Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemistry 1
Uploaded by
Jazzel Avila ParadiseCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemistry 1
Uploaded by
Jazzel Avila ParadiseCopyright:
Available Formats
Glossary
Chapter 2
Atom
The smallest particle of an element
Balanced
chemical
equation
A chemical equation in which the total number of atoms of each kind is the same in reactants and
products
Chemical
compounds
Pure substances composed of atoms combined in definite, fixed ratios
Chemical
equation
A representation of a chemical reaction by the formulas of reactants and products
Chemical
formula
Written combination of element symbols that represents the atoms combined in a chemical compound
Chemical
property
A property that is observable in chemical reactions and changes in the identity of one or more reactants
Chemical
reaction
A process in which one or more pure substances are converted to one or more different pure substances
Coefficient
In a chemical equation, a number written before a formula to balance the equation
Density
Mass per unit volume
Diatomic
molecules
Molecules composed of two atoms
Element
A pure substance composed of only one kind of atom
Energy
The capacity for doing work or causing change
Heterogeneous
mixture
Matter that is not uniform in composition
Homogeneous
mixture
Matter that is uniform in composition
Inorganic
compound
Any compound other than an organic compound
Kinetic energy
The energy of objects in motion
Macroscopic
Large enough to be seen, felt, and handled
Mass
A measure of the quantity of matter in an object
Microscopic
Visible only with the aid of a microscope
Molecular
formula
A chemical formula that illustrates molecules with atomic symbols and subscripts
Molecule
The smallest chemical unit of a compound
Nanoscopic
In the range of the nanometer (0.000000001 m)
Organic
compound
A derivative of the carbon and hydrogen compound
Physical
property
A property that can be observed without changing the identity of a substance
Potential
energy
Energy in storage by virtue of position or arrangement
Products
Substances formed as the result of a chemical reaction
Pure substance Matter with a uniform and fixed composition at the nanoscopic level
Qualitative
Describes information that is not numerical
Quantitative
Describes information that is numerical
Reactants
Substances that undergo chemical change in a chemical reaction
Solution
A homogeneous mixture that may be in the solid, liquid, or gaseous state
Structural
formula
A chemical formula that illustrates the connections between atoms in molecules as straight lines
Subscripts
In chemical formulas, numbers written below the line (for example, 2 in H2O) to show numbers or
ratios of atoms in a compound
You might also like
- Get Some AirDocument3 pagesGet Some AirJazzel Avila ParadiseNo ratings yet
- Fiber PapersDocument15 pagesFiber PapersJazzel Avila ParadiseNo ratings yet
- Taylor Swift's You Belong With MeDocument9 pagesTaylor Swift's You Belong With MeJazzel Avila Paradise100% (1)
- Philippines University Checklist Assessment ToolDocument6 pagesPhilippines University Checklist Assessment ToolJazzel Avila ParadiseNo ratings yet
- PAUL'S HOPEFUL, DEVOTED, RECONCILING MINISTRYDocument3 pagesPAUL'S HOPEFUL, DEVOTED, RECONCILING MINISTRYJazzel Avila ParadiseNo ratings yet
- Guitar ChordsDocument8 pagesGuitar ChordsJazzel Avila ParadiseNo ratings yet
- Guitar ChordsDocument8 pagesGuitar ChordsJazzel Avila ParadiseNo ratings yet
- Excel Geas 2 CoachingDocument29 pagesExcel Geas 2 CoachingJazzel Avila ParadiseNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Study - AMDocument10 pagesFeasibility Study - AMJazzel Avila ParadiseNo ratings yet
- Joannacel A. Paraiso: - Is A Type ofDocument6 pagesJoannacel A. Paraiso: - Is A Type ofJazzel Avila ParadiseNo ratings yet
- Fiber Connection: BPI Davao Main Branch To BPI Family Savings Bank, Quimpo BLVD Branch Total Distance 5.1KmDocument1 pageFiber Connection: BPI Davao Main Branch To BPI Family Savings Bank, Quimpo BLVD Branch Total Distance 5.1KmJazzel Avila ParadiseNo ratings yet
- Silicon Controlled RectifierDocument1 pageSilicon Controlled RectifierJazzel Avila ParadiseNo ratings yet
