Professional Documents
Culture Documents
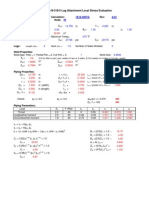
2 PVElite Notes
Uploaded by
ZAKI1983Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2 PVElite Notes
Uploaded by
ZAKI1983Copyright:
Available Formats
ASME B16.
5-2009
(Revision of ASME B16.5-2003)
NPS 1/2 Through NPS 24
Metric/Inch Standard
A N A M E R I C A N N AT I O N A L STA N DA R D
Copyright ASME International
Provided by IHS under license with ASME
No reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS
Licensee=Technip/5931917100, User=Bertoldo, Fabien
Not for Resale, 10/15/2009 01:05:07 MDT
--`,``,`,,,``,,,`,`,,```,``,,`,,-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---
Pipe Flanges and
Flanged Fittings
ASME B16.5-2009
1.9 Denotation
joints not conforming to these limitations is the responsibility of the user.
1.9.1 Pressure Rating Designation. Class, followed
by a dimensionless number, is the designation for pressuretemperature ratings as follows:
Class
150
300
400
600
900
1500
2.3.2 Mixed Flanged Joints. If the two flanges in a
flanged joint do not have the same pressuretemperature
rating, the rating of the joint at any temperature is the
lower of the two flange ratings at that temperature.
2500
1.9.2 Size. NPS, followed by a dimensionless number, is the designation for nominal flange or flange fitting
size. NPS is related to the reference nominal diameter,
DN, used in international standards. The relationship
is, typically, as follows:
NPS
DN
15
20
25
32
40
50
65
80
100
2
4
1
114
112
2
212
3
4
2.4 Rating Temperature
The temperature shown for a corresponding pressure
rating is the temperature of the pressure-containing shell
of the component. In general, this temperature is the
same as that of the contained fluid. Use of a pressure
rating corresponding to a temperature other than that
of the contained fluid is the responsibility of the user,
subject to the requirements of applicable codes and regulations. For any temperature below 29C (20F), the
rating shall be no greater than the rating shown for
29C (20F) (see also paras. 2.5.3 and 5.1.2).
2.5 Temperature Considerations
2.5.1 General. Use of flanged joints at either high
or low temperatures shall take into consideration the
risk of joint leakage due to forces and moments developed in the connected piping or equipment. Provisions
in paras. 2.5.2 and 2.5.3 are included as advisory with
the aim of lessening these risks.
GENERAL NOTE: For NPS 4, the related DN p 25 multiplied
by the NPS number.
PRESSURETEMPERATURE RATINGS
2.5.2 High Temperature. Application at temperatures in the creep range will result in decreasing bolt
loads as relaxation of flanges, bolts, and gaskets takes
place. Flanged joints subjected to thermal gradients may
likewise be subject to decreasing bolt loads. Decreased
bolt loads diminish the capacity of the flanged joint to
sustain loads effectively without leakage. At temperatures above 200C (400F) for Class 150 and above 400C
(750F) for other class designations, flanged joints may
develop leakage problems unless care is taken to avoid
imposing severe external loads, severe thermal gradients, or both.
2.1 General
Pressuretemperature ratings are maximum allowable working gage pressures in bar units at the temperatures in degrees Celsius shown in Tables 2-1.1 through
2-3.17 for the applicable material and class designation.
Tables II-2-1.1 through II-2-3.17 of Mandatory
Appendix II list pressuretemperature ratings using psi
units for pressure at the temperature in degrees Fahrenheit. For intermediate temperatures, linear interpolation
is permitted. Interpolation between class designations
is not permitted.
2.5.3 Low Temperature. Some of the materials listed
in Tables 1A and 1B, notably some carbon steels, may
undergo a decrease in ductility when used at low temperatures to such an extent as to be unable to safely
resist shock loading, sudden changes of stress, or high
stress concentration. Some codes or regulations may
require impact testing for applications even where temperatures are higher than 29C (20F). When such
requirements apply, it is the responsibility of the user
to ensure these requirements are communicated to the
manufacturer prior to the time of purchase.
