Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physics Reviewer
Uploaded by
khoire120 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views3 pagesPhysics, reviewer and self-help guides, velocity, force, principles and manuals.
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPhysics, reviewer and self-help guides, velocity, force, principles and manuals.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views3 pagesPhysics Reviewer
Uploaded by
khoire12Physics, reviewer and self-help guides, velocity, force, principles and manuals.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Physics Reviewer
Law of Universal Gravitation- every object in the universe attracts
every other object with a force directed along the line of the centers
for the two objects that is proportional to the product of their masses
and inversely proportional to the square of the separation between the
two objects. Fg=G x m1m2/r2
ROTATIONAL MOTION
Angular displacement (radians)- Direction is clockwise or
counterclockwise
Rotational speed or angular speed, ( radians per sec)number of rotations of revolutions per unit of time; direction is
clockwise or counter
Tangential speed(m/s)- total distance travelled per unit of time
Angular acceleration(radians/sec squared)- angular velocity
per unit of time
Center/ axis of rotation- 2D object rotates around a center of
rotation; 3D object rotates around a line( axis of rotation)
Moment of inertia, I (kg x m2)- Measure of an objects
resistance to a circular motion; dependent on where the axis of
rotation located
Torque- tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis;
roughly, =rFsin
Angular Momentum- measure of the motion of mass about a
center of rotation; Rotational inertia x angular velocity
WAVE
Wiggle in both space and time; extends from one place to
another (e.g., sound and light waves) Sound waves
cant propagate without a medium, light can
Period- time for one complete vibration( second)
Wavelength- distance b/w any successive identical parts
of a wave(meter)
Frequency- describes how frequent a vibration occurs (it
is the reciprocal of the period; hertz, Hz)
Radio waves (103.1FM=103.1MHz) - electrons in the
antenna of the transmission tower are forced to vibrate
at 103, 100, 000imes per second. This is also the
frequency of the frequency of the wave produced.
Wave speed- speed of periodic motion is related to the
frequency and wavelength of the vibrating object;
WS=WL x F
Transverse- medium moves in a direction perpendicular to
the direction of the wave, the medium is vibrating.
Longitudinal- medium moves in the same direction as the
wave.
INTERFERENCE
Constructive Interference- two or more waves
interfere to produce a wave with increased
amplitude
Destructive Interference- two or more waves
interfere to produce a wave with decreased
amplitude.
Refraction of Sound- sound waves bend when parts of
the wave front travel at different speeds
Speed of Sound- in air 330m/s at 00C; depends on
the wind conditions, temperature and humidity
Resonance- objects vibrate at a certain natural
frequency
Doppler Effect- Change in frequency due to the
motion of the source
PROJECTILE
Is any object which is influenced only by gravity
Projectile Motion- motion of a projectile;
Trajectory- PARABOLIC; both horizontal and vertical
components
Satellite Motion- projectile that falls around earth rather
than into it; speed must be at least 8km/sec.
Fluids- gases and liquids flow
PROPERTIES: ability to flow, ability to not resist
deformation, ability to resist flow
Viscosity- measure of resistance to flow
Buoyancy- upward force that a body exerts on an
immersed object; when an object is submerged, it
displaces water that has a volume equal to the object.
Turbulence- fluid regime characterized by chaotic and
stochastic (random) changes.
Laminar- flow that is not turbulent
Bernoullis Principle- speed of a fluid increases, the
internal pressure in the fluid drops.