- BibingkaDocument1 pageBibingkaJazzel Avila ParadiseNo ratings yet
- Pork Adobo: Can Serve 4-6 PeopleDocument1 pagePork Adobo: Can Serve 4-6 PeopleJazzel Avila ParadiseNo ratings yet
- Pork Adobo: Can Serve 4-6 PeopleDocument1 pagePork Adobo: Can Serve 4-6 PeopleJazzel Avila ParadiseNo ratings yet
- What You Should Know About The Clean Water ActDocument4 pagesWhat You Should Know About The Clean Water ActJazzel Avila ParadiseNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Resp Part 4Document95 pagesResp Part 4Kristian CadaNo ratings yet
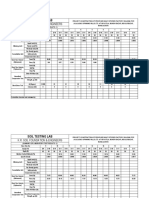
- Soil Testing Lab Results SummaryDocument2 pagesSoil Testing Lab Results SummaryMd SohagNo ratings yet
- Math 2 Unit 9 - Probability: Lesson 1: "Sample Spaces, Subsets, and Basic Probability"Document87 pagesMath 2 Unit 9 - Probability: Lesson 1: "Sample Spaces, Subsets, and Basic Probability"Anonymous BUG9KZ3100% (1)
- 4MB0 02R Que 20160609 PDFDocument32 pages4MB0 02R Que 20160609 PDFakashNo ratings yet
- Karate Writing AssessmentDocument2 pagesKarate Writing AssessmentLeeann RandallNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person Quarter I - Module 2Document26 pagesIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person Quarter I - Module 2Katrina TulaliNo ratings yet
- Ra 11223 PDFDocument34 pagesRa 11223 PDFNica SalazarNo ratings yet
- Physics MCQ Solid State PhysicsDocument15 pagesPhysics MCQ Solid State PhysicsRams Chander88% (25)
- Mathematics Specimen Papers and Mark Schemes UG013054Document102 pagesMathematics Specimen Papers and Mark Schemes UG013054minnie murphy86% (7)
- Applied Physics Mini Launcher Lab ReportDocument12 pagesApplied Physics Mini Launcher Lab ReportTalharashid RamzanNo ratings yet
- Joy Difuntorum-Ramirez CVDocument2 pagesJoy Difuntorum-Ramirez CVJojoi N JecahNo ratings yet
- ES1 Work Panel DatasheetDocument3 pagesES1 Work Panel DatasheetGerardo Alberto Navarro LopezNo ratings yet
- Chime Primary School Brochure TemplateDocument1 pageChime Primary School Brochure TemplateNita HanifahNo ratings yet
- Optimal Inspection and Preventive Maintenance Scheduling of Mining EquipmentDocument9 pagesOptimal Inspection and Preventive Maintenance Scheduling of Mining EquipmentLucia QuispeNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Marketing StrategyDocument4 pagesLiterature Review Marketing Strategyc5td1cmc100% (1)
- English A June 2008 p2Document9 pagesEnglish A June 2008 p2LilyNo ratings yet
- The Golden HarvestDocument3 pagesThe Golden HarvestMark Angelo DiazNo ratings yet
- Gabriel Nobre de Souza - Groningen Mini-MetropolisDocument9 pagesGabriel Nobre de Souza - Groningen Mini-MetropolisGabrielNobredeSouzaNo ratings yet
- PMMC ExperimentDocument2 pagesPMMC ExperimentShyam ShankarNo ratings yet
- LTC2410 Datasheet and Product Info - Analog DevicesDocument6 pagesLTC2410 Datasheet and Product Info - Analog DevicesdonatoNo ratings yet
- EPM Mid Lecture 03 Chapt 1Document17 pagesEPM Mid Lecture 03 Chapt 1Partho Protim MondolNo ratings yet
- CP R77.30 ReleaseNotesDocument18 pagesCP R77.30 ReleaseNotesnenjamsNo ratings yet
- Automated Crime Reporting SystemDocument101 pagesAutomated Crime Reporting SystemDeepak Kumar60% (10)
- Cat IQ TestDocument3 pagesCat IQ TestBrendan Bowen100% (1)
- 2022 - J - Chir - Nastase Managementul Neoplaziilor Pancreatice PapilareDocument8 pages2022 - J - Chir - Nastase Managementul Neoplaziilor Pancreatice PapilarecorinaNo ratings yet
- Gatk Pipeline Presentation: From Fastq Data To High Confident VariantsDocument8 pagesGatk Pipeline Presentation: From Fastq Data To High Confident VariantsSampreeth ReddyNo ratings yet
- Analogue Lab Manual AL7212 V2.1-Panduan Praktek DSR Elektronika-DikonversiDocument235 pagesAnalogue Lab Manual AL7212 V2.1-Panduan Praktek DSR Elektronika-DikonversiAl-FarabiNo ratings yet
- IJRP 2018 Issue 8 Final REVISED 2 PDFDocument25 pagesIJRP 2018 Issue 8 Final REVISED 2 PDFCarlos VegaNo ratings yet
- Description MicroscopeDocument4 pagesDescription MicroscopeRanma SaotomeNo ratings yet
- Helmholtz DecompositionDocument4 pagesHelmholtz DecompositionSebastián Felipe Mantilla SerranoNo ratings yet