2.2 Flanged Joints
--`,``,`,,,``,,,`,`,,```,``,,`,,-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---
A flanged joint is composed of separate and independent, although interrelated components: the flanges,
gasket, and bolting, which are assembled by another
influence, the assembler. Proper controls must be exercised in the selection and application for all these elements to attain a joint that has acceptable leak tightness.
Special techniques, such as controlled bolt tightening,
are described in ASME PCC-1.
2.3 Ratings of Flanged Joints
2.6 System Hydrostatic Testing
2.3.1 Basis. Pressuretemperature ratings apply to
flanged joints that conform to the limitations on bolting
in para. 5.3 and on gaskets in para. 5.4, which are made
up in accordance with good practice for alignment and
assembly (see para. 2.2). Use of these ratings for flanged
Flanged joints and flanged fittings may be subjected
to system hydrostatic tests at a pressure of 1.5 times the
38C (100F) rating rounded off to the next higher 1 bar
(25 psi) increment. Testing at any higher pressure is
2
Copyright ASME International
Provided by IHS under license with ASME
No reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS
Licensee=Technip/5931917100, User=Bertoldo, Fabien
Not for Resale, 10/15/2009 01:05:07 MDT
ASME B16.5-2009
the responsibility of the user, taking into account the
requirements of the applicable code or regulation.
be furnished by agreement between the end user and
manufacturer. In no case shall the bore diameter exceed
the bore of the same size and class lapped flange.
2.7 Welding Neck Flanges
2.8.4 Hub End. The standard flange shall be provided with square cut end. The end user may specify
welding end preparation in accordance with para. 6.7.
Ratings for welding neck flanges covered by this Standard are based upon their hubs at the welding end
having thickness at least equal to that calculated for pipe
having 276 MPa (40,000 psi) specified minimum yield
strength.1 In order to ensure adequate flange hub thickness for flange sizes NPS 2 and larger, the bore of a
welding neck flange, dimension B in the various dimensional tables, shall not exceed B max determined as
follows:
Bmax p Ah 1
C op c
50,000
2.9 Multiple Material Grades
Material for flanges and flanged fittings may meet
the requirements of more than one specification or the
requirements of more than one grade of a specification
listed in Table 1A. In either case, the pressuretemperature ratings for any of these specifications or grades may
be used provided the material is marked in accordance
with para. 4.2.8.
where
Ah p tabulated hub diameter, beginning of chamfer as listed in the dimensional tables
Bmax p maximum permissible diameter for the bore
of a welding neck flange
Co p 14.5 when pc is expressed in bar units or 1.0
when pc is expressed in psi units
pc p ceiling pressure value at 38C (100F), Tables
A-1 and A-2 of Nonmandatory Appendix A
COMPONENT SIZE
3.1 Nominal Pipe Size
As applied in this Standard, the use of the phrase
nominal pipe size or the designation NPS followed
by a dimensionless number is for the purpose of pipe,
flange, or flanged fitting end connection size identification. The number is not necessarily the same as the
flange or flanged fitting inside diameter.
The resultant units for diameter Bmax are the same as
those entered for diameter A.
The tabulated ratings for welding neck flanges are
independent of components to which they may be
attached, and the pressure rating of the flange shall
not be exceeded. Attachment welds should be made in
accordance with the applicable code or regulation. See
para. 6.7 and Figs. 12 through 14 for weld end dimensional requirements.
3.2 Reducing Fittings
Reducing fittings shall be designated by the NPS for
the openings in the sequence indicated in the sketches
of Fig. 2.
3.3 Reducing Flanges
2.8 Straight Hub Welding Flanges
Reducing flanges shall be designated by the NPS for
each opening. See examples in Note (4) of Table 6 (Table
II-6 of Mandatory Appendix II).
2.8.1 Hub Dimensions. Straight hub welding
flanges are an extension of welding neck flanges and
have straight hubs of uniform thickness. With the exception of the following, the straight hub welding flanges
shall have dimensions of the welding neck flanges of
the size and class set forth in Tables 8, 11, 14, 16, 18, 20,
and 22 (Tables II-8, II-11, II-14, II-16, II-20, and II-22 of
Mandatory Appendix II) (see Fig. 15).
MARKING
4.1 General
Except as modified herein, flanges and flanged fittings
shall be marked as required in MSS SP-25, except as
noted in para. 4.2.
