Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemical Compositions of Food
Uploaded by
SueEeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical Compositions of Food
Uploaded by
SueEeCopyright:
Available Formats
Title
Comparison of chemical composition of various food stuf
Introduction
Macromolecules are in all forms of life. These organic compounds
are carbohydrates, lipids and proteins. The presence of these
macromolecules can be tested using diferent reagents.
Carbohydrates are made up carbon,oxygen and hydrogen.They can
be categorized into two groups which are sugar and nonsugars.Sugar consist of monosaccharides and disaccharides while
non-sugar consist of polysaccharides. Monosaccharides are the
simplest form of sugar,disaccharides compose of two
monosaccharides while polysaccharides are compose of long chains
of monosaccharides unit that are bound together by glycosidic
bonds.
Proteins are the building blocks of life. It is made up of long chains
of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. This composition
is tested by using Biurets test.
Lipid are molecules that contain hydrocarbon and is the building
block for structure of living things. It is a non-polar organic
compound which is soluble in organic solvent such as alcohol. It
consists of elements such as carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
The carbohydrate,lipid and protein are tested using their specific
reagent which results in specific colour changes.
Methods
In the experiment for detection of carbohydrate,the materials and
apparatus used are potato,iodine solution,microscope,glass
slide,scalpel, measuring cylinder, sucker, Benedicts
solution,glucose solution,fruit juice,water bath,timer,dilute
hydrochloric acid (HCl) , sodium bicarbonate ( NaHCO3 ), fresh
milk, sodium hydroxide (NaOH), copper sulphate ( CuSO 4 ), coconut
oil, ethanol. The first experiment for starch, a potato was sliced
thinly by using a scalpel.One drop of iodine solution was added to
stain the potato.The stained potato was placed under the
microscope and was observed using two diferent magnification
which are x10 and x40.The stained cells of potato were observed
and recorded in table 1.0
The second experiment of carbohydrate, which is reducing sugar, 1
cm3 of Benedicts solution and 3 cm 3 of glucose solution was
added into a test tube.The test tube was placed into the boiling
water bath which is 90 degrees Celcius for 2 minutes.The test tube
was removed from the water bath and the changes in colour of the
solution were recorded in table 1.1
For the third experiment for carbohydrates, which is non-reducing
sugar, 1 cm 3 of Benedicts solution and 3 cm3 of fruit juice was
added into a test tube. The solution was observed and the colour
changes were recorded in Table 1.2. Then, 3 cm3 of fruit juice and
1 cm 3 of dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl) was added into a another
clean test tube. The solution was boiled in a water bath at 90
degrees Celcius for 3 minutes. The test tube was removed from the
water bath and left to cool at room temperature for 5 minutes. After
cooling, sodium bicarbonate was added into the solution to
neutralize the mixture until the foaming stops. Then, the Benedicts
test was repeated on the mixture. The colour changes were
observed and recorded in Table 1.2.
The next group of test was protein. 2 cm3 of sodium hydroxide
(NaOH) was added into 2 cm 3 of fresh milk in a test tube followed
by four drops of copper(II) sulfate ( CuSO 4 . The mixture was
shaken gently. The colour changes were observed and recorded in
table 1.3.
For the next experiment which is detection of lipid, a measuring
cylinder is used to measure 2 cm3 of ethanol. The ethanol is then
poured into a test tube. A few drops of coconut oil is then added to
the test tube using a sucker. The test tube is shaken gently and the
changes is observed. A few drops of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) is
added into the solution. Then the changes is observed again.
Results
Table 1.0 Iodine test for the presence of starch
Magnification of potato cells
image observed under
microscope
X4
X10
Obeservation
Starch granules are stained blue
black by iodine solution.
Starch granules are stained blue
black by iodine solution.
