Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SAQ Ans 14
Uploaded by
harshanauocOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SAQ Ans 14
Uploaded by
harshanauocCopyright:
Available Formats
Cambridge International AS Level Physics
Answers to self-assessment questions
Answers to SAQs
Chapter 14
1
7 Wavelength of light used, , and separation of
slits, a, remain the same.
x
x
This means that D1 = D2 . Doubling D means x
1
2
must also double, so separation of fringes
x2 = 3.0mm.
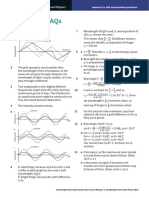
Displacement
resultant
Distance
2 The grid spacing is much smaller than
the wavelength of the microwaves, so the
waves do not pass through. However, the
wavelength of light is much smaller, so it can
pass through unaffected.
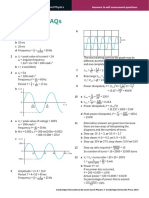
3 Two loudspeakers with slightly different
frequencies might start off in step, but they
would soon go out of step. The interference
at a particular point might be constructive at
first, but would become destructive.
1
8 a
x = D
a . Therefore x a , so decreasing a gives
increased x.
b Blue light has shorter wavelength, so x is less
(xis proportional to).
c For larger D, x is greater, so there is a smaller
percentage uncertainty in x (xis proportional
toD).
9 Rearrange = ax
D to give
9
58910 1.20 = 3.5mm
x = D
a =
0.0002
10
(or wavelength is 34 of previous value, so
spacing of fringes is 34 of previous value)
Displacement
Displacement
Time
12
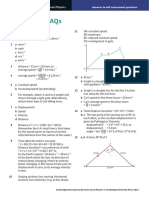
a Rearrange dsin = n so
3.3310
b For n = 3, sin = 0.522, so = 31.5
For n = 4, sin = 0.697, so = 44.2
For n = 5, sin = 0.871, so = 60.6
You cannot have sin > 1. So there are 11
maxima.
Time
resultant
For the second-order maximum, rays from
adjacent slits have a path difference of 2, so
they are in phase.
9
258010 = 0.348, so = 20.4
sin = n
6
d =
resultant
Displacement
11
resultant
6.010
4 The intensity would increase.
5
D and a are fixed. So x1 = x2 and so
1
2
7
3
4.510
2.410
= 1.8103m = 1.8mm
x2 =
7
13
Time
6 D: dark fringe, because rays from slits 1 and
2 differ in path length by one-and-a-half
wavelengths (1 12 ).
E: bright fringe, because the path difference
is 2.
a increases, so the maxima are more spread
out and there may be fewer of them. (Note:
sin .)
b d decreases, so again increases, the
maxima are more spread out and there may
be fewer of them. (Note: sin 1/d.)
Cambridge International AS and A Level Physics Cambridge University Press 2014
Cambridge International AS Level Physics
14
Answers to self-assessment questions
a By calculation, use = ax
D so fringe separation
9
54610 0.80 = 0.87mm
x = D
3
a =
0.5010
so ten fringes have a total width of 8.7mm.
But using a ruler, the student will measure
9mm.
b Separation of lines in grating
1 cm
= 3000
= 3.33106m.
By calculation, rearrange dsin = n so
9
254610 = 0.328
sin = n
=
6
d
3.3310
so = 19.1, but the student will measure 19.
c For the double-slit experiment, a measured
width of 9mm for ten fringes will give a
wavelength of 562nm. For the diffraction
grating experiment, the measured secondorder angle of 19 will give 543nm. Hence the
diffraction grating method is more accurate.
In practice, it is also much more precise
because the fringes are bright and sharp
(well-defined).
15
a For red light, rearrange dsin = n so
9
170010 = 0.350, so
sin = n
6
d =
2.0010
red=20.5
For violet light, rearrange dsin = n so
9
140010 = 0.200, so
sin = n
6
d =
2.0010
violet=11.5
Therefore angular separation
= 20.511.5 = 9.0.
b The third-order maximum for violet light is
deflected through a smaller angle than the
second-order maximum for red light.
