Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lower Limb Motor Exam
Uploaded by
AmjaSaudCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lower Limb Motor Exam
Uploaded by
AmjaSaudCopyright:
Available Formats
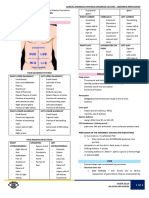
Lower limb motor examination
1-
2-
Introduction:
a.
Wash hands
b.
Introduce yourself
c.
Check patient details name/DOB
d.
Explain the examination
e.
Gain consent
f.
Expose patients legs shorts are most appropriate
g.
Ask if the patient has any pain anywhere before you begin!
General inspection
a.
Observe for clues around the bed wheelchair / walking stick etc
b.
General appearance any limb deformity or posturing?
i. Scars
ii.
Wasting of muscles
iii.
Involuntary movements dystonia, chorea, myoclonus
iv.
Fasciculations: relax the patient leg
v. Tremor parkinsons disease / benign essential tremor
vi.
3-
Posture
Gait:
a.
Ask patient to walk to the end of the room & back assess speed, symmetry &
balance
b.
Tandem (heel-to-toe) gait ask to walk in a straight line heel-to-toe an abnormal
heel-to-toe test may suggest weakness, impaired proprioception or a cerebellar
disorder
c.
Heel walking assesses dorsiflexion power
d.
Toe walking
e.
Rombergs test
i. Ask patient to stand with their feet together and eyes closed
ii.
Observe the patient (ideally for 1 minute)
iii.
Positive test loss of balance (swaying/falling over)
iv.
This suggests a sensory ataxia (defective proprioceptive or vestibular
system)
v. Its important to stand close by the patient during this test to stop them
falling over!
4-
Tone:
a.
Place your hand under a chosen knee abruptly pull it upward to flex it.
b.
Support the thigh and flex and extend the knee to feel if there is resistance
c.
Sit the ptn on the edge of the bed and raise his leg to horizontal plane then suddenly let it go
i. Normally it will oscillate a few
d.
Leg roll roll the patients leg & watch the foot: it should flop independently of the leg
e.
Ankle clonus
i. Position the patients leg so that the knee & ankle are 90 flexed
ii.
Rapidly dorsiflex & partially evert the foot
iii.
Keep the foot in this position
iv.
Clonus is felt as rhythmical beats of dorsiflexion/plantarflexion (>5 is
abnormal)
5-
The power:
a.
Assess one side at a time & compare
b.
Remember to stabilise the joint whilst testing
c.
Hip
i. Flexion (L1/2) raise your leg off the bed & stop me from pushing it down
d.
ii.
Extension (L5/S1) stop me from lifting your leg off the bed
iii.
Abduction (L4/5) move your leg away from the midline
iv.
Adduction (L2/3) stop me from moving your leg away from the midline
Knee
i. Flexion (S1) bend your knee, now stop me from straightening it
ii.
e.
Extension (L3/4) stop me from bending your leg
Ankle
i. Dorsiflexion (L4) point your toes towards your head & dont let me push them down
f.
ii.
Plantarflexion (S1/2) press down on my hand with the sole of your foot
iii.
Inversion (L4) push your foot against my hand
iv.
Eversion (L5/S1) push your foot out against my hand
Big Toe
i. Extension (L5) dont let me push your big toe down
6-
Reflexes
a.
Knee jerk (L3/4)
b.
Ankle jerk (L5/S1)
c.
Plantar response (S1):
i. Run a blunt object along the lateral edge of the sole of the foot, moving towards the little toe
7-
ii.
Observe the great toe
iii.
Normal result = Flexion of the great toe & flexion of the other toes
iv.
Abnormal (Babinski sign) = Extension of the great toe UMN lesion
Coordination:
a.
Heel shin test
b.
Toe finger test
c.