Table 1.1 Reducing sugar
Solution
1cm3 of Benedicts solution +
3cm3 of glucose solution
Table 1.2 Non-reducing Sugar
Solution
1cm3 of Benedicts solution + 3cm3
fruit juice
1cm3 of dilute hydrochloric acid
(HCl) +3cm3 of fruit juice + sodium
bicarbonate (NaHCO3)
Observation
Solution changes in colour from
blue to brick red precipitate
Observation
Solution changes in colour from
orange to green
Solution changes in colour from
orange to green, then to orange yellow
Table1.3 Biuret test for the presence of protein
Solution
Observation
2 cm 3 of fresh milk+2 cm 3 of
NaOH
2 cm 3 of fresh milk+2 cm 3 of
NaOH+ CuSo 4
No changes
Solution changes in colour to violet.
Table1.4 Emulsion test for the presence of lipid
Solution
Observation
Coconut Oil + 3cm3 Ethanol
Cloudy with emulsion
Coconut Oil + 3cm3 Ethanol + NaOH
Cloudy
Discussion
In the carbohydrate experiment for the starch,the colour of iodine
changes from brown to blue black when in contact with the potatos
cells.Starch has 2 components which are amylose and
amylopectin.The amylose component of starch has helical
structure.The iodine is trap inside the helix and this complex gives
intense blue colour.
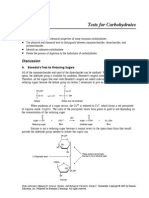
Reducing sugars carry out a type of chemical reaction called as
reduction.The Benedicts test is used to test the reducing sugars
and in the process the reducing sugars are oxidized.When the
glucose is heated with Benedicts solution the glucose decomposes
2+
+
to form products that reduce Cupric (
) ions to Cuprous (
Cu
Cu
)ions. The solution changed to brick red precipitate upon heating in
the water bath with the temperature of 90 degrees Celcius for 2
minutes.
In the experiment to determine the presence of non-reducing sugar,
Fehlings test was carried out. 1 cm 3 Benedicts solution was added
into the 1 cm3 of fruit juice to test the presence of non-reducing
sugars. When the solution turned from orange to green, the
negative result shows that a trace of non-reducing sugars is present.
In a separate test tube, 1 cm3 of dilute hydrochloric acid and
3 cm3 of fruit juice were added together and placed in a water bath
of 90 degrees Celcius to hydrolyse the glycosidic bond. Sodium
bicarbonate was added into the mixture until it stops fizzing, as to
neutralize the solution. The solution turned from orange to yellow
and it proved that sucrose is present in the solution.
The presence of protein is detected by using Biurets test. When 2
cm3 of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) was added to 2 cm 3 of fresh
milk, there is no change in colour. The mixture started to change to
violet colour when four drops of copper(II)sulphate solution were
added.This is explained when cupric ion in alkaline medium forms a
violet coloured complex with peptide bond of protein.The test is
answered by compound having two or more peptide bonds.
Emulsion test is to determine the presence of lipid. Lipids do not
dissolve in water but it dissolves in ethanol. This characteristic is
used in Emulsion test. A few drops of coconut oil is added into a test
tube containing 2 cm3 of ethanol and is gently shaken. The
reaction between lipid and ethanol causes the solution to turn
cloudy. When a few drops of sodium hydroxide is added into the
mixture, the solution forms an emulsion. This is known as
emulsification. A small globule is formed in the solution which
makes it appear cloudy.
Conclusion
The experiment showed the presence of specific chemical
composition in food when tested with the specific reagent. Starch in
the potato reacted to iodine which proved the presence of starch.
The glucose solution showed colour changes to brick red precipitate
when added with Benedicts solution. In the third experiment, the
neutralize fruit juice changed to tangy orange colour when reacted
with Benedicts solution which showed the presence of non-reducing
sugar. Biurets test proved the presence of protein in the fresh milk.
The Suldans test showed emulsion in coconut oil.