Cambridge International AS and A Level Physics Cambridge University Press 2014
You might also like
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level Physicsharshanauoc100% (3)
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level Physicsharshanauoc100% (3)
- Coursebook Answers: Self-Assessment QuestionsDocument1 pageCoursebook Answers: Self-Assessment QuestionslizNo ratings yet
- EOCQ Ans 15Document1 pageEOCQ Ans 15harshanauoc50% (2)
- Worksheet 13 PDFDocument4 pagesWorksheet 13 PDFVijay Bhaskar50% (2)
- Coursebook Answers: Self-Assessment QuestionsDocument2 pagesCoursebook Answers: Self-Assessment QuestionslizNo ratings yet
- 7 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : A F P A Decreases, Therefore The Pressure Exerted On The Floor Will IncreaseDocument2 pages7 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : A F P A Decreases, Therefore The Pressure Exerted On The Floor Will IncreaseRuby Chong100% (1)
- 9 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : 1 B 2 C 3 D 4 D 5 B 6 The Two Units Are: V MDocument2 pages9 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : 1 B 2 C 3 D 4 D 5 B 6 The Two Units Are: V MRuby ChongNo ratings yet
- 14 Worksheet (AS) Waves: 1 The Diagram Shows A Graph of The Displacement of A WaveDocument4 pages14 Worksheet (AS) Waves: 1 The Diagram Shows A Graph of The Displacement of A WaveMahad AsimNo ratings yet
- EOCQ Ans 6Document2 pagesEOCQ Ans 6harshanauoc100% (2)
- Exam Style Answers 11 Asal Physics CBDocument2 pagesExam Style Answers 11 Asal Physics CBAnshul ShahNo ratings yet
- A Level: Circular Motion - AnswerDocument3 pagesA Level: Circular Motion - AnswerAnn OthmanNo ratings yet
- EOCQ Ans 15Document1 pageEOCQ Ans 15harshanauoc50% (2)
- EOCQ Ans 19Document2 pagesEOCQ Ans 19harshanauocNo ratings yet
- Self Assessment Answers 7 Asal Physics CBDocument2 pagesSelf Assessment Answers 7 Asal Physics CBHerman HermanNo ratings yet
- Exam Style Answers 9 Asal Physics CBDocument2 pagesExam Style Answers 9 Asal Physics CBTom ChanNo ratings yet
- Answers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans 10Document2 pagesSAQ Ans 10harshanauoc0% (1)
- Cambridge AS Level Physics SAQ AnswersDocument3 pagesCambridge AS Level Physics SAQ AnswersShaikh Usman AiNo ratings yet
- Coursebook Answers Chapter P2 Asal ChemistryDocument2 pagesCoursebook Answers Chapter P2 Asal ChemistryAditiNo ratings yet
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level PhysicsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- Coursebook Answers Chapter 22 Asal ChemistryDocument6 pagesCoursebook Answers Chapter 22 Asal ChemistryAditiNo ratings yet
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- EOCQ Ans 11Document2 pagesEOCQ Ans 11harshanauocNo ratings yet
- Coursebook Answers: Science in ContextDocument7 pagesCoursebook Answers: Science in ContextAditiNo ratings yet
- Answers To Saqs: Av E Av EDocument2 pagesAnswers To Saqs: Av E Av EWaseem AminNo ratings yet
- Exercise Answers 14 Asal Physics WBDocument4 pagesExercise Answers 14 Asal Physics WBalexandre ricciNo ratings yet
- Coursebook Answers: Self-Assessment QuestionsDocument2 pagesCoursebook Answers: Self-Assessment QuestionslizNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 Topic-7 Astrophysics and Cosmology Answers (End-Of-Chapter & Examzone)Document8 pagesUnit-5 Topic-7 Astrophysics and Cosmology Answers (End-Of-Chapter & Examzone)Avrinox100% (3)
- Coursebook Answers: Science in ContextDocument5 pagesCoursebook Answers: Science in ContextAditiNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans 6Document3 pagesSAQ Ans 6harshanauocNo ratings yet
- EOCQ Ans 21Document2 pagesEOCQ Ans 21Kamran Khan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- 5 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : 1 C 2 D 3 C 4 A 5 D 6 MeteorDocument2 pages5 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : 1 C 2 D 3 C 4 A 5 D 6 MeteorRuby Chong100% (2)
- AS & A Level Physics Workbook AnswersDocument70 pagesAS & A Level Physics Workbook Answersღ꧁Lizzy X Roxiie꧂ღNo ratings yet
- Exam Style Answers 5 Asal Physics CBDocument2 pagesExam Style Answers 5 Asal Physics CBAnshul Shah100% (2)
- SAQ Ans 4Document1 pageSAQ Ans 4Shaikh Usman AiNo ratings yet
- Answers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International AS Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International AS Level PhysicsDuy TôNo ratings yet
- Exam Style Answers 31 Asal Physics CBDocument2 pagesExam Style Answers 31 Asal Physics CBAnshul ShahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Moles and Equations: Homework QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 1: Moles and Equations: Homework QuestionsareebNo ratings yet
- Exam Style Answers 17 Asal Physics CBDocument2 pagesExam Style Answers 17 Asal Physics CBAnshul Shah100% (1)
- Coursebook Answers: Science in ContextDocument4 pagesCoursebook Answers: Science in ContextAditi100% (1)