PRESSURE
Pressure is due to random molecular collisions against
surfaces
Systolic Pressure- higher number, normal reading is
120mm of mercury (mmHg) or less
Diastolic Pressure- lower number, normal reading is 80
mmHg or less
Surface Tension- contractive tendency of the surface of
liquids
Pascals Principle- Pressure applied to an enclosed liquid
is transmitted undiminished to every point in the fluid
and to the walls of the container.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Pacific OceanDocument15 pagesPacific Oceankhoire12No ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- DepEd Learning PortalDocument2 pagesDepEd Learning Portalkhoire12100% (1)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Marcos Vs Sandiganbayan October 6, 1998Document9 pagesMarcos Vs Sandiganbayan October 6, 1998khoire12No ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Envi Laws - CompilationDocument416 pagesEnvi Laws - CompilationSherwin De VeraNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Negotiable Instrument Reviewer: InterestsDocument7 pagesNegotiable Instrument Reviewer: Interestskhoire12No ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Association of Small Landownders Vs Sec of DENRDocument3 pagesAssociation of Small Landownders Vs Sec of DENRkhoire12100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- People Power RevolutionDocument13 pagesPeople Power Revolutionkhoire12No ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Negotiable Instrument - SummaryDocument7 pagesNegotiable Instrument - Summarykhoire12No ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Negotiable Instrument Reviewer: InterestsDocument7 pagesNegotiable Instrument Reviewer: Interestskhoire12No ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- Bo HolstDocument3 pagesBo Holstkhoire12No ratings yet
- MMDA Vs Concerned Citizens of Manila BayDocument28 pagesMMDA Vs Concerned Citizens of Manila Baykhoire12No ratings yet
- Laws and Found Blog - Laurel V Desierto DigestDocument4 pagesLaws and Found Blog - Laurel V Desierto Digestkhoire12No ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Roxas and Co., Inc Vs Court of AppealsDocument22 pagesRoxas and Co., Inc Vs Court of Appealskhoire12No ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Talavera V CADocument3 pagesTalavera V CAkhoire12No ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Luz Vs Sec of DenrDocument16 pagesLuz Vs Sec of Denrkhoire12No ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- LaborDocument72 pagesLaborCherry DuldulaoNo ratings yet
- Food Porn by Anne McbrideDocument9 pagesFood Porn by Anne Mcbridekhoire120% (1)
- Labor Law 1 New CurriculumDocument352 pagesLabor Law 1 New Curriculumkhoire12No ratings yet
- Case Digests On MurderDocument3 pagesCase Digests On Murderkhoire12No ratings yet
- Explosive Weapons and Grave Violations Against ChildrenDocument26 pagesExplosive Weapons and Grave Violations Against Childrenkhoire12No ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Philosophy and LogicDocument3 pagesPhilosophy and Logickhoire12No ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Rerum Novarum (May 15, 1891) - LEO XIIIDocument29 pagesRerum Novarum (May 15, 1891) - LEO XIIIkhoire12No ratings yet
- Weigel Vs Sempio-DiyDocument1 pageWeigel Vs Sempio-Diykhoire12No ratings yet
- Laborem Exercens by John Paul IIDocument43 pagesLaborem Exercens by John Paul IIkhoire12No ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Nature of LogicDocument4 pagesThe Nature of Logickhoire12No ratings yet
- Digest 9 - 11Document9 pagesDigest 9 - 11khoire12No ratings yet
- Right To Information and Power of Imminent Domain DigestsDocument63 pagesRight To Information and Power of Imminent Domain Digestskhoire12No ratings yet
- Macariola Vs Asuncion Case DigestDocument2 pagesMacariola Vs Asuncion Case Digestkhoire1275% (4)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Marcos Vs Sandiganbayan October 6, 1998Document9 pagesMarcos Vs Sandiganbayan October 6, 1998khoire12No ratings yet