You might also like
- Carbohydrates Lab ReportDocument7 pagesCarbohydrates Lab ReportRameesh IshakNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document13 pagesExperiment 3Iqmal Hafidz100% (1)
- Characterizing Biological MacromoleculesDocument5 pagesCharacterizing Biological MacromoleculesAngelo Phillip BautistaNo ratings yet
- Biochem Expt 3 - FLDocument5 pagesBiochem Expt 3 - FLSEAN JODI M. COSEPENo ratings yet
- CARBOHYDRATES Qualitative TestsDocument3 pagesCARBOHYDRATES Qualitative TestsEdith BelenNo ratings yet
- Benedict's Test For Reducing Sugars: CarbohydratesDocument9 pagesBenedict's Test For Reducing Sugars: CarbohydratesRica NorcioNo ratings yet
- Practical 2: Food TestDocument13 pagesPractical 2: Food TestNur Amirah HamzahNo ratings yet
- Tests For CarbohydratesDocument9 pagesTests For CarbohydratesPanasheMuduzu100% (1)
- Experiment 7 Title: Tests For Carbohydrates AimsDocument7 pagesExperiment 7 Title: Tests For Carbohydrates Aimsrenee_soong127No ratings yet
- Detecting Reducing and Non-Reducing SugarsDocument6 pagesDetecting Reducing and Non-Reducing SugarsShayden LeslieNo ratings yet
- Labexercise 10Document11 pagesLabexercise 10Ma Catherine MalanogNo ratings yet
- ProteinDocument5 pagesProteinKirsten CruzadoNo ratings yet
- The Molisch TestDocument12 pagesThe Molisch Testkamaksi100% (1)
- Isolation and Characterization of CarbohydratesDocument4 pagesIsolation and Characterization of CarbohydratesJearweine FormaranNo ratings yet
- Carbs Formal ReportDocument5 pagesCarbs Formal ReportCorina Faye Rosario0% (1)
- BCM Exp 6Document4 pagesBCM Exp 6Fadzal RidzqanNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument29 pagesCarbohydratesFrancis Emmanuel PILAPILNo ratings yet
- Practical 2Document10 pagesPractical 2Wei YiNo ratings yet
- Tinashe Katsuro 210304 Biochemistry ReportDocument4 pagesTinashe Katsuro 210304 Biochemistry ReportTinashe KatsuroNo ratings yet
- 1616 - Biochemical Tests of Carbohydrate, Protein, Lipids and Salivary AmylaseDocument6 pages1616 - Biochemical Tests of Carbohydrate, Protein, Lipids and Salivary AmylaseRishav GopeNo ratings yet
- Biologically Important Molecules: Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids and Nucleic AcidsDocument9 pagesBiologically Important Molecules: Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids and Nucleic AcidsJim Goetz100% (2)
- Carbohydrate Identification TestsDocument6 pagesCarbohydrate Identification TestsHans Louie TabasonNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument2 pagesReportДамир КаримовNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Saliva and HCl on CarbohydratesDocument3 pagesInvestigation of Saliva and HCl on CarbohydratesallenNo ratings yet
- TOPIC: Biological Molecules AIM: Identification of Biochemicals in Pure FormDocument46 pagesTOPIC: Biological Molecules AIM: Identification of Biochemicals in Pure FormManmohan SinghNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis of Carbohydrates Using Common Chemical TestsDocument20 pagesQualitative Analysis of Carbohydrates Using Common Chemical TestsOtencianoNo ratings yet
- Cuso4: Benedict'S Test Is Used To Test For Simple Carbohydrates. The Benedict'S Test Identifies Reducing SugarsDocument10 pagesCuso4: Benedict'S Test Is Used To Test For Simple Carbohydrates. The Benedict'S Test Identifies Reducing SugarsPooja ParmarNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Characterization of CarbohydratesDocument7 pagesIsolation and Characterization of CarbohydratesKyle Dillan LansangNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Analysis and Identify The Given Sample of CarbohydrateDocument3 pagesQualitative Analysis and Identify The Given Sample of CarbohydrateDeepak PradhanNo ratings yet
