Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP1
Uploaded by
Stephanie Joy EscalaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP1
Uploaded by
Stephanie Joy EscalaCopyright:
Available Formats
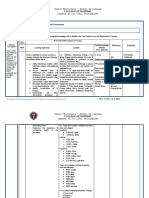
NURSING CARE PLAN # 1
ASSESSMENT
Subjective
cues:
DIAGNOSIS
(NANDABASED)
PLANNING
Short term:
cues:
Incision in
the lower
abdomen
Guarding
Behavior
Facial
grimace
Positioning to
avoid pain
RATIONALE
(cite sources)
Acute Pain
r/t
to
Tissue Trauma After 3 hours of
- Dili na kaayo
Secondary to
nursing interventions:
sakit,
Status
Post
1. the client will
verbalized by
TAHBSO
(Total
state 3ways of
the patient.
Abdominal
- Pain Scale of
relieving pain
Hysterectomy
4 out of 10
such as
Bilateral Salphingo
imagery,
Oophorectomy)
application of
hot and cold
compress and
therapeutic
touch
2. the clients pain
scale will
decrease from
Objective
4 to 2.
-
IMPLEMENTATION
Long term:
At the end of 24
hours, patient will rate
pain as 0 out of 10
Independent
1. Instruct client to report any
improvement/exacerbation
in pain experience.
2. Encourage and assist client
to do deep breathing
exercises.
3. Encourage adequate
periods of rest and sleep,
including uninterrupted
periods of sufficient
duration, meeting comfort
needs, limiting/ avoiding
use of caffeine/ alcohol and
medications affecting REM
sleep. Encourage quiet,
restful atmosphere.
4. Discuss with relatives the
importance of early
detection and reporting of
changes in condition or any
unusual physical
discomforts/ changes.
5. Teach the client and
significant others about the
nonpharmacologic ways to
lessen pain.
EVALUATION
(ACTUAL)
Short term:
1. Unrelieved pain can create
other problems such as
anger, anxiety, immobility,
respiratory problems, and
delay in healing. (MedicalSurgical Nursing, 7th
ed. by Black, Joyce M. and
Jane Hokanson Hawks; p.
443
2. Deep breathing for relaxation
is easy to learn and
contributes to pain relief
and/or reduction by reducing
muscle tension and anxiety.
(Medical-Surgical Nursing, 7th
ed. by Black, Joyce M. and
Jane Hokanson Hawks; p.
479
3. To prevent fatigue. (Nurses
Pocket Guide, 9th ed. by
Doenges, Marilynn, et.al., p.
369)
4. Promotes early detection of
developing complications.
(Fundamentals of Nursing 7th
ed. by Kozier, Barbara, p.
Pain is reduced
controlled to a
tolerable extent
as verbalized.
Relieving
methods are
understood and
demonstrated,
Long term:
6. Increase intake of Vitamin
C
7. Monitor Vital signs
5.
Collaborative/Depende
nt:
8. Administer medications
(particularly analgesics) as
prescribed.
6.
7.
8.
536)
It may be possible to teach
clients a combination of
these techniques to
maximize their opportunities
for self-control over
manifestations of pain.
(Medical-Surgical Nursing, 7th
ed. by Black, Joyce M. and
Jane Hokanson Hawks; p.
476)
To promote healing of
wound. (Nutrition and Diet
Therapy by Peckenpaugh
page 328)
An information baseline
comparison from previous
data. (Manual of Nursing
Procedures Vol. I by
Locquiao, Cruz, Arguelles
and Lontoc page122)
Necessary for treatment of
the underlying cause.
(Nurses Pocket Guide, 9th
ed. by Doenges, Marilynn,
et.al., p. 542) To maintain
acceptable level of pain.