2.8.2 Length Through Hub. The length through hub
shall be 229 mm (9 in.) for NPS 4 and smaller and 305
mm (12 in.) for larger than NPS 4. Other lengths may
be furnished by agreement between the end user and
manufacturer.
4.2 Identification Markings
2.8.3 Bore. The bore diameter shall be equal to B
dimension of the welding neck flange. Other bores may
4.2.1 Name. The manufacturers name or trademark shall be applied.
1
For flanges to be attached to high strength pipe with large
inside diameters resulting from thin wall sections, see MSS SP-44.
4.2.2 Material. Material shall be identified in the
following way:
3
--`,``,`,,,``,,,`,`,,```,``,,`,,-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---
Copyright ASME International
Provided by IHS under license with ASME
No reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS
Licensee=Technip/5931917100, User=Bertoldo, Fabien
Not for Resale, 10/15/2009 01:05:07 MDT
ASME B16.5-2009
Table 1A List of Material Specifications
Nominal Designation
Pressure
Temperature
Rating Table
Applicable ASTM Specifications [Note (1)]
Forgings
Castings
Plates
1.1
CSi
CMnSi
CMnSi
CMnSiV
312 Ni
2-1.1
2-1.1
2-1.1
2-1.1
2-1.1
A 105
A 350 Gr. LF2
...
A 350 Gr. LF6 CI. 1
A 350 Gr. LF3
A 216 Gr. WCB
...
...
...
...
A 515 Gr. 70
A 516 Gr. 70
A 537 Cl. 1
...
...
1.2
CMnSi
CMnSi
CMnSiV
212Ni
312Ni
2-1.2
2-1.2
2-1.2
2-1.2
2-1.2
...
...
A 350 Gr. LF6 Cl. 2
...
...
A 216 Gr. WCC
A 352 Gr. LCC
...
A 352 Gr. LC2
A 352 Gr. LC3
...
...
...
A 203 Gr. B
A 203 Gr. E
1.3
CSi
CMnSi
212Ni
312Ni
C12Mo
C12Mo
2-1.3
2-1.3
2-1.3
2-1.3
2-1.3
2-1.3
A 352 Gr. LCB
...
...
A
A
A
A
1.4
CSi
CMnSi
2-1.4
2-1.4
...
A 350 Gr. LF1 Cl. 1
...
...
A 515 Gr. 60
A 516 Gr. 60
1.5
C12Mo
C12Mo
2-1.5
2-1.5
A 182 Gr. F1
...
...
...
A 204 Gr. A
A 204 Gr. B
1.7
1
2Cr12Mo
Ni12Cr12Mo
3
4Ni34Cr1Mo
2-1.7
2-1.7
2-1.7
A 182 Gr. F2
...
...
...
A 217 Gr. WC4
A 217 Gr. WC5
...
...
...
1.9
114Cr12Mo
114Cr12MoSi
2-1.9
2-1.9
...
A 182 Gr. F11 CL.2
A 217 Gr. WC6
...
...
A 387 Gr. 11 Cl. 2
1.10
214Cr1Mo
2-1.10
A 182 Gr. F22 Cl. 3
A 217 Gr. WC9
A 387 Gr. 22 Cl. 2
1.11
C 2Mo
1
...
...
...
...
...
...
2-1.11
...
A 217 Gr. WC1
A 352 Gr. LC1
515
516
203
203
Gr. 65
Gr. 65
Gr. A
Gr. D
...
...
...
A 204 Gr. C
1.13
5Cr 2Mo
2-1.13
A 182 Gr. F5a
A 217 Gr. C5
...
1.14
9Cr1M0
2-1.14
A 182 Gr. F9
A 217 Gr. C12
...
1.15
9Cr1M0V
A 217 Gr. C12A
A 387 Gr. 91 Cl. 2
2-1.15
A 182 Gr. F91
1.17
1Cr 2Mo
5Cr12Mo
2-1.17
2-1.17
A 182 Gr. F12 Cl. 2
A 182 Gr. F5
...
...
...
...
1.18
9Cr2WV
2-1.18
A 182 Gr. F92
...
...