- Worksheet 15 PDFDocument5 pagesWorksheet 15 PDFVijay Bhaskar0% (1)
- Exam Style Answers 25 Asal Physics CBDocument3 pagesExam Style Answers 25 Asal Physics CBAnshul ShahNo ratings yet
- 6 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010 1Document3 pages6 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010 1Ruby Chong67% (3)
- Coursebook Answers Chapter 28 Asal ChemistryDocument3 pagesCoursebook Answers Chapter 28 Asal ChemistryAditiNo ratings yet
- Exam Style Answers P1 Asal Physics CBDocument2 pagesExam Style Answers P1 Asal Physics CBAnshul ShahNo ratings yet
- Exam Style Answers 13 Asal Physics CBDocument2 pagesExam Style Answers 13 Asal Physics CBAnshul ShahNo ratings yet
- Exam Style Answers 14 Asal Physics CBDocument2 pagesExam Style Answers 14 Asal Physics CBAnshul Shah0% (2)
- Biology AnswersDocument3 pagesBiology Answershari shankar singh100% (1)
- M Schemes 01Document2 pagesM Schemes 01Pathmanathan NadesonNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Physics Workbook Answers: 1 Measurement and MotionDocument16 pagesIGCSE Physics Workbook Answers: 1 Measurement and MotionBasratul RafidNo ratings yet
- Answers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International AS Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International AS Level PhysicsSambandha SilwalNo ratings yet
- EOCQ Ans 4Document2 pagesEOCQ Ans 4harshanauoc75% (4)
- Worksheet (AS) PDFDocument3 pagesWorksheet (AS) PDFMahad AsimNo ratings yet
- CIE Magnetic Force A Level QuestionsDocument3 pagesCIE Magnetic Force A Level QuestionsNMVR0% (1)
- Exam Style Answers P2 Asal Physics CBDocument3 pagesExam Style Answers P2 Asal Physics CBAnshul ShahNo ratings yet
- Exam Style Answers 9 Asal Biology CBDocument3 pagesExam Style Answers 9 Asal Biology CBMighty Warrior GSR100% (1)
- Exam Style Answers 19 Asal Physics CBDocument2 pagesExam Style Answers 19 Asal Physics CBAnshul ShahNo ratings yet
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level PhysicsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- Single slit vs multiple slit comparisonDocument11 pagesSingle slit vs multiple slit comparisonSomala Ashuthosh Reddy 19BEC1081No ratings yet
- 13d-Waves and Optics FR Practice Problems-ANSWERSDocument28 pages13d-Waves and Optics FR Practice Problems-ANSWERSruukiNo ratings yet
- 2bprob Sol 1Document4 pages2bprob Sol 1Muzamil ShahNo ratings yet
- Diffraction Lecture 3-Converted-Pages-2-13,2-11Document22 pagesDiffraction Lecture 3-Converted-Pages-2-13,2-11Somala Ashuthosh Reddy 19BEC1081No ratings yet
- UnitDocument8 pagesUnitharshanauocNo ratings yet
- 2017 p1Document14 pages2017 p1harshanauocNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS Level Physics Answers to SAQs Chapter 14Document2 pagesCambridge International AS Level Physics Answers to SAQs Chapter 14harshanauoc100% (1)
- Harshana Perera (B.SC - BIT, SCJP) 2016 Paper 1Document15 pagesHarshana Perera (B.SC - BIT, SCJP) 2016 Paper 1harshanauocNo ratings yet
- Answers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International AS Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International AS Level PhysicsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level Physicsharshanauoc100% (1)
- A CarDocument6 pagesA CarharshanauocNo ratings yet
- A2 FinalDocument24 pagesA2 FinalharshanauocNo ratings yet
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- EOCQ Ans 22Document2 pagesEOCQ Ans 22harshanauocNo ratings yet
- Answers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International AS Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International AS Level PhysicsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level PhysicsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- W MCQDocument8 pagesW MCQharshanauocNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans 6Document3 pagesSAQ Ans 6harshanauocNo ratings yet
- Answers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International A Level Physicsharshanauoc100% (1)
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level PhysicsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans 3Document2 pagesSAQ Ans 3harshanauocNo ratings yet
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsDocument1 pageAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans 28Document2 pagesSAQ Ans 28harshanauocNo ratings yet
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsDocument1 pageAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans 6Document3 pagesSAQ Ans 6harshanauocNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans 24Document2 pagesSAQ Ans 24harshanauocNo ratings yet
- A Level Physics answers to self-assessment questionsDocument2 pagesA Level Physics answers to self-assessment questionsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans 32Document2 pagesSAQ Ans 32harshanauocNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans 7Document2 pagesSAQ Ans 7harshanauocNo ratings yet