- Testing For Biological MoleculesDocument3 pagesTesting For Biological MoleculessariniNo ratings yet
- EXP2 BIOCHEM Analyzing and Determine Sugars and Starch in Plant Tissues.Document10 pagesEXP2 BIOCHEM Analyzing and Determine Sugars and Starch in Plant Tissues.NUR AMALIA BINTI MAZLEE STUDENTNo ratings yet
- Biology Lab Report (Test For Organic Compunds)Document11 pagesBiology Lab Report (Test For Organic Compunds)Fakhrul Aiman79% (24)
- Carbohydrate Analysis - Qualitative Analysis - ENGLISH VERSIONDocument40 pagesCarbohydrate Analysis - Qualitative Analysis - ENGLISH VERSIONAnggii DestianiiNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Test Determines Glucose ConcentrationDocument2 pagesBiochemical Test Determines Glucose Concentrationshanique thomasNo ratings yet
- Lab 8Document9 pagesLab 8Norjetalexis CabreraNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4: Qualitative Analysis of Simple Carbohydrates Using Benedict's TestDocument2 pagesExperiment 4: Qualitative Analysis of Simple Carbohydrates Using Benedict's TestSaif Khan100% (1)
- Test For CARBOHYDRATESDocument7 pagesTest For CARBOHYDRATESSoham N100% (2)
- BenedictDocument5 pagesBenedictMark Justin LealNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Food TestDocument5 pagesLab 1 Food TestMichael Timson83% (6)
- Zoo 514 P (Principles of Animal Life I) 24-08-23Document40 pagesZoo 514 P (Principles of Animal Life I) 24-08-23Sagheer AhmedNo ratings yet
- The Molisch TestDocument9 pagesThe Molisch TestrawatanandNo ratings yet
- Lab # 2Document7 pagesLab # 2Santos CocNo ratings yet
- Isolation From Chicken Liver and Enzymatic Hydrolysis of GlycogenDocument2 pagesIsolation From Chicken Liver and Enzymatic Hydrolysis of GlycogenKevin Magadia78% (9)
- Barfoed's and Fehling's Tests Distinguish Mono- from DisaccharidesDocument14 pagesBarfoed's and Fehling's Tests Distinguish Mono- from DisaccharidesHans Louie TabasonNo ratings yet
- QUALITATIVE Laboratory ANALYSIS OF Activity 13 SugarsDocument19 pagesQUALITATIVE Laboratory ANALYSIS OF Activity 13 SugarsCelestine MarivelezNo ratings yet
- Bio Lab Report 2Document7 pagesBio Lab Report 2nur ruqayyah74% (19)
- Group 6 - Activity 5 - Properties of CarbohydratesDocument6 pagesGroup 6 - Activity 5 - Properties of CarbohydratesJair Ezer AbaoNo ratings yet
- Biotech FR Exp 2Document14 pagesBiotech FR Exp 2Nico YowNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Manual PDFDocument99 pagesBiochemistry Manual PDFSri KanthNo ratings yet
- Lab Report (Amylase)Document3 pagesLab Report (Amylase)Chew Kian ShengNo ratings yet
- Virtual LAB Output On Qualitative Analysis of CarbohydrateDocument7 pagesVirtual LAB Output On Qualitative Analysis of CarbohydrateEden Ruth Asoy-GoreroNo ratings yet
- Bio Lab Report - Exp 6Document6 pagesBio Lab Report - Exp 6Jim Goetz100% (10)
- Carbohydrates Formal Lab ReportDocument3 pagesCarbohydrates Formal Lab Reportspica25No ratings yet
- Activity 4 Carbohydrates: Specific Reactions I. CarbohydratesDocument7 pagesActivity 4 Carbohydrates: Specific Reactions I. CarbohydratesAlih KathlyannNo ratings yet
- Molisch Test and Benedict TestDocument6 pagesMolisch Test and Benedict Testعلاوي البرشلونيNo ratings yet
- Isolation of Gluten Formal ReportDocument3 pagesIsolation of Gluten Formal ReportReg LagartejaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Plant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterFrom EverandPlant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterNo ratings yet
- Chemistry at Home - A Collection of Experiments and Formulas for the Chemistry EnthusiastFrom EverandChemistry at Home - A Collection of Experiments and Formulas for the Chemistry EnthusiastNo ratings yet