2.1
18Cr8Ni
18Cr8Ni
2-2.1
2-2.1
A 182 Gr. F304
A 182 Gr. F304H
A 351 Gr. CF3
A 351 Gr. CF8
A 240 Gr. 304
A 240 Gr. 304H
2.2
16Cr12Ni2Mo
16Cr12Ni2Mo
18Cr13Ni3Mo
19Cr10Ni3Mo
2-2.2
2-2.2
2-2.2
2-2.2
A 182 Gr. F316
A 182 Gr. F316H
A 182 Gr. F317
...
A 351 Gr. CF3M
A 351 Gr. CF8M
...
A 351 Gr. CG8M
A 240 Gr. 316
A 240 Gr. 316H
A 240 Gr. 317
...
2.3
18Cr8Ni
16Cr12Ni2Mo
18Cr13Ni3Mo
2-2.3
2-2.3
2-2.3
A 182 Gr. F304L
A 182 Gr. F316L
A 182 Gr. F317L
...
...
...
4
Copyright ASME International
Provided by IHS under license with ASME
No reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS
Licensee=Technip/5931917100, User=Bertoldo, Fabien
Not for Resale, 10/15/2009 01:05:07 MDT
A 240 Gr. 304L
A 240 Gr. 316L
...
--`,``,`,,,``,,,`,`,,```,``,,`,,-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---
Material
Group
ASME B16.5-2009
Table 2-1.1 PressureTemperature Ratings for Group 1.1 Materials
Nominal Designation
Forgings
CSi
A 105 (1)
CMnSi
CMnSiV
312Ni
A 350 Gr. LF2 (1)
A 350 Gr. LF6 Cl 1 (3)
A 350 Gr. LF3
Castings
A 216 Gr.
WCB (1)
...
...
...
Plates
A 515 Gr. 70 (1)
A 516 Gr. 70 (1), (2)
A 537 Cl. 1 (4)
...
Working Pressure by Classes, bar
Class
Temp., C
150
300
400
600
900
1500
2500
29 to 38
50
100
150
200
19.6
19.2
17.7
15.8
13.8
51.1
50.1
46.6
45.1
43.8
68.1
66.8
62.1
60.1
58.4
102.1
100.2
93.2
90.2
87.6
153.2
150.4
139.8
135.2
131.4
255.3
250.6
233.0
225.4
219.0
425.5
417.7
388.3
375.6
365.0
250
300
325
350
375
12.1
10.2
9.3
8.4
7.4
41.9
39.8
38.7
37.6
36.4
55.9
53.1
51.6
50.1
48.5
83.9
79.6
77.4
75.1
72.7
125.8
119.5
116.1
112.7
109.1
209.7
199.1
193.6
187.8
181.8
349.5
331.8
322.6
313.0
303.1
400
425
450
475
500
538
6.5
5.5
4.6
3.7
2.8
1.4
34.7
28.8
23.0
17.4
11.8
5.9
46.3
38.4
30.7
23.2
15.7
7.9
69.4
57.5
46.0
34.9
23.5
11.8
104.2
86.3
69.0
52.3
35.3
17.7
173.6
143.8
115.0
87.2
58.8
29.5
289.3
239.7
191.7
145.3
97.9
49.2
NOTES:
(1) Upon prolonged exposure to temperatures above 425C, the carbide phase of steel may be converted to graphite. Permissible but not recommended for prolonged use above 425C.
(2) Not to be used over 455C.
(3) Not to be used over 260C.
(4) Not to be used over 370C.