(Nurses Pocket Guide, 9th
ed. by Doenges, Marilynn,
et.al., p. 368)
You might also like
- Acute Pain AGEDocument2 pagesAcute Pain AGEHarris AustriaNo ratings yet
- Acutepain PneumoniaDocument3 pagesAcutepain PneumoniaJoy SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Control Post-Surgical Pain and Improve BreathingDocument12 pagesControl Post-Surgical Pain and Improve BreathingMayraPagan-Carmenatty100% (1)
- Pott's Disease NCPDocument7 pagesPott's Disease NCPkristel_nicole18yahoNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationKatrina Ponce86% (7)
- NCP Acute PainDocument2 pagesNCP Acute PainLyka Mae DominguezNo ratings yet
- Pain Management GuidelinesDocument3 pagesPain Management GuidelinesMr. BamsNo ratings yet
- Treating Dysmenorrhea Through Education and Pain ManagementDocument3 pagesTreating Dysmenorrhea Through Education and Pain ManagementNadilaNo ratings yet
- NCP1Document2 pagesNCP1Anonymous 75TDy2yNo ratings yet
- 2 Acute Pain Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlansDocument5 pages2 Acute Pain Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care Plansjustin_saneNo ratings yet
- NCP - Acute Pain Related To Presence of Postoperative Surgical IncisionDocument2 pagesNCP - Acute Pain Related To Presence of Postoperative Surgical IncisionRene John Francisco90% (10)
- MI Chest Pain AssessmentDocument5 pagesMI Chest Pain AssessmentDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan of Labor PainDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan of Labor PainKenneth Cole80% (61)
- Acute Chest Pain ManagementDocument2 pagesAcute Chest Pain ManagementErickson Caisido GarciaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPCarl Sagisabal Ibasco100% (3)
- Nursing care plan for pain managementDocument4 pagesNursing care plan for pain managementSugar Capule - ManuelNo ratings yet
- NCP Inc.Document2 pagesNCP Inc.Franklin A. Salaum III100% (1)
- NCP GrandcaseDocument5 pagesNCP GrandcaseSaima BataloNo ratings yet
- Independent:: Surgical Nursing, 7 TH Ed. by Black, Joyce M.Andjane Hokan Son Hawkspg.443)Document4 pagesIndependent:: Surgical Nursing, 7 TH Ed. by Black, Joyce M.Andjane Hokan Son Hawkspg.443)KenPedreso100% (1)
- NCP - PainDocument3 pagesNCP - PainAdrian Mallar100% (2)
- 4 NCP's FinalDocument9 pages4 NCP's FinalZenel Yap100% (1)
- R.O. Appendicitis.: Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Document2 pagesR.O. Appendicitis.: Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Karen Joy ItoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short Term IndependentDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale Evaluation Short Term IndependentChristy BerryNo ratings yet
- NCP Cholecystectomy RevisedDocument7 pagesNCP Cholecystectomy RevisedMariquita Buenafe100% (4)
- NCPDocument10 pagesNCPbabycheska08No ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlanGinel Laquiores100% (1)
- NCPDocument12 pagesNCPJonathan Liscano100% (3)
- CP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanDocument7 pagesCP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanKatherine 'Chingboo' Leonico Laud95% (20)
- NCPDocument4 pagesNCPHannah LopezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Acute Pain: Assessment Evaluation PlanningDocument9 pagesNursing Care Plan Acute Pain: Assessment Evaluation PlanningAngelokeizer GavinoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlansDocument7 pagesNursing Care PlansNicholaiCabadduNo ratings yet
- NCP For PainDocument8 pagesNCP For PainClariz BascoNo ratings yet
- Fear Reduction, Relaxation, AND BiofeedbackDocument14 pagesFear Reduction, Relaxation, AND BiofeedbackriyaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Jan. 13 2011Document8 pagesNursing Care Plan Jan. 13 2011Mayls Sevilla Calizo100% (1)
- Clinical Simulation Day 1 Care Plan ms3 Chest Pain SHDocument3 pagesClinical Simulation Day 1 Care Plan ms3 Chest Pain SHapi-575469761No ratings yet
- RAJIV GANDHI UNIVERSITY OF HEALTH SCIENCES M.SC NURSING DISSERTATION ON EFFECTIVENESS OF PROGRESSIVE MUSCLE RELAXATION TECHNIQUE ON PAINDocument18 pagesRAJIV GANDHI UNIVERSITY OF HEALTH SCIENCES M.SC NURSING DISSERTATION ON EFFECTIVENESS OF PROGRESSIVE MUSCLE RELAXATION TECHNIQUE ON PAINRofidaUpitNo ratings yet
- Age NCPDocument2 pagesAge NCPCharmaine Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Acute Pain NCPDocument6 pagesAcute Pain NCPPesky Pescante-MonterolaNo ratings yet
- Me Nursing Care Plan in AppendicitisDocument2 pagesMe Nursing Care Plan in AppendicitiskathrynmarielNo ratings yet
