Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level Physics
Uploaded by
harshanauocOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level Physics
Uploaded by
harshanauocCopyright:
Available Formats
Cambridge International A Level Physics
Answers to self-assessment questions
Answers to SAQs
Chapter 20
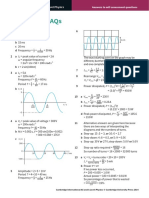
1 Carrier wave frequency is halved, fc=50kHz
Signal wave frequency is halved, fs=5kHz
time for one wave of signal
time for one wave of carrier
Time / s
9 10
c Frequency of signal used to modulate carrier
wave = 5kHz
d Bandwidth = 4535 = 10kHz
7 a
Width of frequency spectrum
= 1700530 = 1170kHz
Number of stations possible
of frequency spectrum = 1170 = 130
= width
bandwidth per station
9
b Very few FM stations are possible. Number
= 1170
200 = 5.85, so only five are possible.
8 If you are concerned about the quality of the
signal that you are listening to, then FM is
better. If you want more stations and are not
in line of sight with the transmitter, then AM
is better.
9 AM covers a larger area than FM. FM can
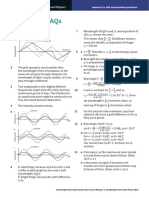
3 a
The difference in amplitude of the carrier
reach all the inhabitants of a town but the
wave increases, i.e. the heights of the lower
expense of aerials and transmitters means
peaks of the waveform fall and the heights of
this is not possible in rural areas.
the higher peaks rise.
b The time interval decreases between
10
a 14 = (18)+(14)+(12); in binary, 1110
successive instances when the signal
b 16 = (116); in binary, 10000
waveform is at its very highest.
11
a Binary 1111 is (18)+(14)+(12)+(11) = 15
4 a
The maximum difference in frequency
b Binary 0001011 is (18)+(12)+(11) = 11
between the signal and the carrier wave
increases, i.e. the signal has higher and lower
12
frequencies.
b The signal increases and decreases in
frequency more times per second.
5 a
Maximum frequency shift
= frequency deviation amplitude
= 8.03.0 = 24kHz
b Maximum frequency of modulated carrier
wave = frequency of carrier wave + maximum
frequency shift = 500+24 = 524kHz
c Number of times per second the modulated 13
carrier wave increases and decreases in
frequency = frequency of signal
= 16000 times a second
a The value on the vertical axis (the voltage)
has only one of two values, 0 or 1.
b Digital signals can be more easily
regenerated, can be stored and processed
more easily, errors in transmission can be
detected and digital electronic systems are
more reliable.
c Noise is introduced, e.g. by random thermal
motion of electrons. The signal is attenuated
due to energy loss (I2Rt) in the wires.
(P )
5.0
Attenuation = 10lg P1 = 10lg 0.0002
2
= 44dB (or a gain of 44dB).
6 a
Amplitude modulation
b Carrier frequency = 40kHz
Cambridge International AS and A Level Physics Cambridge University Press 2014
Cambridge International A Level Physics
14
Answers to self-assessment questions
(P )
c Method
Attenuation = 10lg P1
2
Substituting known values gives
coaxial
) meaning 3 = lg(6.010
)
P
6.010
Taking inverse logs, 10 = ( P )
Rearranging gives P = ( 6.010 )= 6.010 W
103
3
30 = 10lg 6.010
P
2
2
3
= 6.0103mW
15
Signal-to-noise ratio = 10lg(1.0) = 0.0dB
16
a Given that gain and attenuation expressed
in decibels are logarithmic, we can say that
overall gain
= gain in amplifier + gain in cable
= gain in amplifier attenuation in cable
= 3018 = 12dB
P
b Substitute values in gain = 10lg P2
(
(
)
)
P2
So 12 = 10lg
3 ,
1.010
P2
therefore lg
3 = 1.2
1.010
Advantage
Disadvantage
less attenuation,
noise, interference
than wire pair
more expensive
than wire pair
analogue no ADC and DAC
signal
conversion required
more noise,
interference
than digital
space
wave
satellite use
expensive
can be received by
satellite
sky wave worldwide reception
possible with
multiple reflections
reflection by the
ionosphere is
not reliable
Other answers are possible.
( )
1
Take inverse logs to give output power
P2 = 101.21.0103 = 15.8mW 16mW
17
a Coaxial cable contains a central copper core
surrounded by an insulator and a mesh, or
braid, made of copper wires made into a
tube.
An analogue signal can have any value,
within limits, and is not restricted to just a
few values.