23
--`,``,`,,,``,,,`,`,,```,``,,`,,-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---
Copyright ASME International
Provided by IHS under license with ASME
No reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS
Licensee=Technip/5931917100, User=Bertoldo, Fabien
Not for Resale, 10/15/2009 01:05:07 MDT
You might also like
- PVElite Course by Mr. AsgarzadeganDocument79 pagesPVElite Course by Mr. AsgarzadeganSaam Sasanian33% (3)
- Calcu Nozzle NeckDocument15 pagesCalcu Nozzle Necksachmaya0% (1)
- CAESAR II Training Overview PDFDocument5 pagesCAESAR II Training Overview PDFJesus MaestreNo ratings yet
- Load Cases and How They Are Handled by PV EliteDocument7 pagesLoad Cases and How They Are Handled by PV Elitearmvasi100% (1)
- FVC Standard Connections Class 1500 Bore SizesDocument1 pageFVC Standard Connections Class 1500 Bore SizesvincentNo ratings yet
- Allowable Nozzle Loading for Carbon Steel and Stainless Steel PipesDocument1 pageAllowable Nozzle Loading for Carbon Steel and Stainless Steel PipesoberaiNo ratings yet
- 1830 - Fea Fatigue Analysis Report PDFDocument19 pages1830 - Fea Fatigue Analysis Report PDFGabbar SinghNo ratings yet
- Agitator FINITE ELEMENT METHODDocument5 pagesAgitator FINITE ELEMENT METHODRoopesh S AcharyaNo ratings yet
- Pressure Design Straight Pipe (Run Pipe)Document6 pagesPressure Design Straight Pipe (Run Pipe)gembirasekaliNo ratings yet
- Design Procedure For Aes He PDFDocument30 pagesDesign Procedure For Aes He PDFRyan Goh Chuang HongNo ratings yet
- N-318-5 Lug Local StressDocument3 pagesN-318-5 Lug Local StresscohenfuNo ratings yet
- Pveng: Pressure Vessel Engineering LTDDocument11 pagesPveng: Pressure Vessel Engineering LTDSivateja NallamothuNo ratings yet
- Saddle AnalysisDocument17 pagesSaddle AnalysisPEJU0007No ratings yet
- Fatigue Analysis in PV EliteDocument3 pagesFatigue Analysis in PV EliteCostynhaNo ratings yet
- PV Elite Transport A Vertical Vessel in The Horizontal Position PDFDocument3 pagesPV Elite Transport A Vertical Vessel in The Horizontal Position PDFnodyyy100% (1)
- DESIGN OF PRESSURE VESSEL Full Report DEDocument48 pagesDESIGN OF PRESSURE VESSEL Full Report DELuis Muñoz100% (1)
- Nozzle FEA CalculationDocument64 pagesNozzle FEA CalculationberylqzNo ratings yet
- Training Manual For PVelite (Basic Level)Document42 pagesTraining Manual For PVelite (Basic Level)Chl2ist100% (12)
- Max Allowable Nozzle LoadDocument1 pageMax Allowable Nozzle Loaddskr fkshNo ratings yet
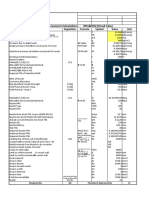
- Notes On Pv-EliteDocument25 pagesNotes On Pv-Elitefahadfiaz100% (1)
- PV Elite WebinarDocument24 pagesPV Elite WebinarAndrea Hank LattanzioNo ratings yet
- PTB E4.18.5 Fixed TubesheetDocument83 pagesPTB E4.18.5 Fixed TubesheetNicolaSaviliNo ratings yet
- Nozzle CheckDocument11 pagesNozzle CheckincaurcoNo ratings yet
- External PressureDocument22 pagesExternal PressureAbhijeet SahuNo ratings yet
- Shell Inputs: Use Asme Code Section-8 Division I (Ug-37)Document34 pagesShell Inputs: Use Asme Code Section-8 Division I (Ug-37)Bashu PoudelNo ratings yet
- WRC 107 Calculation-Circular Attachment On Cylinder (Without Repad)Document3 pagesWRC 107 Calculation-Circular Attachment On Cylinder (Without Repad)naim100% (1)
- SRN Enquiry No. 4855Document51 pagesSRN Enquiry No. 4855AKSHAY BHATKARNo ratings yet
- Cycle Life Analysis Pressure VesselDocument29 pagesCycle Life Analysis Pressure VesselRicardo Paz SoldanNo ratings yet