- Post Operative NCPDocument15 pagesPost Operative NCPMary Heather83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisLighto RyusakiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 043Document22 pagesChapter 043dtheart2821100% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan - Acute PainDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan - Acute PainAJ Tuban Compelio100% (1)
- NCPDocument18 pagesNCPChristian Karl B. LlanesNo ratings yet
- NCP TonsilitisDocument11 pagesNCP TonsilitisGra Cie50% (6)
- SCR 270 L & D Care PlanDocument5 pagesSCR 270 L & D Care PlanRenzo MarcosNo ratings yet
- NCP Acute PainDocument3 pagesNCP Acute PainSatchiko Riko SakuraNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of CVA and NIDDMDocument12 pagesNursing Management of CVA and NIDDMKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics Kawasaki Disease Care PlanDocument9 pagesPediatrics Kawasaki Disease Care PlanValencia Vickers50% (4)
- Intervention EdwardsDocument19 pagesIntervention EdwardsChamCham AquinoNo ratings yet
- NCP UtiDocument1 pageNCP UtiAgentpiinkkNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Pain Management in Anaesthesia Practice among Nurse AnaesthetistsFrom EverandAssessment of Pain Management in Anaesthesia Practice among Nurse AnaesthetistsNo ratings yet
- Holistic Pain Relief: How to ease muscles, joints and other painful conditionsFrom EverandHolistic Pain Relief: How to ease muscles, joints and other painful conditionsNo ratings yet
- The Journey to Pain Relief: A Hands-On Guide to Breakthroughs in Pain TreatmentFrom EverandThe Journey to Pain Relief: A Hands-On Guide to Breakthroughs in Pain TreatmentRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Take Back Your Back: Everything You Need to Know to Effectively Reverse and Manage Back PainFrom EverandTake Back Your Back: Everything You Need to Know to Effectively Reverse and Manage Back PainNo ratings yet
- Step 3 Board-Ready USMLE Junkies 2nd Edition: The Must-Have USMLE Step 3 Review CompanionFrom EverandStep 3 Board-Ready USMLE Junkies 2nd Edition: The Must-Have USMLE Step 3 Review CompanionNo ratings yet
- The Art of Holistic Pain Management: A Practical HandbookFrom EverandThe Art of Holistic Pain Management: A Practical HandbookNo ratings yet
- Anti-Aging Therapeutics Volume XIIIFrom EverandAnti-Aging Therapeutics Volume XIIINo ratings yet
- MaternalDocument5 pagesMaternalStephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- SuctioningDocument11 pagesSuctioningStephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- NCLEXnotesDocument20 pagesNCLEXnotesStephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- Fluids - Electrolyte - 022244Document20 pagesFluids - Electrolyte - 022244Stephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- Herbal Medicine Use and Preparation GuidelinesDocument33 pagesHerbal Medicine Use and Preparation GuidelinesStephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- JustificationDocument2 pagesJustificationStephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- TLG SuctioningDocument5 pagesTLG SuctioningStephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- TLG IV TherapyDocument10 pagesTLG IV TherapyStephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- Procedures and Diagnostics - 025003Document6 pagesProcedures and Diagnostics - 025003Stephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- CV1Document10 pagesCV1Stephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- VS - Labs - 030730Document12 pagesVS - Labs - 030730Stephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- CA Case StudyDocument3 pagesCA Case StudyStephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument2 pagesAbstractStephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- CA2Document5 pagesCA2Stephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- Final (Translated - Nabila Dipatuan)Document12 pagesFinal (Translated - Nabila Dipatuan)Stephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- Final Chapter 1 The ProblemDocument17 pagesFinal Chapter 1 The ProblemStephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- NCM107ESCALADocument3 pagesNCM107ESCALAStephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- Final Chapter 2 RRLDocument17 pagesFinal Chapter 2 RRLStephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- CV1Document10 pagesCV1Stephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- CV1Document10 pagesCV1Stephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- Final Chapter 3 MethodologyDocument31 pagesFinal Chapter 3 MethodologyStephanie Joy Escala100% (3)