Foot taping test
THANK the patient
You might also like
- Lower Limb Neurological Examination OSCE GuideDocument15 pagesLower Limb Neurological Examination OSCE GuideLeen abusarhanNo ratings yet
- pGALS Examination OSCE GuideDocument18 pagespGALS Examination OSCE GuideFanny PritaningrumNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Foot History AND ExaminationDocument46 pagesDiabetic Foot History AND ExaminationRiaNo ratings yet
- Stem reading - 2 minutesDocument1 pageStem reading - 2 minutesPeter SongNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Diseases Part1Document7 pagesGastrointestinal Diseases Part1sarguss14100% (1)
- Cushings Syndrome: Signs and Symptoms Body System Signs and SymptomsDocument6 pagesCushings Syndrome: Signs and Symptoms Body System Signs and SymptomshappyhappylandNo ratings yet
- Kidney Part 1Document5 pagesKidney Part 1sarguss14No ratings yet
- Plantar Fasciitis - A Self Help GuideDocument8 pagesPlantar Fasciitis - A Self Help GuideAjmera HarshalNo ratings yet
- Tumour Marker For Medincine ResidentsDocument58 pagesTumour Marker For Medincine ResidentsSandeep NarayananNo ratings yet
- MUSCULOSKELETAL Assessment ScripyDocument2 pagesMUSCULOSKELETAL Assessment ScripyKristinelou Marie N. ReynaNo ratings yet
- Small Intestine Lesions Comparison ChartDocument9 pagesSmall Intestine Lesions Comparison ChartfadoNo ratings yet
- Examination of The Peripheral Neurological SystemDocument2 pagesExamination of The Peripheral Neurological Systemkenners100% (12)
- Foot and AnkleDocument22 pagesFoot and AnkleMinikutshupNo ratings yet
- Neurological Examination of The Limbs TextDocument8 pagesNeurological Examination of The Limbs Textvidur_talrejaNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb Neurological Examination OSCE Mark SchemeDocument1 pageLower Limb Neurological Examination OSCE Mark Schemefkunpad.tutorial10100% (1)
- PNS Examination 15Document17 pagesPNS Examination 15NolanNo ratings yet
- HerniaDocument5 pagesHerniasarguss14100% (5)
- Stoma Examination - OSCE GuideDocument3 pagesStoma Examination - OSCE GuideAhmed AlkhaqaniNo ratings yet
- Flashcards - Lower LimbDocument6 pagesFlashcards - Lower LimbKhanNo ratings yet
- Far Eastern University - Nicanor Reyes Medical FoundationDocument4 pagesFar Eastern University - Nicanor Reyes Medical FoundationMikee MeladNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Rigid Pes PlanusDocument36 pagesTreatment of Rigid Pes PlanusUbaid AzherNo ratings yet
- Varicose Veins For LOCASDocument22 pagesVaricose Veins For LOCAS431974100% (1)
- Clinical Approach To Abdominal Disorder: Kurniyanto Department of Internal MedicineDocument68 pagesClinical Approach To Abdominal Disorder: Kurniyanto Department of Internal MedicineMonica AnggiNo ratings yet
- Breast CancerDocument6 pagesBreast Cancersarguss14No ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves OverviewDocument17 pagesCranial Nerves OverviewRiki AntoNo ratings yet
- Muscle List Anatomy & Physiology I C. J. Shuster: Name Origin Insertion Action AntagonistDocument9 pagesMuscle List Anatomy & Physiology I C. J. Shuster: Name Origin Insertion Action AntagonistMohamed Tariq AcchhaNo ratings yet
- Common Orthopedic TestsDocument7 pagesCommon Orthopedic Testschandran2679No ratings yet
- Neuro 1 and 2 LabDocument3 pagesNeuro 1 and 2 LabHardikPatelNo ratings yet
- Hip Joint: Important PointsDocument4 pagesHip Joint: Important PointsNamrah AfzalNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Exam PDFDocument2 pagesPelvic Exam PDFRosu GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Procrastinotes: Rehabilitation Medicione Osce Reviewer 1Document14 pagesProcrastinotes: Rehabilitation Medicione Osce Reviewer 1Edwin Elgar CruzNo ratings yet
- CTEVDocument25 pagesCTEVIceBearNo ratings yet
- Physical Exam SheetDocument6 pagesPhysical Exam SheetDidi SaputraNo ratings yet
- Mnemonics Anatomia 1 PDFDocument11 pagesMnemonics Anatomia 1 PDFRocio SandersNo ratings yet
- Examination of The Central Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesExamination of The Central Nervous Systemkenners100% (13)
- Neck Examination PDFDocument2 pagesNeck Examination PDFNizam Mischievous'Lovely Schremo BoyysNo ratings yet
- Spine ExaminationDocument30 pagesSpine ExaminationNadia SalwaniNo ratings yet