- PV Elite Training Presentation (2007)Document52 pagesPV Elite Training Presentation (2007)Anh Vân Trần83% (6)
- Basic PV Elite TrainingDocument54 pagesBasic PV Elite TrainingMinh Tran100% (3)
- WRC-107 Nozzles (PVElite)Document5 pagesWRC-107 Nozzles (PVElite)Alvin SmithNo ratings yet
- Project of Pressure VesselDocument25 pagesProject of Pressure VesselKalkidan DanielNo ratings yet
- External Pressure - Pressure Vessel EngineeringDocument15 pagesExternal Pressure - Pressure Vessel Engineeringarjun100% (1)
- TubesheetDocument8 pagesTubesheetVaibhavNo ratings yet
- Nozzle Pipe Length CalculatorDocument5 pagesNozzle Pipe Length CalculatorRyan Goh Chuang HongNo ratings yet
- Nozzle Reinforcement Calculations: HH1&HH2 (Hand Hole) : Description Regulation Formula Symbol Value UnitDocument1 pageNozzle Reinforcement Calculations: HH1&HH2 (Hand Hole) : Description Regulation Formula Symbol Value Unitmiteshpatel191No ratings yet
- Base Ring Fillet Size CalculationDocument4 pagesBase Ring Fillet Size Calculationmiteshpatel191No ratings yet
- New - Reinforcement of NozzleDocument24 pagesNew - Reinforcement of NozzleVaniya GoelNo ratings yet
- PDIL-Stress Analysis Design Basis PDFDocument13 pagesPDIL-Stress Analysis Design Basis PDFDarshan Panchal100% (1)
- Vessel Nozzle Load DefinitionsDocument2 pagesVessel Nozzle Load DefinitionsrsubramaniNo ratings yet
- PV Elite Training-Notes On PV EliteDocument25 pagesPV Elite Training-Notes On PV EliterakicbgNo ratings yet
- Design Calculation of Nozzle Junction Based On ASME Pressure Vessel Design CodeDocument8 pagesDesign Calculation of Nozzle Junction Based On ASME Pressure Vessel Design CodeYakubu100% (1)
- PVElite Design GuidelinesDocument7 pagesPVElite Design Guidelinesndrarly100% (2)
- 8.0 Torispherical Head Design Calculation Asme Sec. Viii Div. 1Document42 pages8.0 Torispherical Head Design Calculation Asme Sec. Viii Div. 1Muhamad Amar Hakimmie Suhaimi100% (1)
- Allowable Nozzle LoadsDocument7 pagesAllowable Nozzle LoadsSiva baalanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial PV Elite 2005Document23 pagesTutorial PV Elite 2005Fredy David Hutahaean100% (2)
- Lug SupportDocument2 pagesLug SupportSachin5586No ratings yet
- WRC 537 Cige Noz B Op 1Document1 pageWRC 537 Cige Noz B Op 1metroroadNo ratings yet
- NozzlePRO PDFDocument185 pagesNozzlePRO PDFIan CarrNo ratings yet
- Compress CalculationDocument106 pagesCompress CalculationKrupal Patel100% (1)
- Take A Quicker Approach To Staggered BlowdownDocument3 pagesTake A Quicker Approach To Staggered Blowdowngad480No ratings yet
- TU SONRISA - Trumpet in BB 1 PDFDocument1 pageTU SONRISA - Trumpet in BB 1 PDFIvan RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Processo de Consciência Mauro Iasi 1999Document28 pagesProcesso de Consciência Mauro Iasi 1999ViníciusNo ratings yet
- MICAELA (CUMBIA) - Alto Sax. 2Document1 pageMICAELA (CUMBIA) - Alto Sax. 2Alvaro Martin SotoNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledGirija KushwahNo ratings yet
- HITACHI ZAXIS ZX 470LC-5G EXCAVATOR Service Repair Manual PDFDocument32 pagesHITACHI ZAXIS ZX 470LC-5G EXCAVATOR Service Repair Manual PDFMaulana SaputraNo ratings yet
- BookingDocument1 pageBookingarchierick5373No ratings yet
- TU SONRISA - Trumpet in BB 2 PDFDocument1 pageTU SONRISA - Trumpet in BB 2 PDFAndrea GiubileiNo ratings yet
- TU SONRISA - Electric Bass PDFDocument1 pageTU SONRISA - Electric Bass PDFadriantavio86gmail.comNo ratings yet