- Pallia by MMDocument3 pagesPallia by MMStephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- Research ShizDocument2 pagesResearch ShizStephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- WitDocument2 pagesWitStephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- Insect Sting - Concept MapDocument2 pagesInsect Sting - Concept MapStephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- CPDocument3 pagesCPStephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- Narrative PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesNarrative PathophysiologyStephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- Biblio CPDocument2 pagesBiblio CPStephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- AbstractDocument1 pageAbstractStephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- TLG - PostopDocument3 pagesTLG - PostopStephanie Joy EscalaNo ratings yet
- Assingment Human Anatomy ReviseDocument24 pagesAssingment Human Anatomy RevisekrubanNo ratings yet
- Emergency Preparedness and ResponseDocument32 pagesEmergency Preparedness and ResponseMd Rokib ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Cleocin Generic Name: Clindamycin Drug Classification: Antiinfective AntibioticDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Cleocin Generic Name: Clindamycin Drug Classification: Antiinfective AntibioticYura KimNo ratings yet
- Health Declaration FormDocument2 pagesHealth Declaration FormMark Israel DirectoNo ratings yet
- Joc 911151Document8 pagesJoc 911151Daniel BorgesNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Case Study InsightsDocument3 pagesPneumonia Case Study InsightsKayla Callahan50% (2)
- How To Save Your TeethDocument193 pagesHow To Save Your TeethTanon Jaturonnatee100% (2)
- White Photoreactive Resin SDSDocument13 pagesWhite Photoreactive Resin SDSpnpexpertsNo ratings yet
- Lp-Grade 10 HealthDocument17 pagesLp-Grade 10 HealthJovelyn TakilidNo ratings yet
- Inneffective Health Maintenence Care PlanDocument3 pagesInneffective Health Maintenence Care PlanTammy Litzenberger-HarrisNo ratings yet
- Literature review Safety policy programDocument10 pagesLiterature review Safety policy programZay NahNo ratings yet
- Physical Fitness and WelnessDocument11 pagesPhysical Fitness and WelnessKajal RaiNo ratings yet
- 2015 Trauma ManualDocument165 pages2015 Trauma ManualLunaPerfectNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Public Health NursingDocument37 pagesIntroduction to Public Health NursingKailash NagarNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Syndrome in ChildrenDocument12 pagesNephrotic Syndrome in ChildrenLaras Ciingu SyahrezaNo ratings yet
- Modesto City Schools CalendarDocument3 pagesModesto City Schools Calendar2311777No ratings yet
- Equipo Hemodiálisis Dialog IqDocument8 pagesEquipo Hemodiálisis Dialog IqMaria Alejandra Ortiz VelasquezNo ratings yet
- High School DropoutDocument7 pagesHigh School Dropoutapi-318407875No ratings yet
- Romanian Journal Analyzes Oral Rehabilitation Methods for Kennedy I EdentulismDocument8 pagesRomanian Journal Analyzes Oral Rehabilitation Methods for Kennedy I EdentulismBuzoianu Mihaela-AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Meal Planning NotesDocument11 pagesMeal Planning NotesJasmina Sangani100% (5)
- Milieu Therapy & Therapeutic CommunityDocument30 pagesMilieu Therapy & Therapeutic CommunitySaritha SvNo ratings yet
- A Critical Review of The Scientist Practitioner Model For Counselling PsychologyDocument13 pagesA Critical Review of The Scientist Practitioner Model For Counselling PsychologySanja DjordjevicNo ratings yet
- Delicious Indian Dish Palak Paneer and its Health BenefitsDocument27 pagesDelicious Indian Dish Palak Paneer and its Health BenefitsArslan Kamran JuttNo ratings yet
- Ahmad, 2013 MCQDocument6 pagesAhmad, 2013 MCQFadel TrianzahNo ratings yet
- LGBT People More Prone To Mental Health Disorders, Alcohol Misuse - StudyDocument3 pagesLGBT People More Prone To Mental Health Disorders, Alcohol Misuse - StudyAryanThaman ByldeNo ratings yet
- Sitxwhs004 Establish and Maintain A Work Health and Safety SystemDocument61 pagesSitxwhs004 Establish and Maintain A Work Health and Safety SystemHarkamal singhNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument5 pagesDaftar Pustakaanggun pratissaNo ratings yet
- An Example of Argumentative EssayDocument6 pagesAn Example of Argumentative EssayMeli Fauziah67% (3)
- Julian Villalba MD Biography IUATLDDocument2 pagesJulian Villalba MD Biography IUATLDJulian VillalbaNo ratings yet
- The House of Raminten English NewsDocument1 pageThe House of Raminten English Newsdelvino anantaNo ratings yet