- Shoulder ExaminationDocument4 pagesShoulder ExaminationYS NateNo ratings yet
- Lower Limb & HipDocument9 pagesLower Limb & HipENo ratings yet
- YEAR 1 and 2 OSCE Revision: Author: DR Thomas PayneDocument30 pagesYEAR 1 and 2 OSCE Revision: Author: DR Thomas Payneminayoki100% (1)
- Varicose Vein ExaminationDocument9 pagesVaricose Vein ExaminationYS NateNo ratings yet
- (APJ) Common ENT CasesDocument31 pages(APJ) Common ENT CasesApryl Phyllis JimenezNo ratings yet
- GI System Exam GuideDocument8 pagesGI System Exam GuideJaspreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Arterial DiseaseDocument57 pagesArterial DiseaseYil MosNo ratings yet
- Bone Cancer Chart 2012Document8 pagesBone Cancer Chart 2012BigBoostingNo ratings yet
- OSCE DermaDocument8 pagesOSCE DermaameerabestNo ratings yet
- System Exam SummaryDocument4 pagesSystem Exam Summaryespo176No ratings yet
- Female Reproductive AnatomydDocument7 pagesFemale Reproductive AnatomydOneda Ganbatte' KudasaiNo ratings yet
- Some Important Signs in Mcqs and Oral QuestionsDocument3 pagesSome Important Signs in Mcqs and Oral Questionsخلدون سليمNo ratings yet
- Muscles of the Upper Limb: Anatomy and ActionsDocument7 pagesMuscles of the Upper Limb: Anatomy and ActionsKris GulleyNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Exam Guide: Inspection, Palpation, AuscultationDocument23 pagesCardiac Exam Guide: Inspection, Palpation, AuscultationAreza Eka PermanaNo ratings yet
- Xray AbdominalDocument38 pagesXray Abdominalrizki sanNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nerve InjuriesDocument23 pagesPeripheral Nerve InjuriesUmar AzlanNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Syndrome: Dinesh Kumar PDocument42 pagesNephrotic Syndrome: Dinesh Kumar PRiya Sweetsolitude100% (1)
- Vascular Examination 2Document2 pagesVascular Examination 2Yusnida RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Neuro Osce Cheat Sheet LolsDocument1 pageNeuro Osce Cheat Sheet LolsDjan Kurvie ValencerinaNo ratings yet
- Synovial Chondromatosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandSynovial Chondromatosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- GALS ExaminationDocument3 pagesGALS ExaminationShellyanaCindyNo ratings yet
- GALS Examination OSCE GuideDocument10 pagesGALS Examination OSCE GuideSandarekha PereraNo ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis in Adults - Diagnostic EvaluationDocument15 pagesAcute Appendicitis in Adults - Diagnostic EvaluationAmjaSaudNo ratings yet
- Causes of Abdominal Pain in AdultsDocument41 pagesCauses of Abdominal Pain in AdultsAmjaSaud100% (1)
- Name Date of Birth Place of Birth Nationality Contact: Mobile Number E-Mail LanguagesDocument1 pageName Date of Birth Place of Birth Nationality Contact: Mobile Number E-Mail LanguagesAmjaSaudNo ratings yet
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Interstitial Lung DiseaseDocument5 pagesIdiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Interstitial Lung DiseaseAmjaSaudNo ratings yet
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Interstitial Lung DiseaseDocument5 pagesIdiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Interstitial Lung DiseaseAmjaSaudNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb Motor ExamDocument2 pagesUpper Limb Motor ExamAmjaSaudNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of Asthma-1Document6 pagesPharmacotherapy of Asthma-1AmjaSaudNo ratings yet
- Understanding Acid-Base DisordersDocument47 pagesUnderstanding Acid-Base DisordersAmjaSaudNo ratings yet
- Elective Term Application PDFDocument2 pagesElective Term Application PDFAmjaSaudNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of Asthma-1Document6 pagesPharmacotherapy of Asthma-1AmjaSaudNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary FibrosisDocument29 pagesTreatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary FibrosisAmjaSaudNo ratings yet
- Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Treatment & ManagementDocument5 pagesIdiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Treatment & ManagementAmjaSaudNo ratings yet
- Elective Block Book 2012-2013 (Ksuhs Batch 2's Conflicted Copy) (Ksuhs Batch 2's Conflicted Copy)Document28 pagesElective Block Book 2012-2013 (Ksuhs Batch 2's Conflicted Copy) (Ksuhs Batch 2's Conflicted Copy)AmjaSaudNo ratings yet