- 300 BoysDocument2 pages300 BoysJagarlamudi Lakshmi TulasiNo ratings yet
- ADP962Document17 pagesADP962thefikeNo ratings yet
- Product de MESSERDocument20 pagesProduct de MESSERlcoraoNo ratings yet
- Pulsed Laser Deposition (PLD)Document32 pagesPulsed Laser Deposition (PLD)Mohit YadavNo ratings yet
- Cold-rolled steel data sheetDocument3 pagesCold-rolled steel data sheetbaskaran ayyapparajNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Performance in The Construction Industry: CEMEX STUDY 18/5/10 14:34 Page 1Document4 pagesSustainable Performance in The Construction Industry: CEMEX STUDY 18/5/10 14:34 Page 1Nikhil SatavNo ratings yet
- VACUUM PUMP DIAGNOSIS (Overall V Spectrum) - Case - Study - 10Document1 pageVACUUM PUMP DIAGNOSIS (Overall V Spectrum) - Case - Study - 10ho-faNo ratings yet
- Abu Dhabi Oil Refining Doors and Windows SpecDocument16 pagesAbu Dhabi Oil Refining Doors and Windows SpecHalim KazdarNo ratings yet
- Variables For Welding 11-3-2016 - 264B1DF6 PDFDocument2 pagesVariables For Welding 11-3-2016 - 264B1DF6 PDFSameh AminNo ratings yet
- Effects of Temperature On ConcreteDocument10 pagesEffects of Temperature On ConcreteMr PolashNo ratings yet
- Catalog CanDocument416 pagesCatalog CanOCangaceiroNo ratings yet
- 10 Steps To A Better Rheological Measurement PDFDocument44 pages10 Steps To A Better Rheological Measurement PDFHílary VpbNo ratings yet
- Parts IR5000-IR6000Document256 pagesParts IR5000-IR6000Watcharapong KesornsombutNo ratings yet
- FFBL TEST QueryDocument11 pagesFFBL TEST QueryABUBAKARNo ratings yet
- JOWA STP 2010-40 DAEHAN H.1037 Final Dwgs Rev0 PDFDocument118 pagesJOWA STP 2010-40 DAEHAN H.1037 Final Dwgs Rev0 PDFmishaNo ratings yet
- Performance of Concrete by Using Palm Oil Fuel Ash (POFA) As A Cement Replacement MaterialDocument6 pagesPerformance of Concrete by Using Palm Oil Fuel Ash (POFA) As A Cement Replacement MaterialShaik ChandiniiNo ratings yet
- Åîáñôþìáôá AccessoriesDocument10 pagesÅîáñôþìáôá Accessoriesbrane12No ratings yet
- Multi-Directional Reach Truck UFW: SupportDocument12 pagesMulti-Directional Reach Truck UFW: SupportJohn SlorNo ratings yet
- ASTM A53 Grade B PDFDocument1 pageASTM A53 Grade B PDFNugrawan SatriaNo ratings yet
- 4r100 Plano de La CajaDocument12 pages4r100 Plano de La CajaproyectorodrigoleonNo ratings yet
- Διατμητικοί ήλοι - ΠιερήDocument1 pageΔιατμητικοί ήλοι - ΠιερήjojogarciaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Disasters - Alexander L. KiellandDocument8 pagesEngineering Disasters - Alexander L. KiellandAnonymous ka2kX4jNNo ratings yet
- Lubricant Viscocities 140hDocument8 pagesLubricant Viscocities 140hPablo Gaspar D'Agostini AmengualNo ratings yet
- OPW Fil-Master 600 Series Fast-Fill/Fleet-Fill Noz (CC600)Document5 pagesOPW Fil-Master 600 Series Fast-Fill/Fleet-Fill Noz (CC600)Maung OoNo ratings yet
- PNG Standard Classification (Jan 09)Document124 pagesPNG Standard Classification (Jan 09)Christian BarNo ratings yet
- Guide To VRLA Batteries 1927Document8 pagesGuide To VRLA Batteries 1927caplukNo ratings yet
- Rungta College of Engineering and TechnologDocument8 pagesRungta College of Engineering and TechnologBhavika GyakwadNo ratings yet
- Rewocare HV 100 - ApresentaçãoDocument12 pagesRewocare HV 100 - Apresentaçãohenriquefxs2926No ratings yet
- F1 CARS ChassisDocument27 pagesF1 CARS ChassisNikhil Goyal100% (1)
- Design - Pinned - Column Base-PlatesDocument61 pagesDesign - Pinned - Column Base-PlatesYoshua YangNo ratings yet