_mb4073No ratings yet
- Networking: Why Do We Need Computer Network?Document28 pagesNetworking: Why Do We Need Computer Network?Yogita UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- TCP/IP Troubleshooting ToolsDocument10 pagesTCP/IP Troubleshooting ToolsLoredel Doria LueteNo ratings yet
- SBC Essentials & Configuration Student Lab GuideDocument82 pagesSBC Essentials & Configuration Student Lab Guidejohan kotenNo ratings yet
- PCD3 ManualDocument145 pagesPCD3 ManualFloNo ratings yet
- Cisco Evpn VxlanDocument57 pagesCisco Evpn Vxlandafa13No ratings yet
- TCP IP Over ATMDocument12 pagesTCP IP Over ATMmichael_mccabe_18No ratings yet
- (Hand Out) DFN40143 NETWORK SECURITY CHAPTER 1 NETWORK PROTOCOLS AND SERVICESDocument39 pages(Hand Out) DFN40143 NETWORK SECURITY CHAPTER 1 NETWORK PROTOCOLS AND SERVICESNorsyaliza Abd RazakNo ratings yet
- VLSM Practice Exercises Page 1 of 3Document3 pagesVLSM Practice Exercises Page 1 of 3catalin ionNo ratings yet
- Ping and TracerouteDocument10 pagesPing and TraceroutejayNo ratings yet
- Subnet ChartDocument1 pageSubnet ChartKosta StojakovicNo ratings yet
- CN Full Manual r2021Document44 pagesCN Full Manual r2021chandrakanth.bNo ratings yet
- Merging Ravenna Network GuideDocument34 pagesMerging Ravenna Network GuideDavid JacquesNo ratings yet
- Triumph-LS How To Connect With 3GDocument23 pagesTriumph-LS How To Connect With 3GAlexanDre SaLesNo ratings yet
- C++ Network Programming: Systematic Reuse With ACE & FrameworksDocument383 pagesC++ Network Programming: Systematic Reuse With ACE & FrameworksalogargNo ratings yet
- Ccna Class. 1 & 2Document135 pagesCcna Class. 1 & 2ntimamaoNo ratings yet
- Load Balancer For Red Hat Enterprise LinuxDocument50 pagesLoad Balancer For Red Hat Enterprise LinuxDiego Alejandro Rendón ChalarcaNo ratings yet