- June 2014: Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday SaturdayDocument1 pageJune 2014: Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday SaturdayAmjaSaudNo ratings yet
- Breaking Bad News BBNDocument3 pagesBreaking Bad News BBNAmjaSaudNo ratings yet
- June 2014: Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday SaturdayDocument1 pageJune 2014: Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday SaturdayAmjaSaudNo ratings yet
- MSK Block 2011 2012 Male 2012Document30 pagesMSK Block 2011 2012 Male 2012AmjaSaudNo ratings yet
- June 2014: Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday SaturdayDocument1 pageJune 2014: Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday SaturdayAmjaSaudNo ratings yet
- Snakes in India - Tradition and The Truth PDFDocument5 pagesSnakes in India - Tradition and The Truth PDFhoticeforuNo ratings yet
- Change Your Life NowDocument18 pagesChange Your Life NowAbdul Lateef Khan0% (1)
- PhotosynthesisDocument6 pagesPhotosynthesisFuturephd3000No ratings yet
- Who Needs Bypass SurgeryDocument70 pagesWho Needs Bypass SurgerymikikiNo ratings yet
- RECONSTRUCTION MAndibula 2Document62 pagesRECONSTRUCTION MAndibula 2RadianNasution100% (1)
- Introduction To Dental Anatomy: Learning Objec TivesDocument12 pagesIntroduction To Dental Anatomy: Learning Objec Tivesbalkiz mahamedNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Tests for Bile ComponentsDocument8 pagesQualitative Tests for Bile ComponentsSoh Rodriguez100% (1)
- FCA (SA) - Part - II - Past - Papers 10Document30 pagesFCA (SA) - Part - II - Past - Papers 10matentenNo ratings yet
- NCM107 - Midterm - Newborn CareDocument6 pagesNCM107 - Midterm - Newborn CareLjc JaslinNo ratings yet
- COPD and Lower Respiratory Infection GuideDocument4 pagesCOPD and Lower Respiratory Infection GuideIch RamNo ratings yet
- Functional Hypertrophy: The Secret To Increasing Muscle Without Losing Speed and StrengthDocument2 pagesFunctional Hypertrophy: The Secret To Increasing Muscle Without Losing Speed and Strengthtodd455No ratings yet
- Zoology Practical Exam Tips 2024Document62 pagesZoology Practical Exam Tips 2024sureshsooraj426No ratings yet
- FloTrac SetupDocument2 pagesFloTrac SetupTheMIKI4444No ratings yet
- Alzheimer's Disease and Memory Drugs PDFDocument97 pagesAlzheimer's Disease and Memory Drugs PDFbradbaderNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Testosterone MetabolismDocument8 pagesPeripheral Testosterone MetabolismAgung SentosaNo ratings yet
- CVP Insertion Close Tube Thoracostomy RDocument6 pagesCVP Insertion Close Tube Thoracostomy RFaye Nadine T. CABURALNo ratings yet
- Byssinosis PDFDocument8 pagesByssinosis PDFFaza AlhinduwanNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System For MBBSDocument20 pagesAutonomic Nervous System For MBBSjacobsNo ratings yet
- Journey Through DigestionDocument4 pagesJourney Through DigestionJoy JonesNo ratings yet
- India Ink Staining of Proteins On Nitrocellulose PaperDocument6 pagesIndia Ink Staining of Proteins On Nitrocellulose PaperMaggieNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry For Dental Students Shreya NigoskarDocument185 pagesBiochemistry For Dental Students Shreya Nigoskarleeminhoangrybird100% (2)
- The Human Body in Health and Illness e Book 6th Edition Ebook PDFDocument61 pagesThe Human Body in Health and Illness e Book 6th Edition Ebook PDFcraig.suarez45797% (33)
- Figure 1 Human Nervous System Source:courses - Lumenlearning.c Om/microbiology/chapter/anato My-Of-The-Nervous-SystemDocument14 pagesFigure 1 Human Nervous System Source:courses - Lumenlearning.c Om/microbiology/chapter/anato My-Of-The-Nervous-SystemShekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- The Gut Microbiota-Brain AxisDocument15 pagesThe Gut Microbiota-Brain AxisMateo MendozaNo ratings yet
- Aqa Byb1 W QP Jun07Document12 pagesAqa Byb1 W QP Jun07李超然No ratings yet
- LP UapDocument18 pagesLP UapHat MutisalNo ratings yet
- Structure of BacteriaDocument13 pagesStructure of BacteriaRirin UtariNo ratings yet
- DLL SampleDocument6 pagesDLL SampleJenny Domincel PrudenteNo ratings yet
- Blueprint of LifeDocument42 pagesBlueprint of Lifesophiehee1234No ratings yet
- Ayurveda Physical BodyDocument11 pagesAyurveda Physical BodyanantNo ratings yet