A space wave is an electromagnetic wave
above 30MHz that is not reflected or
refracted back to Earth by the ionosphere
and may be received by a satellite in space or
be detected by line of sight within the Earths
atmosphere.
A sky wave is an electromagnetic wave that is
reflected or refracted back to the Earth by the
ionosphere.
b Space wave frequency greater than 30MHz,
wavelength less than 10m
Sky wave frequency between 3 and 30MHz,
wavelength between 10 and 100m
Cambridge International AS and A Level Physics Cambridge University Press 2014
You might also like
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsShameema NasreenNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans 4Document1 pageSAQ Ans 4Shaikh Usman AiNo ratings yet
- Answers To Saqs: Av E Av EDocument2 pagesAnswers To Saqs: Av E Av EWaseem AminNo ratings yet
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level PhysicsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans 8Document1 pageSAQ Ans 8harshanauocNo ratings yet
- Cambridge AS Level Physics SAQ AnswersDocument3 pagesCambridge AS Level Physics SAQ AnswersShaikh Usman AiNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans 28Document2 pagesSAQ Ans 28harshanauocNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans 24Document2 pagesSAQ Ans 24harshanauocNo ratings yet
- A Level Physics answers to self-assessment questionsDocument2 pagesA Level Physics answers to self-assessment questionsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsDocument1 pageAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level PhysicsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans 30Document2 pagesSAQ Ans 30harshanauocNo ratings yet
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans 6Document3 pagesSAQ Ans 6harshanauocNo ratings yet
- Answers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans 3Document2 pagesSAQ Ans 3Shaikh Usman AiNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans 10Document2 pagesSAQ Ans 10harshanauoc0% (1)
- SAQ Ans 7Document2 pagesSAQ Ans 7harshanauocNo ratings yet
- Answers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International AS Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International AS Level PhysicsDuy TôNo ratings yet
- EOCQ Ans 11Document2 pagesEOCQ Ans 11harshanauocNo ratings yet
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level Physicsharshanauoc100% (3)
- EOCQ Ans 15Document1 pageEOCQ Ans 15harshanauoc50% (2)
- Cambridge International AS Level Physics Answers to SAQs Chapter 14Document2 pagesCambridge International AS Level Physics Answers to SAQs Chapter 14harshanauoc100% (1)
- Self Assessment Answers 7 Asal Physics CBDocument2 pagesSelf Assessment Answers 7 Asal Physics CBHerman HermanNo ratings yet
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level PhysicsDocument1 pageAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level Physicspratama putraNo ratings yet
- Coursebook Answers: Self-Assessment QuestionsDocument1 pageCoursebook Answers: Self-Assessment QuestionslizNo ratings yet
- Answers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International AS Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International AS Level PhysicsSambandha SilwalNo ratings yet
- Exam Style Answers 9 Asal Physics CBDocument2 pagesExam Style Answers 9 Asal Physics CBTom ChanNo ratings yet
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsShameema NasreenNo ratings yet
- Exercise Answers 14 Asal Physics WBDocument4 pagesExercise Answers 14 Asal Physics WBalexandre ricciNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans 1Document2 pagesSAQ Ans 1danielmahsaNo ratings yet
- Answers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International AS Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International AS Level PhysicsSambandha SilwalNo ratings yet
- M Schemes 01Document2 pagesM Schemes 01Pathmanathan NadesonNo ratings yet
- 15 Waves Worksheet Mark Schemepdf Stowmarketphysic - 5a1e69761723dda133336339Document2 pages15 Waves Worksheet Mark Schemepdf Stowmarketphysic - 5a1e69761723dda133336339Н. Наранцацралт100% (1)
- Chapter 10 Exam Style QuestionsDocument4 pagesChapter 10 Exam Style QuestionsParth BabardesaiNo ratings yet
- 5 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : 1 C 2 D 3 C 4 A 5 D 6 MeteorDocument2 pages5 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (AS) : 1 C 2 D 3 C 4 A 5 D 6 MeteorRuby Chong100% (2)