- Executive Order 272Document1 pageExecutive Order 272khoire12No ratings yet
- Motion of Particles Through Fluids 221Document27 pagesMotion of Particles Through Fluids 221SAYEENo ratings yet
- CHP 5 SolutiomsDocument2 pagesCHP 5 SolutiomsSana AshfaqNo ratings yet
- InertiaDocument37 pagesInertiarospazitaNo ratings yet
- Forces Worksheet ExplainedDocument8 pagesForces Worksheet ExplainedAnasua BasuNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws0Document74 pagesNewton's Laws0K.s. BalajiNo ratings yet
- Unit IV Assembly of Parts PDFDocument16 pagesUnit IV Assembly of Parts PDFSudhakarNo ratings yet
- Forces and Equilibrium Word ProblemsDocument4 pagesForces and Equilibrium Word ProblemsOGBAGA ONOME JAMESNo ratings yet
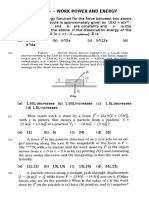
- PHYSICS - WORK, POWER AND ENERGY FORMULASDocument3 pagesPHYSICS - WORK, POWER AND ENERGY FORMULASSandeepKumarNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion - NewtonDocument17 pagesLaws of Motion - NewtonpseudonimNo ratings yet
- GSC101 HandoutsDocument316 pagesGSC101 HandoutsYaman Askary100% (1)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- EUROMAT I-CAL-GUI-018 - Calibration - Guide - No. - 18 - WebDocument156 pagesEUROMAT I-CAL-GUI-018 - Calibration - Guide - No. - 18 - WebSruthi SatheeshNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 05 Torque, Angular Momentum, and EquilibriumDocument10 pagesChapter # 05 Torque, Angular Momentum, and EquilibriumSIR USMAN KHAN100% (4)
- Project 1Document10 pagesProject 1partoNo ratings yet
- AMT 3102 Module 01 Principle of Static CCArbozoDocument14 pagesAMT 3102 Module 01 Principle of Static CCArbozokim shinNo ratings yet
- Syllabus For The National Physics Olympiad of BangladeshDocument2 pagesSyllabus For The National Physics Olympiad of BangladeshStanwood CoxNo ratings yet
- Orbital Mechanics - Gen - SolutionsDocument18 pagesOrbital Mechanics - Gen - SolutionsNouman1203No ratings yet
- Vector Mechanics Engineers Statics 8th BeerDocument8 pagesVector Mechanics Engineers Statics 8th Beercerebro50% (2)
- Complementary Relativity - Beyond The Lorentz Transformations - Eng+ItaDocument39 pagesComplementary Relativity - Beyond The Lorentz Transformations - Eng+ItaLeonardo RubinoNo ratings yet
- Torques and Rotational EquilibriumDocument5 pagesTorques and Rotational EquilibriumHopia QuintelNo ratings yet
- The New Law of Electrical Power FormationDocument37 pagesThe New Law of Electrical Power Formationdragon314159No ratings yet
- General Relativity For Pedestrians - First 5 LecturesDocument11 pagesGeneral Relativity For Pedestrians - First 5 LecturesBir HanuNo ratings yet
- Exam 1Document6 pagesExam 1api-375738241No ratings yet
- UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION - Notes PDFDocument5 pagesUNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION - Notes PDFJohnston ThevarajahNo ratings yet
- MCQ Electromagnetism Self-AssessmentDocument2 pagesMCQ Electromagnetism Self-AssessmentJunaidKhanNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Science Unit 4 EngDocument3 pagesGrade 10 Science Unit 4 Engruvini suraweeraNo ratings yet
- NASA warns of asteroid threatDocument5 pagesNASA warns of asteroid threatIshaan PuriNo ratings yet
- 7 Momentum and ImpulseDocument16 pages7 Momentum and ImpulseJohn Angelo RamosNo ratings yet
- Level Past Paper Questions - Physics O: TOPIC-15 Static Electricity PAPER-1 Multiple Choice 1Document8 pagesLevel Past Paper Questions - Physics O: TOPIC-15 Static Electricity PAPER-1 Multiple Choice 1elty Tan0% (1)
- Class Xi PhysicsDocument160 pagesClass Xi PhysicsAdarsh DhawanNo ratings yet
- Minimum Index Density (Relative Density)Document9 pagesMinimum Index Density (Relative Density)Peter John RoblesNo ratings yet
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsFrom EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (94)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismFrom EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (500)