- Simple Past Tense The Elves and The Shoemaker Short-Story-Learnenglishteam - ComDocument1 pageSimple Past Tense The Elves and The Shoemaker Short-Story-Learnenglishteam - ComgokagokaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11, 12 Curve Tracing and EnvelopeDocument37 pagesChapter 11, 12 Curve Tracing and EnvelopeNitish PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Distance Learning 2016 Telecom AcademyDocument17 pagesDistance Learning 2016 Telecom AcademyDyego FelixNo ratings yet
- DirtyMobs' Ultimate Matchup GuideDocument5 pagesDirtyMobs' Ultimate Matchup GuideTempest JannaNo ratings yet
- Merry Almost Christmas - A Year With Frog and Toad (Harmonies)Document6 pagesMerry Almost Christmas - A Year With Frog and Toad (Harmonies)gmit92No ratings yet
- Numl Lahore Campus Break Up of Fee (From 1St To 8Th Semester) Spring-Fall 2016Document1 pageNuml Lahore Campus Break Up of Fee (From 1St To 8Th Semester) Spring-Fall 2016sajeeNo ratings yet
- EY The Cfo Perspective at A Glance Profit or LoseDocument2 pagesEY The Cfo Perspective at A Glance Profit or LoseAayushi AroraNo ratings yet
- The Sims FreeplayDocument14 pagesThe Sims FreeplayFlorianNo ratings yet
- VDA ChinaDocument72 pagesVDA Chinatuananh1010No ratings yet
- A Case of DrowningDocument16 pagesA Case of DrowningDr. Asheesh B. PatelNo ratings yet
- People v. Cresencia ReyesDocument7 pagesPeople v. Cresencia ReyesAnggling DecolongonNo ratings yet
- Epithelial and connective tissue types in the human bodyDocument4 pagesEpithelial and connective tissue types in the human bodyrenee belle isturisNo ratings yet
- Ash ContentDocument2 pagesAsh Contentvikasbnsl1No ratings yet
- Philhis Handouts Week 1Document5 pagesPhilhis Handouts Week 1Jeen JeenNo ratings yet
- 59-33 ATO Implementation Journal KSA 100Document18 pages59-33 ATO Implementation Journal KSA 100nicolas valentinNo ratings yet
- Corporation Law Quiz AnswersDocument3 pagesCorporation Law Quiz AnswerswivadaNo ratings yet
- Christian Appraisal of Feminist Ideologies Among Nigerian Women 2020Document78 pagesChristian Appraisal of Feminist Ideologies Among Nigerian Women 2020Nwaozuru JOHNMAJOR ChinecheremNo ratings yet
- Theo 5Document2 pagesTheo 5chingchongNo ratings yet
- 2018 World Traumatic Dental Injury Prevalence and IncidenceDocument16 pages2018 World Traumatic Dental Injury Prevalence and IncidencebaridinoNo ratings yet
- Prophetic Prayer Declarations - September, 2021Document5 pagesProphetic Prayer Declarations - September, 2021Jelo RichNo ratings yet
- 14-15 TDP HandbookDocument28 pages14-15 TDP Handbookapi-266268398No ratings yet
- Neoclassicism: Romanticism Realism ImpressionismDocument16 pagesNeoclassicism: Romanticism Realism ImpressionismErika EludoNo ratings yet
- Dreams and Destiny Adventure HookDocument5 pagesDreams and Destiny Adventure HookgravediggeresNo ratings yet
- Source: Sonia S. Daquila. The Seeds of RevolutionDocument6 pagesSource: Sonia S. Daquila. The Seeds of RevolutionJulliena BakersNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report - 1st and 2nd SemDocument41 pagesAccomplishment Report - 1st and 2nd Semshailean azulNo ratings yet
- 2200SRM0724 (04 2005) Us en PDFDocument98 pages2200SRM0724 (04 2005) Us en PDFMayerson AlmaoNo ratings yet
- Performance AppraisalsDocument73 pagesPerformance AppraisalsSaif HassanNo ratings yet
- German composer known for political worksDocument4 pagesGerman composer known for political worksGeorge PikNo ratings yet
- The BrigadeDocument517 pagesThe Brigadele_chiffre4860100% (3)
- Liquid Hydrogen As A Propulsion Fuel, 1945-1959Document341 pagesLiquid Hydrogen As A Propulsion Fuel, 1945-1959Bob AndrepontNo ratings yet