- M Schemes 02Document3 pagesM Schemes 02Pathmanathan Nadeson22% (9)
- Coursebook Answers: Self-Assessment QuestionsDocument2 pagesCoursebook Answers: Self-Assessment QuestionslizNo ratings yet
- Ch05 HWDocument2 pagesCh05 HWDilini WijesingheNo ratings yet
- Exam Style Answers 31 Asal Physics CBDocument2 pagesExam Style Answers 31 Asal Physics CBAnshul ShahNo ratings yet
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsShameema NasreenNo ratings yet
- M Schemes 03Document2 pagesM Schemes 03Pathmanathan Nadeson25% (4)
- Exam Style Answers 29 Asal Physics CBDocument2 pagesExam Style Answers 29 Asal Physics CBAnshul ShahNo ratings yet
- Projectiles 1 MSDocument7 pagesProjectiles 1 MSAhmedNo ratings yet
- 26 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (A2) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Document3 pages26 Marking Scheme: Worksheet (A2) : AS and A Level Physics Original Material © Cambridge University Press 2010Arsal MasoodNo ratings yet
- Exam Style Answers 17 Asal Physics CBDocument2 pagesExam Style Answers 17 Asal Physics CBAnshul Shah100% (1)
- Answers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsMuhammad Ahmed ZamanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER End-of-chapter test marking schemeDocument1 pageCHAPTER End-of-chapter test marking schemeAmberNo ratings yet
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level BiologyDocument1 pageAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level Biologyfaraz ahmedNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans P2Document2 pagesSAQ Ans P2ThithiraNo ratings yet
- CIE Magnetic Force A Level QuestionsDocument3 pagesCIE Magnetic Force A Level QuestionsNMVR0% (1)
- CH 4 Vectors End of Chapter Test AnswersDocument1 pageCH 4 Vectors End of Chapter Test AnswersAmberNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Moles and Equations: Homework QuestionsDocument2 pagesChapter 1: Moles and Equations: Homework QuestionsareebNo ratings yet
- EOCQ Ans 6Document2 pagesEOCQ Ans 6harshanauoc100% (2)
- Exam Style Answers 28 Asal Physics CBDocument2 pagesExam Style Answers 28 Asal Physics CBAnshul ShahNo ratings yet
- Wireless Technology Questions1 - AnswerDocument11 pagesWireless Technology Questions1 - Answerapi-26355935100% (11)
- Assignment No 2 CCNDocument5 pagesAssignment No 2 CCNAHSAN BAIGNo ratings yet
- Numericals On Multiple Aces ControlDocument9 pagesNumericals On Multiple Aces ControlSureshNo ratings yet
- EC4011 Excercise Sheet 1 2017 PDFDocument1 pageEC4011 Excercise Sheet 1 2017 PDFakella kartikNo ratings yet
- Questions: Practice SetDocument6 pagesQuestions: Practice SetAseel AlmamariNo ratings yet
- UnitDocument8 pagesUnitharshanauocNo ratings yet
- 2017 p1Document14 pages2017 p1harshanauocNo ratings yet
- A CarDocument6 pagesA CarharshanauocNo ratings yet
- Answers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- Answers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International AS Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International AS Level PhysicsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- A2 FinalDocument24 pagesA2 FinalharshanauocNo ratings yet
- Harshana Perera (B.SC - BIT, SCJP) 2016 Paper 1Document15 pagesHarshana Perera (B.SC - BIT, SCJP) 2016 Paper 1harshanauocNo ratings yet
- EOCQ Ans 19Document2 pagesEOCQ Ans 19harshanauocNo ratings yet
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS Level Physics Answers to SAQs Chapter 14Document2 pagesCambridge International AS Level Physics Answers to SAQs Chapter 14harshanauoc100% (1)
- Answers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International AS Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International AS Level PhysicsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- EOCQ Ans 15Document1 pageEOCQ Ans 15harshanauoc50% (2)
- SAQ Ans 3Document2 pagesSAQ Ans 3harshanauocNo ratings yet
- W MCQDocument8 pagesW MCQharshanauocNo ratings yet
- EOCQ Ans 22Document2 pagesEOCQ Ans 22harshanauocNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans 10Document2 pagesSAQ Ans 10harshanauoc0% (1)
- Answers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To EOC Questions: Cambridge International A Level Physicsharshanauoc100% (1)
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsDocument1 pageAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level PhysicsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level PhysicsDocument2 pagesAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International As Level Physicsharshanauoc100% (3)
- SAQ Ans 6Document3 pagesSAQ Ans 6harshanauocNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans 28Document2 pagesSAQ Ans 28harshanauocNo ratings yet
- A Level Physics answers to self-assessment questionsDocument2 pagesA Level Physics answers to self-assessment questionsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans 24Document2 pagesSAQ Ans 24harshanauocNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans 32Document2 pagesSAQ Ans 32harshanauocNo ratings yet
- Answers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsDocument1 pageAnswers To Saqs: Cambridge International A Level PhysicsharshanauocNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans 7Document2 pagesSAQ Ans 7harshanauocNo ratings yet
- SAQ Ans 6Document3 pagesSAQ Ans 6harshanauocNo ratings yet
- Basics of Small Scale Fading and PHY Layer DesignDocument18 pagesBasics of Small Scale Fading and PHY Layer DesigntazebNo ratings yet
- S5bandplan HF V 1 7 A3Document1 pageS5bandplan HF V 1 7 A3Samphan TreepisanNo ratings yet
- Fa-150 Service ManualDocument327 pagesFa-150 Service ManualChristian Kenneth Parazo78% (9)
- TEL312 Electronic Communication Fundamentals HomeworkDocument7 pagesTEL312 Electronic Communication Fundamentals HomeworkInacia ZanoNo ratings yet
- URC4220 Remote CodesDocument40 pagesURC4220 Remote CodesTheSadist007No ratings yet
- Tangram - Software - Manual 2022 06 14Document103 pagesTangram - Software - Manual 2022 06 14PabloNo ratings yet
- Solutions to Antenna Practice ProblemsDocument2 pagesSolutions to Antenna Practice ProblemsBajeNo ratings yet
- A REPORT ON MIMO IN WIRELESS APPLICATIONS - FinalDocument11 pagesA REPORT ON MIMO IN WIRELESS APPLICATIONS - FinalBha RathNo ratings yet
- Vol 4 - Info. Tech - INTERSYSTEM INTERFERENCE STUDY BETWEEN DVB-T AND UMTSDocument15 pagesVol 4 - Info. Tech - INTERSYSTEM INTERFERENCE STUDY BETWEEN DVB-T AND UMTSwilolud6720No ratings yet
- Organisational Structure of AIRDocument10 pagesOrganisational Structure of AIRShubham Nag75% (4)
- Boulder Amateur TV Repeater's Newsletter-112Document13 pagesBoulder Amateur TV Repeater's Newsletter-112Benjamin DoverNo ratings yet
- Wihh Halim PK HLPDocument3 pagesWihh Halim PK HLPHarry NuryantoNo ratings yet
- Improve HSPA THP 3G & Sharing Traffic 2G-3GDocument2 pagesImprove HSPA THP 3G & Sharing Traffic 2G-3GAhmad FauzaniNo ratings yet
- Panasonic ST50 Operating InstructionsDocument111 pagesPanasonic ST50 Operating Instructionslouell350No ratings yet
- Impact of Foreign Pay TV On Local ContentDocument64 pagesImpact of Foreign Pay TV On Local ContentJulius YarNo ratings yet
- C&S Antennas FANLITEDocument4 pagesC&S Antennas FANLITEIsmail AyNo ratings yet
- Option 1: Bandwidth To Multiplex Information Rate CalculationDocument4 pagesOption 1: Bandwidth To Multiplex Information Rate CalculationYathish H GowdaNo ratings yet
- First ReportDocument25 pagesFirst Reportshonick2No ratings yet
- Vote Scan Overview PDFDocument1 pageVote Scan Overview PDFMatthew GarciaNo ratings yet
- Antenna Design Using Ansoft HFSSDocument6 pagesAntenna Design Using Ansoft HFSSMaxwellNo ratings yet
- Antena Yagi Neagra Telwave TWDS-7088 PDFDocument1 pageAntena Yagi Neagra Telwave TWDS-7088 PDFVirgil PeiulescuNo ratings yet
- Cost289 Final ReportDocument88 pagesCost289 Final ReportkyfeeeNo ratings yet
- Noise Effects Communication ChannelDocument2 pagesNoise Effects Communication ChannelCristel BautistaNo ratings yet
- Grilla DTHDocument1 pageGrilla DTHgabriela.comsanjoseNo ratings yet
- 5 CF 78 CF 8 B 17 BDocument1 page5 CF 78 CF 8 B 17 Bionut Gaming&VlogNo ratings yet
- Digital Modulation Technique FinalDocument78 pagesDigital Modulation Technique FinalNathan TonoNo ratings yet
- Garry MillerDocument30 pagesGarry MillerJam RagaNo ratings yet
- Ele 2Document16 pagesEle 2milton1987No ratings yet
- Television and Video Engineering: Unit-5Document57 pagesTelevision and Video Engineering: Unit-5Anonymous GTb7FF3sTrNo ratings yet
- BARC India TerminologiesDocument4 pagesBARC India TerminologiesPratikKamatNo ratings yet